Market changes quickly, keeping information updated, optimizing strategies, and controlling emotions are key to long-term stable profits.
Key Points
– Cryptocurrency contracts allow traders to speculate or hedge flexibly without holding actual assets, and leverage amplifies profit opportunities, but risks also increase.
– Risk management is crucial—proper use of stop-loss orders, controlling position sizes, and cautious leverage to avoid liquidation and ensure fund safety.
– Strategies vary by experience—beginners are advised to first learn trend trading and breakout trading, while advanced traders can try scalping, arbitrage, funding rate trading, and other advanced strategies.
– Continuous learning and trading discipline—market changes quickly, keeping information updated, optimizing strategies, and controlling emotions are key to long-term stable profits.
Contract trading has always played an important role in traditional financial markets, helping investors speculate, hedge risks, and manage funds. In the cryptocurrency market, contract trading has rapidly risen, allowing traders to profit from the high volatility of digital assets like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH).
However, how do cryptocurrency contracts actually work? What strategies are suitable for beginners, and which are for advanced traders? In this article, we will start with the basics, delve into practical trading strategies, and share key risk management principles to help you master this high-risk but opportunity-filled trading market.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Cryptocurrency Contract Trading
Trading Strategies for Beginners
– Trend Trading
– Breakout Trading
– Moving Average (MA) Crossover Strategy
– Scalping
– Arbitrage
– Hedging Strategies
– Funding Rate Trading
– RSI (Relative Strength Index)
– MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
– Bollinger Bands
– Fibonacci Retracement
– Volume Analysis
– Market News and Events
– On-chain Data Analysis
– Macroeconomic Factors
– Market Sentiment Analysis
Risk Management and Leverage Control
– Key Risk Management Strategies
– Common Trading Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Introduction to Cryptocurrency Contract Trading
What are Cryptocurrency Contracts?
Cryptocurrency contracts are a type of derivative that allows traders to buy and sell based on market price changes without holding actual assets. These contracts stipulate buying or selling cryptocurrency at a predetermined price on a specific date, but the most popular type in the market today is Perpetual Futures. Perpetual contracts have no expiration date and maintain price proximity to the spot market through a Funding Rate mechanism.
The biggest advantage of contract trading is flexibility—traders can choose to go long (betting on price increases) or short (betting on price decreases), finding trading opportunities whether the market is bullish or bearish. Unlike spot trading, contract trading does not require actual possession of cryptocurrency but instead amplifies trading scale through leverage for price speculation or risk hedging.
Why Choose Contract Trading Over Spot Trading?
The main attraction of contract trading is leverage, which can amplify returns but also increases risk. For example, with 5x leverage, if the coin price rises by 2%, your profit will be magnified to 10%; however, if the price drops by 2%, your loss will also be magnified 5 times. Therefore, leverage use needs to be managed cautiously.
Another key advantage is risk hedging. If you hold cryptocurrency in spot but are concerned about short-term price declines, you can hedge by shorting contracts; even if the market drops, your contract position can still profit, offsetting losses in your spot position. This strategy is common among long-term investors, miners, or traders looking to reduce market volatility risks.
Risks to Note
High Volatility + Leverage = Rapid Losses
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, with prices capable of significant fluctuations in a short time. When high leverage combines with market volatility, small price movements can quickly lead to substantial losses, even triggering forced liquidation. Liquidation occurs when the account margin is insufficient to cover potential losses, and the exchange will automatically close positions to prevent further losses. Therefore, risk management is crucial when trading with leverage.
Basis Risk and Funding Rate Risk
Cryptocurrency contract prices do not always move in perfect sync with the spot market, and there may be price deviations between the two, known as basis risk. When the market is highly volatile or lacks liquidity, contract prices may significantly deviate from spot prices, affecting traders' expected returns.
Additionally, perpetual contracts use a Funding Rate mechanism, where long and short position holders must periodically pay each other fees to keep contract prices close to spot prices. If market sentiment is extremely skewed towards one side (e.g., a large number of investors going long), the funding rate may rise significantly, thereby cutting into your trading profits.
Counterparty and Exchange Risks
Not all cryptocurrency contract exchanges are strictly regulated; many are located in regions with unclear regulations and may face risks of hacking, fund misappropriation, or even exchange bankruptcy. If an exchange faces a financial crisis, your funds may become inaccessible.
To mitigate these risks, it is advisable to choose exchanges with high trading volumes and good reputations, and to avoid storing all funds on a single platform.
Regulatory Risks
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) have long classified cryptocurrency contracts as high-risk speculative products and have increased regulation. Some exchanges may restrict users' access to funds due to policy limitations or even exit certain markets. Therefore, it is essential to understand relevant laws and regulations before trading to avoid being affected by policy changes.
