Introduction
DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network) incentivizes users to share personal resources through token rewards, aiming to establish a broad infrastructure network covering areas such as storage space, communication bandwidth, cloud computing, and energy. The DePIN token plays a core role in network operations, facilitating governance, service payments, and staking, all of which drive the growth of the network: the token reward structure encourages more resource investment, thereby enhancing coverage and service quality. Optimized services attract more customers, which in turn increases the utilization of DePIN infrastructure and the demand for tokens. Through sound token economics, DePIN can effectively address the challenges of project cold starts, thereby fostering a thriving ecosystem, which is the DePIN flywheel effect.
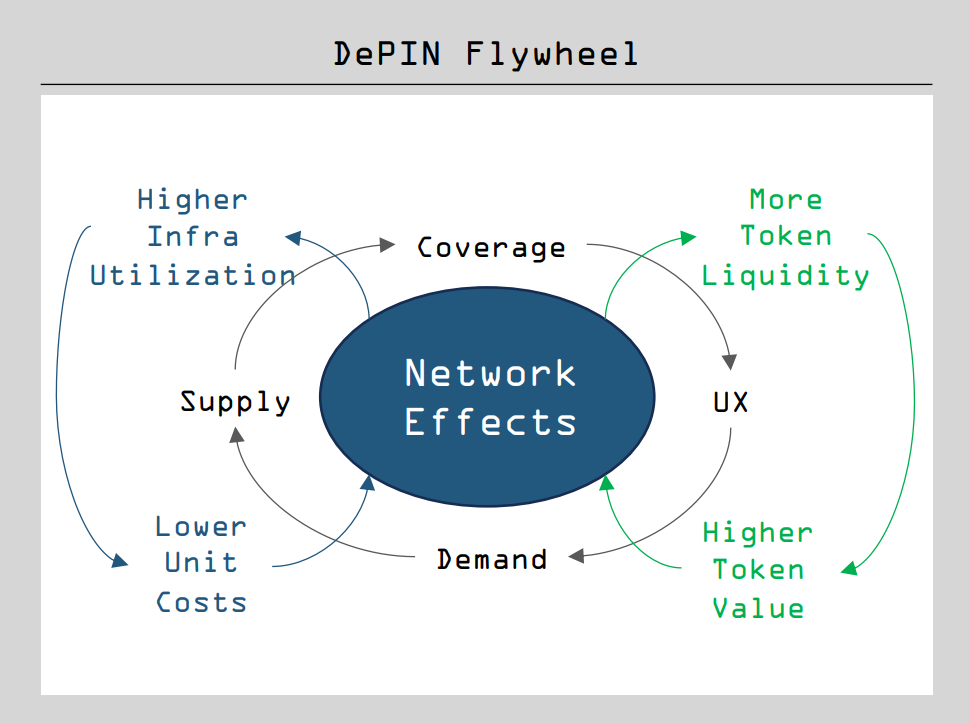
DePIN Flywheel
Compared to traditional physical infrastructure, DePIN offers several advantages, including horizontal scalability, community control, and efficient cost operations. This article will explore key tracks and projects in the DePIN space, including storage (Filecoin, Arweave), computing (Render, io.net, Akash, Aethir), AI (Bittensor, ASI, Virtual Protocol), and other tracks (Helium, Livepeer, Hivemapper). Finally, we will assess which blockchain platforms are suitable for developing DePIN projects.
Storage
Storage networks originate from the incentive layer of the IPFS protocol and have the potential to evolve into a modular blockchain data availability layer. Storage space can be utilized for cold storage and hot storage based on the specific design of the network. However, many storage projects are still in the early stages of ecosystem development, often leading to market oversupply.
Filecoin
Filecoin is one of the largest decentralized storage networks, built on the peer-to-peer InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) protocol. Unlike traditional storage solutions that rely on specific devices or cloud servers for data access, IPFS supports permanent referencing of content independent of location. Filecoin enhances the incentive layer with its native cryptocurrency FIL, promoting reliable storage and data access. Filecoin was launched by Protocol Labs, founded by Juan Benet (the creator of IPFS and Filecoin), and is particularly suitable for cold storage. As of October 2024, Filecoin has generated approximately 4.28 million blocks and has a network storage capacity of 4.7 exbibytes (EiB). A total of 1,837 data clients have uploaded about 2.4 EiB of data. The network currently supports 2,050 active miners who collectively commit approximately 149.7 million FIL, accounting for 7.49% of the total token supply.
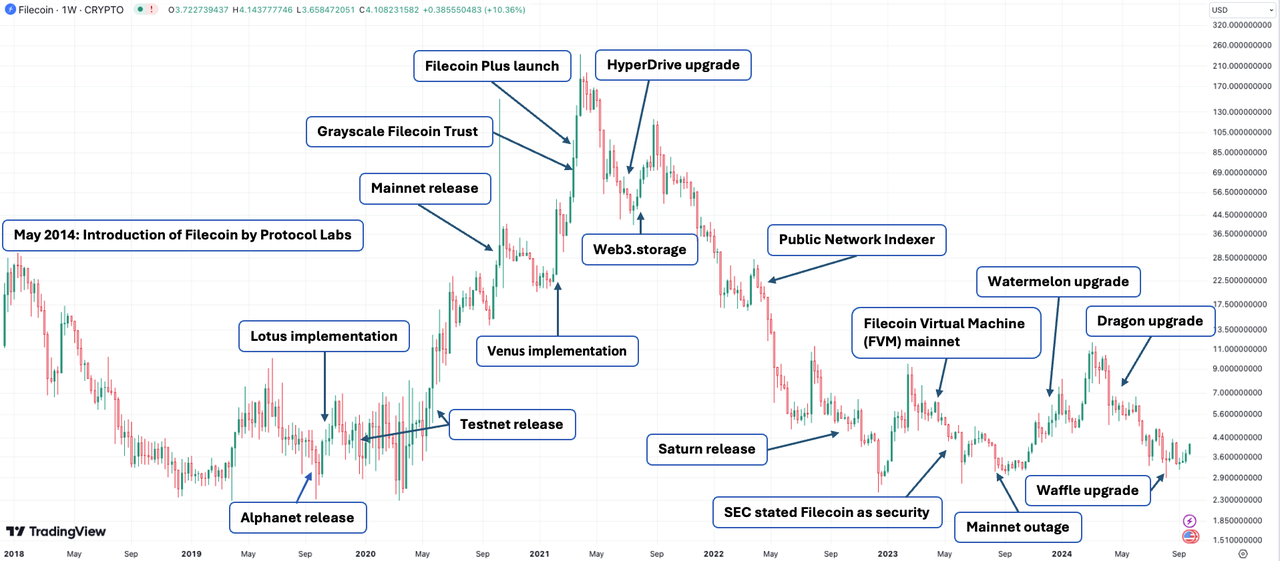
History of Filecoin
Filecoin has launched Filecoin Plus to incentivize quality data storage, Station to improve retrieval speed, Saturn for content delivery, Storacha for hot object storage, and a new Curio Storage operating platform for SPs, among others. Filecoin is not only focused on improving the network but has also introduced innovative solutions such as the permanent storage solution provided by Lighthouse, file-sharing tools offered by Fileverse, NFTs supporting games and music, and more applications. Additionally, the introduction of the Filecoin Virtual Machine (FVM) transforms Filecoin into a dual-layer network, combining the data availability layer (DA) and the smart contract layer, providing opportunities to build a DeFi ecosystem for decentralized applications (DApps). Collaboration with IoTeX has made Filecoin the preferred storage foundation for its DePIN layer network, laying the groundwork for future DePIN prosperity. With the launch of InterPlanetary Consensus (IPC), DApps can enhance scalability and customization by deploying "subnets" or layer two networks on top of the Filecoin network.
As of October 2024, over 4,300 contracts have been deployed on FVM, and the total value locked (TVL) reached a historical high of 63 million FIL (approximately $273 million) in the second quarter of 2024. However, the development of the Filecoin ecosystem remains highly concentrated on FIL's liquid leasing. The storage utilization rate of Filecoin is relatively low, around 30%. The net deposit total of the Filecoin network is slightly over $100 million, with over 60% concentrated in GLIF, a liquid leasing protocol that facilitates the lending and borrowing of FIL to balance supply and demand between FIL holders and miners. Filecoin lacks compelling innovations and has failed to stand out among other emerging DePIN stars.
