Currently, what are the top ten most profitable protocols in the DeFi field?
Author | Huo Huo

After experiencing the high prices in the cryptocurrency field in 2021, the market has cooled down this year. However, in this calm state, the cryptocurrency infrastructure has been able to develop and solidify, such as those DeFi protocols with strong income, real demand, and positive returns. Looking at the overall market, there is a trend of shifting from "fat protocols and thin applications" to "fat applications."
What are fat and thin protocols and applications? This is because the early Internet was like a "thin protocol network," consisting of things like TCP, IP, and HTTP that formed the foundation of the Internet but were not noticed by people. The value of these protocols is captured by application software, i.e., apps. For example, the apps we use now, such as Douyin, WeChat, and Meituan, are "thin protocol fat applications."
However, on the basis of decentralized blockchain, value is concentrated in the shared protocol layer, with only a small portion of value distributed in the application layer, hence it is called a "fat" protocol and "thin" application stack.
Today, we will continue to provide an overview of this topic and take a look at the top ten most profitable protocols in the DeFi field.
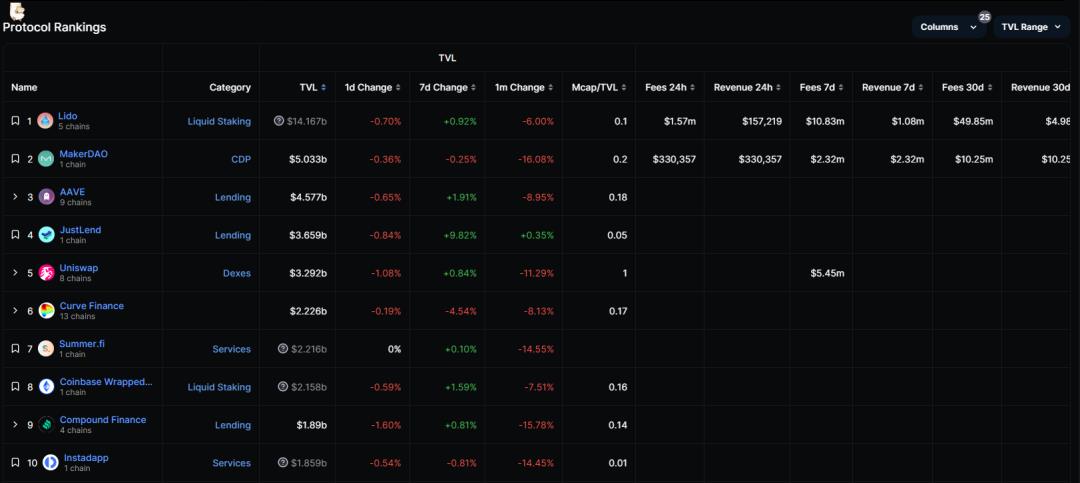
Source: defillama September 9th data
01 Lido
Lido is currently the largest staking protocol in the market, founded in 2020, mainly providing liquid staking solutions for ETH and other PoS blockchains.
After users deposit PoS assets into Lido, their tokens will be staked in the PoS blockchain through the Lido protocol. This allows them to earn staking rewards and also utilize staking to obtain tokenized assets for additional returns.