Trading Strategies for Beginners
If you are a beginner in cryptocurrency contract trading, it is recommended to start with simple, stable strategies, focusing on risk control and market learning. Here are four contract trading strategies suitable for beginners:
Trend Trading
"The trend is your friend." The core principle of trend trading is to follow the trend, where traders need to identify the main market direction (upward, downward, or sideways) and trade in accordance with the trend.
How to Identify Trends?
– Use moving averages (like the 50-day and 200-day moving averages): If the short-term moving average is above the long-term moving average and prices keep making higher highs, it indicates an upward trend.
– Conversely, if the short-term moving average falls below the long-term moving average and prices keep making lower lows, the market may be in a downward trend.
Entry Timing
- – Confirm the trend direction: If prices are rising with increasing volume, it is usually a reliable trend signal, and you can consider entering the market.
Exit Timing
- – Trend Weakening: If prices break below key moving averages or make lower lows, you should consider stopping losses to prevent further losses.
Beginners Should Avoid: Counter-Trend Trading
- – Beginners are not advised to attempt counter-trend trading (like shorting in an upward trend) as it requires more precise timing and carries higher risks.
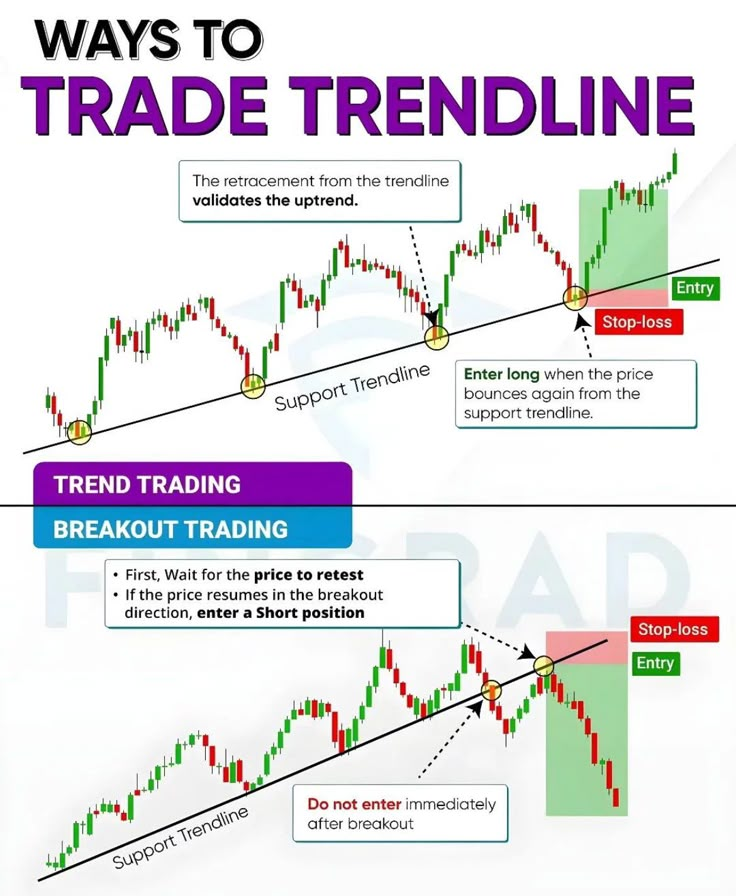
Image Credit: Pinterest
Breakout Trading
The goal of this strategy is to enter the market when prices break through key support or resistance areas, capturing strong market trends.
How to Identify Breakouts?
– Look for trading ranges: Observe whether the market is oscillating between clear support and resistance, for example, ETH has been in the $1,500 to $1,600 range for a long time.
– Wait for volume confirmation: Effective breakouts are usually accompanied by a surge in volume, indicating that market funds are starting to flow in.
How to Avoid False Breakouts?
– A false breakout refers to a price briefly breaking through a key level and then quickly retreating, leading traders to be "fooled" by the price action.
– Set a stop-loss: If you buy (go long) after breaking a resistance level, you can set the stop-loss below the original resistance level (which has now become support) to avoid significant pullbacks from false breakouts.
Image Credit: Pinterest
Moving Average Crossovers
Moving averages are used to smooth price fluctuations and help traders identify trend changes.
Golden Cross
- – When a short-term moving average (like the 50-day) crosses above a long-term moving average (like the 200-day), it indicates that the market may enter a strong upward trend, suitable for going long.
Death Cross
- – When a short-term moving average crosses below a long-term moving average, it means the market is entering a downward trend, suitable for going short or reducing positions.
Applicable Market Conditions
- – The moving average crossover strategy performs better in "trending markets," but in sideways or choppy markets, moving averages may cross frequently, leading to an increase in false signals (whipsaws), affecting trading accuracy.
