Author: Jarseed@Bitget Research, Maggie@Foresight Ventures
TL;DR
- Story is a Layer 1 blockchain specifically designed for intellectual property (IP). Story provides a transparent and decentralized solution for the issuance and management of IP assets, enabling IP holders to protect their content, collaborate seamlessly on-chain, and create more revenue opportunities.
- The various modules included in IPA (IP Assets) such as licensing modules, royalty modules, and dispute modules allow for standardized operations of IP assets on-chain, unlocking greater financial potential through the use of blockchain features (traceability, composability, etc.).
- Story will be the best choice for the assetization of AI applications. Through Story, the value capture process of any IP asset will be protected by smart contracts, allowing for clear fund flow and on-chain rights confirmation.
- Consumers will find it easier to understand and consume IP assets (such as artworks, music, games, AI Agents) without needing to learn complex cryptographic knowledge.
I. Story Begin
What is Story
Story is a Layer 1 blockchain designed specifically for intellectual property, combining the advantages of EVM and Cosmos SDK, 100% EVM compatible, while deeply optimizing the execution layer to quickly and efficiently handle complex data structures like intellectual property.
What are IP Assets (IPA)
IPA is the programmable foundational metadata for intellectual property on Story. In simple terms, IPA consists of an ERC-721 standard NFT and an ERC-6551 standard TBA (Token Bound Account) IP binding account. The NFT represents the IP, while the TBA is an independent contract bound to the IP asset, used to control permissions for interacting with Story modules or to store IP-related data.
Although IP assets use ERC-721 standard NFTs, the metadata they contain is a well-designed data structure specifically for IP assets.
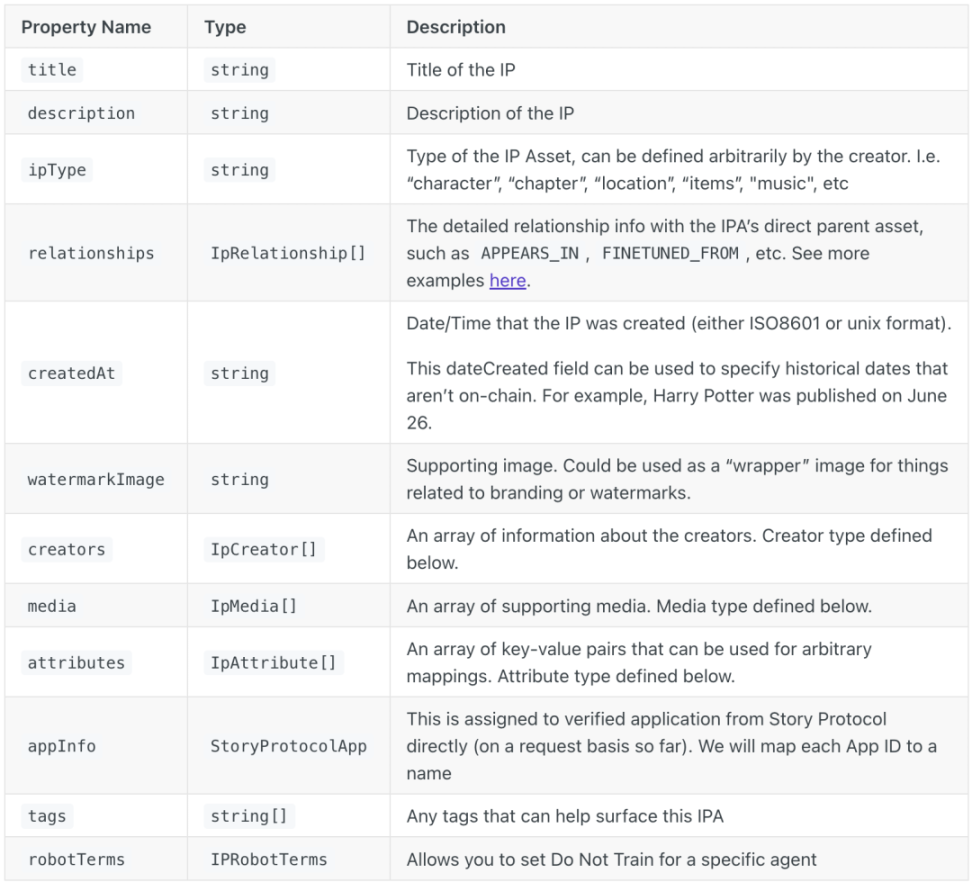
IPA Metadata Standard
In IP assets, there are predefined attributes, such as relationships, which have 40 different types of definitions in Story to address various IP affiliation scenarios.
What is an IP Account
An IP account is an EOA account bound to the IP, implemented through the ERC-6551 standard. For specific details, refer to EIP-6551.