FIL is the lifeblood of the Filecoin network, used for governance rights, storage payments, network fuel, SP collateral, and network incentives, with a market capitalization of $5.35 billion and a circulating supply of 30%, with an annual inflation rate of up to 27%. From September 2023 to September 2024, over 46.5 million FIL were mined, while approximately 1.4 million FIL were burned during the same period. 70% of the total is used for minting rewards, with the remaining 30% held by Protocol Labs and the Filecoin Foundation. In minting rewards, as much as 38.5% of FIL is minted based on network performance, and 16.5% of FIL will be gradually released according to a six-and-a-half-year decay plan, meaning that about 97% of these tokens will be released over approximately 30 years. From a supply and demand perspective, the supply of FIL mainly comes from newly minted tokens, which are affected by high inflation, while demand is primarily related to the demand for storage services. However, the ecosystem mainly caters to miners, aiming to address low capital utilization. Therefore, the price of FIL is significantly influenced by miners.
Arweave
Arweave is a decentralized network that provides permanent data storage and hosting services, protected by an open decentralized network of miners who earn rewards in the form of $AR tokens by storing and replicating data. Arweave employs an innovative data structure called Blockweave and a unique consensus mechanism called Spora (Succinct Proof of Random Access). This mechanism requires miners to link each new block to the previous block and a randomly selected historical block, ensuring data scalability, redundancy, and stability. Users pay a one-time fee for permanent storage; however, only a portion of $AR (16.67%) is immediately paid to miners as an initial storage fee. The remaining portion is allocated to a fund, which will gradually release $AR over 200 years. This fund mechanism incentivizes miners to provide permanent storage while reducing the circulating supply of $AR, thereby enhancing its value.
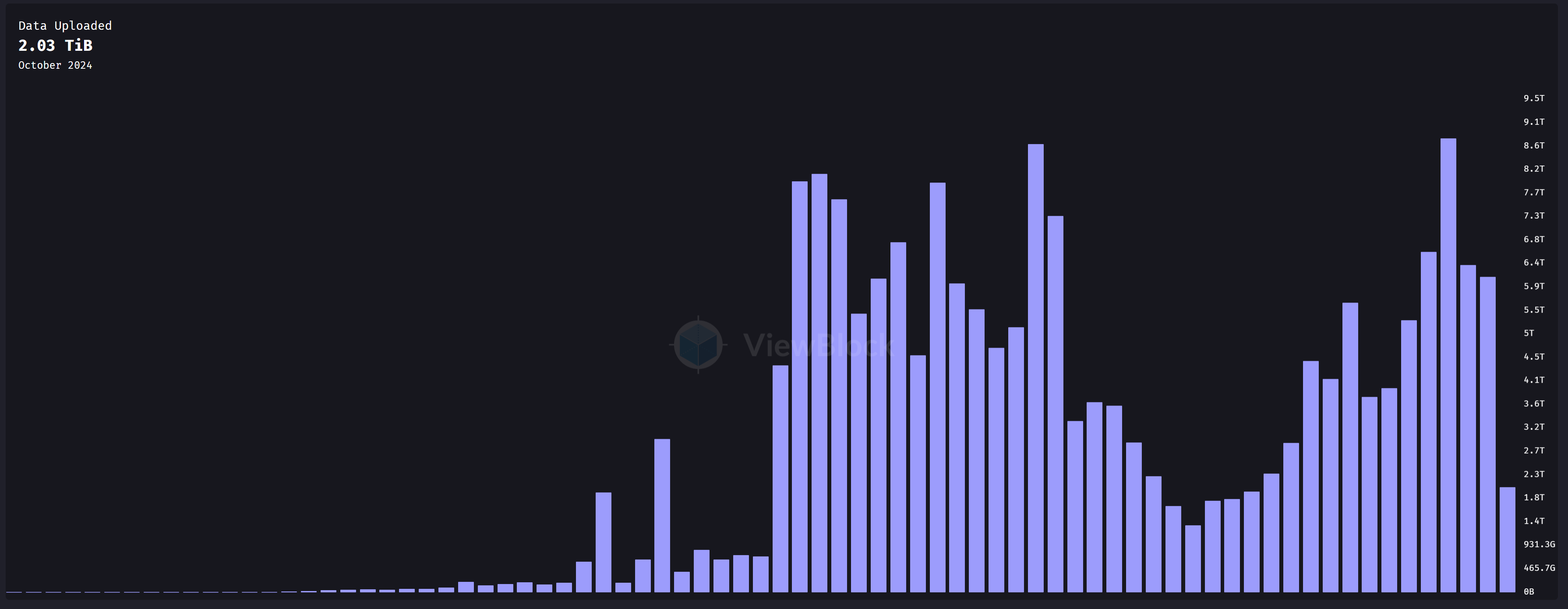
Monthly Data Upload Volume of Arweave
Arweave's permanent storage mechanism is particularly suitable for low-volume but high-value data, such as historical documents and NFTs. As of October 10, 2024, the cost to store 1GB of data is approximately 0.74868 AR ($13.60), making permanent storage financially feasible for many projects. Additionally, the permanent decentralized network built on Arweave—permaweb—consists of a set of modular interchangeable protocols, making Arweave a potential data availability layer for decentralized applications. For example, the parallel computing project AO allows a large number of processes to be stored and executed on Arweave, with the potential to airdrop $AO tokens to $AR holders. Despite these advancements, the monthly uploaded data remains relatively low, at about 6.5 TiB (storage costs approximately 5,000 AR). Although AO will launch the governance token $AO, $AR cannot directly capture the value of the AO ecosystem.
The $AR token has multiple functions, including governance rights, fee payments, and miner rewards, with a fully diluted valuation (FDV) of $1.18 billion and a circulating ratio of 99%.
Summary
In contrast, Filecoin is primarily optimized for hot storage, with the longest operational history and the largest storage capacity—approximately 7,000 times that of Arweave. However, the circulating ratio of $FIL is only 30%, with an annual inflation rate of up to 27%. There is insufficient organic demand for $FIL, and its price is mainly influenced by miners. Additionally, the development of the Filecoin Virtual Machine (FVM) ecosystem has not met expectations. Aside from liquid leasing projects for mining, there is a lack of prominent projects within the ecosystem. In comparison, Arweave is designed for cold storage, with nearly all of its supply in circulation. Under the Endowment mechanism, demand for Arweave services will reduce the circulation of AR and push Arweave into a deflationary state. Although current demand for Arweave remains relatively small, its ecosystem demonstrates greater innovation, particularly with projects like AO, adding an appealing dimension to its attractiveness.
Computing
Compared to the oversupplied storage track, the computing track overall shows higher demand characteristics, primarily concentrated in areas such as 3D rendering and AI model training. CPU networks are suitable for general computing, while GPU networks are better suited for parallel computing. Although different projects have different business models and target customers, the source of demand remains the most critical factor.
Render Network
Render Network is a distributed GPU rendering platform based on Solana, allowing users to provide or utilize computing power and perform complex cloud rendering and other computing tasks using the $RENDER token. Within the platform, creators and node operators serve as the demand and supply sides of the computing ecosystem, respectively. To efficiently match GPU supply and demand, Render Network employs a multi-tier pricing strategy that considers factors such as speed, cost, security, and node reputation. Render Network is proposed and supported by OTOY, Inc., the parent company and creator of Octane Render, a leading professional rendering solution widely used by Hollywood studios and artists, which has received an Oscar for its contributions to the field.
Render Network relies on OTOY's powerful 3D rendering technology and strong relationships with major tech companies, offering real and diverse application scenarios: First, Octane Render's customers can directly access Render through subscription accounts, and all tasks that can be rendered using Octane Render GPU can be rendered on Render Network, establishing the most basic and solid demand for the platform. Second, Octane X can be applied to Apple's powerful M series chips, which have been used in iPads and Macs. In the future, Octane X may also expand to Vision Pro, and if Vision Pro is widely adopted, Render's decentralized GPU could become a supplementary computing resource for spatial computing. Third, collaborations with Stability AI and Endeavor allow optimized Stability AI models to run at low cost on Render Network's peer-to-peer consumer GPU pool, and integrations with FEDML (an open-source framework for federated learning), Beam (a gaming network), and io.net (another decentralized GPU network) have similar effects. In September 2024, the proposal to include Nosana (a decentralized AI inference network, with the mainnet planned to launch in January 2025) as Render's next computing client has been approved and added to the development roadmap. Render nodes can complete Nosana's computing tasks and return the results to Nosana, further enhancing the demand for Render Network.
