The World Economic Forum, in collaboration with Accenture and KPMG, has released an authoritative report.
Author: New Intelligence Source

Image Source: Generated by Boundaryless AI
As the wave of technology surges forward, artificial intelligence (AI) has deeply integrated into all aspects of the socio-economic landscape, becoming a core force driving industrial transformation and innovative development.
In this context, the World Economic Forum (WEF), in partnership with Accenture and KPMG, has published a report that undoubtedly provides us with an authoritative perspective on the future development trajectory of AI.
The report gathers insights from various sources, presenting a comprehensive view of the opportunities and potential of AI in the future through in-depth industry research, cutting-edge technology analysis, and precise understanding of global trends.
Whether you are a practitioner focused on technological innovation, a financial professional seeking investment directions, or an ordinary citizen concerned about social development, you can find inspiration in this report to prepare in advance and embrace the infinite possibilities of the AI era.
Report 1: "AI in Action: Beyond Experimentation to Transform Industry 2025"
Artificial intelligence is developing at an unprecedented speed, particularly in fields such as natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and generative AI.
The report "AI in Action: Beyond Experimentation to Transform Industry 2025," co-authored by the World Economic Forum (WEF) and Accenture, explores the opportunities, current adoption status, and future potential of AI by 2025, aiming to provide organizations with a responsible and transformative framework for AI adoption.

Report Link: https://www.weforum.org/publications/industries-in-the-intelligent-age-white-paper-series/cross-industry/
Here are the key points of the report:
Opportunities of AI
Efficiency and Cost Savings: Generative AI not only optimizes workflows and costs but also significantly enhances productivity. For example, a virtual engineer developed by a technology provider optimized building management through real-time data, reducing HVAC energy costs by 25% and cutting maintenance scheduling time by 90%.
Revenue Growth: Companies that adopt AI early are already seeing 15% higher revenues than their peers, with this figure expected to double by 2026. Generative AI helps designers quickly generate diverse patterns through personalized design tools, directly driving sales and revenue growth.
Enhanced Customer Experience: AI has shifted from a unique differentiator to a fundamental requirement for all businesses to remain competitive. For instance, the London Stock Exchange Group uses AI-driven Question and Answer Services (QAS) to reduce customer query resolution times by 50%.

Current Status of AI Adoption
Industry Adoption: The telecommunications, financial services, and consumer goods industries are leading in AI adoption. Generative AI is particularly prominent in industries reliant on human capital, such as healthcare, financial services, and media entertainment.
Functional Adoption: Marketing and sales, product and service development, service operations, and risk management are the functions with the highest AI adoption rates. These functions typically generate or digitize large amounts of structured and unstructured data, allowing AI models to train and scale more effectively.
Organizational Adoption: Despite a surge in AI investment and usage, most organizations are still in the early stages of AI adoption. 74% of companies report facing challenges in scaling AI adoption, with only 16% of enterprises ready for comprehensive AI-driven transformation.
Future Potential of AI
Comprehensive Automation of Complex Tasks: AI agents can work collaboratively to achieve comprehensive automation of complex repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on higher-level tasks. For example, by 2028, industries such as manufacturing and financial services will see significant benefits from AI agents managing production lines, optimizing supply chain operations, and handling customer support.
More Contextualized and Personalized Decision-Making: Integrating advanced reasoning capabilities into generative AI applications will make AI systems more effective in assisting humans to navigate complex environments and make context-aware decisions. For instance, in the healthcare sector, AI will support personalized treatment plans.
Enhanced Personal Efficiency and Capabilities: AI-integrated handheld devices, advanced edge AI, and compact language models have the potential to revolutionize work by automating tasks, managing schedules, and providing real-time information.

Foundations for Successful AI Implementation
Ecosystem Collaboration: Companies are increasingly collaborating with cloud providers, AI technology companies, startups, and public institutions to access resources and expertise.
Stakeholder Trust in AI: Trust is key to AI success. 61% of people are hesitant to rely on AI systems, primarily due to concerns about data security and third-party involvement.
Industry Self-Governance: Organizations are creating self-governance frameworks to complement regulations, ensuring that AI deployments align with corporate values and regional laws.
Talent and Organization: Organizations need to prioritize employee development, enabling staff to adapt to technological changes and lead AI-driven value creation.
Cybersecurity: AI-driven cyber threats such as deepfakes, targeted phishing, and data breaches are emerging risks. Organizations need to incorporate AI cyber risks into cross-organizational risk management.
Digital Core: Deploying scalable AI strategies relies on establishing a strong digital core, including AI applications and digital platforms, data and AI "backbones," and physical and digital infrastructure.
Report 2: "Blueprint for Intelligent Economies"
Artificial intelligence is driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution, promoting economic growth and fostering innovation across industries and society.
However, many countries may not be able to enjoy the economic and social benefits of the intelligent era due to a lack of energy-intensive AI infrastructure, advanced computing power, high-quality data, and AI skills. Without intervention, technological innovation may not only fail to benefit the world equally but could also exacerbate the existing digital divide.

