From the initial vision to the three-phase deployment, Babylon has innovatively redefined the interaction between Bitcoin and advanced blockchain ecosystems, ultimately forming a multi-chain secure market.
Original link: https://x.com/reflexivityres/status/1896651361397166380
Original title: "Babylon Overview Q1 2025"

Introduction
Over the past decade, Bitcoin has firmly held the top position in the global cryptocurrency market due to its security and value. Its design is simple and immutable, combined with the PoW consensus mechanism, making it a leader in the digital asset space. However, despite a market capitalization of approximately $2 trillion, Bitcoin's potential in more complex blockchain applications has yet to be fully realized.
In contrast, other cryptocurrencies that utilize PoS networks—such as Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos-based chains—have demonstrated the economic potential of staking and smart contracts, leading to a boom in decentralized applications (dApps), liquidity provision, and lending. However, many PoS chains face funding challenges at launch, struggling to gather enough capital to build a robust validator community and defend against attacks.
The Babylon protocol was born to integrate the advantages of Bitcoin with various Layer 1 PoS platforms, unlocking Bitcoin's capital value in a trustless manner by directly anchoring to the Bitcoin blockchain. Babylon does not convert BTC into wrapped assets through bridging, nor does it rely on large custodians; instead, it builds a unique Layer 1 to create Bitcoin's staking infrastructure.
In other words, Babylon is not a "Bitcoin sidechain" or an L2 solution that relies on bridging; it is an independent, fully functional Layer 1 developed based on the Cosmos-SDK. It can run its own dApps and support an entire ecosystem while gaining economic security from Babylon's Bitcoin staking protocol.
This report will delve into the design of the Babylon protocol, focusing on its characteristics as a Layer 1, its mission to bring practical value to Bitcoin, and the gradually forming ecosystem around it.
Babylon as Layer 1
The core goal of Babylon is to support Bitcoin staking, but its team positions Babylonchain as a Bitcoin Security Network (BSN), competing directly with mainstream Layer 1s like Ethereum, Solana, and Sui to attract developers, users, and capital into the Bitcoin ecosystem. Unlike those that rely solely on bridging or deploying smart contracts on other chains, Babylon is building a chain with the following capabilities:
Autonomously set consensus rules and evolve independently.
Utilize Cosmos SDK, integrating the Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol (IBC).
Support its own dApps, allowing developers to unleash their creativity in a Turing-complete environment while linking to Bitcoin's security.
Manage real BTC staking on the Bitcoin mainnet through dedicated on-chain logic.
Babylon aims to compete with Layer 1s like Solana or Sui through high throughput, an active developer community, and a large user base. Its unique advantage lies in the fact that the architecture of Babylonchain incorporates staked BTC, rather than relying solely on the market value of newly issued tokens to ensure security.
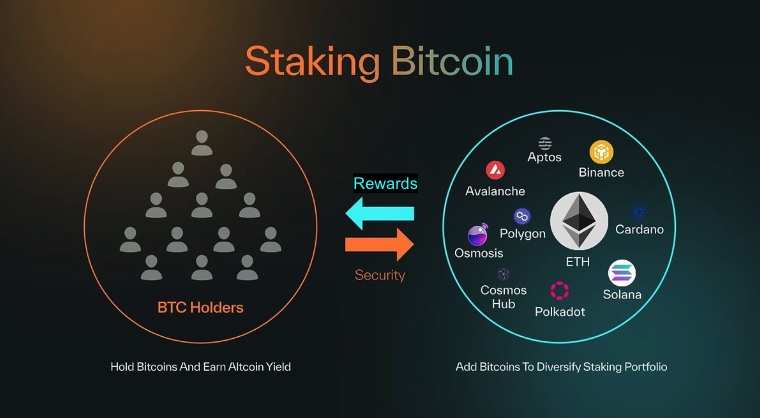
Babylon L1 itself is a PoS-based blockchain that operates consensus by selecting validators and finality providers (FPs) based on the amount of delegated BTC. Users do not need to bridge BTC onto the chain; instead, they lock BTC directly on the Bitcoin blockchain into a specific script and then delegate their voting rights to an FP on Babylon. This means that no third-party custodian holds the BTC, and stakers always maintain self-custody, which is the core of Babylonchain's security model.
