Author: Rishabh Nagar
Translated by: Felix, PANews
Currently, doing anything on-chain feels like assembling furniture from IKEA—there are many steps, it's confusing, and there's always a risk of messing it up. It gets even more chaotic when you have to switch between different blockchains. You need to remember every step, be wary of scams, calculate fees, and not lose your mind in the process.
Now, imagine that you don’t have to perform various operations across different blockchains—buying, exchanging, sending tokens through bridges, yield farming, and then exchanging back to your favorite cryptocurrency—all you have to do is say out loud what you want, and magically, everything is done safely and smoothly. This is exactly what "intents" aim to achieve.
Why Are Intents Important in the Crypto World?
Intents are like digital wishes. They help users accomplish what they want to do on the internet, such as sending money or voting directly and automatically. In the crypto world, understanding intents is crucial because they allow users to control their actions without needing intermediaries or companies. This makes things faster, cheaper, and safer.
Suppose you want to send a letter to a friend. Traditionally, you would hand it to a postal worker, who might first take it to a large office, and then another person would deliver it to your friend. This is how things typically work in today’s tech world.
Now, imagine if you could just press a button, and your letter magically appears in your friend's hands. This is what decentralized intents look like—skipping the middleman and doing what you want directly, safely, and quickly. This is important because it means you don’t have to worry about interference from others, slowing things down, or losing the letter.
Introduction to Decentralized Intents
Intents are at the core of the goals individuals want to achieve—whether it's a simple asset transfer or a more complex execution of a series of coordinated transactions. Traditionally, these intents are managed through centralized systems, but blockchain technology increasingly allows for their realization in a decentralized manner.
For example, consider the intent to participate in a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) vote. In a traditional setup, you would need to interact with a centralized platform where votes could be manipulated, delayed, or even censored. In contrast, in a decentralized system, this intent is expressed through smart contracts, which can automatically collect votes, tally them, and make decisions without needing a central authority.
This shift towards decentralized intent realization is significant because it represents a break from reliance on centralized intermediaries, empowering users with greater control, transparency, and security over their actions. It allows for the creation of systems that can directly realize intents without unnecessary barriers or the risk of third-party interference.
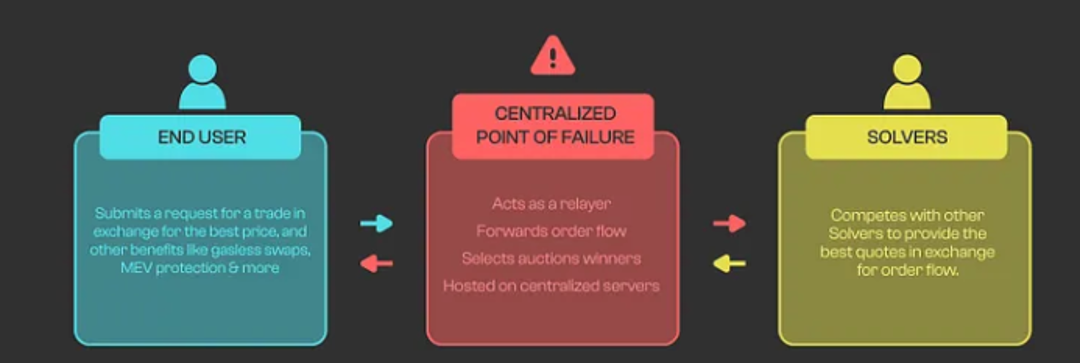
Source: Paraswap
Intents in Decentralized Applications
In a decentralized world, intents can be simple or complex. Simple intents might resemble executing a trade on a DEX, where a user's desire to exchange one cryptocurrency for another is processed directly on-chain, and the trade is automatically completed once the necessary conditions are met.
However, intents can also be quite complex. Imagine a scenario where a user wants to optimize their portfolio across multiple decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, balancing yield farming, liquidity provision, and automated trading strategies. This involves not just one action but a series of coordinated interactions with various protocols, each with its unique requirements and risks. Here, intents are multifaceted and require complex mechanisms to ensure they are realized in the most efficient manner.
