The most radical round of tariff policies since the 1930s is having a profound impact on the macroeconomy and the cryptocurrency market.
Author: Moulik Nagesh, Binance Research

Key Points
In 2025, trade protectionism led by the United States made a strong comeback. Since Donald Trump resumed the presidency in January 2025, the U.S. has raised concerns about a global trade war by implementing a series of large-scale new tariffs—targeting both specific countries and particular industries. Just in the past week, the U.S. launched a new round of "reciprocal" tariffs, prompting other countries to announce countermeasures.
This report will analyze how these tariffs (the most aggressive since the 1930s) are affecting the macroeconomy and the cryptocurrency market. We will examine tariff levels, macroeconomic trends (including inflation, growth, interest rates, and Federal Reserve outlook), and their impact on the performance, volatility, and correlation of crypto assets based on data. Finally, we will explore key points to watch in the future and the market outlook for crypto assets in an environment of stagflation and protectionism.
The 2025 Tariff Resurgence
After several years of relative trade peace, 2025 saw a rapid reversal. In the first few days of President Trump's return to the White House, he began fulfilling his campaign promises by imposing tariffs on a wide range of imported goods—covering specific countries and industries.
Trade tensions escalated further on April 2. On that day, the U.S. announced comprehensive "reciprocal" tariffs and designated the day as "Liberation Day," marking a new turning point in this round of global trade war. Many countries that previously viewed their trade relations with the U.S. as normalized have now undergone a fundamental shift. Key events from the past week include:
● Base Tariff: The U.S. announced a new 10% uniform tariff on all imported goods, reversing decades of trade liberalization. This base rate took effect on April 5.
● Targeted Tariffs: On top of the base rate, higher country-specific tariffs were added. President Trump referred to these as "reciprocal" tariffs, aimed at countries that impose high barriers on U.S. products. Notably, Chinese goods will incur an additional 34% tariff—resulting in a total tariff rate of 54% when combined with the existing 20%. Other countries' targeted tariffs include: 20% on EU goods, 24% on Japanese goods, 46% on Vietnamese goods, and 25% on automobile imports. Canada and Mexico were not included in the new list as they had already been subjected to a 20% tariff in February.
● Global Retaliation: U.S. trade partners quickly responded. By mid-February, several countries that had been taxed early announced countermeasures. Canada, having failed to secure an extension on U.S. tariffs, decided to impose a 25% tariff on all U.S. imports. China also responded early and escalated further on April 4, announcing a 34% tariff on all U.S. imports.
With the implementation of "reciprocal" tariffs and escalating trade tensions, more countries are expected to introduce their own countermeasures. The EU has clearly stated it will respond soon, and several other major economies have also developed relevant counterattack plans. While the full extent of the global response remains unclear, all signs currently indicate that a broad trade war involving multiple fronts is forming.
Chart 1: "Liberation Day" Tariffs on April 2, 2025, Affecting Up to 60 Countries, Including Several Major U.S. Trade Partners Note: This table reflects the "reciprocal" tariffs imposed by the U.S. on its top ten import source countries as of April 2.
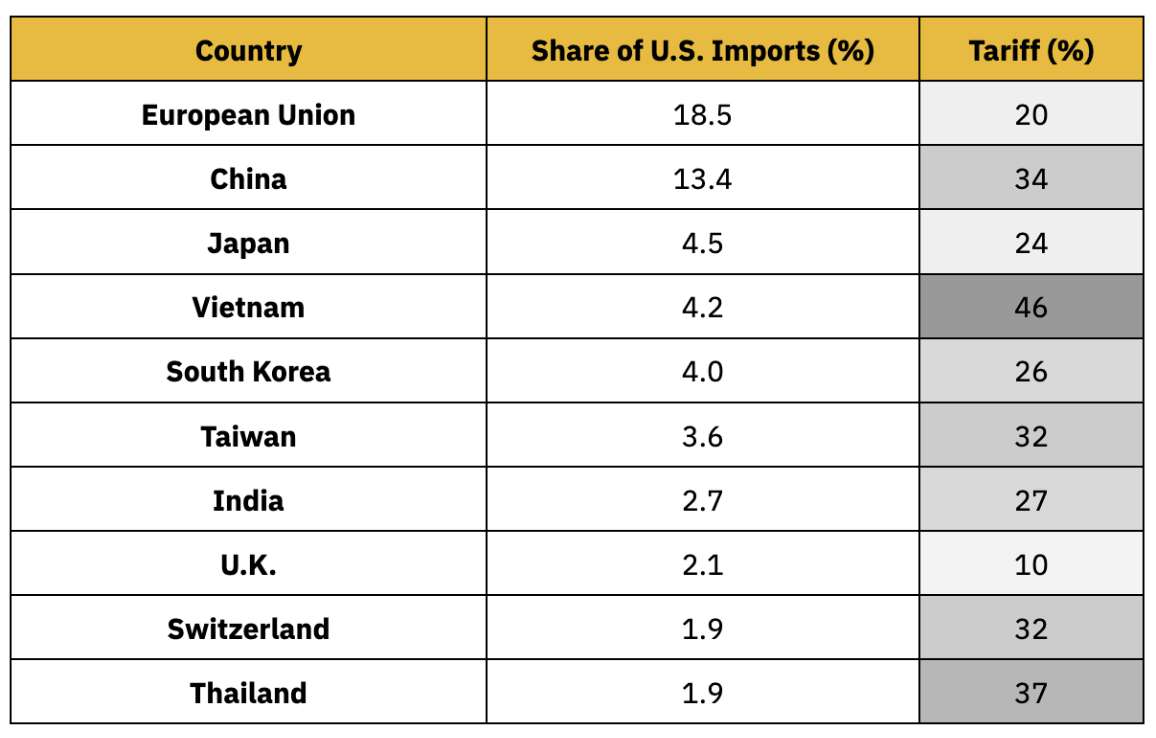
Source: BBC, X (@WhiteHouse), Binance Research, as of April 3, 2025
These policies have caused U.S. import tax rates to soar to their highest level since the implementation of the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act in 1930, which imposed comprehensive tariffs on thousands of goods during the Great Depression. According to existing data, the average tariff rate in the U.S. has risen to about 18.8%, with some estimates even reaching 22%—a dramatic leap compared to 2.5% in 2024.