Babylonchain's Security Model
Babylon's BTC staking infrastructure and Babylonchain both employ multi-layered cryptographic security mechanisms, placing them at the forefront of the BTC staking ecosystem. The specific operations are as follows:
- BTC locked on the Bitcoin main chain: A dedicated script called a "bond contract" ensures that funds cannot be moved until the staker unbinds or the staking period expires.
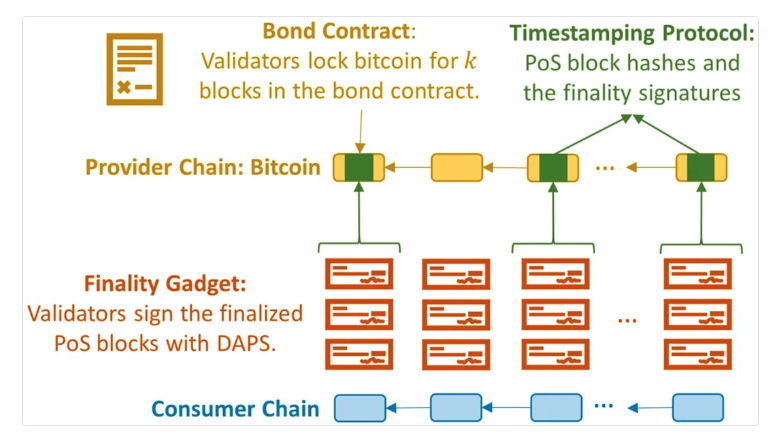
Utilize Extractable One-Time Signatures (EOTS): Thanks to Bitcoin's native Schnorr signatures, if a validator double-signs a block, their private key can be extracted, allowing anyone to broadcast a transaction to destroy a portion of the staked BTC on the Bitcoin chain.
Block finality signatures: Validators sign blocks on Babylonchain with a special key, and if they sign contradictory final states, they will face penalizable losses.
Regular anchoring to Bitcoin: On-chain data will be periodically embedded into the Bitcoin blockchain, ensuring that long-range attacks or state rollbacks cannot occur unnoticed. However, for Babylon, timestamps are just one part of its security system.

This layered design means that any malicious attacks on Babylonchain or other BSNs will be hindered by the risk of actual BTC loss. This is precisely why Bitcoin is referred to as the ultimate security cornerstone—destroyed BTC cannot be easily recovered.
Why Build an Independent Layer 1?
Why build a new chain from scratch instead of relying on existing infrastructure? Simply put, advanced staking functionalities require more precise control over staking logic, penalty mechanisms, and cross-chain coordination, which exceeds the capabilities of traditional bridging or contract-based solutions.
The uniqueness of Babylonchain lies in:
Managing staking and penalties: As a Layer 1, Babylonchain ensures the security of Bitcoin staking without trust in intermediaries, is enforceable, and maintains self-custody. It achieves the penalty mechanism by encrypting the extraction of private keys during double-signing, incentivizing honest behavior and deterring malicious actors without deploying complex bridging contracts or sidechains on Bitcoin.
Empowering the developer ecosystem: Providing a Turing-complete environment allows developers to create dApps that rely on Bitcoin capital.
Serving as an optional hub: Other PoS chains (and even specific L2s, oracles, or data availability layers) can choose to "purchase security" from the staked BTC aggregated by Babylon, making Babylonchain the control center for these interactions.
Babylon not only addresses technical security challenges but also aims to bring Bitcoin's user base and brand influence into a new ecosystem. By attracting significant liquidity and providing comprehensive developer tools, Babylon is determined to challenge existing Layer 1s and has a pathway to achieve this goal.
Specifically, the success of Babylonchain relies on creating real utility for BTC:
Supporting native dApps: The ultimate goal is to create DeFi protocols that accept BTC as collateral while allowing users to retain control of their funds. However, as of Q1 2025, staked BTC cannot yet be directly used in DeFi on Babylonchain, currently relying on custodial liquid staking tokens (LSTs). LST services represent users' staked BTC and mint tokens representing the staked position on PoS chains.