In these cases, decentralized mechanisms like smart contracts, oracles, and decentralized or off-chain solvers begin to play a role in executing complex intents in a trustless and transparent manner. In traditional systems, these complex tasks would be impossible without centralized control.
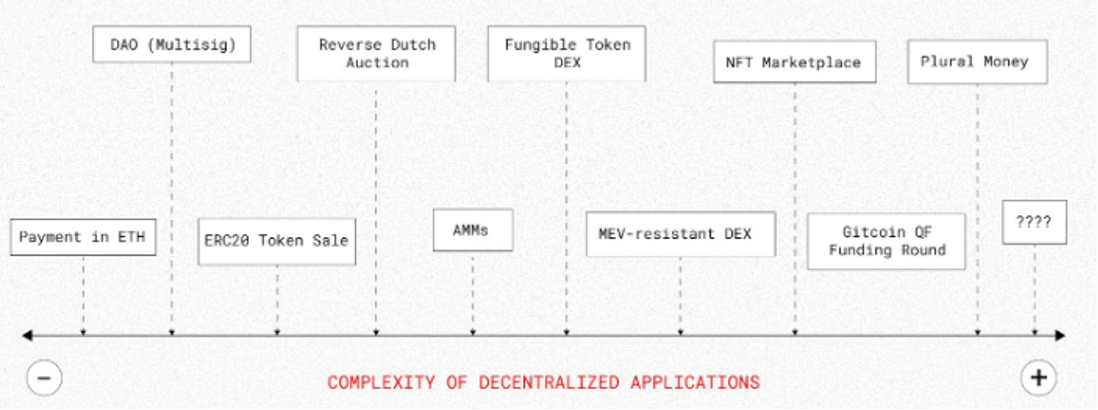
Source: Anoma
What is Chain-Agnostic and Why Do We Need Intents?
Chain-Agnostic means you can do what you want on any blockchain. Imagine using the internet: it doesn’t matter which Wi-Fi you connect to—you just want to send a message or watch a video.
In the crypto world, intents are like your digital instructions or wishes. To make them work smoothly across different blockchains, a Chain-Agnostic approach is needed. This way, you can easily and securely realize your intents on any blockchain without needing to understand or care about the differences between them.
Intents' Chain-Agnostic Nature
Intent-Centric Models in the Current Ecosystem
In various blockchain ecosystems, intent-centric models are becoming a way to simplify user interactions and enhance the efficiency of dApps. For example, in ecosystems like Ethereum, intents are often handled through smart contracts that manage everything from DeFi transactions to NFT trades. These systems are designed to ensure that once a user expresses an intent, the underlying infrastructure takes care of the rest, including finding counterparties, executing trades, and recording them on the blockchain.
In other ecosystems, such as Polkadot or Cosmos, intent-centric architectures are being explored to leverage the inherent interoperability features of these networks. For instance, in Polkadot, intents can be realized across different parachains, allowing users to interact with various dApps without worrying about the underlying technical differences between chains. Similarly, Cosmos is experimenting with cross-chain intent realization, enabling users to initiate actions on one chain and complete them on another while maintaining high levels of security and decentralization.
