Original Compilation: zhouzhou, BlockBeats
Today, the surge in Swarms has caught everyone's attention, and the entire community is buzzing around two hot topics: the "anxiety" rumors surrounding AI16Z founder Shaw, and the alleged infringement of OpenAI's Sama on the Swarm multi-agent framework. Some speculate that the driving force behind this wave of excitement may be the emergence of the AI Agent based on Mcs. This agent not only answers medical knowledge questions but is also regarded as the most accessible and practical delivery product within the Swarms architecture. The founder behind it, Kye Gomez, is a 20-year-old "genius," who dropped out of high school and spent three years developing the multi-agent coordination framework Swarms, running 45 million agents to serve sectors like finance, insurance, and healthcare, showcasing hardcore capabilities.
Roller Coaster Trend
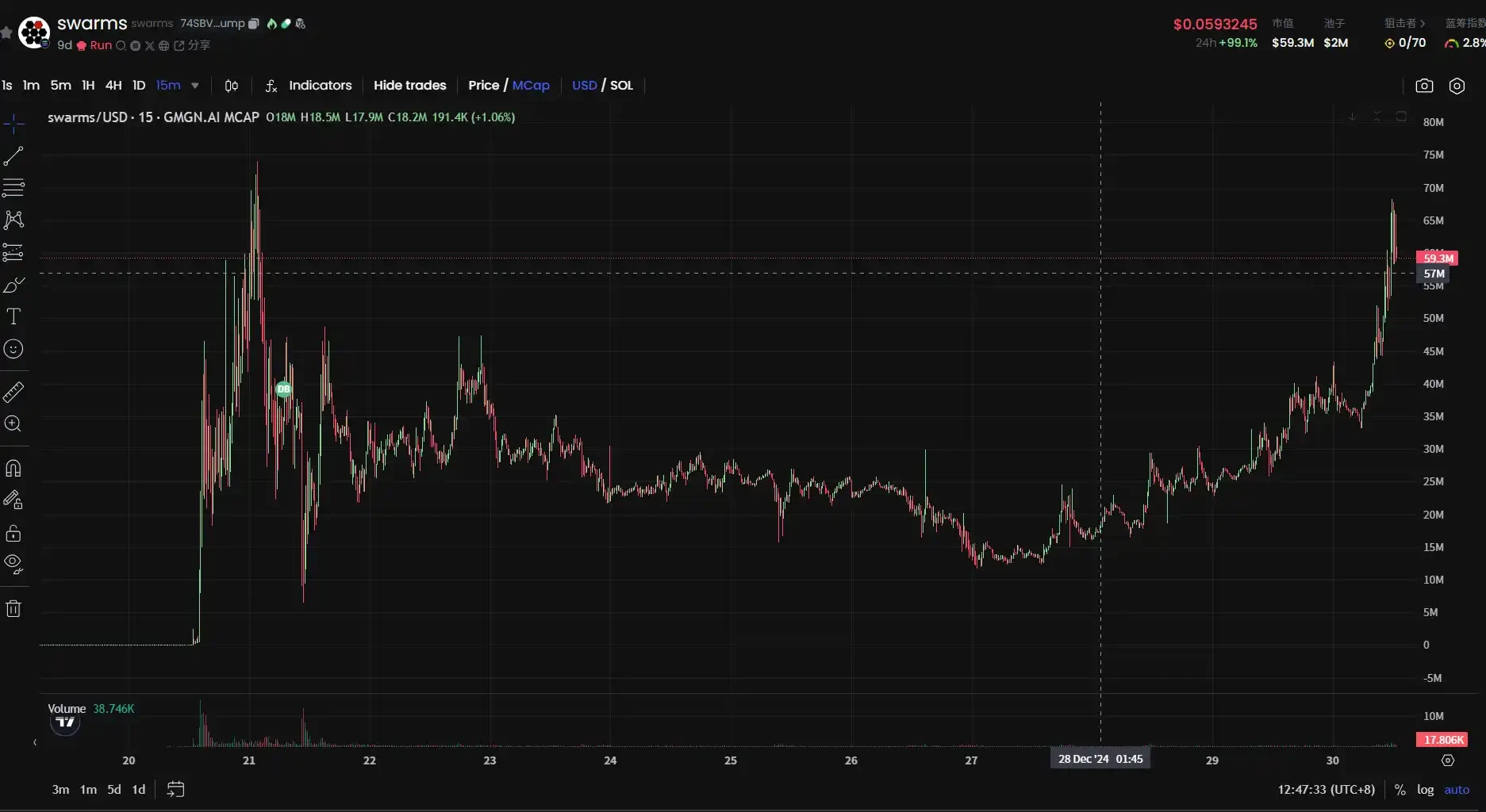
After the Swarms token was launched on December 18, it quickly surged to a market cap peak of $74.2 million on the 21st. Unfortunately, the good times didn't last long, and the market cap plummeted like a roller coaster to a low of around $6 million.