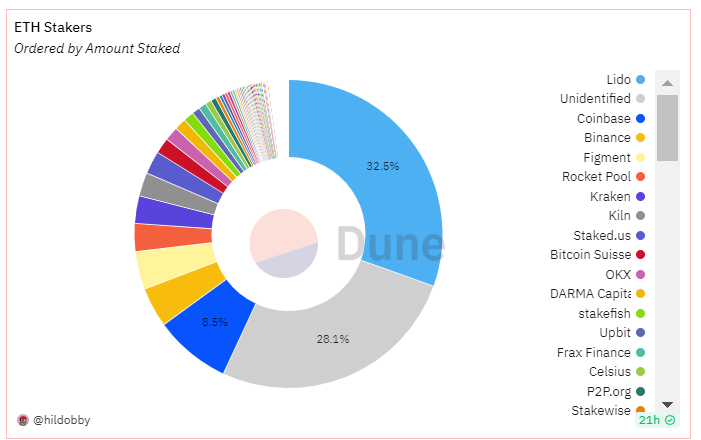
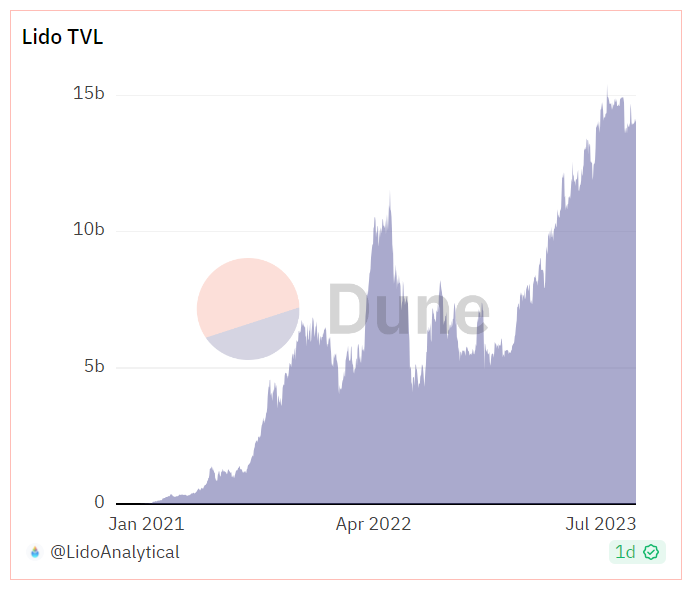
Since the beginning of this year, Lido's TVL has been consistently rising. Why has Lido been able to develop into the largest staking protocol in the market, with the highest TVL in DeFi protocols, occupying 32.5% of the staking track, nearly four times that of the second-place Coinbase, with a TVL market of nearly $14.2 billion? The main reasons are as follows:
1) First-mover advantage, user-friendly for novices:
Since the launch of the ETH 2.0 contract in December 2020, many ordinary users were not willing to lock in 32 ETH directly. At that time, PoS and PoW had not yet merged, and ETH could only flow from the PoW chain to the PoS chain unidirectionally, resulting in the loss of liquidity. In this context, Lido was born. Therefore, the project itself was born to address the staking issues during the transition of Ethereum, making Lido the preferred choice for ordinary users to participate in ETH 2.0 staking, leading to tremendous growth.
2) Support for multiple mainstream public chains: Including Solana (SOL), Polygon (MATIC), Polkadot (DOT), and Kusama (KSM), with a strong ecosystem. Due to the large user base and portfolio, the liquidity on Lido is also the highest compared to other platforms, thus creating a Matthew effect. Especially after the upgrade of Ethereum Shanghai, the network effect of Lido in stETH is more pronounced.
Currently, Lido's profit model mainly relies on taking a 10% cut from staking rewards as income, with 5% going to staking node operators and another 5% entering the Lido treasury for governance.
According to reports, despite activating the function to withdraw staked ETH earlier this year, the protocol still sees a large net inflow of ETH deposits every month. The July report released by the Ethereum staking protocol Lido showed that the total locked value (TVL) exceeded $15 billion for the first time since May 2022, with the staked ETH expected to exceed 8 million in September. With this development trend, Lido will continue to maintain its advantage in the medium term, doubling its profits.
02 MakerDAO
MakerDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization on the Ethereum blockchain, dedicated to advancing the development of cryptocurrency lending. Founded in 2015, it is the longest-running project on the Ethereum blockchain and currently ranks second in TVL, at around $5 billion.
MakerDAO consists of the DAI, pegged to the US dollar, and the Maker protocol, a smart contract on the Ethereum blockchain (a dApp). DAI is built on top of the Maker protocol and was launched in 2017.
As the first DAO organization established on Ethereum, DAI currently ranks No. 1 in the application scale of decentralized stablecoins, and MakerDAO has also made significant contributions in the DeFi field. MakerDAO's overcollateralization mechanism eliminates the risk of "printing money out of thin air" and is a breakthrough development that operates entirely on-chain, addressing the risk of centralized custody.