$RENDER is a governance token with functions for fee payment, computing rewards, and governance rights, with a fully diluted valuation (FDV) of $2.81 billion and a circulating ratio of 74%. After transitioning to a burn and mint equilibrium (BME) model, $RENDER can be viewed as a commodity asset: the amount burned depends on the demand for Render Network, while the minting amount will be adjusted according to the growth demand of the network, meaning that an increase in demand for Render Network will make $RENDER a deflationary asset and raise its price. However, from January 8, 2024, to September 10, 2024, the burn rate as a percentage of emissions was only 3.83%, and the total burn amount accounted for only 0.02% of the total supply. This indicates that $RENDER still faces inflationary pressure, and its adoption in practical applications remains insufficient.

Render's BME
io.net
io.net is a decentralized GPU network built on Solana, aimed at aggregating idle computing resources from data centers, miners, crypto projects (such as Render Network and Filecoin), and individual users to meet the growing demand for computing tasks, particularly in the fields of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML). The network uses the $IO token for payments and to incentivize participants. The founding team has a background in developing institutional-level quantitative trading systems for the U.S. stock market and cryptocurrency market, successfully raising $30 million in Series A funding. This funding was led by Hack VC and included participation from Multicoin Capital, Solana Ventures, OKX Ventures, Aptos Labs, and others.
io.net utilizes decentralized cluster frameworks such as Ray and Kubernetes, enhancing control over more than 300,000 verified GPUs, providing users with flexible access to GPU resources. The platform allows for rapid deployment of clusters within 90 seconds, costing only a fraction of traditional cloud service providers (such as AWS), saving 20-30% in expenses. Additionally, io.net employs a multi-layered, collaborative structure and reverse tunneling technology to ensure scalability, reliability, and secure access to remote computing resources. Notably, io.net abstracts the GPU lending and management process through three main components—IO Worker, Explorer, and Cloud—simplifying the user experience.
However, the network currently faces challenges in utilization, with only 2% of clusters fully operational. Actual computing tasks are mostly concentrated on high-performance GPUs, such as Nvidia H100 and A100 models, while consumer-grade GPUs, like the RTX 4090, have almost no workload. This disparity is primarily due to insufficient upload and download bandwidth. Although some high-end configurations can reach 10 Gbps, this bandwidth is still 2-3 orders of magnitude lower than what is required for training large language models (LLMs). Therefore, consumer-grade GPUs are mainly limited to small-scale distributed training or other tasks that do not have high parallel computing demands. In fact, high-performance GPUs are typically also configured with high bandwidth (for example, the RTX 4090 has a high bandwidth of 1 Tbps) to maximize computing power potential, and data centers even achieve high bandwidth through specific hardware connections, which is nearly impossible for decentralized GPUs. Additionally, stability issues (many consumer-grade devices experience failures, particularly Nvidia RTX and Apple M series devices) and the low proportion of $IO reward distribution further hinder broader adoption.
$IO is a governance token with governance rights, fee payments, computing rewards, value accumulation, and staking yields, with an FDV of $1.5 billion, but a circulating ratio of only 15%. 37.5% of $IO will be issued and paid to suppliers and their stakers as rewards, following a model of gradually decreasing inflation, with distributions to suppliers and their stakers occurring every hour for 20 years. Revenue generated by io.net will be used to buy back and burn $IO. Nodes and $IO holders can stake $IO to ensure the integrity of the network and earn rewards. The inflation rate for 2025 will be 7.03%, and it will decrease by approximately 12% each year until 2044.
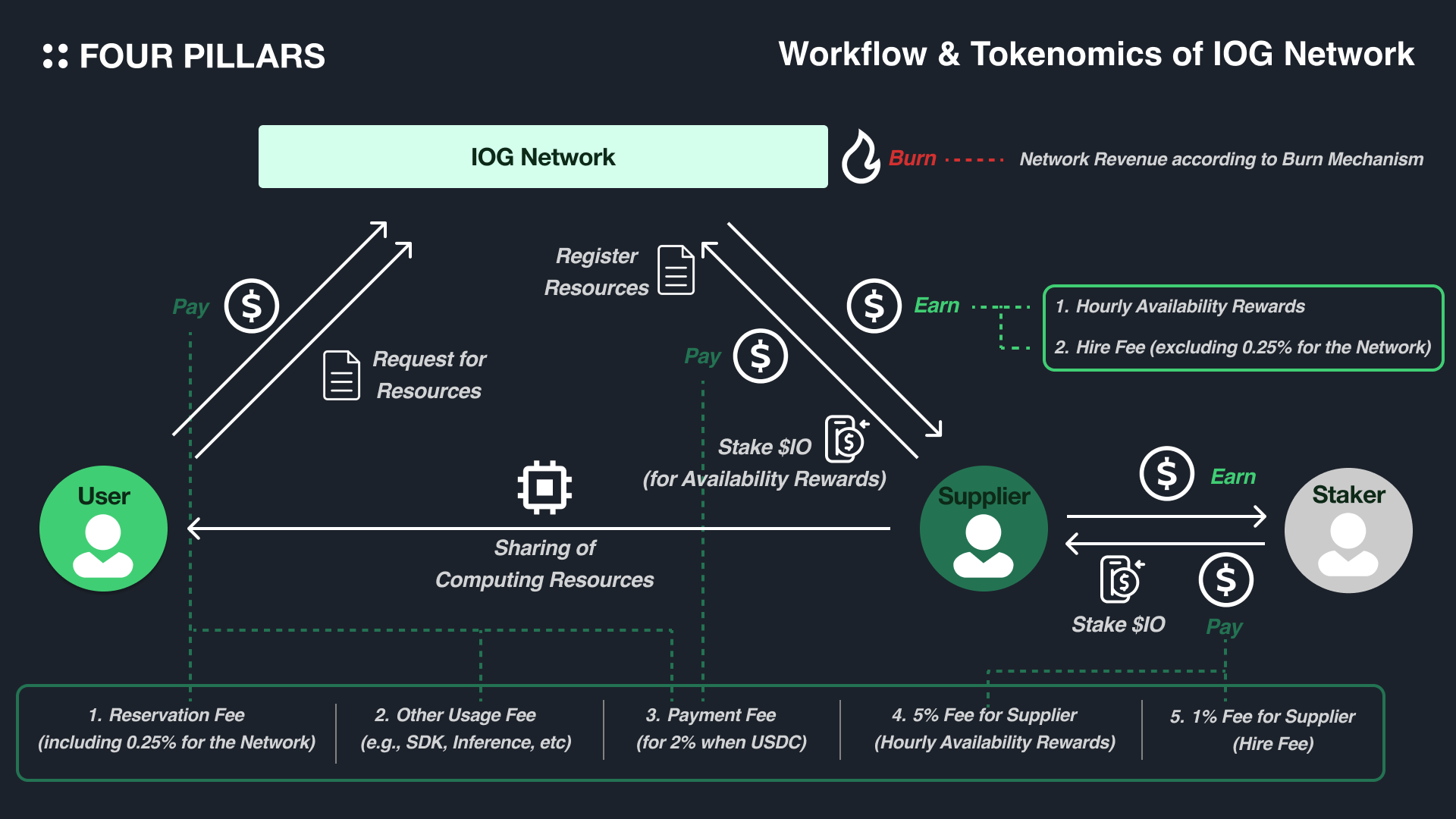
IO's Token Economics
Akash Network
Akash is a blockchain based on Tendermint, built using the Cosmos SDK, providing a decentralized cloud computing (CPU and GPU) marketplace. The Akash network consists of four main components: Akash Service Providers (Supplier), Akash Network (Platform), Akash Tenants (Demander), and $AKT (currency and equity). A typical leasing process is as follows: Akash Service Providers offer their computing resources, run Kubernetes clusters, and bid for deployments; the Akash Network utilizes a DPoS consensus algorithm to convert these resources into standardized computing resources, providing a reverse auction market and recording data; Akash Tenants describe their container deployment requirements, set prices, and choose service providers. $AKT is used to match supply and demand and stake to ensure network security. The founders are primarily seasoned experts and serial entrepreneurs from the cloud infrastructure and software engineering fields, helping Akash raise $2.8 million.
