Last week (from November 12 to 15), the 7th Devcon was held in Bangkok, focusing on the current challenges facing Ethereum, solutions, and the roadmap for future development. The three most discussed themes were Beam Chain, the Pectra upgrade, and the unification of Ethereum L2.
Author: https://x.com/Presto_Research/
Translation: Blockchain in Plain Language

1. Beam Chain
The highlight of the entire Devcon was undoubtedly Justin Drake’s (drakefjustin) speech about Beam Chain on the first day at 5 PM. Beam Chain is a long-term improvement proposal for Ethereum's consensus layer, aimed at addressing existing limitations and leveraging the latest technological innovations such as ZK proofs to "clean up technical debt." The speech proposed nine major upgrades under three categories:
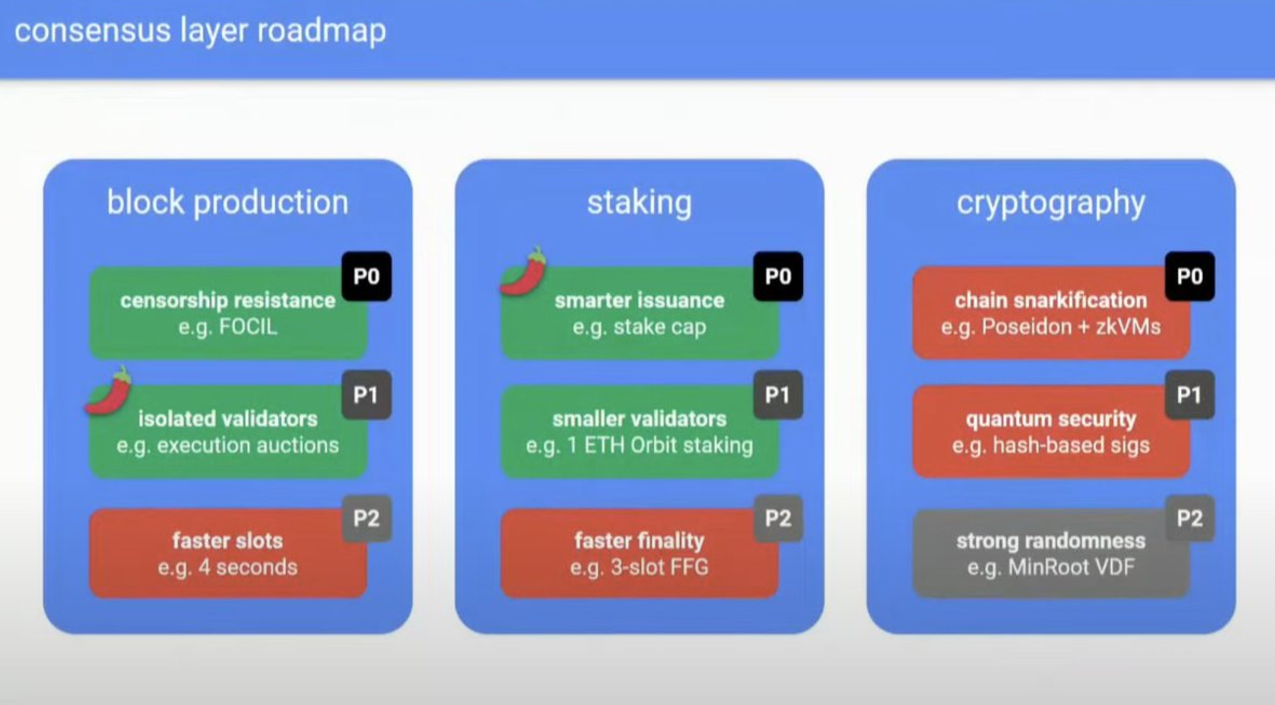
Source: Devcon
1) Block Production
1) Anti-censorship: As proposed in EIP-7805, the "Inclusion List" mechanism ensures that transactions are not censored by centralized block builders.
2) Validator Isolation: A proposal to adopt the Attester-Proposer-Separation (APS) mechanism to reduce reliance on intermediaries and achieve further decentralization in block production.
3) Faster Time Intervals: Reducing block time from the current 12 seconds to 4 seconds, speeding up block processing and transaction finality.
2) Staking
Smarter Issuance Mechanism: Proposing to set a staking cap to optimize Ethereum's issuance model, balancing between inflation and deflation.
Lower Validator Threshold: Reducing the staking requirement to 1 ETH to promote decentralization and allow more users to participate as validators.
Faster Finality: Proposing a 3-slot (36 seconds) finality mechanism to replace the current 15-minute transaction confirmation time.
3) Cryptography
On-chain Zero-Knowledge: Enhancing consensus security through the use of ZK-SNARKS, supporting zkVM-based execution, and aggregating signatures into ZK proofs.