MakerDAO's current sources of income are:
1) Stability fee income from the surplus collateral vault
2) Liquidation penalty income from the liquidation vault
3) Stablecoin exchange transaction fees
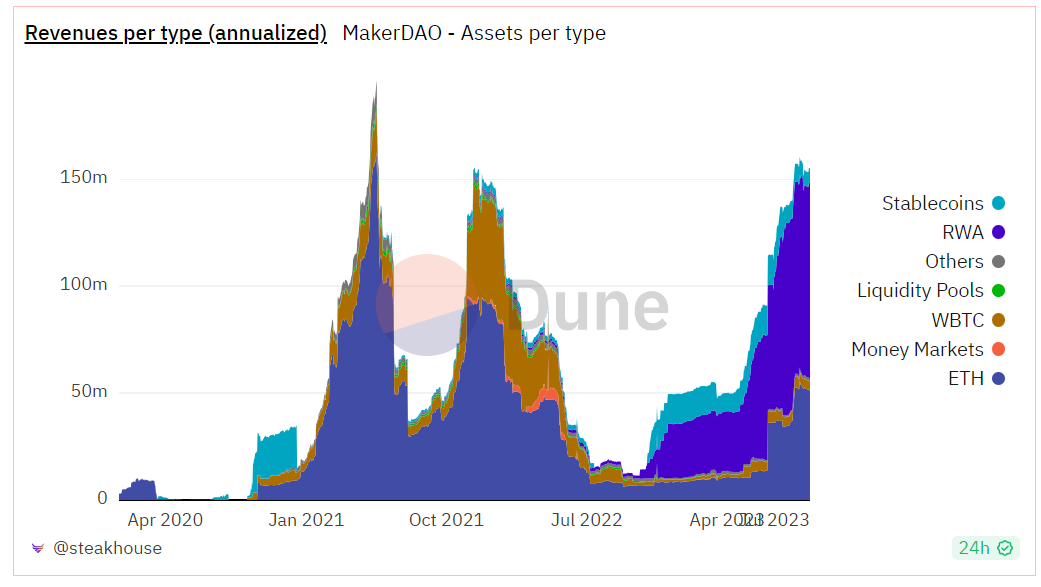
Before 2022, the stability fee and liquidation fee collected from the ETH-Assets vault on MakerDAO were the largest sources of income each month. However, with the increasing investment in RWA (real-world assets), it is evident that the current reliance on RWA for profits is as high as 56.4%. This clearly shows that RWA contributes the most to the protocol's income.
03 AAVE
Aave is also one of the cryptocurrency lending protocols, formerly known as ETHLend, created in Switzerland in 2017 to allow people to borrow cryptocurrencies and RWAs without the need for a centralized intermediary. Initially built on the Ethereum network, all tokens on the network also use the Ethereum blockchain to process transactions. Aave has since expanded to other blockchain networks, including Avalanche, Fantom, and Harmony, among others.
Users can deposit various cryptocurrencies into AAVE's smart contracts to form a "deposit pool," which can be used to provide lending services to other users. Borrowers need to provide collateral to ensure the safety of the loan, while depositors can earn interest on their deposits.
The AAVE token plays an important role in the protocol, used for governing the protocol and paying fees. AAVE's advantage is its support for multiple cryptocurrencies and high liquidity, but it also comes with risks, as lending and collateral are affected by price fluctuations in the cryptocurrency market.
Similar to MakerDAO, Aave generates income by collecting various fees on its platform. It then deposits these earnings into the Aave community treasury, where AAVE token holders have the right to decide how to use these funds.
Specifically, some of the ways Aave collects fees include:
1) Borrowing fees: Fees charged to borrowers on the platform, typically ranging from 0.01% to 25%, depending on the borrowed asset, loan-to-value ratio, and loan term;
2) Flash loan fees: Fees charged to users using the platform's "flash loan" feature, allowing them to borrow funds without collateral for a short period. The fee is typically 0.09% of the borrowed amount;
3) Other feature fees: In V3, Aave will provide additional fees, such as liquidation, instant liquidity, portal bridges, etc.;
Currently, AAVE's TVL is approximately $4.5 billion, and its trend is generally consistent with the market trend.
04 Justland

JustLend is a decentralized lending protocol based on TRON, launched by Justin Sun in the third quarter of 2020. Its name is derived from the first four letters of the founder's name.