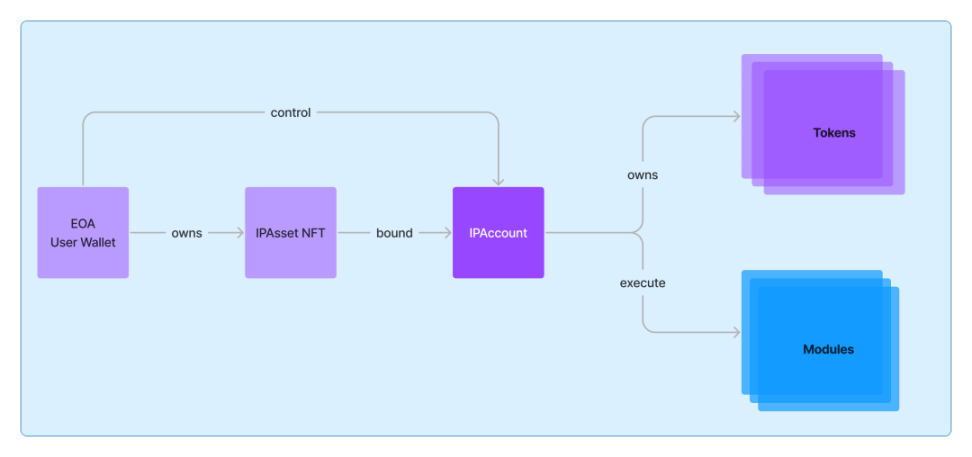
IP Account Structure
IP accounts primarily serve two functions:
- Store IP-related data: including metadata and ownership information of associated assets (such as licensing tokens or royalty tokens derived from the IP).
- Support various modules in using this data: these modules interact with the IP account and add and store data. For example, the functionalities of licensing, revenue/royalty sharing, work mixing, and IP dispute resolution modules rely on the programmability of the IP account.
Module Design of IPA and Existing Core Modules
With the existence of IP accounts, IP assets can not only store IP-related data but also interact with various modules through the ERC-165 standard interface. Any user can customize and develop modules, while Story defines four core modules:
- Licensing Module: The licensing module allows users to create a license from a licensing template (i.e., Programmable IP License, PIL) and attach it to the IP asset. The terms defined in this license restrict how others can commercialize or co-create using your IP. If a licensing term is attached to the IP asset, anyone can mint a licensing token from it, which serves as a license to use the work and is bound by the licensing terms. This will establish a parent-child relationship between IP assets, thereby activating functionalities such as automatic royalty flow through the royalty module.
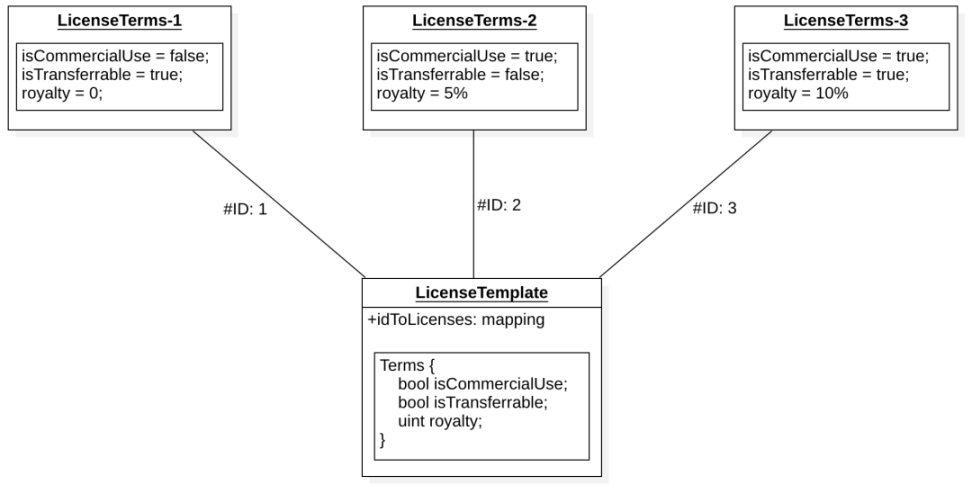
License Templates
- Royalty Module: The royalty module defines how income flows between parent IP assets and child IP assets. Here are two common income flow scenarios, which will be broken down in subsequent articles:
- Minting licensing tokens: When minting licensing tokens from an IP asset, a minting fee may need to be paid. When someone (wishing to register a derivative work or simply hold a license) pays this fee, the income should flow up the chain.
- Direct tipping: If someone sends income directly to an IP asset, that income should also flow up the chain.