For reference, the average tariff rate in the U.S. has typically remained between 1-2% over the past few decades; even during the U.S.-China trade frictions that erupted in 2018-2019, it only rose to around 3%. Therefore, the measures in 2025 represent an unprecedented tariff shock in modern history—almost equivalent to a return to the protectionism of the 1930s.
Chart 2: The Rise in U.S. Tariffs Has Elevated Import Tax Rates to Their Highest Levels in Nearly a Century
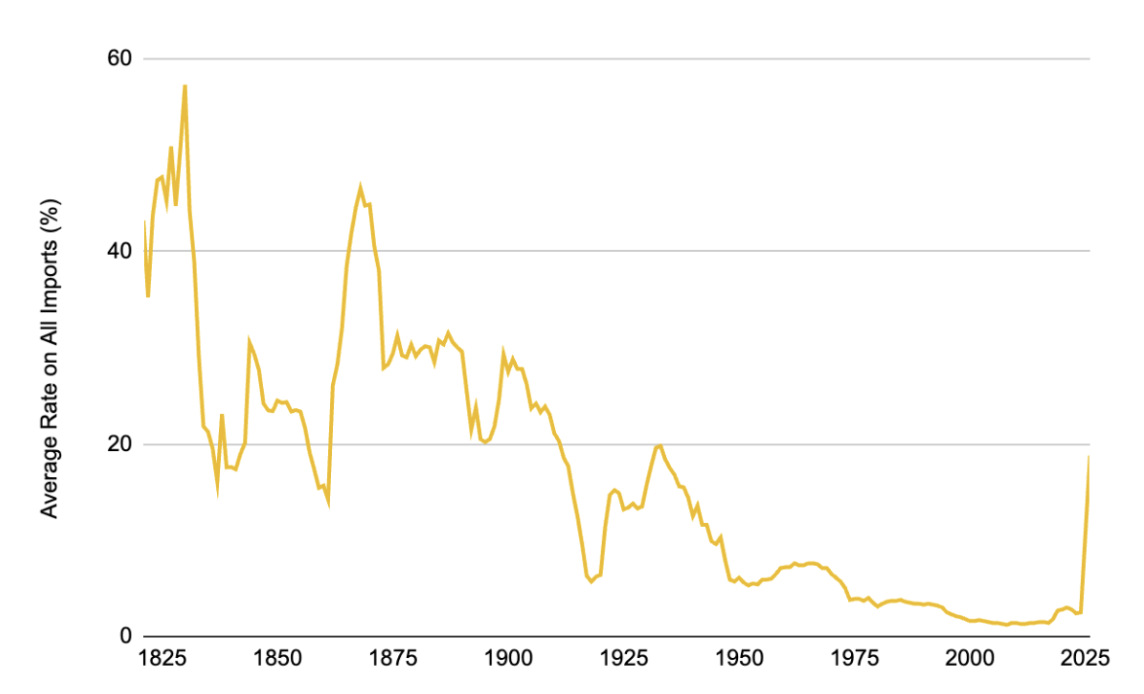
Source: Tax Foundation, Binance Research, as of April 3, 2025
Market Impact: Cooling Demand, Rising Risk Aversion, and Soaring Volatility
1. Cooling Demand and Rising Risk Aversion
Market sentiment has clearly shifted to caution, with investors exhibiting typical "risk-averse" behavior in response to the tariff announcements. The total market capitalization of the cryptocurrency market has dropped by about 25.9% from its January peak, erasing nearly $1 trillion in value, highlighting its high sensitivity to macroeconomic instability.
Cryptocurrency assets have closely followed the stock market, both facing cooling demand, widespread sell-offs, and entering correction territory. In contrast, traditional safe-haven assets like bonds and gold have performed well, with gold continuously reaching historical highs, becoming a refuge for investors amid rising macro uncertainty.