JustLend offers various DeFi solutions, including JustStable, JustLend, JustSwap, JustLink, and cross-chain tokens, forming an algorithmic asset pool to allow users to earn interest on various asset categories. Users can generate returns by providing assets and obtain digital assets by providing collateral, and stake TRX on the TRON blockchain.
The core DeFi product on the network is JustStable, supported by the USDJ pegged to the US dollar. JustStable is a cross-border stablecoin lending platform where users can borrow stablecoins by providing collateral.
JustLend's current profit model mainly includes:
1) Interest rate differential: The platform generates income from borrowers by charging high interest rates and paying low interest rates to depositors, with the difference being the platform's source of profit;
2) Lending fees: The platform may charge borrowers a certain fee;
3) Platform token appreciation: If there is a platform token, its value may increase by encouraging users to use the token to pay fees or receive discounts.
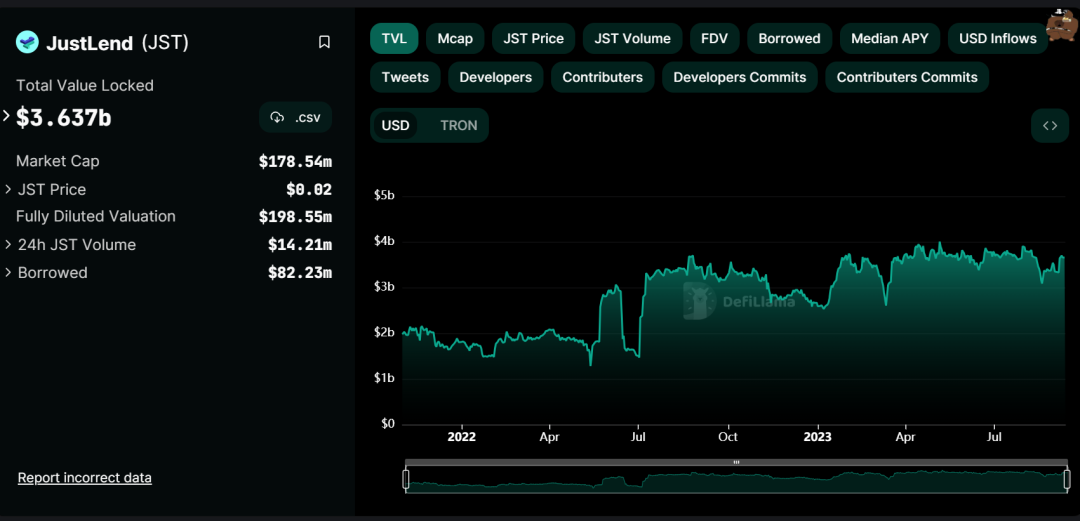
JUSTLend has developed rapidly because of its lucrative APY rewards for deposits in the lending market, sometimes reaching up to 30%. Its project advantage lies in its reliance on the TRON ecosystem, which has garnered a large number of users and resources. Therefore, despite the bleak market conditions, its TVL has increased to approximately $3.6 billion, ranking fourth.
05 Uniswap
Uniswap is a DEX created in 2018 and built on Ethereum. The idea was initially proposed by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin and founded by former Siemens mechanical engineer Hayden Adams. To date, the technology behind Uniswap has undergone multiple iterations. It has now evolved to Uniswap v3, one of its most significant changes being the improvement of capital efficiency and enhanced market liquidity.
As an automated liquidity protocol, Uniswap's trades do not require any order book or any centralized intermediaries, meaning users can trade directly without intermediaries, bringing a high level of decentralization and censorship resistance to the market, making it a leading project in the DEX track.
Currently, Uniswap's TVL is approximately $3.3 billion. However, due to the protocol's decentralization, the creators of Uniswap do not take a cut from any transactions conducted on the protocol. Liquidity providers on Uniswap control trades and charge fees for their services.
Uniswap has adopted different fee structures for its V3 pools, with fees ranging from 0.01%, 0.05%, 0.3%, and 1%. However, for V2 pools, the standard fee rate is 0.3%. These fees are automatically added to the liquidity pool, but liquidity providers can withdraw them at any time. Transaction fees are distributed based on the liquidity provider's share in the pool, with some fees used for Uniswap's development iterations.