Aggregating security: For emerging blockchains or L2s looking to quickly gain strong security, Babylon can serve as an anchor, providing "Bitcoin-level economic security" while allowing stakers to earn multiple rewards.
Bitcoin-first developer experience: Many developers are eager to build applications on Bitcoin but are limited by its scripting language or bridging constraints; Babylonchain's approach simplifies this process.
Three Phases of Mainnet Deployment
The mainnet deployment of Babylonchain is divided into three phases, each focusing on different objectives. This phased strategy ensures that core subsystems are thoroughly tested, allowing users, developers, and external PoS chains to synchronize with the network's evolution.
Phase One – Supply-Side Guidance
The first phase focuses on acquiring and organizing the supply side of Bitcoin staking, laying the foundation for Babylonchain. Users stake real BTC through a dedicated script on the Bitcoin mainnet, locking funds in a self-custodial manner. In the future, these stakers will take on PoS voting responsibilities (or delegate to FPs) once the Babylon blockchain is fully launched. However, in the first phase, the primary task is to validate user interest and test the staking infrastructure.
Stakers lock BTC in a time-lock script through on-chain transactions, typically with a lock-up period of about 15 months. The first phase deliberately disables the penalty mechanism, meaning stakers will not be penalized for improper behavior; this design aims to reduce complexity and allow participants to freely experiment with staking and unbinding.
Initially, the protocol set a staking cap of 1,000 BTC to test interest and infrastructure. Subsequently, more windows (Cap-2 and Cap-3) were opened to allow more BTC to flow in. By the end of the first phase, over 56,000 BTC had been staked, with more than 135,000 stakers. In December, a well-known entity staked 10,000 BTC, demonstrating strong confidence in its trustless design. The first phase validated the demand and trust of diverse holders in the self-custodial BTC staking model through these caps.
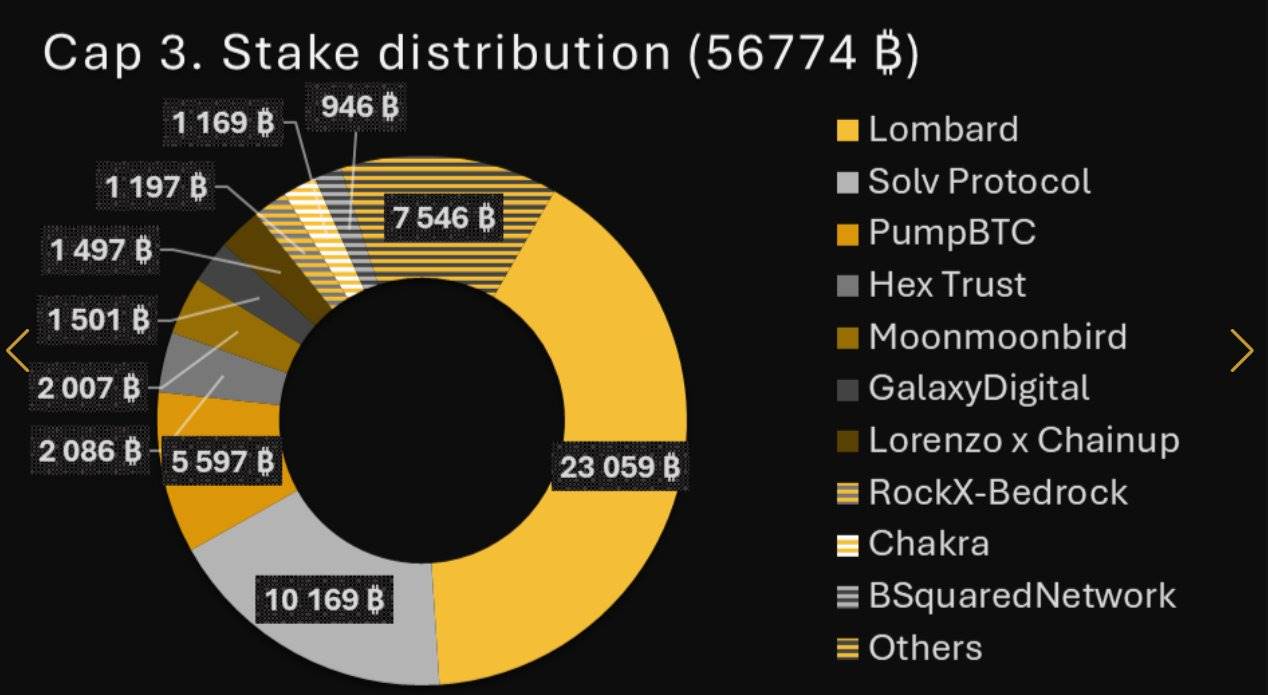
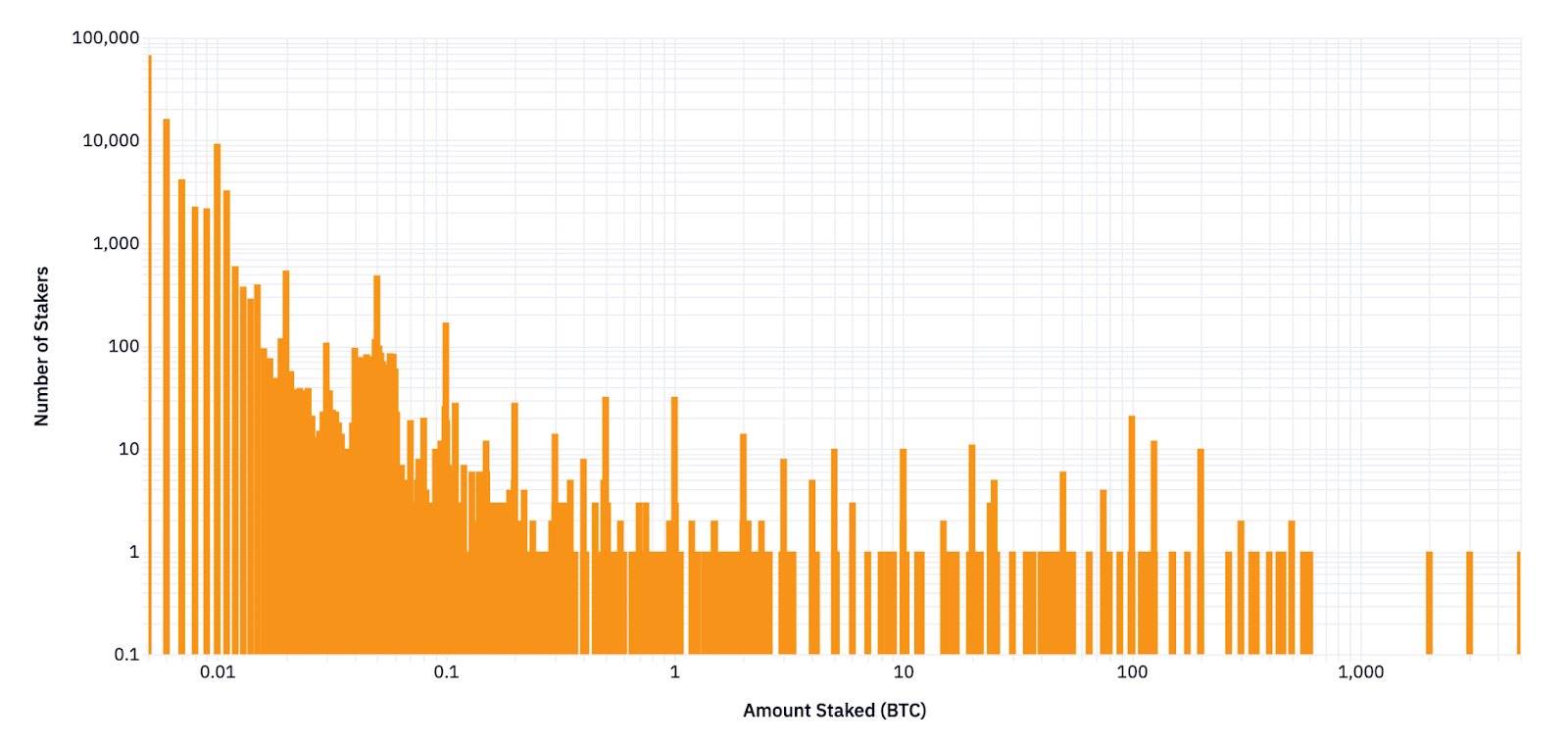
In addition, the protocol employs a points mechanism rather than direct token rewards to track staker participation, measuring the amount of staked BTC, duration, and associated FPs to assess user activity without pre-allocating native tokens.