Following that, it oscillated around $13 million until the 27th, when it began to rebound, pushing from a low of $12 million up to $30 million, and then skyrocketing nearly threefold to close to $70 million, almost breaking the previous high. Today's trading volume was also impressive, soaring to $60.8 million. Many netizens felt this wave of excitement resembled a roller coaster experience in the crypto world.
The Future Code Behind Swarms
Behind the roller coaster price trend is a group of AI agents working together like a well-coordinated team, collaborating to tackle complex challenges. The collective intelligence and coordination capabilities far exceed the limitations of a single agent, which is the goal pursued by Kye Gomez's Swarms project. However, creativity and ideas alone are not enough; what truly makes all this possible is the core technology launched by Swarms—Swarm Node (SNAI). It can be said that SNAI is the "nerve center" of the AI agent world, providing strong support and assurance for seamless collaboration between agents.
"Genius Boy" Founder
The core founder behind Swarms, Kye Gomez, is hailed as a "genius boy" in the field of artificial intelligence, showcasing astonishing hardcore capabilities at just 20 years old. Although he dropped out of high school, he developed the multi-agent coordination framework Swarms in just three years and successfully operated 45 million AI agents, providing high-quality services across multiple industries such as finance, insurance, and healthcare, demonstrating the impressive strength of this young talent.
In his research on autonomous and collaborative AI agents, he not only developed the "super-efficient SSM + MoE model" and "hybrid flow model" but also delved into AI alignment and its potential in biology and nanotechnology. In fact, among Kye's many projects, Swarms is just one of his high-quality endeavors; his talents are deeply hidden, and upon further investigation, one can find many other excellent projects he has worked on.
For example, Agora serves as an open-source AI research lab focusing on the intersection of AI with biology and nanotechnology, while Pegasus explores natural language processing and embedding models. He has also participated in the open-source implementation of AlphaFold3. Kye's resume and achievements signal the rise of a true technological innovator.
Swarms AI Agent Orchestration Framework and Core Functions
Next, let's analyze the genius boy's Swarms project, which aims to develop and promote an enterprise-grade production-ready multi-agent orchestration framework. In simple terms, the core function of Swarms is to enable multiple AI agents to collaborate like a team, using collective intelligence to solve complex problems. It not only supports seamless integration with external AI services and APIs to expand functionality but also provides agents with nearly unlimited long-term memory to enhance contextual understanding while allowing for customizable workflows. For enterprise-level needs, Swarms boasts high reliability and scalability, ensuring optimal performance through automatic optimization of language model parameters. In this way, Swarms can leverage the collective intelligence among agents to tackle complex challenges more easily than a single agent.
The Swarms project stands out with its strong technological barriers and market performance. After nearly three years of stable operation, its AI agent orchestration framework has already provided efficient solutions to numerous enterprises on its official website. From data processing to customer service and report generation, Swarms has significantly improved business efficiency through automation while notably reducing operational costs, showcasing its impressive capabilities. As an open-source project, Swarms has also sparked enthusiastic attention in the developer community, with over 2.1K stars on GitHub, gaining the wisdom and support of many developers. Thus, all that Swarms has accumulated confirms the maturity and innovation of its technology.
SNAI
Twitter users seem to agree that the next stage for AI agents is group collaboration (Agent Swarms), achieving more efficient work through communication and cooperation among multiple agents. This approach allows agents from different frameworks to interact and leverage their specialized advantages to perform better in specific tasks and scenarios.
Swarm Node (SNAI) serves as an auxiliary to realize Agent Swarms, a serverless infrastructure designed to support the Swarm concept. SNAI addresses all technical challenges of running AI agents, allowing users to avoid concerns about hardware and infrastructure costs, and easily deploy, coordinate, and manage agents through Python scripts. It also supports chain interactions, scheduling, and multi-language operations, providing new possibilities for small creators who cannot run agents around the clock or lack hardware support.
Users do not need to pay server fees but only for the actual execution time used, making SNAI more efficient than other subscription-based solutions. The uniqueness of SNAI lies in the fact that its agents are not isolated but can collaborate in a "chained" manner, forming a Swarm.
The role of the Swarm is to delegate tasks to different agents, with each agent focusing on a specific task and passing the results to the next agent upon completion. Through REST API and Python SDK, other applications can easily integrate SNAI, and users can flexibly coordinate the behavior of their Swarm (e.g., when to run and which data to use).