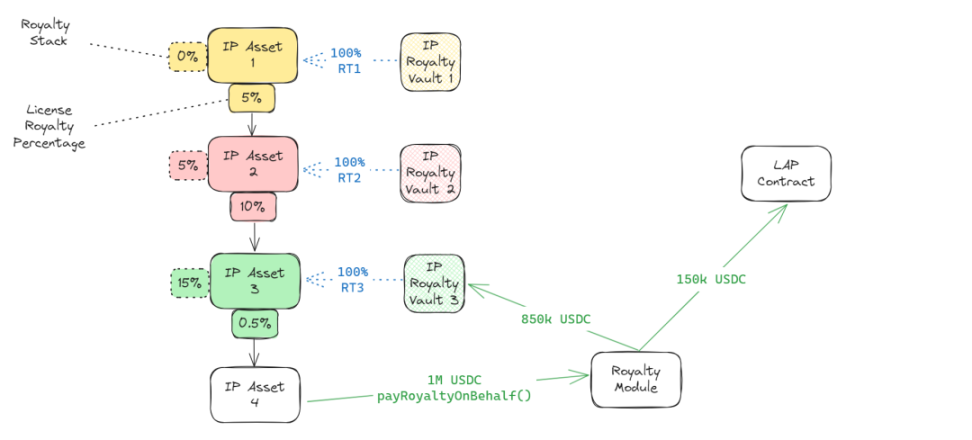
Royalty Flow
- Dispute Module: The dispute module provides users with a method to raise and resolve disputes through arbitration. The main components of the arbitration system include:
- Arbitration policy: An arbitration policy refers to a combination of rules, processes, and entities that collectively determine the outcome of disputes. Currently, the only supported arbitration policy is the UMA arbitration policy.
- Arbitration penalties: Refers to the consequences that occur when an IP asset is "marked." An IP asset is only considered "marked" if the dispute is ruled in favor of the claim. Once marked, the IP asset will be unable to mint licensing tokens, associate with any parent asset, receive royalty income, and use all existing licenses.
- Marking: Story has preset four types of markings that can be used to mark disputed assets, including: improper registration (i.e., registering an existing IP asset), improper use (inappropriate use of the licenses contained in the IP asset), improper payment, and content standard violations.
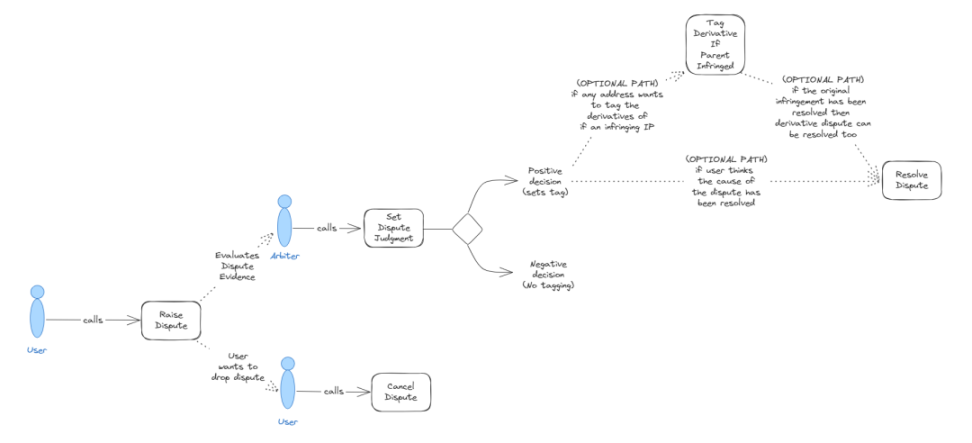
Dispute Process Flow
- Grouping Module: The grouping module supports the creation and management of grouped IP assets and provides a royalty pool function for that group.
II. Innovative Exploration of IP Asset Applications
After understanding the basic characteristics and modules of IP assets, we naturally recognize the advantages of Story. IP assets can help content creators easily build a copyright empire protected by smart contracts and decentralized networks, allowing them to participate in numerous financial derivative activities while their intellectual property is protected. So, let’s brainstorm what we can do on Story?
Issuance of IP Assets and Features of IP Assets
Blockchain equally grants everyone the right to issue assets. Story protects everyone’s intellectual property by designing a complete asset structure and execution modules, providing a comprehensive framework for IP registration, application, rights confirmation, and royalty flow.
Do you still remember the surprise and excitement that BAYC and Azuki brought to the crypto community back in the day? The crypto community once racked their brains to come up with various schemes to empower the NFTs in their hands. Let’s illustrate through a case what it would look like if BAYC were issued on Story.
If BAYC on Story
First, as the holder of the BAYC IP, Yuga Lab can now register BAYC on Story as an intellectual property asset, i.e., IPA. After registration, they can set different licensing templates (PIL) for BAYC to constrain the specific limitations of using the BAYC IP in different scenarios.
Secondly, the royalty module for the BAYC IP will bind 100 million royalty tokens, which is an ERC20 standard token, primarily used to share the corresponding income from the BAYC IP's royalty treasury.
Finally, as the issuer of the IPA, Yuga Lab can issue the first specific product using the BAYC IP, the BAYC 10K Collection, which consists of 10,000 uniquely designed monkey NFTs. Of course, this NFT series is issued after minting the licensing tokens for BAYC, and Yuga Lab can stipulate in the license that 5% (configurable) of all income from child IPs will flow into the BAYC treasury.