Among all major DePIN projects, Akash has the most CPUs (approximately 20,000). Its CPU utilization rate ranges from 15% to 70%, currently at a low level of 20%. Despite having the historically largest available CPU pool, Akash's daily revenue is only about $4,000, indicating that the demand for computing resources from real-world applications remains insufficient. This may be because large-scale computing tasks are typically handled more efficiently by GPUs, which excel in parallel processing. To address low utilization and meet the enormous demand for AI/ML training, Akash entered the GPU leasing market in August 2023 and currently has about 500 GPUs. However, the number of GPUs on Akash is negligible compared to io.net and Aethir, and the results of training foundational models on Akash GPUs in collaboration with ThumperAI (a generative AI startup) have also fallen short of expectations. AI model training conducted on Akash Network's decentralized cloud platform is still in its early stages.
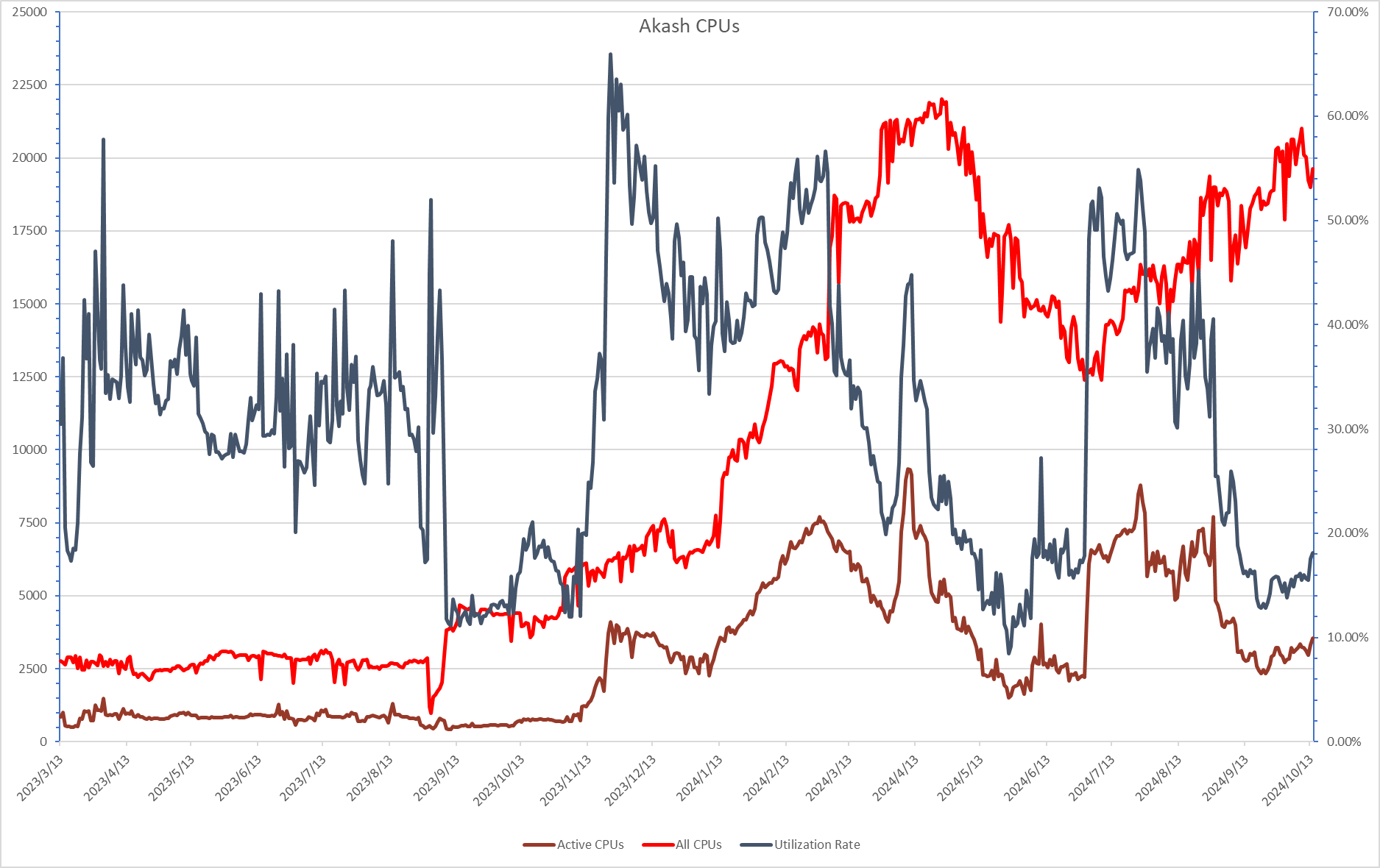
Akash's CPU Utilization Rate
$AKT is a governance token with functions including governance rights, computing rewards, fee payments, fee discounts, value accumulation (token burn), and staking yields, with a market capitalization of $995 million and a circulating ratio of 63.92%, and an annual inflation rate of 13.00%. AKT 2.0 introduces transaction fees, which are extracted from the fees paid by tenants to service providers, serving as a network tax to ensure the security of the Akash network. Fees paid using $AKT enjoy discounts (20% discount for $USDC, but only 4% for $AKT). Service providers also need to pay a manufacturing fee when providing liquidity to the market. Transaction fees, manufacturing fees, and inflation rewards will be injected into the rewards distribution pool. Tokens in the rewards distribution pool will be redistributed to $AKT stakers, service providers, the community, developers, and contributors to the ecosystem through token burns. Currently, the community pool is approximately $30 million (accounting for 4.7% of the circulating supply), and the annual staking yield for $AKT is 15.39%, with over half of the circulating supply already staked.
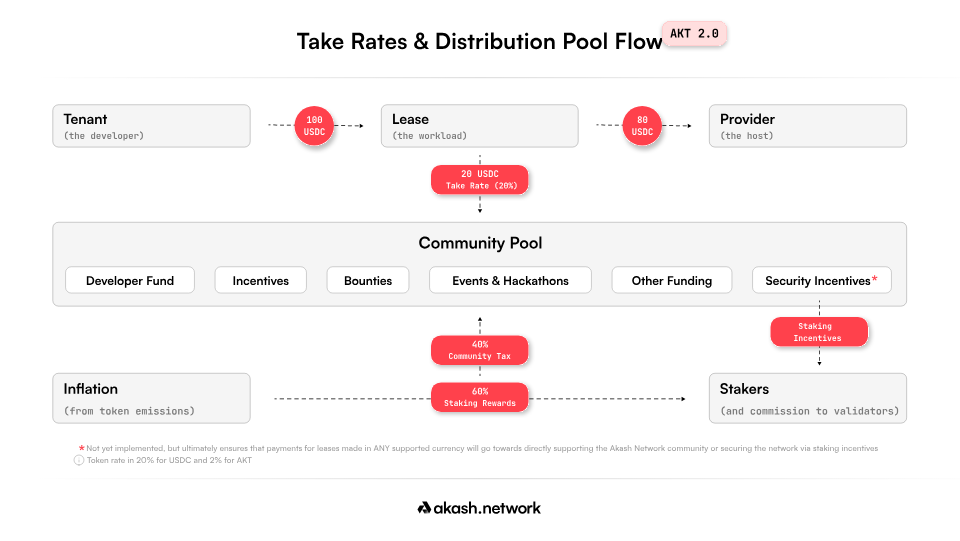
AKT 2.0
Aethir
Aethir is a decentralized cloud computing network that aggregates over 43,000 enterprise-grade GPU chips from node operators and GPU providers, distributing them to users in need of on-demand cloud computing resources, primarily applied in AI, gaming, and virtualization computing. The founding team consists of seasoned professionals from the gaming, edge computing, and blockchain industries, helping Aethir raise $9 million in Pre-Series A funding from well-known venture capital firms such as Sanctor Capital, Hashkey, Merit Circle, and CitizenX, and securing approximately $140 million by selling over 91,000 checker nodes.
In the Aethir network, there are three important categories of miners: Containers, Checkers, and Indexers, responsible for executing and presenting virtual endpoints for cloud-based applications; maintaining the integrity and performance of Containers; and optimizing the matching between users and Containers. Containers and Checkers, as the primary providers of computing power and service integrity, must stake $ATH to operate and face the risk of slashing while earning most of the revenue. In the Aethir network, 20% of the service fee is paid by users in $ATH, which is used for transactions between customers and service providers, while the remaining 80% is paid to Containers. Additionally, Aethir allocates 50% of the total supply of $ATH as rewards for Containers and Checkers to maintain the decentralization and sustainability of the ecosystem.