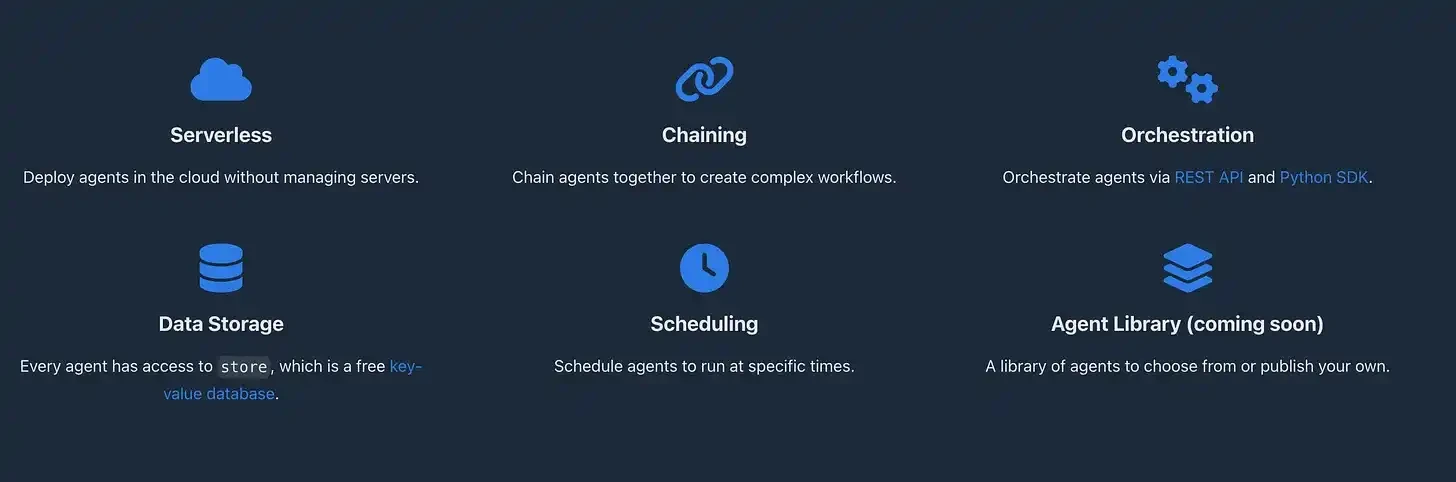
But that's not all; as the SNAI framework is still in its early development stage, many new features will be added in the future, including data storage (a mini cloud database allowing agents to share selected data), task scheduling (running agents at specific times), and an agent library (ready-made agents created by the community for running, customizing, and optimizing). Additionally, SNAI will achieve multi-language compatibility, currently providing a Python client for simplified API operations and planning to support agents deployed in languages like Go, Rust, TypeScript, C#, and PHP. The community has already begun developing a TypeScript client, with plans to support more languages in the future.
Just this week, there have been over 500 builds—these "dependencies" are used to optimize the execution efficiency of AI agents. There have been over 10,000 executions—instances where agents were paused after being launched. SNAI only charges for active running time, significantly enhancing the flexibility of agent operations.

The core features of SNAI include support for serverless operation of agents, allowing developers to integrate agents into codebases, enabling chained collaboration and interaction coordination among agents, while adopting a pay-per-use model that significantly reduces infrastructure costs and lowers the entry barrier for AI agent infrastructure.
Confronting AI16Z
Both Swarms and AI16Z hold significant influence in the AI agent field, with ongoing controversies on Twitter. Despite some similarities, they differ in technical architecture and applications. Swarms adopts a collaborative "team" framework, completing complex tasks and improving efficiency through the cooperation of multiple AI agents. In contrast, AI16Z's Eliza framework resembles a flexible "coordinator," emphasizing multi-platform support and multi-model integration, capable of quickly adapting to various scenarios. Below, we will compare the two agents from two aspects.
Technical Framework and Architecture
Swarms operates like a disciplined team, supporting multiple AI agents to work collaboratively. With autonomy, modularity, and scalability, it enables efficient cooperation among AI agents, excelling at breaking down complex tasks and executing operations with "clear division of labor and seamless cooperation." On the other hand, AI16Z's Eliza framework acts more like an all-around coordinator, focusing on multi-platform operation and multi-model integration while emphasizing interaction among agents, showcasing its unique characteristics in flexibly adapting to various application scenarios.
AI Models and Applications
In terms of AI models and applications, Swarms focuses more on how to cleverly integrate existing AI models to enhance enterprise-level automation and team efficiency through task orchestration and teamwork. It resembles a meticulous commander, adept at properly allocating multiple forces and concentrating on "how to do better." Conversely, AI16Z's Eliza framework offers developers greater freedom, supporting various AI models (such as Llama, Claude) and providing applications with more flexibility to handle a range of scenarios from social media management to financial transactions, thus delivering a versatile solution. One focuses on collaboration, while the other emphasizes diversity; both are equally innovative in their applications, each with its strengths.
Overall, Swarms and AI16Z are exploring the future of AI agents through distinctly different paths. Swarms resembles a disciplined team, impressing enterprise-level users with efficient collaboration and hardcore technology, while AI16Z's Eliza acts more like a versatile free player, showcasing limitless potential through flexible adaptation and diverse scenarios. In this era of fierce competition, the story of AI agents is just beginning. Who will stand out in this race? We shall see!
Reference Content:
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