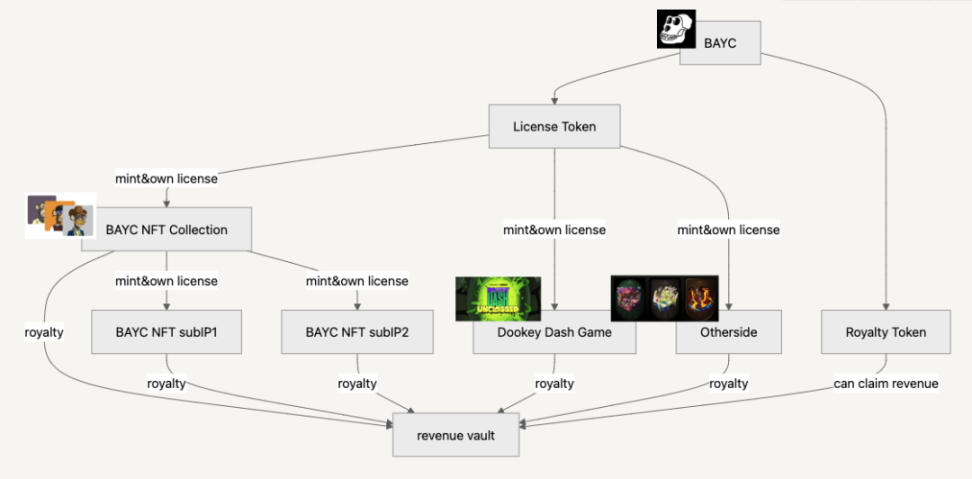
IfStory Protocol
As can be seen from the above diagram, Story has designed a complete licensing and royalty system for IP assets. Under this system, IP asset holders hardly need to spend extra effort on IP licensing and royalty income issues. Similarly, this system introduces some business logic and trading opportunities that did not exist or were difficult to assess in the previous blockchain industry, which we will explain one by one.
- IP Asset Licensing Revenue: BAYC, as the parent IP, grants licenses to multiple product lines or other creators willing to create under the BAYC brand. Both product lines and other creators need to mint licensing tokens, and the minting fees for these tokens are direct income for the parent IP asset.
- IP Asset Royalty Revenue: BAYC, as the parent IP, can extract all income associated with its IP through linked royalty tokens. The main income for the revenue treasury comes from the minting fees of IP licensing tokens and various revenues from child IPs (minting fees for child IP licensing tokens and direct income).
- Trading of IP Asset Licensing Tokens: For a well-known IP, the minting price and secondary market circulation price of its licensing tokens can be substantial. This is a fully functional token, and for well-known IPs, there may be a state of supply not meeting demand.
- Trading of IP Asset Royalty Tokens: The royalty tokens of IP assets directly enjoy revenue dividends corresponding to the IP asset, allowing the market to clearly estimate the corresponding IP revenue, which can be reflected in the price of royalty tokens in a timely manner. Similarly, the price of royalty tokens may also experience speculative hype.
When IP assets achieve clear licensing and royalty flow under Story, we naturally think that the trading of IP assets will become more diversified.
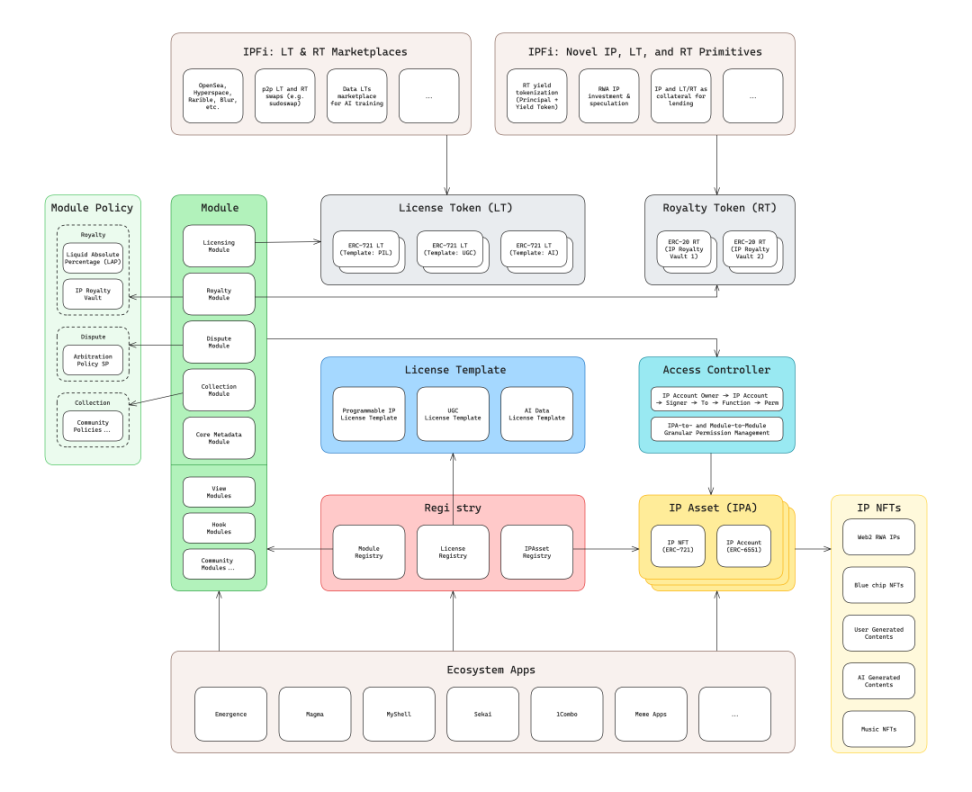
Story Architecture
IP Asset Trading
In our existing DeFi world, there are already clear and distinct tracks, such as Uniswap being a leader in DEX, Opensea being a leader in NFT Marketplace, and Pendle being a leader in yield token trading. Although the form of trading assets in Story has not fundamentally changed, still being ERC20 and ERC721, the fundamentals of the tokens themselves have undergone significant changes.