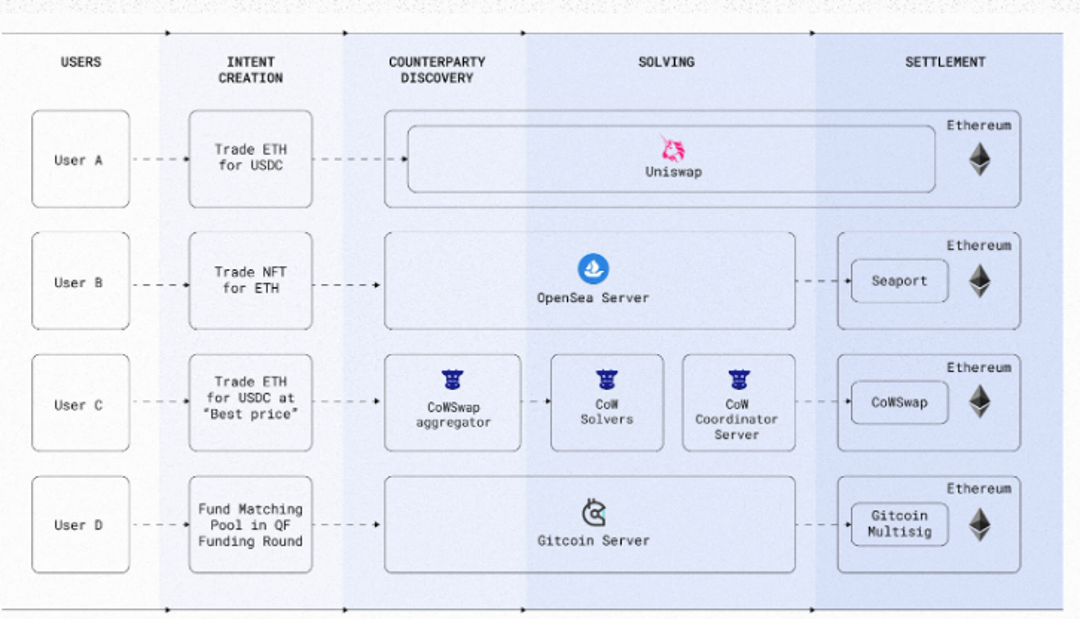
Source: Anoma
The Need for a Chain-Agnostic Framework
Despite these advancements, the current ecosystem remains largely fragmented, with most intents tied to specific blockchains. This fragmentation can lead to inefficiencies. A Chain-Agnostic framework aims to overcome these challenges by providing a unified system where intents can be expressed, processed, and realized on any blockchain, regardless of its underlying architecture.
In a Chain-Agnostic model, intents are a universal expression not limited to any single application or chain. For example, a user might express the intent to trade tokens, and regardless of whether the trade occurs on Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or another blockchain, the network will process this intent in the most efficient manner. This approach not only simplifies the user experience but also enables greater interoperability and composability between dApps across different chains.
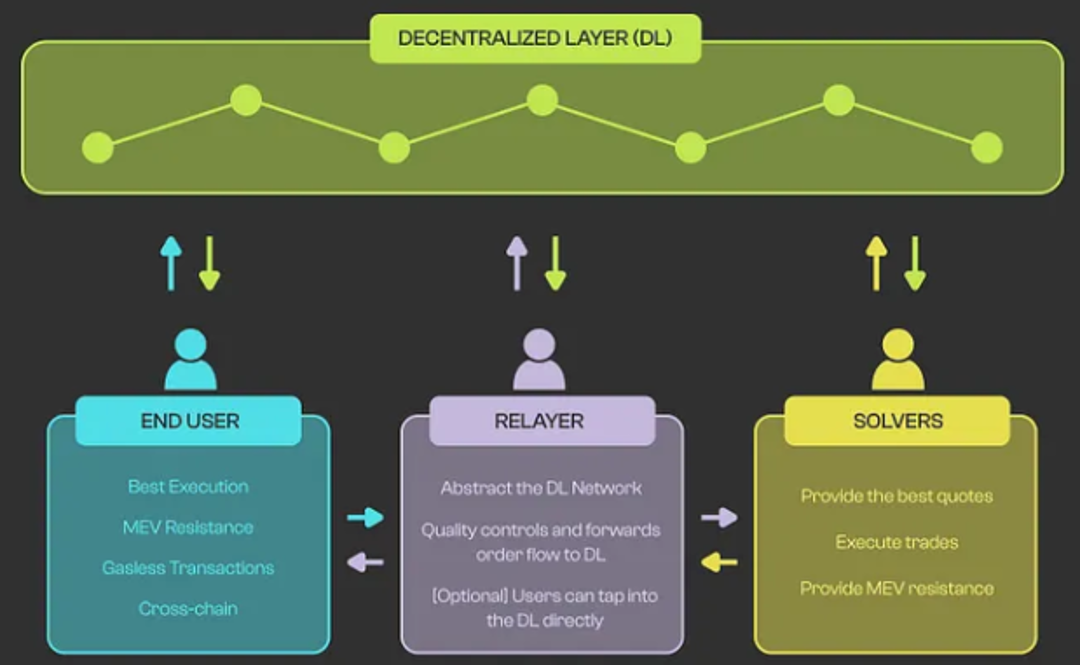
Source: Paraswap
Building a Chain-Agnostic Architecture
To build an intent-centric Chain-Agnostic architecture, several key components are needed:
- Universal Intents: Intents must be designed to be flexible and adaptable, capable of being executed on any blockchain without modification.