Report Link: https://www.weforum.org/publications/blueprint-for-intelligent-economies/
The "Blueprint for Intelligent Economies," co-authored by the World Economic Forum (WEF) and KPMG, aims to create inclusive growth through comprehensive collaboration.
This blueprint is divided into three interrelated levels:
Building the Foundation: This includes sustainable AI infrastructure, high-quality datasets, responsible AI models, and effective capital investment channels.
Developing New Intelligent Economies: This involves reimagining core activities across industries by embedding intelligent applications, workflows, devices, and robotics.
Human-Centric Approach: This aims to enhance human potential through high-quality education, skills development, and workforce training, while establishing ethical, safe, and secure guardrails.
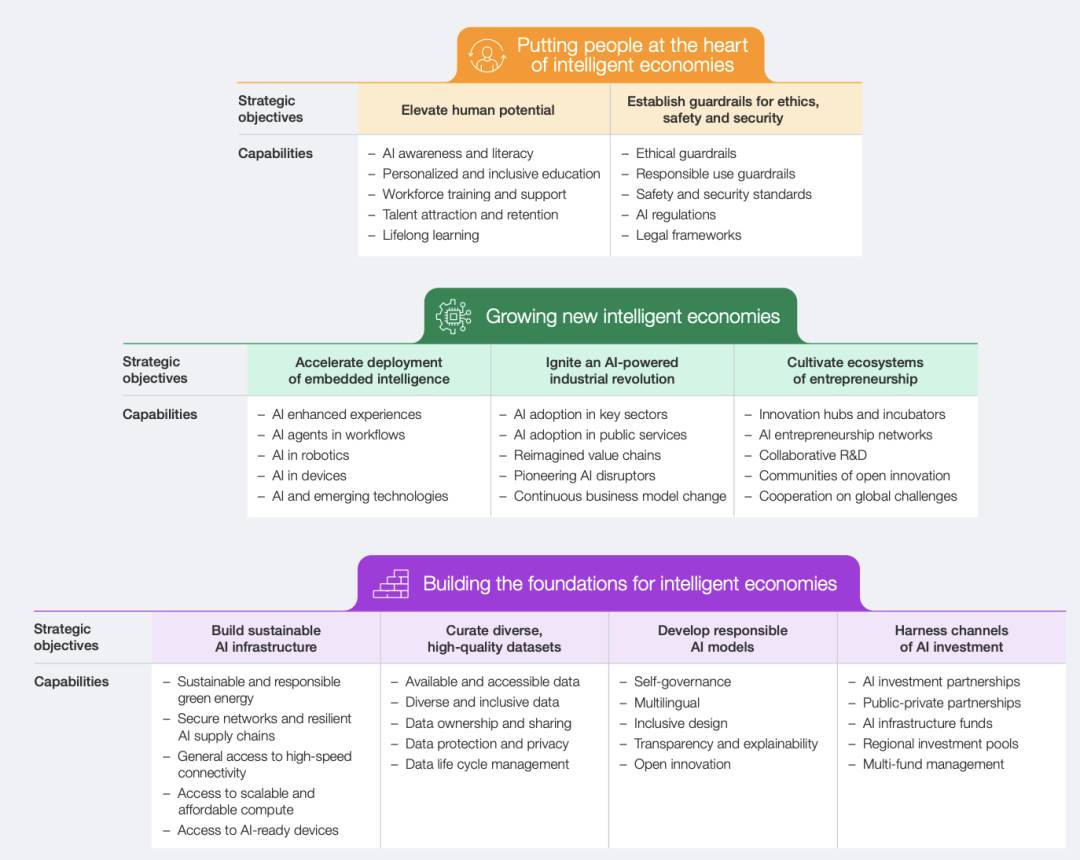
The blueprint proposes three strategic goals:
Building Sustainable AI Infrastructure
Challenges: High energy consumption, large-scale investment requirements, insecure AI supply chains, digital divides, and high costs of internet devices.
Success Cases: Microsoft signed an agreement with the U.S. to purchase carbon-free energy, reopening the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant to provide green energy for its data centers. The World Bank launched a $10 billion renewable energy program aimed at increasing renewable energy capacity by 15 GW.
Key Capabilities: Sustainable and responsible green energy, secure networks and resilient AI supply chains, high-speed connectivity, scalable and affordable computing power, AI-ready devices.
Curating Diverse and High-Quality Datasets
Challenges: Accessing high-quality data, data inequality, data ownership, advancements in AI technology, and trust in AI.
Success Cases: Japan's Fugaku LLM is an open-source large language model with at least 60% of its training data sourced from Japan. The UAE government collaborated with G42 to develop the LLM "Jais" based on modern standard Arabic.
Key Capabilities: Available and accessible data, diverse and inclusive data, data ownership and sharing, data protection and privacy, data lifecycle management.
Establishing Ethical, Safe, and Secure Guardrails
Challenges: Mitigating bias, addressing the evolving regulatory environment, ensuring AI safety, implementing responsible AI practices, and uncertainties around AI intellectual property and law.
Success Cases: The EU's AI Act categorizes AI applications by risk levels and sets requirements for high-risk areas. The U.S. and U.K. collaborated through the AI Safety Research Institute to develop a shared AI model testing framework.
Key Capabilities: Ethical guardrails, responsible use guardrails, safety and security standards, AI regulations, legal frameworks.
WEF
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an international non-governmental organization headquartered in Davos, Switzerland. It is also known as the "Davos Forum" due to its inaugural meeting in Davos, Switzerland. The WEF is committed to promoting sustainable development of the global economy, society, and environment through public-private cooperation.
As the forum's influence expands and the level of participants rises, the World Economic Forum has been regarded as the "unofficial highest-level international economic meeting," serving as one of the most important unofficial gatherings for world leaders, business figures, and leaders of civil and social organizations to discuss global economic issues. Corporate members participating in the forum include over 1,000 large companies and enterprises from more than 70 countries and regions worldwide.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