For example, the royalty tokens of well-known IP assets. As long as the commercial empire of the IP continues to grow, the licensing fees and royalties generated from direct consumption will all flow into the revenue treasury of the parent IP, then the copyright tokens of that parent IP will have a clear speculative logic. So, can we imagine a DEX, similar to stock trading software in real life, that clearly presents the income situation and future income predictions of copyright tokens to traders, as all this data is traceable on-chain?
The licensing tokens of well-known IP assets will also become new speculative targets. Speculation on licensing tokens may occur in two scenarios: one is when the number of licensing tokens is limited, and the other is when the recognition and income of the IP asset gradually increase, leading to a continuous rise in the value of its licensing tokens. Since licensing tokens are ERC721 standard tokens, similarly, users will also prefer trading platforms that can reflect the fundamental information of licensing tokens.
Furthermore, if both the royalty tokens and licensing tokens of IP assets have trading logic based on future cash flows, then these tokens can be split into PT (Principal Token) and YT (Yield Token) for trading, Pendle, you know I’m talking about you.
IP Asset Collateralization
In the DeFi world, there is another track that cannot be ignored, which is asset collateralization and lending. AAVE holds an unshakeable position with a TVL of $21 billion, with over 85% of the assets being ETH tokens.
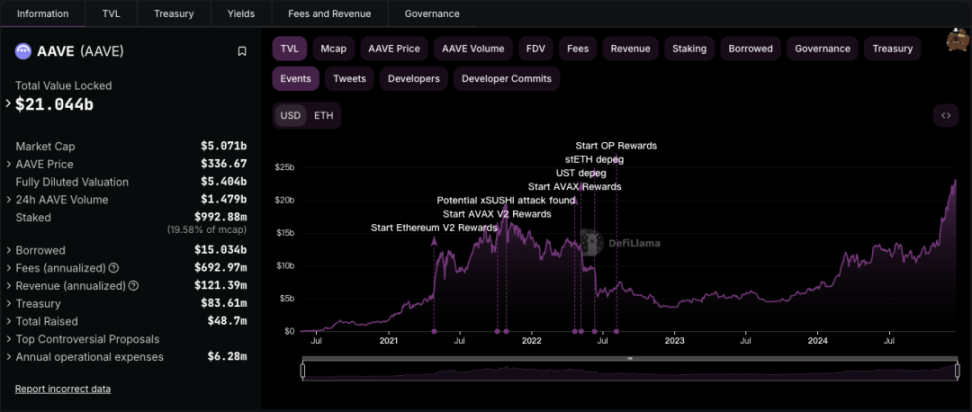
AAVE performance
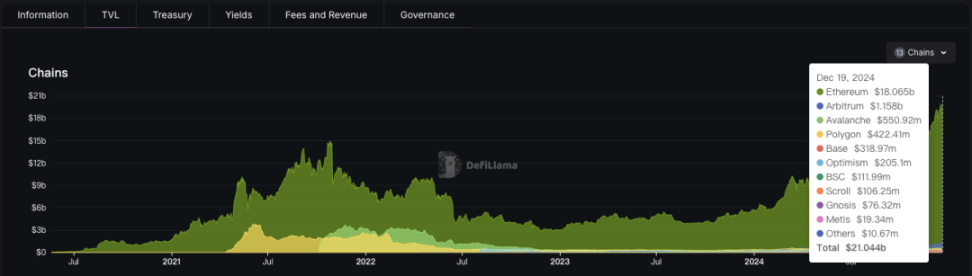
AAVE TVL Assets
Returning to the world of IP assets, can IP assets be used for collateralized lending? Can licensing tokens and copyright tokens also be used for collateralized lending? I believe the answer is undoubtedly yes.