Chart 3: Since the Initial Tariff Announcement, the Cryptocurrency Market Has Fallen 25.9%, the S&P 500 Index Has Dropped 17.1%, While Gold Has Increased by 10.3%, Continuously Setting Historical Highs
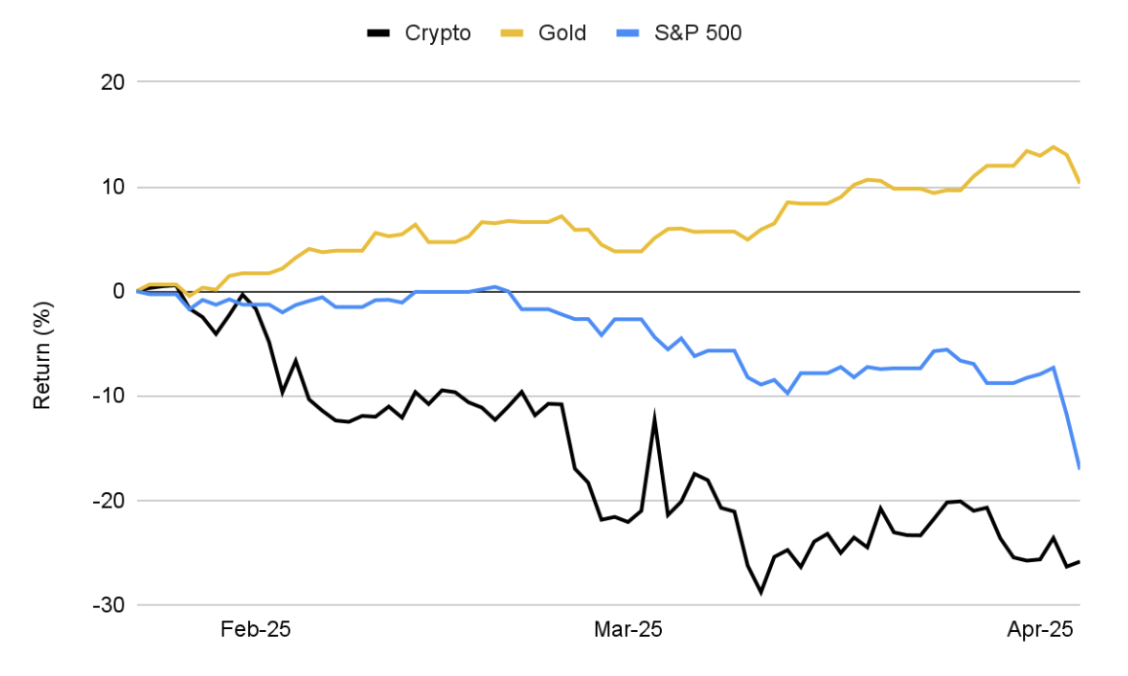
Source: Investing.com, CoinGecko, Binance Research, as of April 4, 2025
The severe market reaction also highlights the characteristics of cryptocurrency assets during intense "risk-averse" periods: Bitcoin (BTC) fell by 19.1%, with most mainstream altcoins experiencing similar or even greater declines. Ethereum (ETH) dropped over 40%, while high-beta sectors (such as meme coins and AI-related tokens) plummeted more than 50%. This round of sell-offs erased most of the gains in the cryptocurrency market since the beginning of the year; as of early April, even BTC's year-to-date (YTD) returns have turned negative—despite its strong performance in 2024.
Chart 4: In the Macroeconomic Panic Triggered by Tariffs, Altcoins Have Experienced Declines Significantly Greater Than Bitcoin, Intensifying Market Pessimism
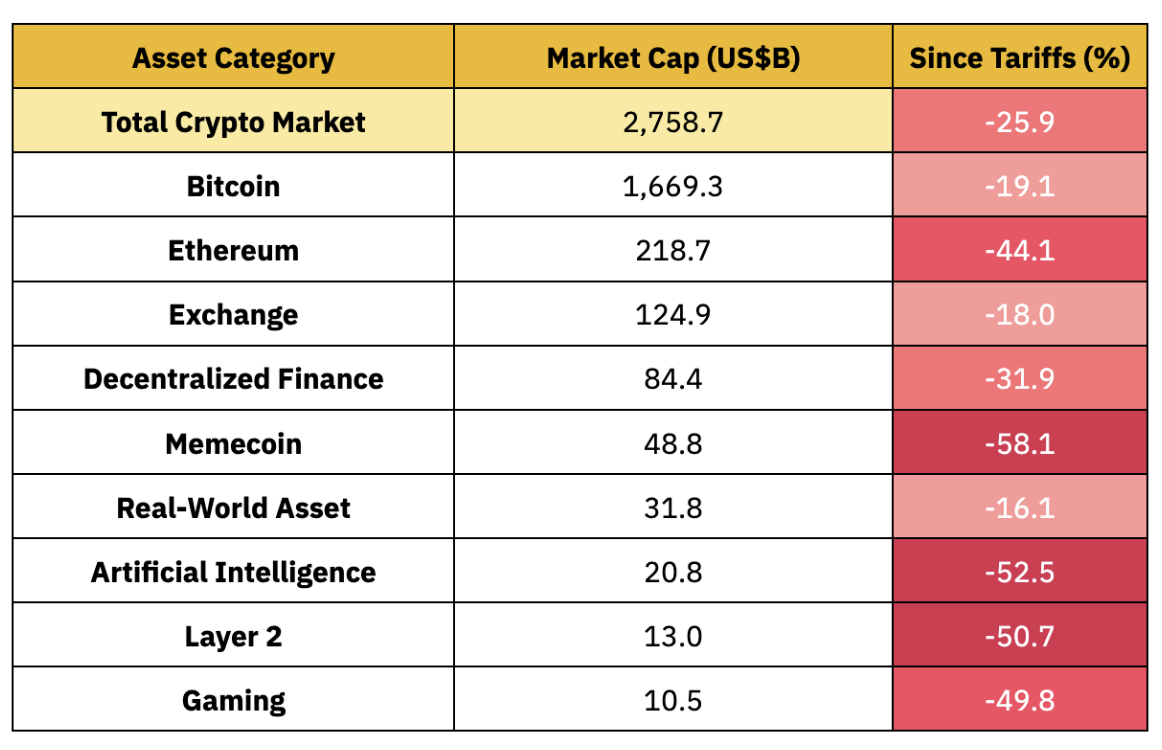
Source: CoinGecko, Binance Research, as of April 4, 2025
As the cryptocurrency market increasingly exhibits characteristics of a risk asset, if the trade war continues, it may further suppress capital inflows and dampen demand for digital assets in the short term. Capital may remain on the sidelines or shift to gold and other assets perceived as safer. This sentiment is also reflected in a recent fund manager survey, where only 3% of respondents indicated they would allocate to Bitcoin in the current environment, while 58% preferred gold.