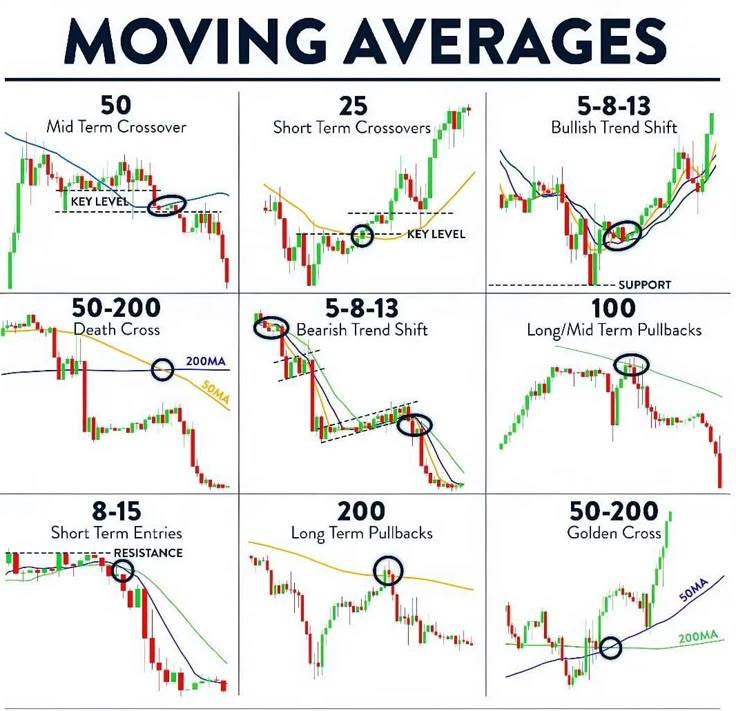
Image Credit: Pinterest
Advanced Trading Strategies
Experienced traders can explore more advanced strategies that require faster decision-making, larger capital investments, and more professional analysis. The goal of these strategies is to exploit market inefficiencies, lock in arbitrage opportunities, or reduce risk through hedging.
Scalping
Scalping is an ultra-short-term trading strategy that aims to gain small profits from price fluctuations over very short periods, typically holding positions for just a few seconds to a few minutes.
Execution Speed
- – Scalpers usually use 1-minute or shorter candlestick charts and require ultra-low latency order execution to ensure they can enter and exit the market instantly.
Risk Control
- – A single large loss can instantly wipe out dozens of small profits, so strict stop-loss execution is extremely important.
Trading Cost Management
- – Due to the extremely high frequency of scalping trades, trading fees can severely erode profits. Therefore, scalpers typically choose platforms with low fees or rebate mechanisms.
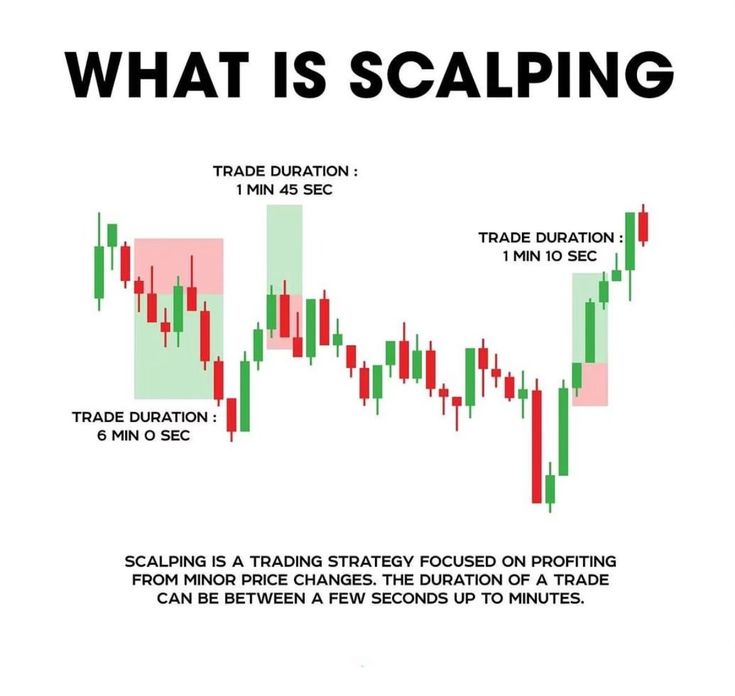
Image Credit: Pinterest
Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage trading exploits price differences between different markets or contract types to earn low-risk returns.
Spot and Contract Arbitrage
- – Traders buy assets in the spot market while simultaneously shorting (selling) the same asset's contract in the futures market. If the futures price is higher than the spot price, arbitrageurs can lock in profits as the prices converge.
Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
- – Different exchanges may have different quotes for the same asset. Traders can buy at a lower-priced exchange and sell at a higher-priced exchange to profit from the price difference.
Arbitrage Trading Considerations
– Low risk but low return: Arbitrage trading is generally considered a lower-risk strategy, but profits are usually small, requiring significant capital investment to achieve meaningful returns.
– Execution speed is crucial: Price differences typically last only a very short time, so execution speed and trading costs will affect the feasibility of arbitrage trading.
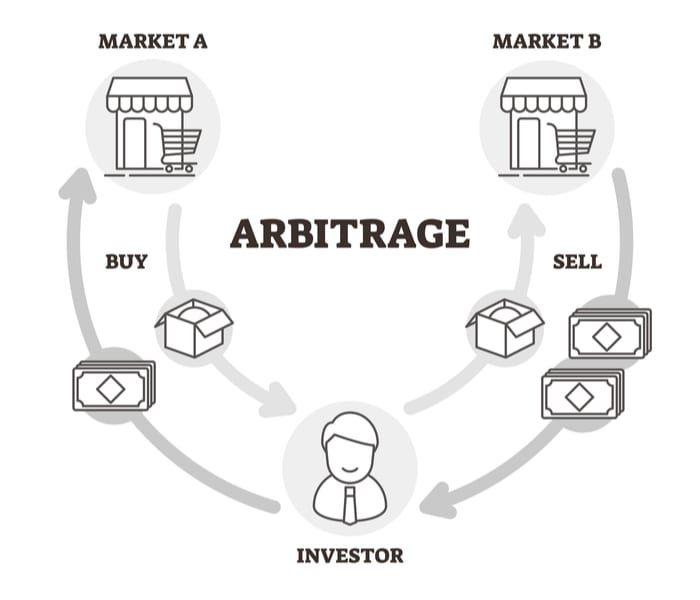
Image Credit: Pinterest
Hedging
Hedging is not aimed at direct profit but rather at reducing the impact of market price fluctuations on existing positions, avoiding excessive unilateral exposure.
Long Position Hedging
– If a trader holds ETH long-term but is concerned about a short-term price drop, they can short ETH/USDT contracts to offset potential losses.
– If the ETH price drops, the profit from the contract will partially offset the losses from the spot position.
Delta-Neutral Strategy
- – Some professional traders or miners use a Delta-Neutral strategy, holding equal amounts of long and short positions to bring their market exposure close to zero, reducing the impact of market fluctuations.
Hedging Costs
- – Hedging typically requires paying a funding rate, and certain contract types may have premiums, so hedging is not free, but it can reduce the impact of extreme market fluctuations on the portfolio.
Image Credit: Forex Academy
Funding Rate Trading
In Perpetual Futures, exchanges use a funding rate to keep contract prices close to spot prices. The funding rate is a periodic payment mechanism between long and short positions; when the perpetual contract price is higher than the spot price, longs typically pay shorts, and vice versa.
Arbitrage Funding Rate
- – When the funding rate is extremely high, traders can short perpetual contracts and go long in the spot or quarterly contract market to gain funding rate subsidies, with market direction changes having minimal impact on the trade.
Funding Rate as a Market Sentiment Indicator
– Extreme funding rates often indicate excessive preference for one side in the market; for example, when the funding rate is too high, it suggests that the market is overcrowded with longs, which may signal a market reversal.
– Many advanced traders look for contrarian trading opportunities based on extreme funding rate data.