- Decentralized Counterparty Discovery: The system must include a decentralized mechanism for discovering counterparties that can realize intents, regardless of which chain they operate on.
- Cross-Chain Solvers: Solvers responsible for executing intents must be able to operate across multiple blockchains, determining the best path to realize intents based on factors like speed, cost, and security.
- Universal Settlement: Finally, the results of completed intents must be recorded in a manner recognized by all blockchains, ensuring that users' actions are validated and secure.
What Technical Components Are Involved in Decentralized Intents?
Core Components:
- Universal Intents: These are adaptable building blocks that allow users to express outcomes in decentralized systems.
- Solver Mechanisms: Decentralized agents interpret and realize these intents, working across different blockchains to achieve user goals, whether it's a simple token exchange or a complex operation. Think of solvers as digital personal assistants that listen to your wishes (intents) and find the best way to realize them across multiple blockchains.
- Counterparty Discovery: In a multi-chain ecosystem, the decentralized process of finding entities that match and realize intents is crucial, ensuring that the correct counterparties can be identified without centralized control.
Challenges Facing Decentralized Memory Pools
Open vs. Closed Memory Pools: Open memory pools allow any solver to access and process intents, increasing transparency but also introducing risks like front-running. On the other hand, closed memory pools offer higher security at the cost of decentralization. The challenge lies in balancing openness and security, ensuring that intents are processed fairly and efficiently across different blockchains. Everyone can see what’s happening, but there’s a risk that someone might try to use your ideas before you do. Closed memory pools are akin to private messages—safer but with lower transparency.
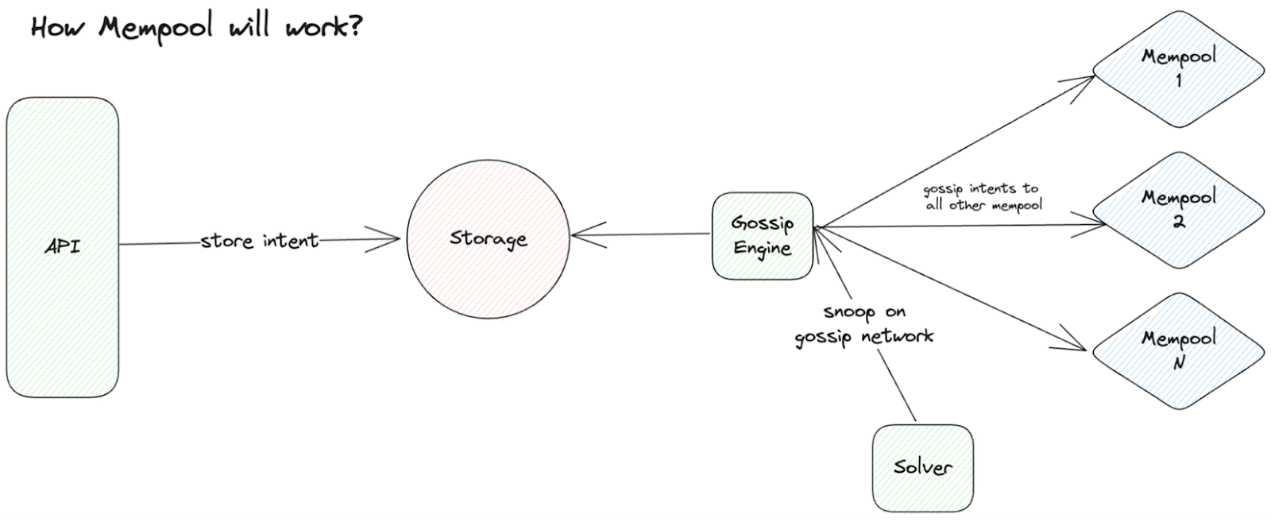
Source: Ethresearch
How Ethereum Addresses the Intent Problem?