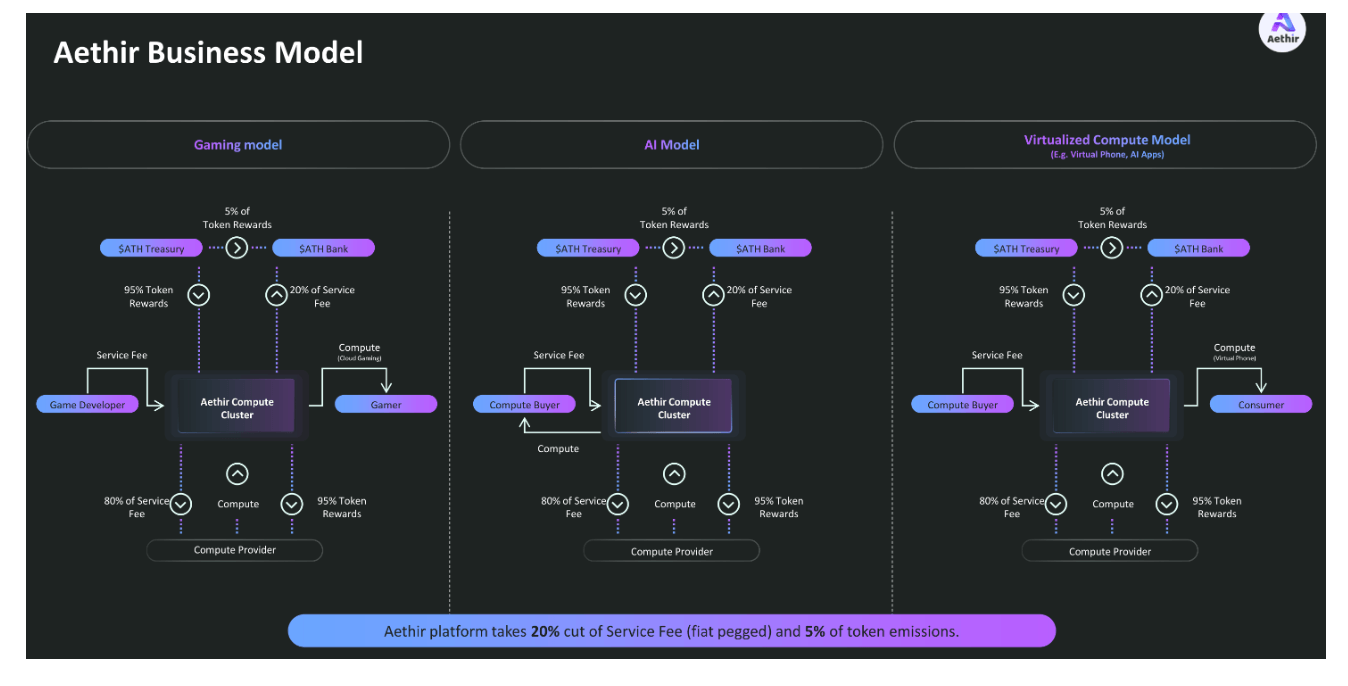
Aethir Business Model
Aethir has deployed over 3,000 H100/A100 GPUs globally and continues to increase, providing efficient and smooth high-end GPU resources while overcoming various challenges. Aethir focuses more on the B2B enterprise market, primarily concentrating on cloud gaming, AI, cloud mobile, and edge computing, generating over $36 million in recurring revenue annually.
Cloud Gaming: Collaborating with large cloud gaming companies like Well-Link Tech, which has 200 million users, and the giant in the extended reality field, Meta48; partnering with XPLA to launch a $10 million gaming project ecosystem subsidy program; Unite and GameCentric have also joined the Aethir network.
AI: Aethir announced a $50 million airdrop exchange with io.net, collaborating on marketing and community efforts. In addition to on-demand supply of H100 chipsets, Aethir also offers Aethir Earth, a bare-metal GPU cloud service optimized for AI applications.
Cloud Mobile: Aethir launched the first Web3 cloud mobile phone, APhone, whose compute-intensive features are supported by Aethir's decentralized cloud infrastructure, currently boasting around 46,000 users and offering a customizable unique Web3 app store, AppNest.
Edge Computing: Additionally, Aethir has sold over 32,000 high-performance edge computing devices, Aethir Edge (priced at $1,299 each), reserving up to 23% of $ATH for Aethir Edge users. The Aethir Foundation also announced that from November 2024 to mid-2025, each Aethir Edge device will receive an additional 100 $ATH rewards daily, meaning a daily income of about $8, based on the current price of $ATH, with a payback period of about six months. To reduce sales pressure, edge rewards will be distributed according to a vesting schedule: 30% will be released immediately, 30% after 90 days, and the remaining 40% after 180 days. Simultaneously purchasing Aethir Edge and hedging $ATH may present a good mining opportunity. Furthermore, Aethir announced an interactive node exchange with Sophon's ZK chain, allowing Aethir community users to earn $ATH staking rewards on the staking platform while also earning Sophon Points (SP) on the Sophon platform, which will bring airdrop expectations for $ATH holders.
$ATH is Aethir's governance token, with governance rights, staking yields, and fee payment functions, achieving a market capitalization of $2.35 billion and a circulating ratio of 9.66%.
Summary
Many computing projects, such as Render, io.net, and Aethir, face common challenges of low circulating supply, high inflation rates, and lack of token utility. In contrast, Akash demonstrates a relatively healthy circulating rate and inflation rate. When comparing these projects, Render primarily focuses on 3D rendering, positioning itself as a solution for augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and spatial computing. io.net resembles a consumer-oriented GPU rental market, although it faces latency issues that limit large-scale parallel computing applications. Akash's robust token economics stand out, and the launch of AKT 2.0 brings additional utility to the $AKT token. However, Akash focuses more on CPU resources rather than GPUs, which also results in the smallest market capitalization among the four projects.
Aethir, on the other hand, resembles an enterprise-oriented GPU rental market, boasting the broadest collaborations, the most funding support, and offering the most promising roadmap among the four projects. It is preparing to establish a comprehensive intelligent computing ecosystem, but its financial operations remain somewhat opaque.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Decentralized AI protocols leverage decentralized computing power and the decentralized structure of blockchain to deploy, train, and manage AI models. This approach aims to prevent control by a single centralized entity, transforming AI into a public resource and empowering smaller AI researchers, fostering innovation in one of the most influential technologies of this century. Currently, the crypto AI field leads in activity, with 33.9% of crypto developers participating, but this field accounts for only 1.1% of the overall crypto market capitalization, indicating that it is still in the early stages of development with significant potential.
Decentralized AI Systems
Unlike centralized systems, where models are closed, unverifiable, and controlled by a single entity, decentralized AI systems open the network, allowing different models from around the world to join and compete, providing the most accurate and efficient inferences while earning rewards to support model fine-tuning and continuous improvement. Typical protocols include Bittensor and Spectral Labs.
Bittensor
Bittensor is a representative protocol in this field. Bittensor consists of miners, validators, and subnet owners. Each subnet owner is responsible for an AI application and designs a reward economy to incentivize validators and miners, ensuring the sustainable operation and efficient functioning of the application. Miners act as the "brain" of the network, providing their respective AI models to compete for effective inference; validators serve as the "quality controllers" of the outputs from miners. For example, a subnet owner designs a "ChatBPT" subnet, where miners provide their corresponding large language models (LLMs) to answer user questions, and validators check the answers provided by miners (ensuring they are accurate and appropriate) before presenting them to the end users.
TAO is the native token of Bittensor, capped at 21 million, similar to Bitcoin, and undergoes halving every four years. It is expected that before the first halving, the inflation rate of TAO will reach 37%, with the halving anticipated around November 2025. As of October 2024, the circulating supply of TAO is 7.7 million, with 77% of the circulating tokens already staked. Each subnet registration requires at least 100 TAO, and in practice, the average staking amount for subnet owners must reach 2,000 TAO (approximately $1.1 million). Subnet owners are entitled to 18% of the subnet's issuance, while validators and miners can receive 41% of the issuance each. If a subnet performs the worst among other subnets within seven days of activation, it will be deactivated.