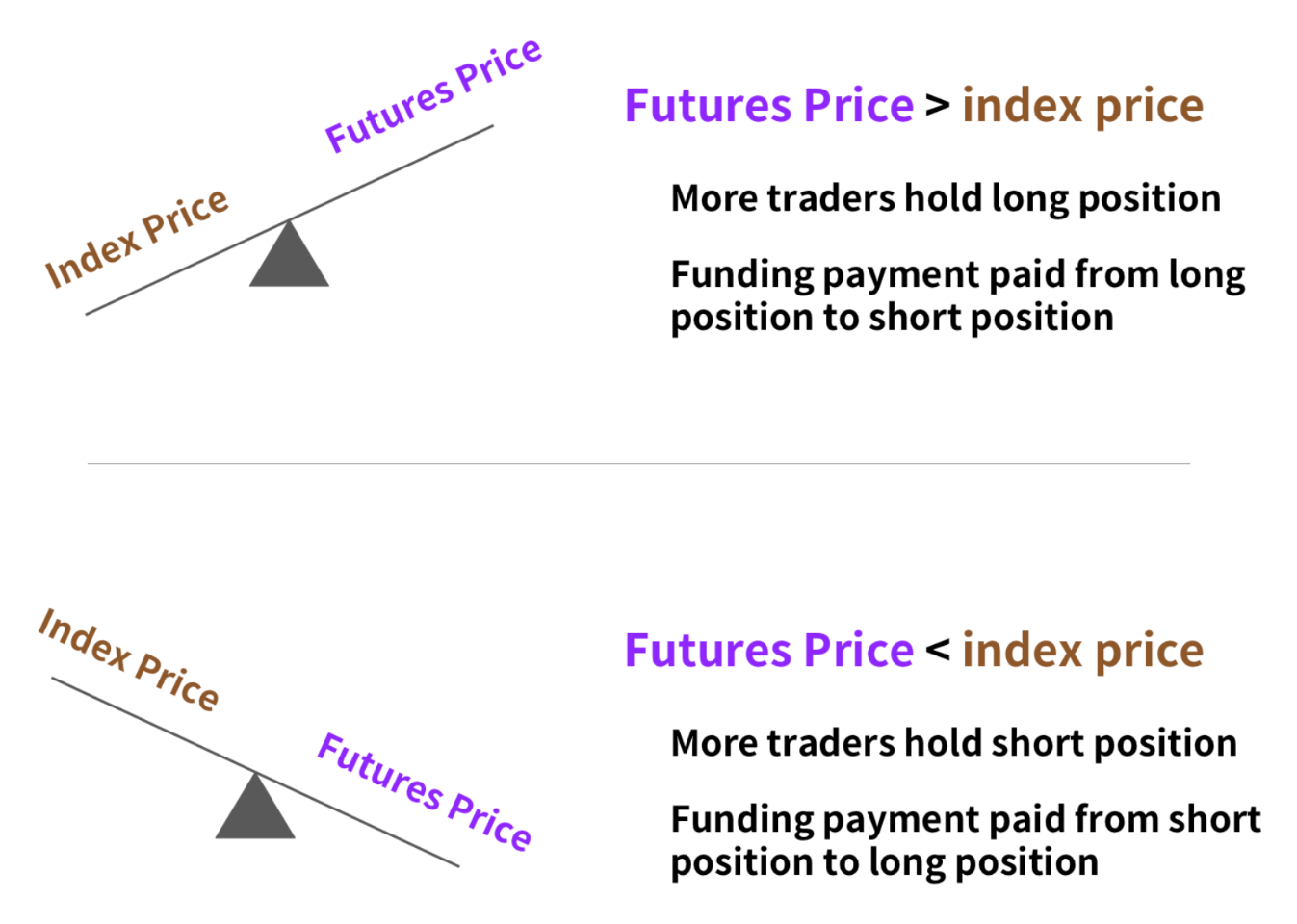
Image Credit: Biqutex
Technical Analysis Methods
In cryptocurrency trading, technical analysis (TA) is an important tool for many traders. By using price charts and technical indicators, traders can better assess market trends and develop trading strategies.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
– RSI is primarily used to measure market momentum, with values ranging from 0 to 100. When RSI is above 70, it indicates that the market may be overbought, while below 30 may indicate oversold conditions.
– If prices keep making new highs but RSI is declining, this may signal weakening market momentum, alerting traders to proceed with caution.
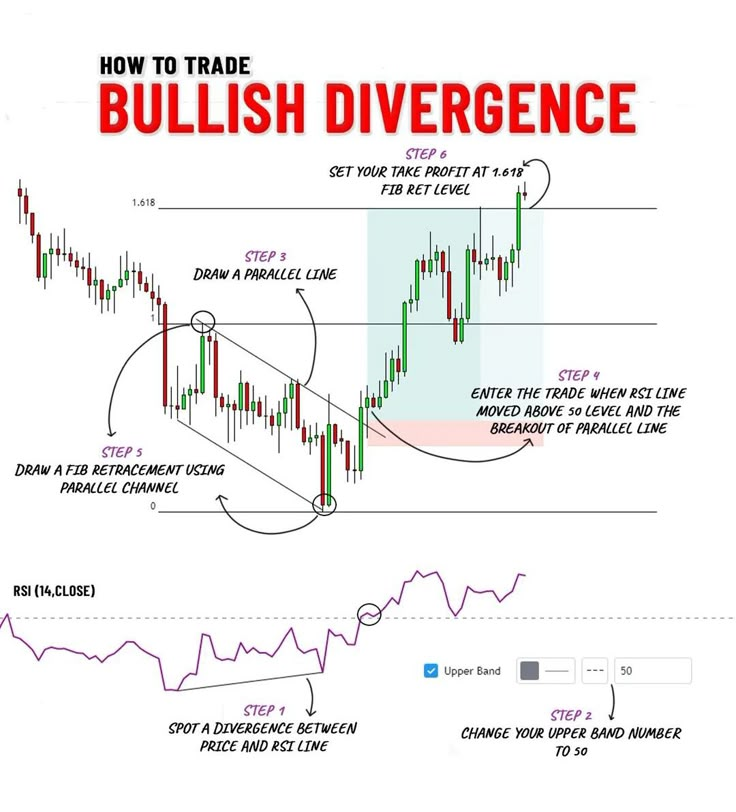
Image Credit: Pinterest
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
– This is a trend-following momentum indicator composed of two moving averages.