Chart 5: Only 3% of Global Fund Managers View Bitcoin as the Preferred Asset Class in the Context of a Trade War
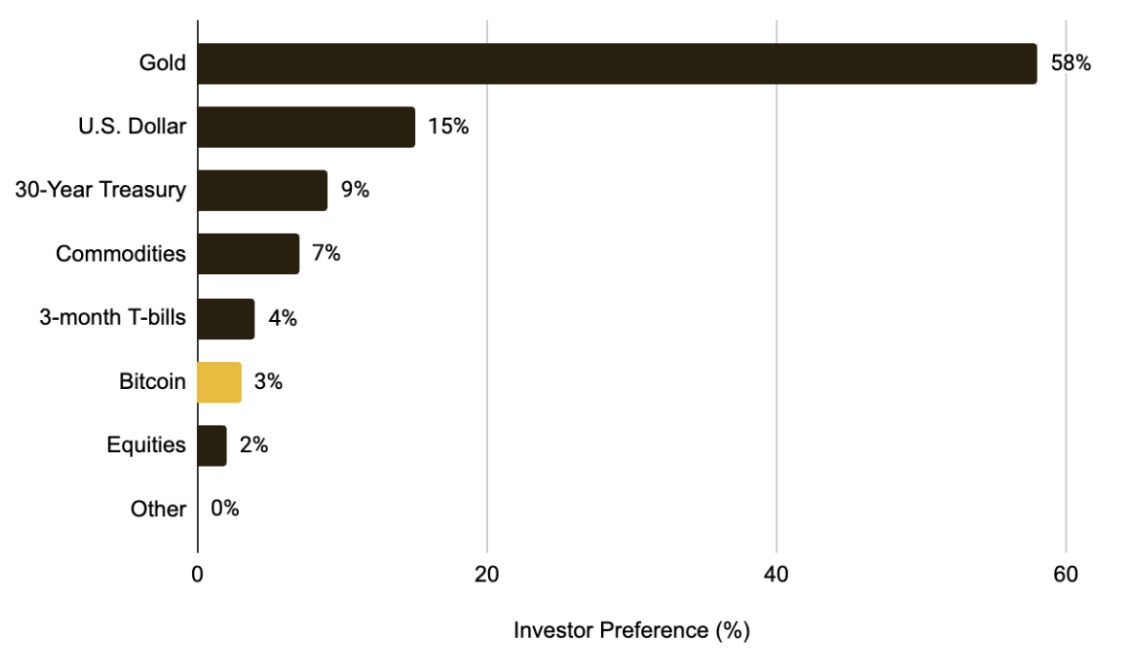
Source: BofA Global Fund Manager Survey, Binance Research, as of February 2025
2. Soaring Volatility
The market's sensitivity to tariff policies is evident, with each major announcement triggering significant price fluctuations. Over the past few months, BTC has experienced multiple large price swings—including one of the largest single-day declines since the COVID-19 crash in 2020. At the end of February 2025, when Trump suddenly announced plans to impose tariffs on Canada and the EU, BTC dropped about 15% in the following days, while its actual volatility surged significantly. ETH exhibited similar behavior, with its one-month volatility skyrocketing from around 50% to over 100%.
These market behaviors underscore the cryptocurrency market's extreme sensitivity to sudden policy changes in the current high-uncertainty macro environment. In the near future, if policy directions remain unclear or the trade war escalates further, the market will likely maintain high volatility. Historical experience also indicates that volatility may gradually decrease only after the market fully digests and prices in the new tariff policies.