06 Curve Finance
Curve Finance is an automated market maker protocol launched in January 2020, aimed at providing a DEX built using AMM architecture, focusing mainly on mainstream stablecoins, synthetic assets, derivatives, etc. It primarily operates on Ethereum but has also been deployed on multiple chains such as Fantom, Polygon, Avalanche, Arbitrum, and Optimism.
On Ethereum, Curve is one of the most popular AMMs. It facilitates low-cost and low-slippage exchanges between stablecoins in a non-custodial manner. It is also a decentralized liquidity aggregator, allowing anyone to add their assets to several different liquidity pools and earn fees.
Curve's fees range between 0.04% and 0.4%. These fees are distributed between liquidity providers and veCRV holders. Its main profit model includes:
1) Transaction fees: Curve charges a certain percentage of fees from user transactions;
2) Lending and stablecoin exchange: Curve provides lending and stablecoin exchange services, generating fees from them;
3) Synthetic asset trading: It supports synthetic asset trading, attracting more liquidity and generating revenue.
Curve Finance holds a central position in the DeFi field. In August 2020, Curve DAO was created, and the native token CRV was issued. Since then, the protocol's TVL has steadily increased, becoming the largest DEX in terms of TVL. After experiencing over a year of turmoil in the crypto world, especially after the re-entry vulnerability incident in August, the protocol's locked TVL still ranks at the forefront of major DeFi protocols, at around $2.2 billion. Apart from its popular liquidity pools, another reason is its high dependence on other blockchain protocols, allowing for various combinations of decentralized applications.
07 SummerFi

SummerFi, formerly known as Oasis, originated from MakerDAO and was born in 2016, earlier than the stablecoin DAI launched in 2017. OasisDEX was MakerDAO's first DEX deployed on Ethereum. Its primary purpose at the time was to allow the exchange of Maker governance token MKR for WETH. In June 2021, as part of the dissolution of the Maker Foundation, the development and operation of Oasis.app were transferred from the Maker Foundation to its own entity.
The platform has recently been renamed Summer.fi, symbolizing a bright, joyful, and relaxing image, and also implying the team's vision to provide a beautified experience for traders.
Summer.fi currently offers three main services: lending, leverage, and staking. Like other decentralized protocols, Summer.fi charges fees for its services. These fees, in the case of borrowing funds, are similar to interest rates but are called stability fees. These fees are not consistent and vary based on different vaults and tokens, determined by MKR token holders, ranging from 0% to 4.5%. Other applicable fees include:
1) Borrowing: This feature does not charge any fees; instead, users incur ETH transaction gas costs;
2) Leverage: A fee of 0.2% is charged, and similarly, ETH transaction gas costs apply;
3) Staking: To enjoy this feature, a fee of 0.04% is charged;
4) Stop-loss: To close a vault, a fee of 0.2% is required, and transaction gas costs are incurred when triggering protection.
Since its establishment in 2021, TVL has been steadily rising to its peak during the bull market cycle, currently settling at approximately $2.2 billion, ranking seventh.
08 Coinbase Wrapped Staked ETH
Coinbase Wrapped Staked ETH was launched in June 2022, representing Ethereum staked on Coinbase as a token project, enabling it to function like an ERC-20 token and be compatible with DApps on the Ethereum blockchain. 1 WETH is equivalent in value to 1 ETH.
Users can wrap ETH into cbETH at no cost, trade it on Coinbase, and use it on DEXs such as Uniswap and Curve. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with DeFi applications and provide rewards for staked ETH without locking it. It achieves secure, fee-free custody of ETH, provides liquidity, and is compatible with various DeFi platforms.
Users can earn an annual interest rate of 3.3% on Coinbase and additional returns through different DeFi protocols. Supported by Coinbase's robust security measures, cbETH provides a user-friendly way to maximize staking rewards and is considered a secure and transformative utility token in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
In the cbETH whitepaper released by Coinbase in August 2022, it stated: "We hope that cbETH will be widely adopted in transactions, transfers, and usage in DeFi applications." "Through cbETH, Coinbase aims to contribute to the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem by creating highly practical wrapped tokens and open-source smart contracts."