– When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it usually indicates that market momentum is strengthening, which may be a buy signal. However, in choppy markets, MACD can be misleading, so it is recommended to use it in conjunction with other analysis tools.
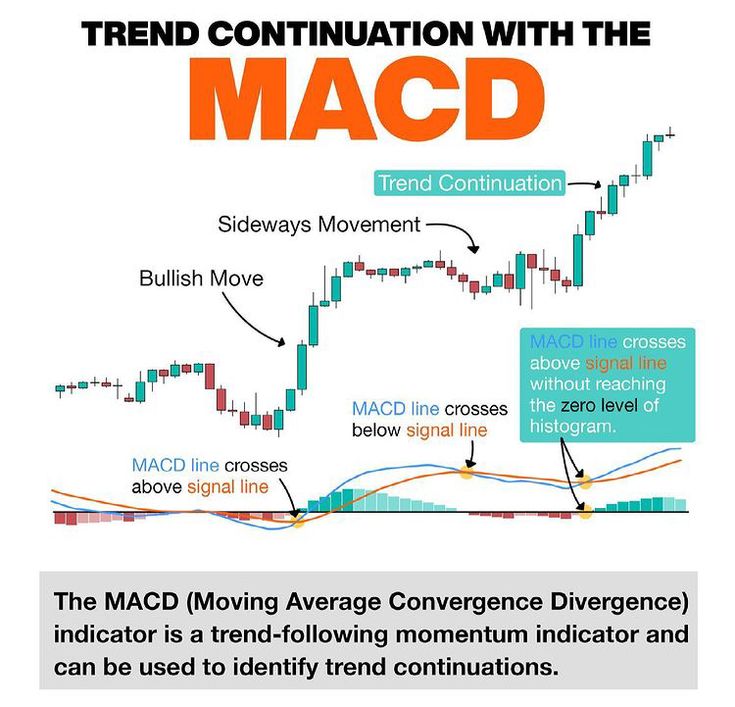
Image Credit: Pinterest
Bollinger Bands
– Composed of a simple moving average (SMA) in the middle and upper and lower bands that widen or narrow with market volatility.
– When Bollinger Bands narrow (a "squeeze"), it usually indicates that the market is about to experience significant volatility. If prices touch the upper band, it may indicate that the market is overbought, while touching the lower band may indicate oversold conditions.
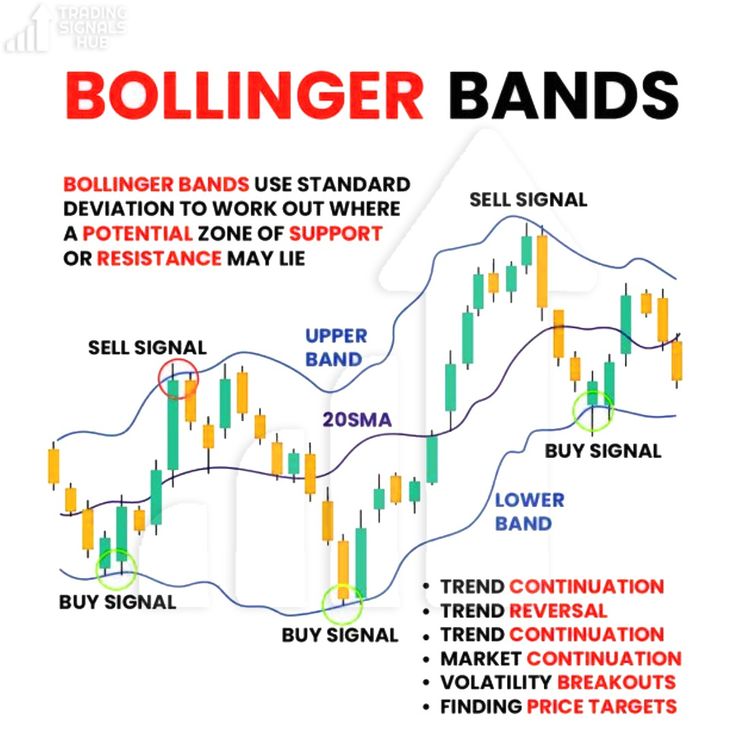
Image Credit: Pinterest
Fibonacci Retracement
– Primarily used to identify potential support and resistance levels, especially the key levels of 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%.