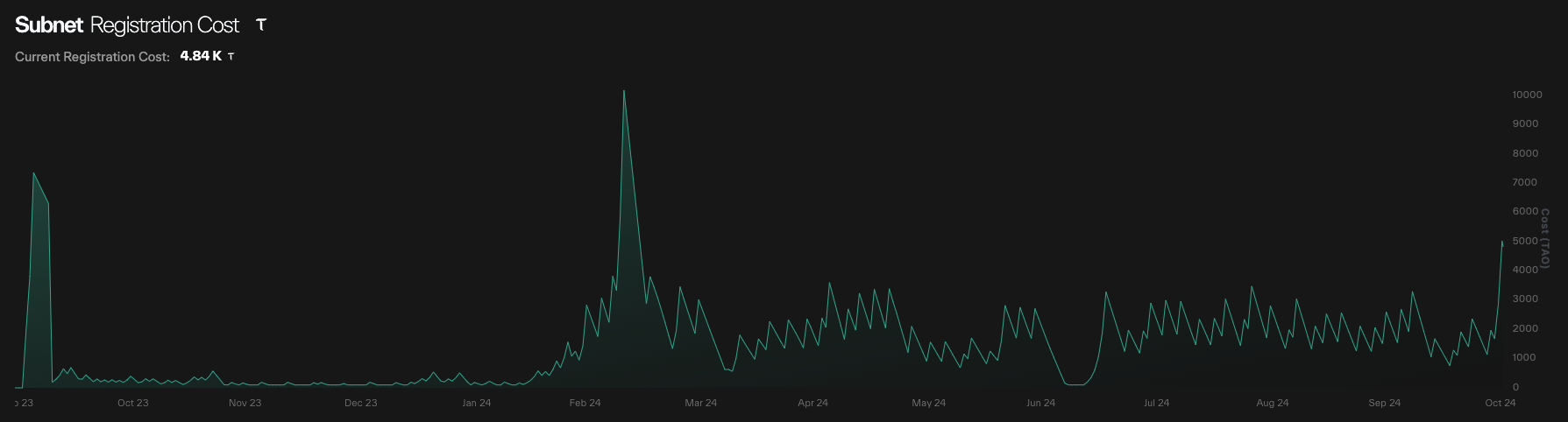
Subnet Registration Costs
Despite the fair issuance of TAO in 2021, the current token distribution is unbalanced due to low early participation. The top ten validators hold 60% of the circulating supply of TAO. Additionally, miners have been accused of using the emission mechanism to generate low-quality inference results, while validators have failed to detect these issues. As more agents, including AI-focused venture capital and mining companies from Bittensor, join Bittensor, it is launching a staking-based consensus mechanism to score utility, further aligning the interests of validators with the performance of miners. Bittensor has also introduced dynamic TAO, addressing monopoly trends in the root network by introducing non-tradable "subnet tokens" or dTAO, allowing TAO holders to purchase dTAO for their favorite subnets, which will drive up the price of that subnet's dTAO. Emission rewards will be distributed based on the price of each subnet's dTAO. This open market issuance method could significantly increase the number of subnets and have a substantial impact on the TAO token. Finally, Bittensor plans to bring EVM-compatible smart contracts to the network and introduce DeFi applications such as liquid staking, lending, stablecoins, and AI-driven user protocols.
Decentralized AI Market
The decentralized AI market enables the deployment and operation of AI models and provides developers with tools for seamless integration. Protocols in this field typically offer computing resources and establish incentive economic frameworks to encourage decentralized contributions for on-chain training and fine-tuning. Notable protocols in this area include the Artificial Superintelligence Alliance (ASI) and Zero1 Labs.
Artificial Superintelligence Alliance (ASI)
ASI was launched in March 2024 by Fetch.ai, SingularityNet, Ocean Protocol, and Cudos (Cudos proposed to provide decentralized computing for the alliance in September 2024). ASI is dedicated to developing decentralized AI technologies from four different domains. First, ASI focuses on neural-symbolic large language models (LLMs) that minimize hallucinations and undergo decentralized training and inference through verifiable data sources. Second, OpenCog's Hyperon is a cognitive architecture that connects LLMs with other deep neural networks (DNNs) to perform efficient and practical functions. Third, leveraging Ocean's data farming program, it aims to create a time-series prediction machine—World Model. Finally, similar to the second domain, ASI also aims to develop "algorithmic chemistry" to integrate different AI agents to perform practical tasks.
The ASI token is a composite of FET, AGIX, OCEAN, and CUDOS tokens in varying proportions. The ASI token can be used across all four alliance protocols, including governance rights within these protocols, as a payment token to create, deploy, and operate automated agents on Fetch's Agentverse, staked to manage AI reputation, and to publish AI services on the SingularityNet marketplace or purchase data services from Ocean's Predictoor, and buy AI computing power on Cudos Intercloud. Currently, tokens of AGIX, OCEAN, and CUDOS are migrating to FET, and the second phase of FET to ASI will be announced soon.
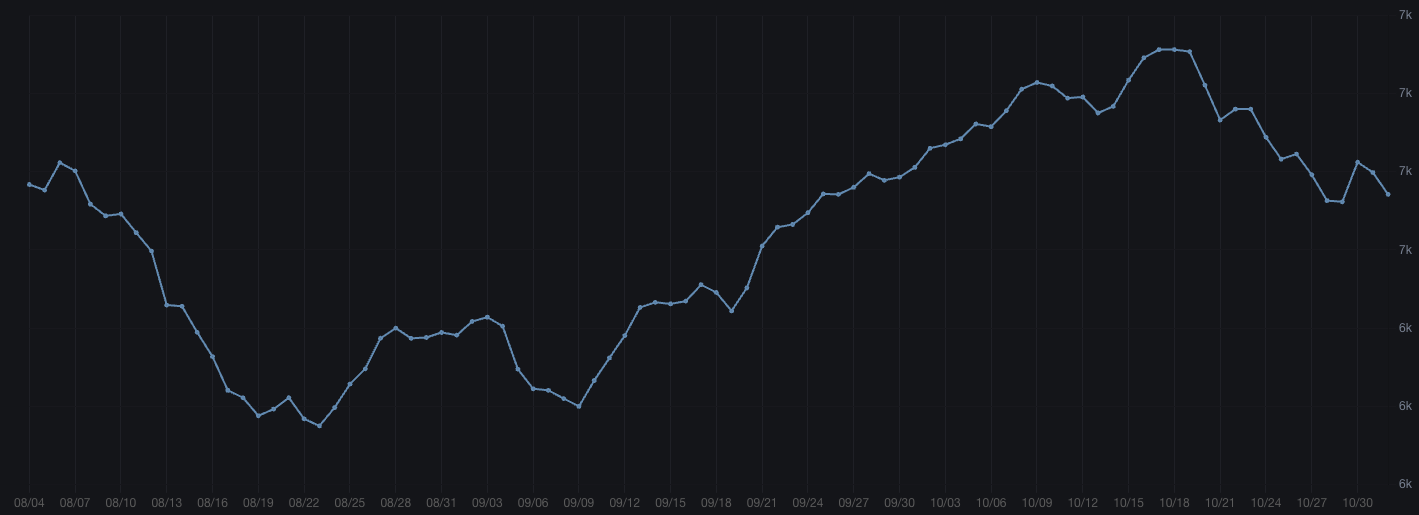
Fetch.ai Network 30-Day Active Accounts
According to MarketsandMarkets (1), the AI agent market is expected to grow at a robust compound annual growth rate of 44.8% by 2030. The valuation of ASI or FET will heavily depend on the growing demand for AI agents within the ASI ecosystem. As the leading protocol in the alliance, the Fetch.ai network has approximately 6,700 active users monthly, with 30 active agents currently operating in the Agentverse, totaling 950 interactions. Recent AI-agent-meme hype may trigger growth to attract appropriate attention and capital to support the implementation of AI agent technologies.
Decentralized AI Initial Offering (IAO)
The crypto industry is well-positioned to leverage capitalism to establish shared ownership of AI, promoting fair and community-driven ownership and governance frameworks. By aligning profit incentives with collective interests, this approach democratizes AI innovation and ensures fair value sharing. The decentralized structure of crypto supports sustainable, inclusive models that drive the development of capitalism-driven shared ownership in the evolving digital economy. Leading protocols include Ora Protocol, ANKR's Neura, and Virtual Protocol.
The crypto industry is ideally situated to leverage capitalism to establish shared ownership of artificial intelligence, promoting fair, community-driven ownership and governance frameworks. By aligning profit incentives with collective interests, this approach democratizes AI innovation and ensures fair value sharing. The decentralized structure of crypto supports sustainable, inclusive models that advance capitalism-driven shared ownership in the evolving digital economy. Leading protocols include Ora Protocol, ANKR's Neura, and Virtual Protocol.
Virtual Protocol
Virtual Protocol was launched in December 2023 on Ethereum with its TGE and will be deployed on Base in March 2024. Virtual aims to reshape the landscape of NPCs (non-player characters), virtual companions, and AI-generated content (AIGC) by introducing the concept of shared ownership of AI agents and the initial agent offering (IAO).