Overall, backed by the largest compliant CEX Coinbase in the United States, with a large user base and resources. In terms of profit, wrapping staked ETH into cbETH is free, but Coinbase, as a validator node for Ethereum, takes a portion of the staking rewards as its delegation fee, ranging from 0.5% to 4.5%. Born in the trough of the crypto cycle and combined with the development of the staking track, it has been in a slow growth state, currently with approximately $2.1 billion in TVL.
Compound Finance is a decentralized protocol launched in 2018, built on the Ethereum network, allowing users to lend and borrow crypto assets without any third parties involved. It is also an algorithmic money market protocol that provides a way for users to earn interest on their savings. It focuses on maximizing idle crypto assets in locked wallets to generate profits and stable passive income. This means that anyone with a Web 3.0 wallet (such as MetaMask) can access it and start earning by staking.
Compound initially received funding from venture capitalists. Then, the Token COMP was created, giving holders the right to fees and governance of the protocol, leading to a more decentralized governance.
Currently, Compound Finance operates in a decentralized manner and is compatible with the EVM. The latest version of the protocol, Compound V3, brings several improvements, making it more secure, user-friendly, lower risk, and easier to manage.
Compound Finance competes with JustLend, MakerDAO, AAVE, and others mentioned earlier. Although it has been surpassed in recent years, as a pioneer in the liquidity mining model, it has made significant contributions to user profitability in DeFi lending and asset liquidity promotion.
Compound Finance's profit model is similar to its competitors, mainly coming from the interest rate differential between borrowing and lending interest. The interest rate for the token borrowed by users on the platform is determined by the borrowing and lending volumes in the platform through an algorithm. The platform retains 10% of the borrowing interest as platform revenue and distributes the remaining interest equally among the token depositors.
Compound Finance currently has a TVL of nearly $1.9 billion. According to DefiLlama, the total TVL is greatly affected by the cryptocurrency market cycle, but even so, it still ranks within the top ten.
10 InstaDapp
Instadapp is a middleware protocol that simplifies and unifies the frontend of DeFi, acting as an aggregator. Founded in 2018, its goal is to simplify the complexity of DeFi and ultimately become the unified frontend of DeFi, enabling convenient asset management. It has currently integrated mainstream DeFi protocols through smart wallets and bridging protocols, including Maker, Aave, Compound, and Uniswap, and also supports functions such as migrating collateral assets between protocols.
The current vision of InstaDApp seems to be to become the gateway to DeFi, catering to both ordinary users and developers and asset managers. Referring to successful internet companies such as Google and Taobao, they are essentially aggregators or "platforms." However, a considerable portion of DeFi users still lack understanding of InstaDApp, and its success will require market validation.
Instadapp has three products: Avocado, Instadapp Pro, and Instadapp Lite.
Avocado is an account-abstracted Web3 wallet; Instadapp Pro aggregates multiple DeFi protocols into an upgradeable smart contract layer; and Instadapp Lite, launched after the upgrade in Shanghai, is designed for various stETH-related strategies and is a vault limited to ETH deposits only.
Lite v2 enhances income through market cycle operations to strengthen LSD returns, and Instadapp takes 20% of the income. Even so, depositors can still earn slightly higher returns than Lido stETH, demonstrating the high efficiency of its capital operations.
Currently, the main profit model is Instadapp charging a 20% fee on profits, which is then transferred to the DAO responsible for distribution and use. However, it is currently running steadily, with a total TVL of approximately $1.8 billion, but is affected by market cycles.
11 Conclusion
From the above TVL ranking data, it is clear that the DeFi sector is still the leading sector in the entire cryptocurrency industry. Uniswap and Curve dominate the trading track, while MakerDAO, AAVE, and Compound rule the lending track. Lido provides a strong decentralized staking solution for ETH2.0, AAVE's security module innovation improves fund security, and Curve Finance's algorithm provides lower slippage for large stablecoin trades. JUSTLand and Coinbase Wrapped Staked ETH have accumulated a large user base and resources with the support of TRON and Coinbase, respectively.
In the evolving DeFi ecosystem, these projects play crucial roles, driving continuous innovation and development in the blockchain and cryptocurrency space.
What are your thoughts on these rapidly growing TVL applications?
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