– Traders often look for buying or selling opportunities near these levels or assess whether the market will experience a trend reversal.
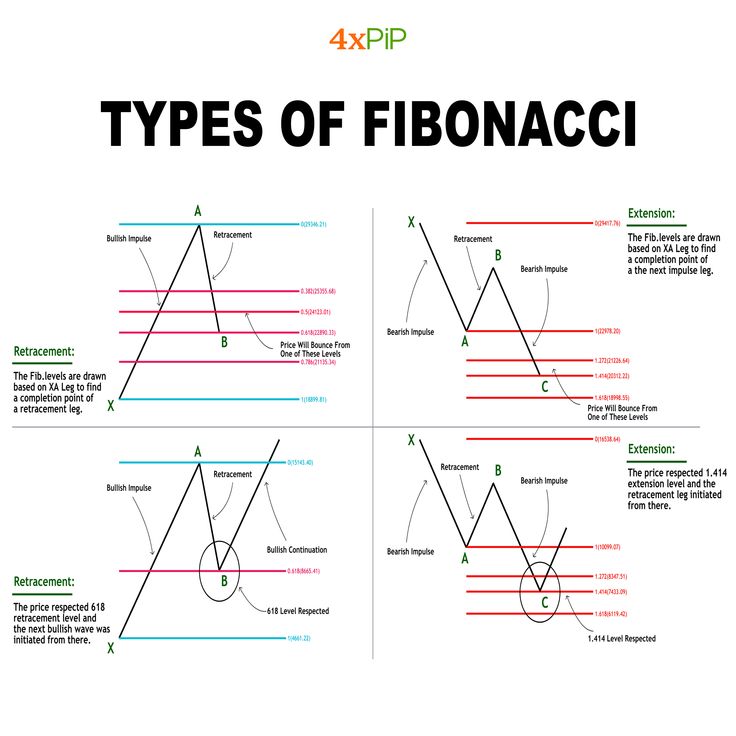
Image Credit: Pinterest
Volume Profile Analysis
– By analyzing the volume at different price ranges, traders can identify market support, resistance, and breakout areas.
– The Point of Control (POC) is usually the price area with the highest volume, which may become a key support or resistance level in future price action and is worth paying close attention to.
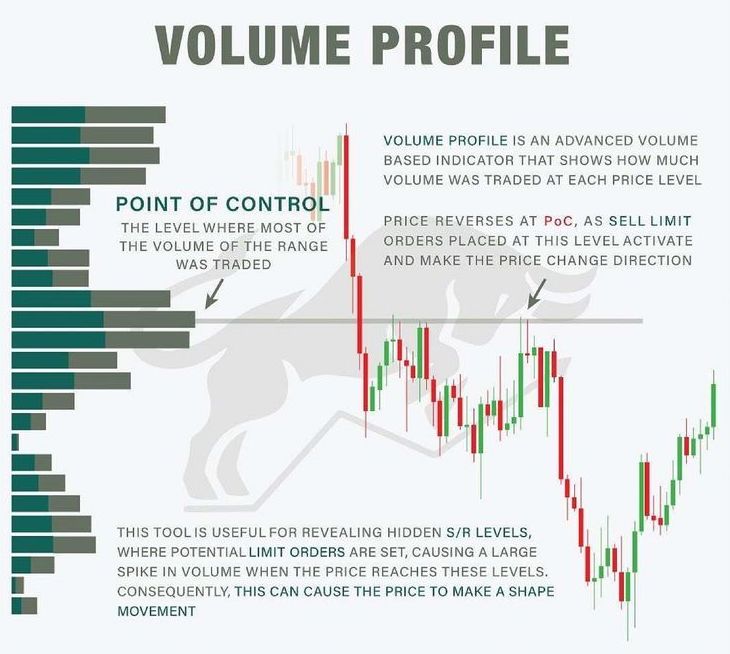
Image Credit: Pinterest
Fundamental Analysis Methods
Technical analysis (TA) primarily relies on charts to predict price movements, while fundamental analysis (FA) focuses on broader market factors to assess the long-term value of cryptocurrencies.
Market News and Events
– Regulatory announcements, major partnerships, exchange listings, and macroeconomic news often trigger significant market volatility.
– It is advisable to set alerts for key economic data (such as the Federal Reserve's interest rate decisions), as the trends in the cryptocurrency market are often related to changes in investor sentiment in the stock market.
Image Credit: Crypto Panic
On-Chain Data
– As a unique advantage of the cryptocurrency market, public blockchains allow anyone to analyze transaction volumes, the number of active addresses, and token distribution.