This section focuses on a specific case study: ERC-4337, a new standard on the Ethereum chain that changes how user accounts and intents are handled. It aims to provide users with greater flexibility and security by enabling smart contract wallets to independently execute complex operations.
Overview of ERC-4337
ERC-4337 introduces an account abstraction system in Ethereum designed to make smart contract wallets (SCWs) more independent and powerful. This new standard allows users to execute complex operations through their wallets without relying on externally owned accounts (EOAs), addressing a major limitation in the current Ethereum setup.
Key Features:
User Operations (UserOps): ERC-4337 uses UserOps instead of traditional transactions. These are user-signed operations that detail the desired actions. Multiple UserOps are collected into another memory pool and bundled together by a specialized entity known as a bundler. These bundles are then processed as a single transaction, improving efficiency.
Censorship Resistance: The construction of ERC-4337 is as decentralized as possible. It ensures that no single entity can censor or manipulate UserOps by allowing permissionless participation. If all bundlers refuse to process a UserOp, the system's permissionless nature will encourage new bundlers to enter the network and capture potential profits, making the system resilient.
Security Measures: To prevent abuse and attacks, ERC-4337 enforces several rules:
- Gas Usage Limits: By limiting the gas available during the UserOp validation phase, bundlers are protected from denial-of-service attacks.
- Validation Rules: To prevent operations from being unfairly invalidated, ERC-4337 separates the validation phase from the execution phase, ensuring that validated operations remain valid as long as the account state has not changed.
- Reputation System: Bundlers also use a reputation system to manage entities that require lenient validation rules, ensuring these entities do not easily compromise the network.
Importance of a Unified Memory Pool
ERC-4337 emphasizes the need for a unified memory pool where all bundlers follow the same rules. This uniformity can prevent memory pool fragmentation, where different rules might lead to smaller, more isolated memory pools that are more susceptible to censorship and attacks. Having all bundlers adopt a consistent set of rules ensures a stronger and more resilient network, similar to how multiple Ethereum clients adhere to the same protocol rules.
Challenges and Solutions
- Fragmentation Risk: If different bundlers apply different rules, the network may fragment, leading to smaller and less secure memory pools. ERC-4337 addresses this issue by establishing a comprehensive testing suite and reference implementations to ensure all bundlers can operate compatibly and securely.
- Security Exceptions: While ERC-4337 sets strict rules, exceptions are allowed in certain cases. If bundlers maintain security and compatibility with the main network, they can participate in alternative memory pools with different rules. This flexibility allows for innovation while maintaining the overall security and integrity of the system.
The Future of Decentralized Intents
The future of decentralized intents lies in overcoming the challenges posed by the current limitations of blockchain infrastructure and the broader ecosystem. As intents shift from traditional transaction-based systems to more declarative, user-centered models, there is significant potential for improving user experience, reducing inefficiencies, and enhancing privacy.
Key Focus Areas:
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: Future developments must enable intents to operate seamlessly across multiple blockchains, leveraging the strengths of each blockchain while maintaining user control and asset custody.
- Decentralized Infrastructure: The design of intent pools (whether permissioned or permissionless) will play a crucial role. A decentralized approach that allows open access while ensuring security and trust is vital for scaling intent-based applications.
- Reducing Centralization Risks: As the adoption of intents grows, especially with standards like ERC-4337, there is a risk of centralization if intent execution is dominated by a few entities. The ecosystem must foster competition and innovation to prevent monopolies and ensure fair execution.
Challenges:
- Trust and Transparency: Developers must carefully balance the need for privacy and security with the demand for transparency, ensuring that users can trust the systems handling their intents without sacrificing the core principles of decentralization.
- Research and Innovation: The field is still in its infancy, and ongoing research is crucial to address the complexities of intent expression, execution, and integration across different domains. Emerging projects like Anoma, SUAVE, and Portikus are laying the groundwork, but much work remains to be done.
- Despite the challenges, decentralized intents will make the blockchain space more accessible, secure, and user-friendly—ultimately allowing everyone to easily realize their digital wishes.
Related Reading: Open Intents: Can ERC-7683 Become the "Walmart" Supermarket for Inter-Chain Intent Coordination on Ethereum?
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