Phase Two – Activation of Babylonchain
Building on the success of the first phase, the second phase transitions Babylon from simple staking to a fully operational blockchain, executing Bitcoin staking security on a large scale. The locked BTC shifts from being a placeholder to actively protecting assets. FPs that obtain sufficient BTC delegation will directly participate in the on-chain consensus of Babylonchain.
The BTC locked in the first phase becomes the economic backbone of Babylonchain's PoS consensus. FPs (and self-delegating stakers running their own nodes) are responsible for block finalization and validation, with malicious actions leading to real financial losses. Once the penalty mechanism is implemented, any violation of consensus rules will trigger the destruction of staked BTC on the Bitcoin mainnet.
The second phase continues to utilize Bitcoin for anchoring, with an upgraded timestamp protocol embedding key events of Babylon into Bitcoin blocks regularly, preventing malicious rollbacks.
Transitioning from Placeholder to Real Security
In the first phase, stakers "pre-placed" BTC; now, this capital actively supports the consensus of Babylonchain. This shift provides the network with a strong security budget from the outset, which is extremely rare for a new chain. The second phase also positions Babylon as a direct competitor to existing Layer 1s, standing out due to its reliance on punishable BTC rather than solely on a native token economy.
The implications for the Babylon ecosystem include:
Enhanced Validator Accountability: Once the penalty mechanism is implemented, FPs and validators must maintain impeccable key management and behavior, or they will permanently lose staked BTC.
Developer Influx: A highly secure chain supporting BTC LSTs running on (permitted) CosmWasm attracts dApp developers looking to engage with Bitcoin users.
Promotion of Multi-Staking: Once Babylon's own PoS consensus stabilizes, attention will shift to providing cross-chain security for other networks. The success of the second phase is crucial for building confidence in multi-staking.
Phase Three – Multi-Staking and Widespread Adoption
The third phase aims to achieve Babylonchain's goal of creating a multi-chain security market, where each unit of staked BTC can simultaneously protect multiple PoS systems. Babylon aims to become the preferred hub for BSNs, opening its BTC reserves to blockchains looking to rent security validation capabilities.
Specifically, users (or FPs) can allocate their staked BTC to multiple PoS networks, each offering native token rewards. This creates an ecosystem where stakers earn overlapping rewards, and consuming chains gain robust protection from Bitcoin's economic power. Any PoS chain, L2, oracle, or data availability project can choose to join the security of Babylonchain. These chains are referred to as "Bitcoin Security Networks" (BSNs), outsourcing part of their consensus security to Babylon's staked BTC and paying participants stable rewards or fees.
Babylonchain oversees the cross-chain staking process, validating delegations, collecting malicious evidence, and executing penalties when necessary, ensuring consistent security standards across all participating networks.
Impact on BTC Holders
Stakers can decide how to allocate BTC across consuming chains, earning diverse tokens and rewards. This disrupts the traditional narrative of Bitcoin as a static store of value, transforming it into an active asset with multiple earning opportunities, all while maintaining the trustless security of the Bitcoin mainnet.
As more chains compete for Bitcoin security and offer competitive APRs, the market demand for holding and staking BTC may rise, potentially altering mainstream investors' perceptions of Bitcoin's utility in the long term.
