At first glance, it would appear that the success of Base, the top Ethereum layer-two (L2) network by total value locked (TVL) would benefit the Ethereum ecosystem, but according to a Standard Chartered Bank report, Base is actually contributing to Ethereum’s demise and has already extracted roughly $50 billion in market capitalization from the network.
Coinbase, the largest cryptocurrency exchange in the U.S. launched Base in 2023 as a low-cost solution for Ethereum app development. There were several other successful L2s already in existence by then, such as Arbitrum and OP Mainnet, but it didn’t take long for Base to assert itself as the cheapest and fastest option.
Soon Base was not only leading other L2s by way of volume, but it was also raking in big profits from all the activity on its platform. But unlike other L2s that have tokens and keep their profits within the Ethereum ecosystem, Base simply offloads its profits onto Coinbase’s balance sheet.
In Q4 2024, Coinbase recorded $68 million in “other transaction revenue” that was “largely driven by higher sequencer revenue on Base,” according to the exchange’s shareholder letter released in February. That comes out to $272 million when annualized. Standard Chartered says extracting that much value from Ethereum has led to the evaporation of $50 billion in market cap from the network.
“Base, a layer 2 that was developed to address the problem of scalability on Ethereum, is passing all of the profit (fee revenue minus data recording fees) it extracts to Coinbase, its corporate owner,” the report states. “We estimate that GDP [gross domestic product] lost to Base has already reduced ETH’s market cap by $50 billion.”
To add insult to injury, Standard Chartered expects the erosion of Ethereum’s value to worsen as Base enjoys even more success. One way the bank arrives at crypto price targets is by estimating a token’s future price based on how much that token will be worth if denominated in bitcoin ( BTC). For ether ( ETH), Standard Chartered uses the ETH- BTC price ratio.
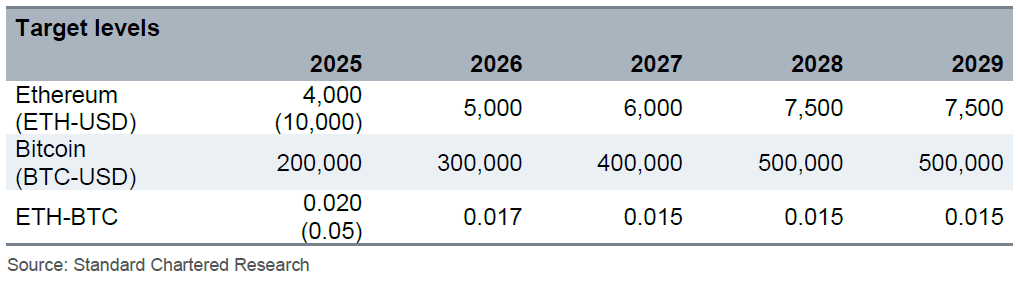
(Various price targets for ether / Standard Chartered Bank)
“We think ETH- BTC will continue to head lower over the next two years, from the current level of 0.023 to 0.015 by 2027 – the lowest level since early 2017,” the bank’s report states. “This gives us ETH-USD levels of $4,000 at end-2025 (versus $10,000 previously).”
Several aspects of Ethereum’s developmental focus have exacerbated the problem. The report points the finger at the blockchain’s transition to proof-of-stake and maybe even more so, the March 2024 Dencun upgrade.
“Since the Dencun upgrade in March 2024, lower fees on Ethereum have led to higher net issuance,” the report explains. “This trend probably began after ETH switched from a proof-of-work to a proof-of-stake concept.”
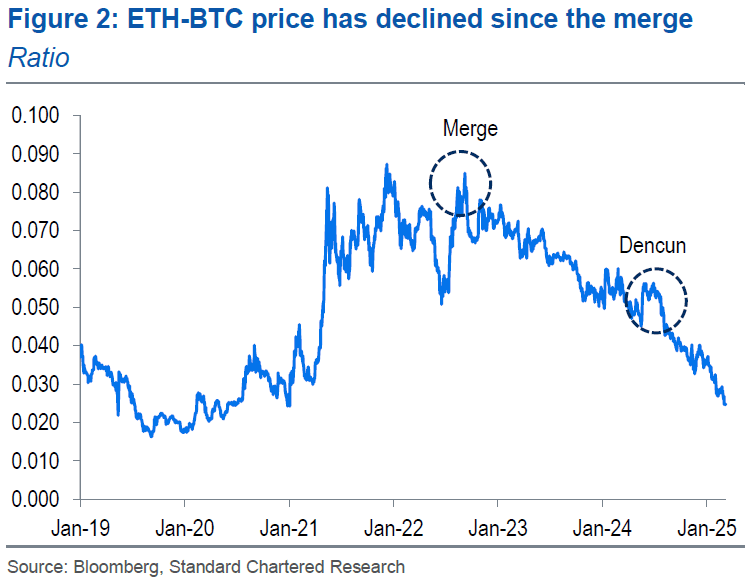
(Ethereum’s woes can be traced to the Merge and the Dencun upgrades / Standard Chartered Bank)
Normally, lower fees are a good thing for long-term sustainability. The lower revenues from fees are compensated for by an increase in volume and activity. But because Base doesn’t reinvest its profits back into the Ethereum ecosystem, the low fee environment ends up eroding value, according to Standard Chartered.
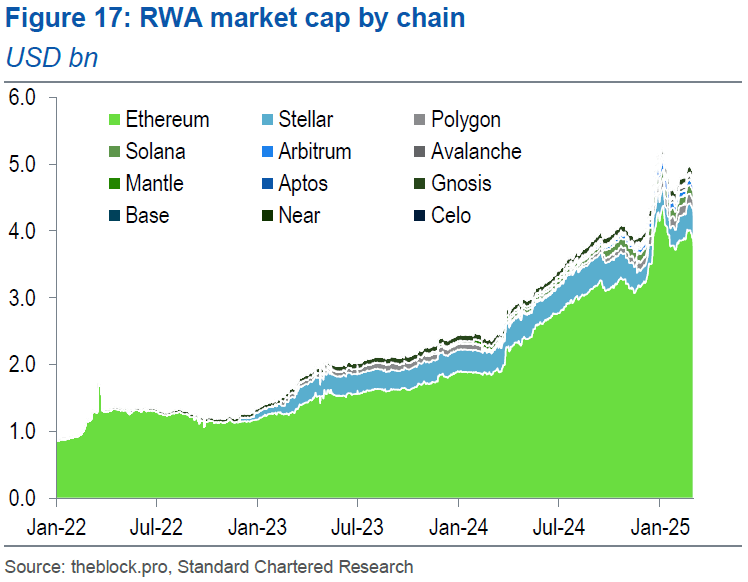
(RWA is one of the longer-term solutions that could rectify Ethereum’s current low fee environment problem / Standard Chartered Bank)
With that in mind, the bank recommends at least five solutions: increasing demand for on-chain storage, raising Ethereum’s gas limit, encouraging tokenization of real-world assets (RWA), augmenting spot ether exchange-traded fund (ETF) inflows, and even petitioning the Ethereum Foundation to tax all L2s.
“One solution would be for Ethereum to tax layer 2s for operating in the Ethereum ecosystem,” the report recommends. “We think enabling Base to extract value in the way that it currently does is a mistake.”
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