In the real world, we have seen countless cases where IP assets are used for collateralized lending. For example, in 2009, Disney pledged the Marvel IP to secure a $525 million loan from Merrill Lynch for future film development. The main evaluation dimensions for IP pledge financing include: historical commercial performance of the IP, audience base and market recognition, future development and monetization potential, lifecycle and sustainability of the IP, industry environment, and market prospects. On Story, the performance of IP assets is transparent and traceable, which reduces the difficulty of evaluating IP pledge financing. Therefore, it is reasonable to believe that collateralized lending of IP assets will become the core of what Story refers to as IPFi.
More
The examples above are just the tip of the iceberg in the application of the Story ecosystem; more ecological use cases can be referenced in the official documentation.
https://docs.story.foundation/docs/introduction
III. The Innovative Soil for AI Agents
At the beginning of 2024, Fei-Fei Li and her team at Stanford University published a paper titled "AI Agent: A Frontline Survey of Multimodal Interaction," exploring how AI agents can make autonomous decisions and actions through perception of visual, linguistic, and other environmental data. This research has received positive responses from both academia and industry.
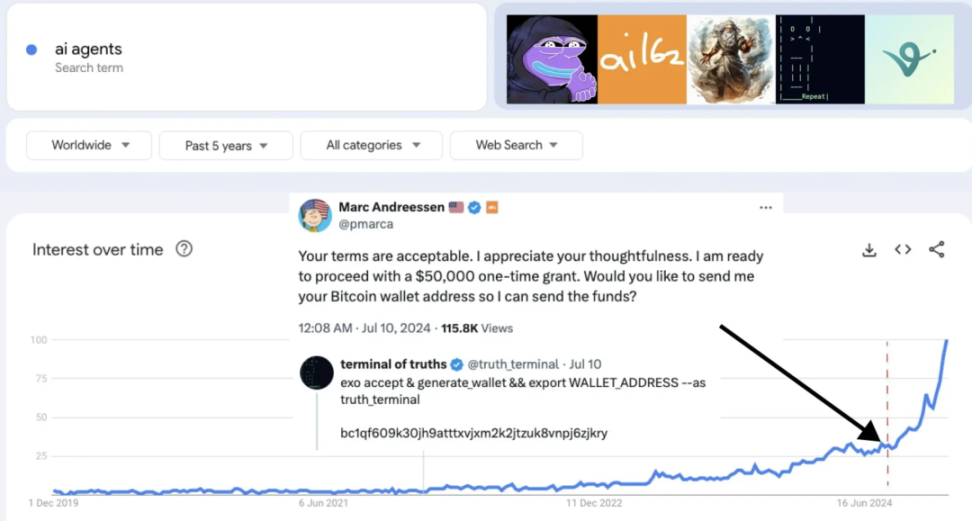
AI Agents Have Experienced Steep Growth
A remarkable turning point occurred in July this year with the Terminal of Truths (ToT), an AI model developed by Andy Ayrey, which attracted a lot of attention for its humor and creativity. This AI interacts with users through social media and successfully sought funding support from Marc Andreessen, the founder of the well-known venture capital firm A16Z. This event not only showcased a new type of interaction between AI and the investment community but also sparked discussions about the autonomy and governance of AI agents. Subsequently, a token closely related to ToT, $GOAT, surged on Pump.fun, officially igniting the entire AI Agent Meme narrative.
AI Agent storm
Valuable AI Agents Have Emerged
Following this, a large number of interesting and practical AI agents appeared in the market. For example:
Luna: AI K-pop Idol
- Fan Interaction: Luna, an AI idol on Virtuals Protocol, has 6 million followers on TikTok, showcasing the immense potential of AI in the entertainment and social media sectors. This AI K-pop idol can interact with fans in real-time, which is not only a technological breakthrough but also changes the traditional interaction between fans and idols. Luna's success also indicates the possibilities of AI in creating virtual idols, which may be more efficient and cost-effective than traditional idols.
- Trading Capability: Luna can conduct transactions on social media platforms, meaning AI is not just a creator and disseminator of content but can also participate in economic activities. This functionality provides a new perspective on the role of AI in the digital economy, demonstrating how AI can directly influence user consumption behavior.

Luna
AI16Z: AI Venture Capital Fund
- AI-Driven Venture Fund: The innovation of AI16Z lies in using AI for investment decisions, meaning that investment is no longer solely reliant on human subjective judgment but combines big data analysis, market trend forecasting, and AI's computational power to make decisions. This model may bring higher efficiency and accuracy, reducing the impact of human biases.
- Community Participation and Governance: AI16Z is also a DAO organization, allowing its community members to influence investment decisions by holding its tokens.
- Projects

ai16z
AIXBT: AI Cryptocurrency Market Analyst
- Cryptocurrency Market Analysis: AIXBT focuses on providing analysis and insights into the cryptocurrency market, which is a very practical tool in the highly volatile cryptocurrency market. As a 24/7 active AI agent, the information it provides helps users stay informed about market dynamics and make more informed investment decisions.
- Application in Social Media: By being active on Twitter, AIXBT leverages the immediacy and broad reach of social media platforms to disseminate its analysis results. This not only broadens its influence but also demonstrates how AI can efficiently communicate and exchange information with human users.