Chart 6: During This Phase, BTC's One-Month Actual Volatility Rose Above 70%, While ETH Exceeded 100%, Reflecting Severe Market Fluctuations Following the Tariff Announcement
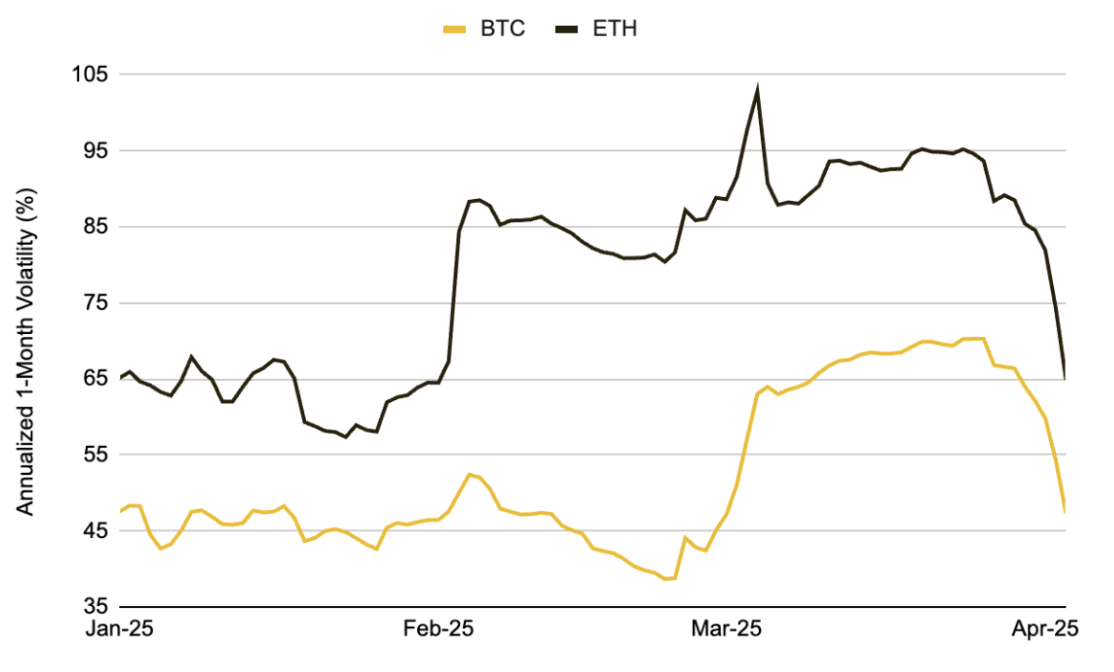
Source: Glassnode, Binance Research, as of April 4, 2025
Macroeconomic Impact: Inflation, Stagflation Concerns, Interest Rates, and Federal Reserve Outlook
1. Inflation and Stagflation Concerns
The new tariffs effectively impose a large amount of additional taxes on imported goods, coinciding with the Federal Reserve's efforts to curb price growth, thereby exacerbating inflationary pressures. The market has begun to show concerns that these measures may disrupt the process of inflation decline. Market indicators such as one-year inflation swaps have surged above 3%, while expectations in consumer surveys have risen to around 5%, indicating a widespread belief that prices will continue to rise over the next 12 months.
At the same time, economists warn that if the trade war escalates fully and triggers a global retaliatory response, the loss of global economic output could reach $1.4 trillion. U.S. per capita real GDP is expected to decline by nearly 1% initially. Fitch Ratings noted that if a comprehensive tariff regime persists, most economies may enter recession, stating that "the current high level of U.S. tariffs has rendered most economic forecasting models ineffective."
With rising inflation expectations and concerns about growth, the risk of the global economy slipping into stagflation (a coexistence of economic stagnation and rising prices) is increasingly prominent.
Chart 7: Changes in Macroeconomic Conditions in 2025 Drive One-Year Expected Inflation Upward and Growth Expectations Downward
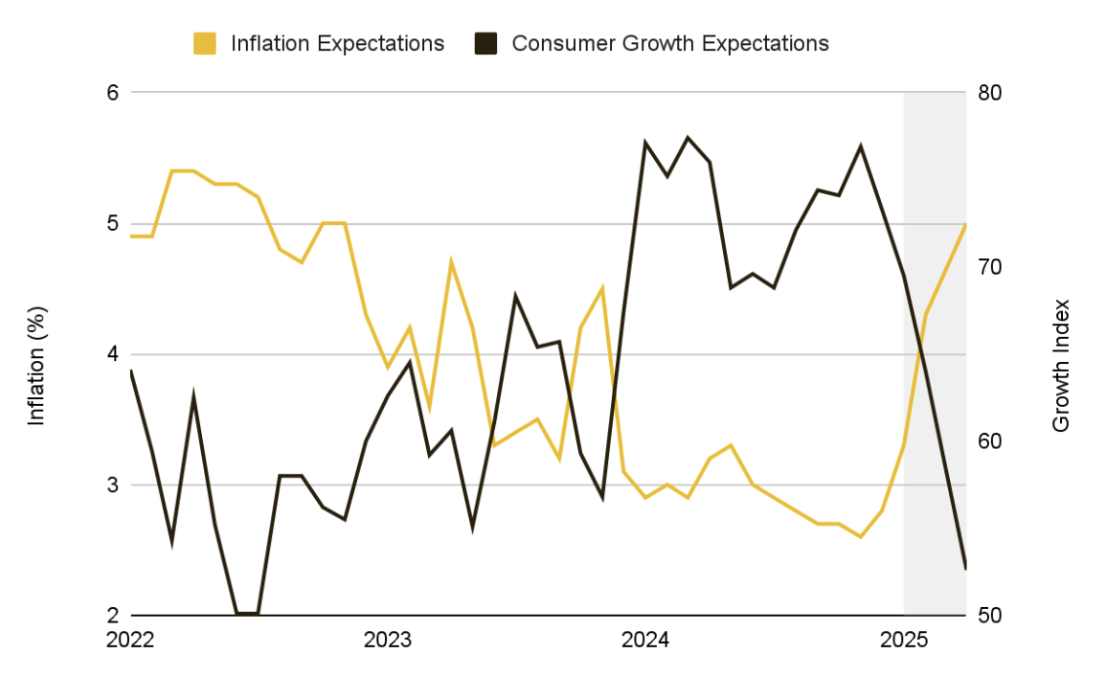
Source: University of Michigan, Binance Research, as of April 5, 2025
2. Interest Rate Outlook and Federal Reserve Stance
Federal funds futures data show that market expectations for interest rate cuts in the coming months have risen significantly. This marks a clear shift in attitude—just weeks ago, the Federal Reserve was firmly committed to curbing inflation, but now, due to rising concerns about economic growth prospects, the market has begun to anticipate a potential shift towards easing monetary policy to support the economy.