Babylon Ecosystem
One of the notable successes of the first phase of the Babylon Bitcoin staking protocol is the emergence of new collaborations. Over 150 FPs—including well-known institutions like P2P, Galaxy Digital, and InfStones—have registered to receive BTC delegations. Major custodians like Anchorage Digital and Hex Trust have also integrated with the protocol, allowing institutional clients to natively stake BTC.

Additionally, a wave of liquid staking token (LST) protocols has emerged around the first phase, allowing users to easily lock BTC and hold derivative tokens representing their staked positions. Projects like Lombard, PumpBTC, and Lorenzo have launched initiatives managing tens of thousands of BTC.

These developments demonstrate the widespread demand for BTC rewards and signal greater potential following the launch of Babylon Layer 1:
DeFi Protocols: BTC can be used for underlying chain security while serving as collateral in lending pools or decentralized stablecoins.
Data Availability and Oracle Services: Projects relying on cross-chain data can leverage the aggregated security of Babylonchain.
Innovative dApps: Through CosmWasm, developers can build advanced financial and social applications, all supported by real BTC collateral.
Lombard is a key partner of Babylonchain, dedicated to integrating Bitcoin into reward-generating activities while maintaining self-custody. Lombard recently received support, with its "liquid Bitcoin" approach closely linked to Babylon's staking infrastructure.
LBTC (Liquid Bitcoin) Token
At the core of Lombard is the LBTC token, which serves as a tradable on-chain certificate for staked BTC within the Babylon protocol. Users deposit BTC into an address controlled by Lombard, which stakes on their behalf and mints LBTC. Users can utilize LBTC in lending protocols, decentralized exchanges, or other yield strategies while contributing to the security market of Babylonchain by staking BTC. This partnership exemplifies a "win-win": Lombard helps users maintain liquidity, while Babylon gains more BTC staked, enhancing both ecosystems in the process.
PumpBTC is a user-oriented liquid staking platform that helps BTC holders maximize their on-chain yield potential. It is rooted in Babylon's native staking model.
PumpBTC simplifies the staking process by issuing transferable assets after users stake BTC through Babylon's self-custody script. These assets serve as "tickets" to access various DeFi strategies, allowing users to maintain liquidity while locking BTC. The PumpBTC platform actively seeks opportunities across multiple PoS chains integrated with Babylon. As more networks become Bitcoin Security Networks, PumpBTC can direct stakers' funds to the highest-yielding environments—strengthening the expanding market based on BTC returns.
Since PumpBTC inherits the trustless and punishable security of Babylonchain, participants are shielded from typical cross-chain risks. In cases of validator misconduct, punishable staking ensures that malicious actors face real economic penalties—reducing the likelihood of network-level exploitations.
Lorenzo is an L2 infrastructure that extends Bitcoin's utility to complex yield operations. It directly integrates with Babylon's staking mechanism, ensuring that its BTC holders can participate in advanced DeFi scenarios without sacrificing autonomy. At the same time, Lorenzo offers structured financial products, such as automated market-making or derivative positions, all supported by Babylon's security baseline. The project provides native aggregation, managing complexity off-chain while periodically reverting to Bitcoin to ensure reliability. By collaborating with Babylon, Lorenzo ensures that the finality of the aggregation and the honesty of validators are backed by retrievable BTC, thereby reducing the need for external trust.
Through interoperability with the Cosmos ecosystem and other IBC-supporting networks, Lorenzo's L2 can seamlessly transfer data and value across different chains. As a result, BTC holders can access a variety of dApps, liquidity pools, and staking markets.
Bitcoin Security Network (BSN)
As the third phase approaches, multiple PoS chains have announced plans to become BSNs on Babylonchain, including Corn. Becoming a BSN means these chains officially integrate with Babylonchain, bringing several strategic advantages to PoS chains:
On-Demand Security: Each chain can pay rewards to Bitcoin (BTC) stakers to "borrow" shared security.