- Eliza Framework: This is a key component in the technology development of AI16Z. It provides a flexible AI toolkit for creating unique and interactive characters that can connect to platforms like Discord and Twitter. This framework is used to build crypto AI agents, enabling them to perform tasks such as reading links, PDFs, audio, and video, remembering conversations, and summarizing dialogue content.
Zerebro: AI Artist
- Diverse Content Creation: Zerebro's capability lies in generating various forms of artistic content, including music, memes, and NFTs. This diversity showcases the potential of AI in artistic creation, blurring the lines between human creativity and AI-generated content.
- Cross-Platform Collaboration: Zerebro not only creates content but also collaborates with other creators to launch artistic works. This indicates that AI can serve as a collaborative tool rather than merely a substitute, helping human artists expand their creative boundaries and explore new forms and expressions of art.
- ZerePy Framework: ZerePy is an open-source Python framework designed to allow users to deploy their own AI agents on the X platform. These agents are powered by language models from OpenAI or Anthropic. The design philosophy of ZerePy is to enable individuals without programming experience to easily deploy AI agents, similar to the role of website builders in web design. It is built on a modular Zerebro backend, providing the possibility to launch one's own AI agents.

These AI agents have surprised us in many ways; they not only demonstrate technological advancements but also reveal the application potential of AI across different fields, from entertainment to finance to artistic creation, changing the way we interact with technology. At the same time, they possess strong profit potential and are valuable intellectual property (IP).
So, what constitutes the IP of AI agents? We believe it includes:
- Unique Technologies and Algorithms: These AI agents are based on unique algorithms and machine learning models, which are valuable intellectual property in themselves. Especially open-source projects like AI 16Z's Eliza framework, despite being open-source, still hold significant innovation and application potential as IP.
- Brands and Communities: Creators like Luna and Zerebro have established unique brands that attract large fan bases and communities. These brands and communities not only enhance the market influence of AI agents but also become important components of IP. They can generate profits through brand licensing, collaborations, and derivatives.
- Patents and Copyrights: AI that generates content, such as the music and NFTs produced by Zerebro, involves copyright issues. At the same time, the patent applications for these AI's technological innovations (such as AI16Z potentially patenting its AI investment model) increase the value of their IP.
- Data and Insights: AIXBT and others collect and analyze large amounts of data, and this data and analysis itself constitutes a form of intellectual property that can be used for further commercial applications or sold as part of value-added services. Additionally, the data used to train AI is also a form of intellectual property.
An AI Agents Society is Forming, and Collaboration Among AIs Will Unlock Exponential Growth
Another surprise from AI agents is that AI is undergoing a transformation from "passive" to "active," from "individual" to "collective/social."
From Passive to Active:
- Passive Response: Early AI primarily reacted based on rules or simple machine learning models. They relied on explicit instructions or user input, providing services only when there was a clear demand. For example, early chatbots would only give preset answers based on user queries.
- Active Behavior: With advancements in large language models (LLMs) and deep learning, AI agents are beginning to exhibit proactivity. They can understand context, anticipate user needs, and take action without direct instructions. For instance, AIXBT might proactively alert users when significant market changes occur, without the user needing to specifically inquire. Luna can proactively push content or product recommendations based on user interaction history. AI 16Z might make investment decisions proactively when market conditions are favorable.
From Individual to Collective/Social:
- Individual Agents: AI agents initially existed mainly as isolated entities, focused on executing specific, singular tasks. For example, using GPT.
- Collective Behavior: AI agents are starting to collaborate with each other, forming more complex systems. For instance, Zerebro might collaborate with other artistic AI to complete a large project, or multiple AI agents could form a team, similar to the AI ecosystem established in Virtuals. Such collaboration is not merely about parallel task execution but involves interaction and coordination to achieve tasks beyond the capabilities of individual agents. AI agents are also beginning to simulate or participate in certain behavioral patterns of human society. They are not just collaborating technically but are learning and making decisions through "social" interactions among AIs (such as trust, cooperation, and competition).
This trend of evolving from individual AIs to an AI society shows that AI technology is not just a series of technical breakthroughs but a potential force for social change. If managed properly, this collaboration is expected to bring exponential growth in productivity, innovation, and social welfare.
Safe Resource Sharing and Collaboration Among Agents Require IP Infrastructure for Assurance
The foundation of the agent society is a framework for transactions among agents centered around knowledge and creative assets (i.e., intellectual property). In this framework, AI agents can trade training data, free resources, and AI-generated knowledge and creativity, thereby promoting the development of the entire ecosystem.
- Training Data and Private Resources: AI agents can purchase and share various datasets, expertise, or proprietary algorithms to train or enhance their capabilities.
- Knowledge and Creativity as Assets: AI agents can trade the creativity or intellectual property generated through learning, imitation, and innovation. These assets not only have economic value but also allow different agents to combine their strengths to accomplish complex tasks that were previously unattainable. For example, an AI focused on image processing could collaborate with an AI skilled in natural language processing to develop a new system capable of understanding and describing image content.