Chart 8: Market Expectations for Rate Cuts in 2025 Continue to Rise, Currently Anticipating Four 25 Basis Point Cuts—Significantly Higher Than the Previous Expectation of Just One Cut
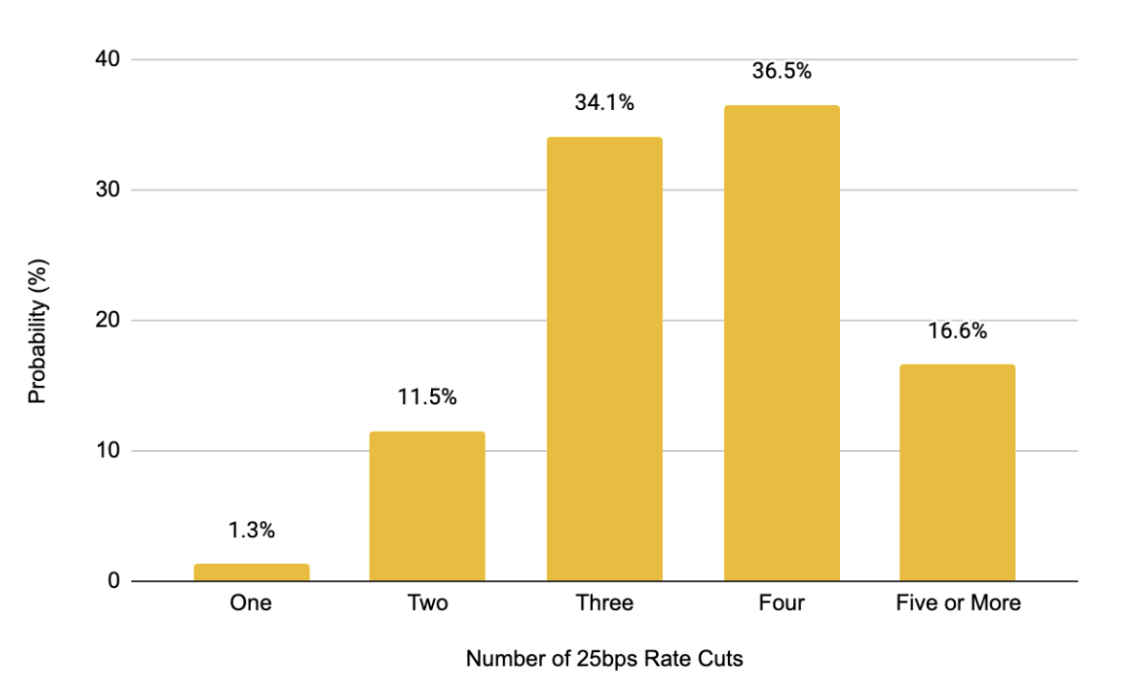
Source: CME Group, Binance Research, as of April 4, 2025
This shift in sentiment is reflected in the public statements of Federal Reserve officials. They have expressed concerns, emphasizing that the new round of tariffs is contrary to previous economic policy guidelines. The Federal Reserve now faces a difficult choice: to tolerate the additional inflation brought on by tariffs or to maintain a hawkish stance at the risk of further suppressing growth?
"The scale of tariffs announced in recent weeks has exceeded expectations, and their impact on inflation and growth—especially the cumulative effect—needs to be closely monitored."
— Jerome Powell, April 4, 2025
In the short term, the Federal Reserve seems committed to maintaining stable long-term inflation expectations. However, monetary policy decisions will continue to rely on data, depending on which signal—inflation or growth—appears weaker. If inflation significantly exceeds targets, the stagflation environment may limit the Federal Reserve's ability to respond. This uncertain policy outlook also exacerbates market volatility.
Outlook
1. Correlation and Diversification Allocation
The evolving relationship between cryptocurrency assets and traditional markets is becoming a focal point—Bitcoin, as the dominant asset in the market, serves as the best window to observe this change. The "risk aversion" event triggered by the trade war has significantly affected the correlation structure between BTC and the stock market as well as traditional safe-haven assets.
Since tariffs were first mentioned on January 23, the initial market response was inconsistent—Bitcoin's movements were somewhat independent of stocks, causing their 30-day correlation to drop to –0.32 on February 20. However, as trade war rhetoric escalated and risk aversion sentiment spread, this value rose to 0.47 in March, indicating an increased short-term linkage between Bitcoin and overall risk assets.