IBC and Interoperability: Babylonchain is built on the Cosmos SDK and the Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol (IBC), allowing integrated networks to communicate seamlessly. This creates a smooth environment where tokens, data, and security can flow freely between different chains in a trustless manner.
Multi-Chain Staking Economy: A staker's BTC may earn small amounts of rewards from five different networks, but these combined rewards could exceed the returns from traditional BTC bridging or lending markets, providing significant incentives for stakers.
The goal of this layered security mechanism is to bring a similar effect to Ethereum's "re-staking" for Bitcoin, but it uses BTC as the ultimate capital base, fully operating on Babylonchain.

Developer Empowerment and dApp Potential
For an emerging native Layer 1 chain, attracting and supporting an active developer community is one of the core elements of growth. Babylon achieves this through thoughtful initiatives, such as providing highly flexible smart contracts via CosmWasm, supporting upgradable logic, and being compatible with a wide range of DeFi and NFT use cases. Additionally, Babylonchain supports cross-chain communication (IBC), allowing it to directly interoperate with the broader Cosmos ecosystem, enabling dApps on Babylonchain to tap into vast liquidity pools and even share user bases across multiple IBC-supporting chains.
These two features are highly attractive to dApp developers, but Babylonchain believes that its native access to Bitcoin is what truly enhances its appeal compared to other Layer-1 ecosystems. While it does not replicate Bitcoin's PoW environment, it offers "remote staking" that can be integrated at the contract level. Developers can build applications that rely on punishable staked BTC for finance, gaming, and other fields, minimizing reliance on trust.
Bringing Utility to Bitcoin
To understand the profound significance of the Babylon protocol, consider its implications for Bitcoin as an asset. Historically, Bitcoin has had two undisputed native uses:
Holding (Store of Value)
Consumption/Transfer (Medium of Exchange)
Beyond this, bridging, wrapping tokens, and lending on centralized platforms all require reliance on external entities or custodians. Babylon introduces staking as a native use case for Bitcoin, allowing BTC holders to protect PoS networks without relying on custodians or wrapped assets, while offering the following unique advantages:
Non-Custodial: Stakers do not need to hand over BTC to third parties; they lock it in a dedicated script on the Bitcoin chain.
Punishable: If a staker's key maliciously signs blocks (e.g., double-signing to attack a PoS chain), the key will be cryptographically exposed, allowing for the destruction of the corresponding BTC.
Self-Custody: Users can unbind and withdraw BTC from the staking script at any time, subject only to the unbinding schedule. Once the unbinding period is over, users regain ownership of regular BTC UTXOs.
The impact on Bitcoin is significant. For the first time, BTC holders can earn staking rewards through a minimally trusting process while retaining the principle of Bitcoin self-sovereignty. Meanwhile, the broader ecosystem gains access to the largest crypto asset in a punishable manner, representing an unprecedented form of capital injection.
Conclusion
From the initial vision to a three-phase deployment, ultimately forming a multi-chain security market, Babylon innovatively redefines the interaction between Bitcoin and advanced blockchain ecosystems. Babylon Labs has not merely focused on bridging or timestamping but has created a complete Layer 1 environment that leverages the economic power of Bitcoin. This approach has been validated by tens of thousands of BTC stakers in the first phase, reflecting a strong demand from users to transform BTC into an asset that can generate returns and secure chain safety.
Looking ahead, the development trajectory of Babylonchain will reshape the discussion around "using Bitcoin." BTC holders gain a truly native way to earn rewards for the first time, while decentralized networks acquire a reliable source of security. As Babylonchain Layer 1 matures, developers can build dApps that integrate the robust monetary properties of Bitcoin with the expressiveness and scalability of PoS blockchains.
Disclaimer: This report is commissioned by Babylon Labs. This research report is indeed a research report. It is not intended as financial advice, and you should not blindly assume that any information is accurate without confirming it through your own research. Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies, and other digital assets carry significant risks, and nothing in this report should be construed as an endorsement to buy or sell any asset. Never invest more than you are willing to lose, and understand the risks you are taking. Please conduct your own research. All information in this report is for educational purposes only and should not be the basis for any investment decisions.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