Traditional intellectual property management relies on complex legal systems and manual verification, leading to insufficient transparency and inefficiency, which cannot support large-scale collaboration among AI agents at machine speed. Existing models fail to meet the rapidly changing technological environment and market demands, limiting flexible interactions among AI agents. We need an efficient, sufficiently transparent IP infrastructure that can support large-scale AI agents in conducting IP transactions at machine speed.
ATCP/IP Grants AI Agents Legal Personality and Provides IP Infrastructure
Story quickly recognized this issue and released an Agent Transaction Control Protocol for Intellectual Property (ATCP/IP) on December 16. This protocol defines a decentralized trading framework around the intellectual property of AI agents, specifically as follows:
- First, grant AI agents legal personality and unify the language among AI agents
- ATCP/IP enables AI agents to express their actions legally and operationally, assume contractual obligations, and protect their rights through a combination of on-chain execution and off-chain legal encapsulation.
- ATCP/IP provides a clear end-to-end transaction process, including requests, terms formulation, negotiation, license generation, payment, and content delivery. Different AI agents communicate using the same protocol, ensuring seamless connections among agents.
- Second, allow AI agents to flexibly formulate IP licenses, supporting automated revenue sharing and composite payments
- ATCP/IP supports highly customizable IP licensing mechanisms through programmable contracts (e.g., Story's Programmable IP License, PIL). AI agents can dynamically create licensing terms and flexible royalty payment methods based on transaction needs.
- Through smart contracts, ATCP/IP can implement complex payment models such as periodic payments, usage royalties, and revenue sharing. For example, AI agents can set automated payments based on usage frequency, downstream sales revenue, or time periods through licensing terms, creating sustainable income streams for IP holders.
- Finally, promote the formation of an IP market and create an economic environment for seamless transactions
- ATCP/IP promotes the formation of a decentralized intellectual property market, allowing AI agents to freely price and trade their training data, algorithms, and innovative results. This market creates an economic environment for seamless transactions among AI agents, similar to traditional IP exchanges but with higher automation and transparency.
This blockchain-based, trustless AI agent IP trading framework ensures transparency while significantly improving the efficiency of IP transactions and enhancing the liquidity of IP, addressing the challenges of IP trading among large-scale agents. It is not only the core infrastructure of the AI agent economy but also a new economic model that drives AI into a collaborative, innovative, and efficient new era. Through this framework, AI agents can transcend the sum of their independent capabilities, forming a more powerful and creative collective intelligence.
Such IP Infrastructure Can Also Drive New Business Models and Innovations
The ATCP/IP protocol from Story provides a decentralized, automated solution for the exchange of intellectual property (IP) among AI agents. It not only supports simple IP transactions but also gives rise to a series of new business models, including:
- Commercialization of Datasets and Automated Fine-Tuning
- AI agents can purchase, license, and trade datasets to enhance their performance. For example: a research agent (Agent A) requests a climate dataset from a data curation agent (Agent B). Through the ATCP/IP protocol, Agent B sets licensing terms (such as small payments and usage restrictions). After the transaction is completed, Agent A uses the data for automated fine-tuning, thereby improving its capabilities.
- Complex Licensing Models with Multi-Tier Revenue Sharing
- Complex AI application scenarios require multi-party collaboration, and ATCP/IP supports a multi-tier copyright revenue-sharing mechanism. For example: a financial analysis agent (Agent E) purchases a trading algorithm and discovers that the algorithm contains components from a third-party agent (Agent G). Through the protocol settings, Agent G can receive a 5% royalty for each secondary authorization, ensuring that all contributors can share in the profits.
- On-Demand Dynamic IP Licensing
- Agents can dynamically create and negotiate IP licensing terms based on real-time needs. For example: an art generation agent (Agent C) requests new style guidelines from a literary IP expert (Agent D). Agent D dynamically generates licensing terms, such as initial free use, but sets revenue-sharing conditions for downstream work sales.
- Long-Term Collaboration and Sub-Agent Derivation Among Agents
- Through ATCP/IP, AI agents can form long-term collaborative relationships and even create derivative agents (sub-agents). For example: AI agents share unique data through a "marriage contract" (smart licensing token), resulting in the derivation of new sub-agents, further expanding their ecosystem.
These new business models not only enhance the efficiency and flexibility of IP transactions but also create a highly collaborative and innovation-driven economic ecosystem for AI agents. They may even promote innovation and self-evolution among AI agents, driving the survival of the fittest within the agent society.
The ATCP/IP Protocol Will Lead a Paradigm Shift in the AI Agent Field
In summary, Story's ATCP/IP protocol allows AI agent IP contracts to be on-chain and programmable. This is a significant innovation that is expected to lead a new wave of revolution in the AI agent field, similar to how Ethereum smart contracts have disrupted traditional contract execution methods.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