Virtual agents can be categorized into two types: IP agents and functional agents. IP agents serve as virtual companions, fine-tuned through community contributions. Luna is the most famous AI agent in the virtual protocol, with its market cap increasing by approximately 2000% within a week after the market frenzy over the GOAT token endorsed by another AI agent called Truth Terminal on X in October. However, LUNA is not just an AI meme coin. It represents partial ownership of Luna, and the revenue generated by Luna will be used to buy back and burn LUNA tokens, increasing the accumulated value for token holders if Luna's influence grows. Luna has 537,000 followers on TikTok, along with two other AI agents, Olyn and Iona. Reportedly, the TikTok account has generated about $700 in revenue through live streaming. Additionally, Luna can access its X account, chat on Telegram, and autonomously trade on Base using the perception mode v2.0 without supervision.
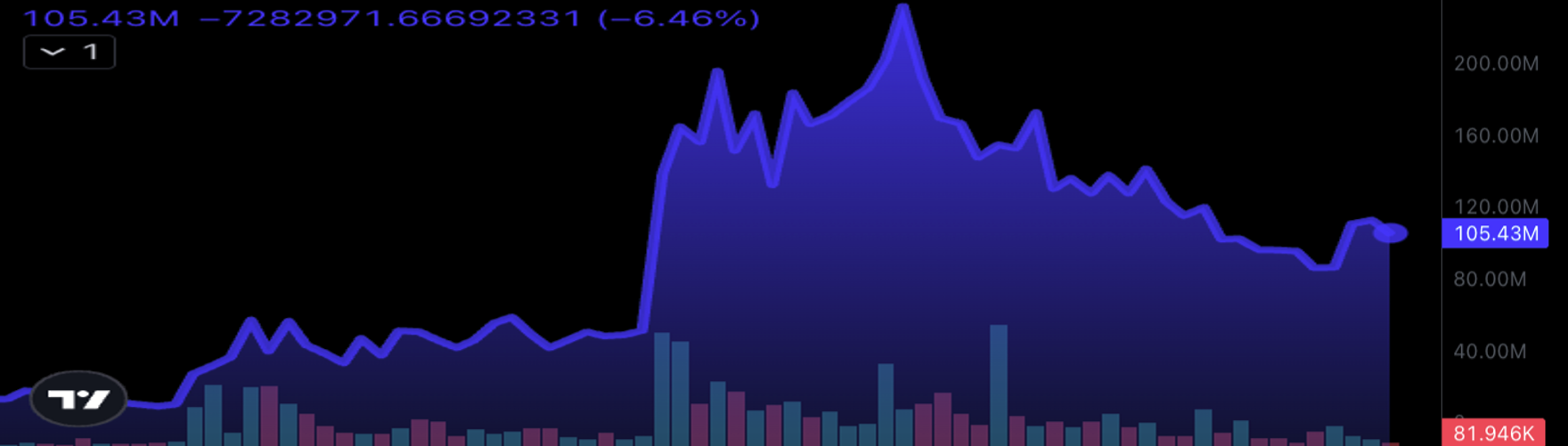
LUNA Market Cap at the End of October
On the other hand, functional agents like Generative Autonomous Multimodal Entities (G.A.M.E) aim to enable developers to create multi-agent stimuli that autonomously interact in virtual environments by processing inputs, planning, reasoning, searching algorithms, self-reflection, and generating responses while learning from past interactions with long-term memory processors. By continuously evaluating the outcomes of actions and dialogues, GAME allows agents to refine their knowledge over time and improve their planning and performance. These features provide personalized generative gaming environments for different players, with unique NPCs responding in customized ways based on player decisions and interactions.
VIRTUAL serves as the foundational liquidity pair for each agent token created in the IAO. A specific amount of VIRTUAL will be locked by the agent creator to create the initial liquidity pool for the new agent token. This pool will remain locked for ten years. In return, creators will be eligible to receive a portion of the transaction fees involving the agent token, providing sustainable incentives for creators to operate the agents. The tax rate may decrease based on future conditions. VIRTUAL also acts as the payment token for anyone licensing the use of agents through an API, with paid VIRTUAL used to buy back and burn agent tokens. After the protocol V2 upgrade, the top three agent liquidity pools will be eligible for 60 million VIRTUAL emissions within the first 12 months. Liquidity providers can further delegate voting rights to validators to oversee the validation and approval of AI models before deployment and use blind testing Elo rating models to rate contribution submissions. VIRTUAL is closely tied to the demand for existing agents and newly created agents to encourage more liquidity providers to delegate and lock new funds in the agent liquidity pools. Currently, with 306 agents created, approximately 15.2 million or 1.5% of the total supply of VIRTUAL is in the agent liquidity pool.
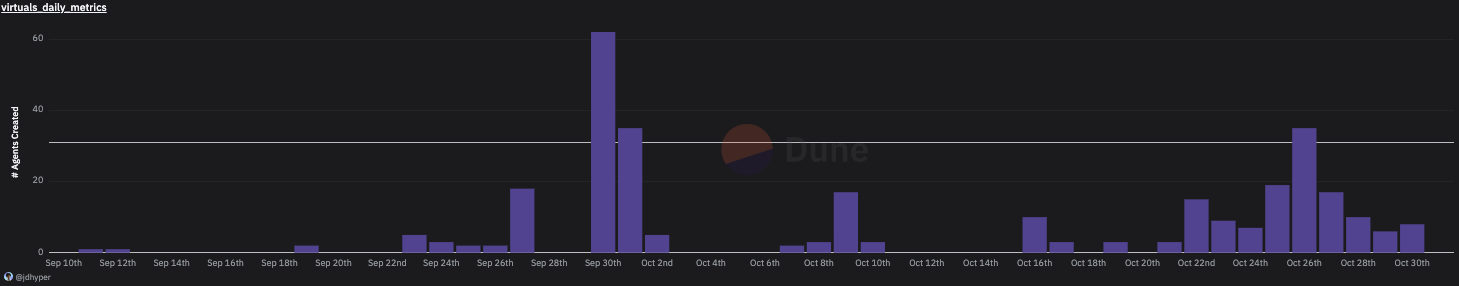
Agents Created in the Virtual Protocol
Summary
In summary, decentralized AI systems rely on the increase of network subnets to increase the number of tokens staked and removed from circulation. The next initiatives of Bittenor, dTAO, and EVM implementation will lay the groundwork for a significant increase in the number of subnets in the network. The decentralized AI market depends on the organic demand for AI deployed in the market and users/protocols, which often presents challenges, as organic and sustainable agent demand is typically low in the current phase of crypto AI. Due to speculative factors, decentralized initial AI offerings will easily attract market attention. Protocol tokens are designed to lock for each new token issuance, creating an environment for sustainable increases in new token issuance or high organic demand for specific AI models and agents, which is necessary to reduce the supply of protocol tokens in circulation.
Other DePIN
Helium Network
The Helium Network is a decentralized wireless network built on Solana that allows individuals and organizations to deploy and operate wireless networks through token incentives. Helium Network was founded in 2013 by Amir Haleem, Shawn Fanning, and Sean Carey, raising $364.8 million from prominent venture capital firms such as a16z, Multicoin Capital, and Tiger Global Management. Starting with IoT devices and LoRaWAN wireless technology, Helium aims to cover a broader range of communication networks and become a "network of networks," including decentralized network protocols (DNP) for LoRaWAN, 5G/WiFi, CDN, VPN, energy, and more.
Helium uses a Burn-and-Mint Equilibrium (BME) mechanism to balance the supply and demand of its native token $HNT. The Helium ecosystem introduces a non-transferable utility token pegged to the US dollar—Data Credits (DC, 1 DC = $0.00001), which can only be generated by burning $HNT and are used to pay network fees (including for subnets). Helium issues predictable $HNT to increase its supply. When demand for the Helium network increases, more DC is required, leading to the burning of more $HNT. When the amount burned exceeds the amount minted, the circulation of $HNT decreases, and its intrinsic value rises.