In contrast, the correlation between Bitcoin and traditional safe-haven assets like gold has significantly weakened—the previously neutral to positive relationship turned into a negative correlation of –0.22 by early April.
These changes indicate that macroeconomic factors, particularly trade policy and interest rate expectations, are increasingly dominating cryptocurrency market behavior, temporarily suppressing the market structure that was originally driven by supply and demand logic. Observing whether this correlation structure persists will help understand Bitcoin's long-term positioning and its diversification value.
Chart 9: Initial Responses Diverged; As the Trade War Escalated, BTC's Correlation with the S&P 500 Increased, While Its Correlation with Gold Continued to Weaken
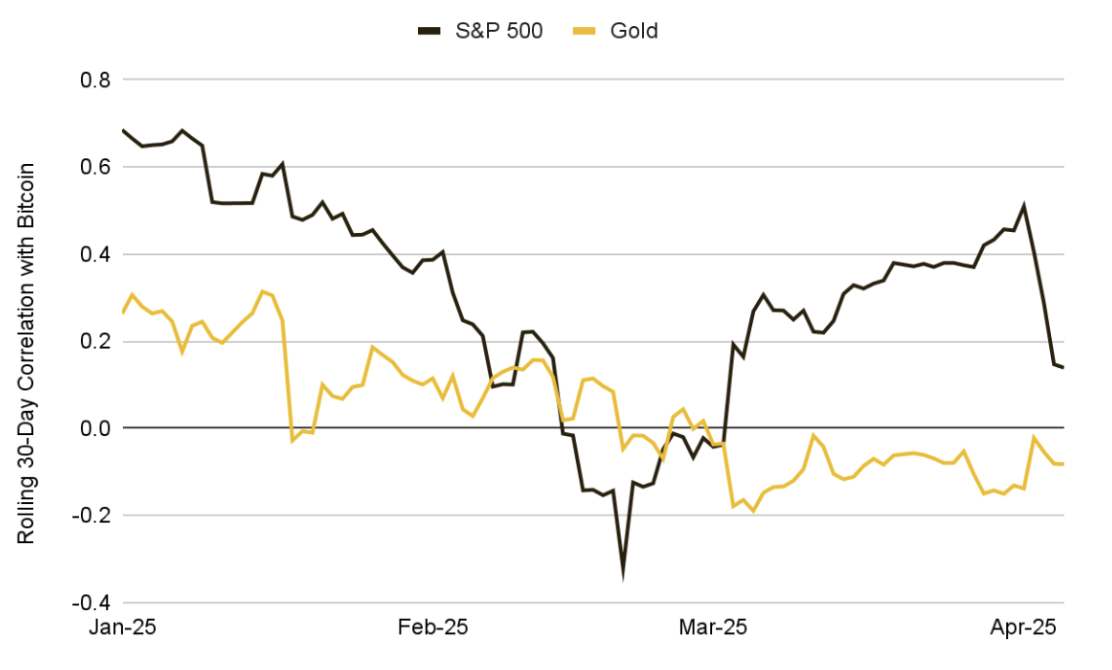
Source: Investing.com, Binance Research, as of April 5, 2025
2. Reclaiming the Safe-Haven Asset Narrative
Although recent macro and liquidity shocks have highlighted the "risk attributes" of cryptocurrency assets, the long-term trend remains unchanged: Bitcoin's correlation with traditional markets typically rises under extreme pressure but gradually declines as the market stabilizes. Since 2020, the 90-day average correlation of BTC with the stock market has been about 0.32, while with gold it has only been 0.12, indicating that it has maintained a certain degree of separation from traditional asset classes.
Even in the wake of the recent tariff announcements, BTC has shown some resilience on trading days when certain traditional risk assets weakened. Meanwhile, the supply from long-term holders continues to rise—indicating that core holders have not significantly reduced their positions during recent volatility, but rather show strong confidence.
This behavior suggests that despite increased short-term price volatility, Bitcoin may still re-establish a more independent macro identity.