Quantum Security: Adopting cryptographic schemes based on hash signatures to counter future quantum computing threats, which are resistant to quantum attacks.
Strong Randomness: Using Verifiable Delay Functions (VDFs) to generate unbiased randomness for validator selection.
4) Future Outlook
After the announcement, there were concerns on Crypto Twitter about the five-year timeline of the roadmap. However, Justin Drake assured the community that updates will be rolled out gradually. Given that Ethereum is actively addressing current user experience challenges, this progress is worth continued attention in the future.
2. Pectra Upgrade
The Pectra upgrade is an important milestone in Ethereum's development, initially envisioned as a precursor to the more complex Fusaka upgrade (Verkle transition). However, as of October 2024, the Pectra upgrade has expanded to include the most Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), comprising ten significant code changes. To manage complexity, the upgrade is divided into two phases, with the first part planned for activation on the mainnet in early 2025.
The main goals of the Pectra upgrade are to improve Ethereum's PoS mechanism, optimize user experience, and enhance data availability (DA) capabilities.
Validator and Network Health
EIP-7251: Raising the maximum effective staking balance to 2048 ETH while maintaining a minimum threshold of 32 ETH. This adjustment allows large node operators to consolidate validators while enabling independent stakers to benefit from compound rewards. By reducing the total number of validators, it alleviates network pressure as Ethereum approaches 1.6 million validators (November 2024), addressing network bottleneck issues.
User Experience Optimization
EIP-7702: Introducing a new transaction type that allows external accounts (EOA) to delegate code execution through an authorization list. It supports the following features:
Batch Processing: Allowing users to approve and spend tokens in one go;
Fee Payment by Third Parties: Allowing third parties to pay transaction fees;
Permission Downgrading: Restricting account access permissions. These improvements make account management more efficient and flexible for users.
EIP-2537: Introducing support for zero-knowledge cryptography (providing precompiled functions for efficient cryptographic operations on the BLS12-381 curve), significantly enhancing the efficiency of privacy applications and Rollup solutions.
Data Availability Improvements
EIP-7742: Preparing for the elastic Blob data capacity changes in Ethereum. By removing redundant maximum validation of Blobs in the execution layer and delegating dynamic Blob target management to the consensus layer, higher scalability is achieved during expansion adjustments.
3. Unifying Ethereum L2

Source: @hal2001
1) Fragmentation in the Ethereum Layer 2 Ecosystem
Ethereum's Layer 2 (L2) solutions have played a revolutionary role in addressing scalability issues, making transactions faster and cheaper. However, with the proliferation of these solutions, they have also introduced a significant challenge: fragmentation. Each L2 chain is an independent ecosystem with unique rules, interfaces, and liquidity pools. This fragmentation complicates cross-chain operations for users and developers. For example, transferring assets between L2s or executing governance votes requires complex bridging mechanisms, leading to poor user experience, higher costs, and inefficiencies.
2) Intent: A Bridge for Seamless Cross-Chain Operations
The concept of "intent" serves as a unifying link in Ethereum's fragmented ecosystem, capable of addressing this issue. Users can declare their intended operations, such as token swaps or NFT transfers, without manually managing the complexities of each L2. "Intent" can be viewed as a universal "order form" that clearly specifies the goals users wish to achieve. Just as an online ordering system coordinates multiple warehouses to fulfill requests, intent abstracts the technical details of operation chains, making the experience smoother.
ERC-7683 standardizes the expression and execution of these intents, ensuring interoperability between the Ethereum mainnet, L2, and sidechains. It provides the necessary structure for cross-chain communication, integrating fragmented systems under the same framework. This coordination eliminates inefficiencies, allowing operations to flow smoothly within the Ethereum ecosystem, ultimately making the system more cohesive and user-friendly.
3) Creating Synergies: ERC-7683 and EIP-7702
When "intent" is combined with EIP-7702 (focused on account abstraction), its power becomes even more pronounced. EIP-7702 allows externally owned accounts (EOA) to temporarily act as smart contract wallets during transactions. This innovation eliminates the need for users to create dedicated smart contract wallets for complex transactions (such as cross-chain operations).
The combination of ERC-7683 and EIP-7702 enables users to initiate complex cross-chain interactions directly from their EOAs. For example, a user can declare an intent to swap tokens on L2, transfer the proceeds to another chain, and execute governance votes—all in a seamless transaction. By combining the standardization of intent with the flexibility of account abstraction, the Ethereum ecosystem can provide a smoother user experience.
4. Conclusion
Ethereum has long been committed to improving scalability, but this year's Devcon showcased a strong trend toward addressing various user experience issues that have been overlooked in the past. While there are still many long-term goals ahead, it is worth watching how Ethereum continues to evolve into a better product. Looking forward to seeing you at the next Devcon!
Article link: https://www.hellobtc.com/kp/du/11/5547.html
Source: @Presto_Research
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