– For example, the NVT ratio assesses whether the current market is overvalued or undervalued by comparing the market capitalization of the blockchain to its transaction volume.
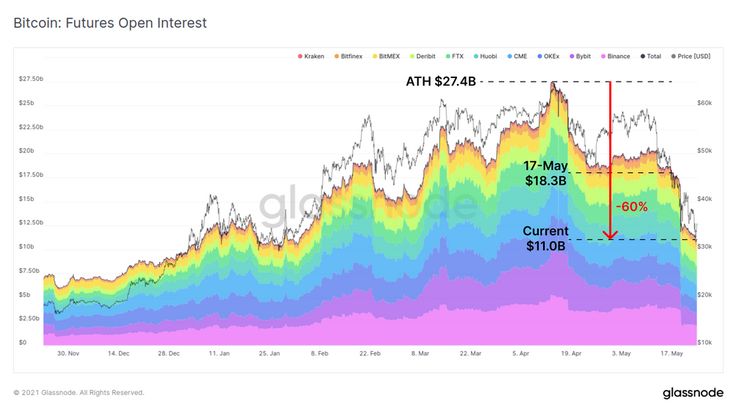
Image Credit: Glassnode
Macroeconomic Factors
- – Interest rates, inflation, and global capital flows can all impact the cryptocurrency market. If central banks tighten monetary policy (such as raising interest rates), risk assets (including cryptocurrencies) may face selling pressure.
Image Credit: Trading Economics
Market Sentiment Analysis
– Tools like the "Crypto Fear & Greed Index" can measure the overall state of market sentiment.
– When market sentiment is extremely greedy, it may indicate that the market is overheated and at risk of a pullback; conversely, extreme fear may suggest that the market is about to bottom out, presenting a rebound opportunity.
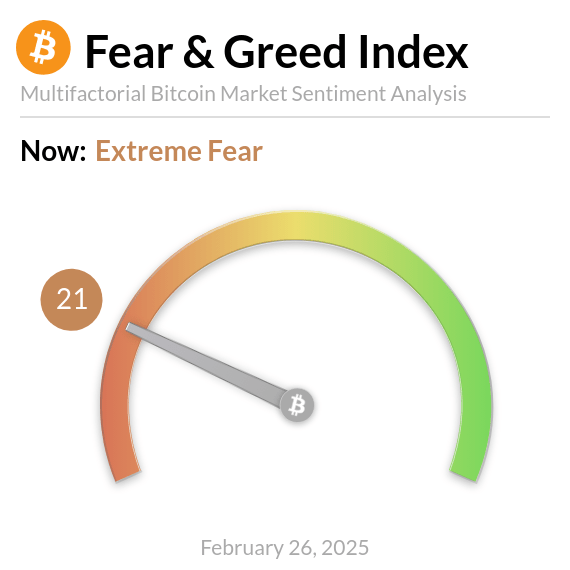
Image Credit: Crypto Briefing
Risk Management and Leverage Control
Cryptocurrency contract trading is fast-paced and highly volatile, making risk management crucial. Without proper controls, leverage can wipe out your account in an instant.
Key Risk Management Strategies
– Set stop-loss orders: Always set a stop-loss point based on your trading plan, rather than arbitrarily choosing a percentage.
– Position management: The risk for each trade should be limited to 1-2% of the total account balance, and adjust position sizes to ensure that a 5% price fluctuation does not exceed your risk tolerance.
– Leverage control: Avoid using extremely high leverage; it is recommended to keep it between 2-5 times to reduce the risk of forced liquidation.
– Prevent liquidation: Set stop-loss orders in a timely manner to avoid being passively liquidated after reaching the liquidation price and incurring high fees. Use isolated margin to ensure that a single trade does not affect the entire account balance.
– Risk/reward ratio: Set trading targets at a 2:1 or higher reward ratio to ensure that profit opportunities outweigh risks.
– Emotion control: Avoid FOMO (fear of missing out), panic trading, and greed; always execute according to your trading plan rather than being influenced by market sentiment.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls
– Over-leveraging: High leverage can lead to high returns but also increases the risk of liquidation.
– Impulsive trading: Trading randomly under the influence of market sentiment often leads to losses.
– Lack of trading strategy: Random entry and unplanned trading make it difficult to achieve stable profits.
– Trading against the trend: Trading against a strong trend has a low success rate and high risk.
– Ignoring trading costs: Exchange fees and funding rates can gradually erode your profits.
– Overtrading: Trading too frequently can increase the error rate; sometimes, not trading is the best trade.
Mastering risk management and avoiding these mistakes can help you enhance trading stability, extend your market survival time, and increase the likelihood of long-term profitability.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