Chart 10: Since 2020, Bitcoin's Long-Term Correlation with Traditional Assets Remains Moderate: 0.32 with the S&P 500 and 0.12 with Gold
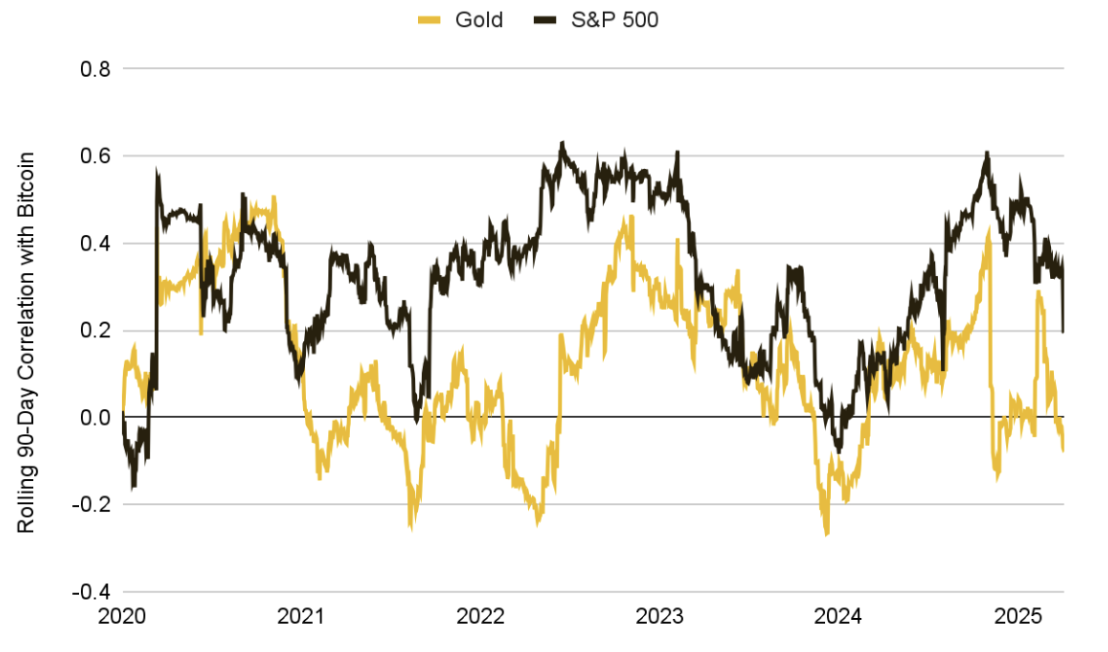
Source: Investing.com, Binance Research, as of April 5, 2025
The key question is whether BTC can return to a long-term structure of low correlation with the stock market. A similar trend was observed during the banking turmoil in March 2023, when BTC successfully decoupled and strengthened amid a stock market downturn.
Now, as the trade war intensifies and global markets begin to adapt to a long-term fragmented trade landscape, whether Bitcoin can once again be viewed as a "sovereign-free, permissionless" safe-haven asset will determine its future macro role. Market participants will closely monitor whether BTC can retain this independent value proposition.
One potential path is to reclaim its appeal during periods of currency inflation and fiat currency depreciation, especially when the Federal Reserve shifts towards easing. If the Federal Reserve begins to cut rates while inflation remains high, Bitcoin may regain favor as a "hard asset" or inflation hedge.
Ultimately, this process will determine BTC's long-term positioning as an asset class—and its diversification utility within investment portfolios. This also applies to other mainstream altcoins, which exhibit stronger risk attributes in the current environment and may continue to rely on BTC-driven market sentiment.
3. The Cryptocurrency Market in a Stagflation and Protectionism World
Looking ahead, the cryptocurrency market will face a complex macro environment dominated by trade policy risks, stagflation pressures, and a breakdown of global coordination. If global growth continues to weaken and the cryptocurrency market fails to establish a clear narrative, investor sentiment may further decline.
A prolonged trade war will test the resilience of the entire industry—potentially leading to a depletion of retail capital, a slowdown in institutional allocations, and reduced venture capital funding. Key macro variables to closely monitor in the coming months include:
● Trade Dynamics: Any new tariff lists, unexpected easing measures, or significant bilateral changes (such as U.S.-China negotiations or further escalations) will directly impact market sentiment and inflation expectations.
● Core Inflation Data: Upcoming CPI and PCE data are crucial. If they unexpectedly rise due to import cost pressures, stagflation concerns will intensify; if the data is weak, it may alleviate pressure on central banks and enhance the appeal of risk assets (including cryptocurrencies).
● Global Growth Indicators: Declining consumer confidence, slowing business activity (PMI), a weak labor market (rising unemployment claims, slowing non-farm employment), corporate profit warnings, and an inverted yield curve (a common recession signal) may further trigger risk aversion in the short term. However, if macro weakness accelerates expectations for monetary easing, it could provide support for the cryptocurrency market.
● Central Bank Policy Path: How the Federal Reserve and other major central banks seek to balance inflation and recession will determine liquidity across various assets. If they refuse to cut rates against a backdrop of slowing growth, risk assets will continue to be pressured; if they shift towards easing, it could lead to a broad uplift. If real interest rates decline (whether due to policy or persistent inflation), long-duration assets like Bitcoin may benefit. Divergence in central bank policies (e.g., the Federal Reserve turning dovish while the European Central Bank remains hawkish) may also trigger cross-border capital flows, further exacerbating volatility in the cryptocurrency market.
● Cryptocurrency-Specific Policy Events: Approvals for ETFs, strategic BTC reserves, and key legislative advancements may become independent catalysts in the current macro backdrop, potentially breaking the "macro binding" state of cryptocurrency assets and re-emphasizing their uniqueness. However, caution should also be exercised regarding reverse risks, such as regulatory delays or unfavorable litigation developments, which could produce negative feedback.
Conclusion
The most radical round of tariff policies since the 1930s is having a profound impact on the macroeconomy and the cryptocurrency market. In the short term, the cryptocurrency market may continue to exhibit high volatility, with investor sentiment swaying with trade war news.
If inflation remains high while growth slows, the Federal Reserve's response will become a critical turning point: if it shifts towards easing, the cryptocurrency market may rebound due to rising liquidity; if it maintains a hawkish stance, pressure on risk assets will persist.
If the macro environment stabilizes and a new narrative emerges, cryptocurrency assets may regain their long-term safe-haven status, and the market could be poised for recovery. Until then, the market may maintain a volatile pattern and remain highly sensitive to macro news. Investors need to closely monitor global dynamics, maintain diversified asset allocations, and seek opportunities amid potential market dislocations brought about by the trade war.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