Following the HIP-51 proposal, each DNP built on the Helium network has its own SubDAO, equipped with its governance token (DNT), which manages its network parameters, such as Proof-of-Coverage (PoC—a consensus mechanism for hotspot operators to deploy hotspots in underserved areas), mining rewards, and data. Under a similar two-year halving plan, both HNT and each DNT have a fixed maximum supply, but SubDAOs like Mobile and IoT can adjust the conversion rate between DC and DNT to control the issuance of DNT, balancing DNT inflation and the incentives for subnet hotspot expansion. SubDAOs have relatively high financial autonomy, but the Helium network can still govern SubDAOs through $veHNT and treasury reserves. Users can delegate $veHNT, influencing the utility score of the subnet DAO, ultimately increasing the issuance of treasury reserves for the DNP SubDAO. Each SubDAO treasury provides a one-way exchange between DNT and HNT, based on their exchange rate. This exchange rate typically undervalues DNT, providing a minimum price for DNT, thus ensuring its value, while premiums/discounts and trading volumes in the secondary market reflect the actual value of DNT.
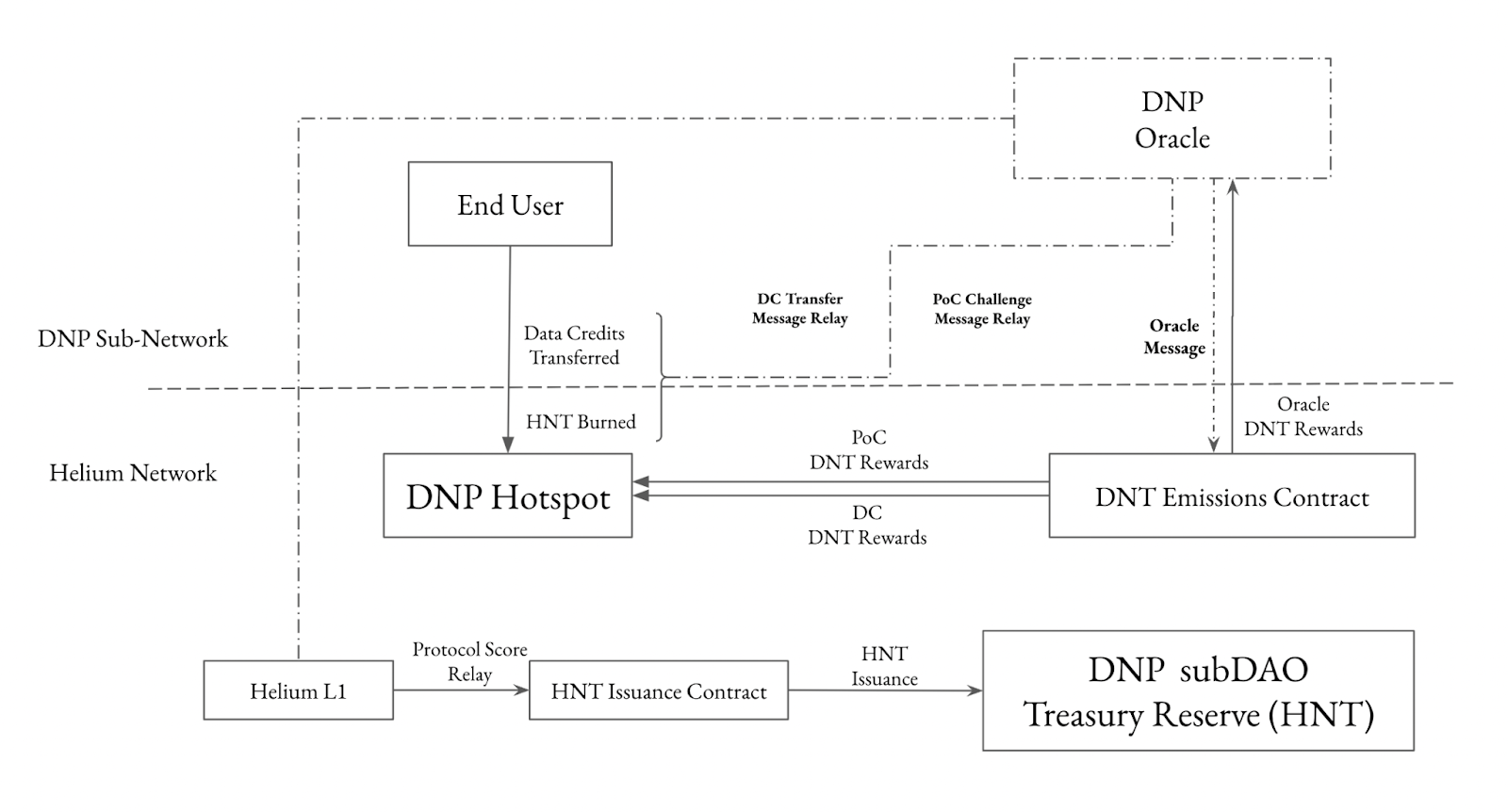
The relationship between Helium and subDAOs
Currently, there are two subnets: the IoT network (LoRaWAN) and the Mobile network (5G/WiFi), each with its native tokens $IOT and $MOBILE. Although the Helium mobile network only began operations in April 2021, it quickly became Helium's primary source of revenue, while the Helium IoT network has stagnated: 98% of DC is burned in the Mobile network, $MOBILE has a 48.02% premium in the secondary market, and half of the $HNT is issued to the Mobile network treasury. In contrast, after selling officially licensed hotspot devices worth hundreds of dollars, the daily trading volume of $IOT in the Helium IoT network is only about $10,000, indicating extremely low actual utilization of IoT hotspots. The reason can be attributed to the nature of the IoT market—broad coverage but limited data transmission.
Token
$IOT
$MOBILE
Utility Score
363,670,976,926
973,929,562,628
Active Hotspots
355,996
18,462
Onboarding Fees
$14,250,808.50
$194,010
veHNT delegated
598,502,751
624,148,052
DC burned (24h, 1 DC=0.00001 USD)
9,780,594
552,799,701
Treasury (HNT)
5,296,985
7,054,768
DNT Premium in Secondary Market
-2.49%
48.02%
MarketCap
$22,436,947
$60,879,276
Circulating Ratio
16%
44%
Volume (24h)/MarketCap
0.05%
4.08%
Proportion of $HNT Emissions to subnetwork treasury (%)
20%
50%
To increase the utilization of the IoT network and expand into the solar power and battery storage markets, Helium has approved and is developing a new energy subnet (ENERGY). Through a gateway with energy capabilities, users will be able to connect energy resources from multiple manufacturers and activate and incentivize decentralized generation, responsive storage, and grid management networks. The Energy subnet will transmit sensor data through existing IoT infrastructure and support dual mining rewards for IoT and Energy.
In contrast, the Helium Mobile network has successfully expanded its application scenarios and priced its services competitively and close to actual demand. Collaborations with T-Mobile and Solana Saga have helped Helium overcome regulatory challenges and accumulate real users. The Mobile network has signed a five-year exclusive agreement with T-Mobile, a leader in 5G in the US. When Helium's signal is weak, Helium 5G network users can seamlessly switch to the T-Mobile 5G network and enjoy unlimited voice, text, and data services nationwide for just $20 per month. With the increasing sales of the Solana Saga smartphone, the 30-day free Helium mobile subscription has also facilitated the growth of the mobile network. Users can earn $MOBILE by sharing their location and use it to pay phone bills or shop in the Helium mobile store. By 2024, the number of deployed Mobile hotspots is expected to grow more than tenfold to 26,280, with registered users increasing nearly fourfold to 118,767.
$HNT is a governance token with governance rights, service incentives, fee payments, and staking rewards, with a market cap of $1.47 billion and a circulation ratio of 77%.
Livepeer
Livepeer is a decentralized video streaming network built on Arbitrum, providing live and on-demand services such as transcoding and distribution. Founded in 2017 by software engineers Doug Petkanics and Eric Tang, Livepeer has raised a total of $52 million from well-known investors such as Northzone and Coinbase Ventures. In March 2021, Grayscale also established the Livepeer Trust. Despite initial investments and some growth, the circulating share count has only increased by 10.7% over three years since its inception.
In the Livepeer ecosystem, there are two key participants—Orchestrators and Delegators, who play critical roles. About 100 Orchestrators provide the computing power needed for tasks such as transcoding, bitrate conversion, and format packaging, delegating these tasks to Transcoders in exchange for fees from broadcasters and rewards in Livepeer's native token $LPT. Over 3,600 Delegators support specific Orchestrators by staking $LPT tokens to maintain network security. Despite these operational roles, Livepeer's financial performance is concerning. The network struggles to generate sufficient organic demand, hindering its ability to achieve sustainable cash flow. Meanwhile, the distribution of token incentives has led to significant dilution of token value. Livepeer's annual revenue is only $300,000, while annual token incentives reach $80 million, resulting in a hundredfold gap between the two.
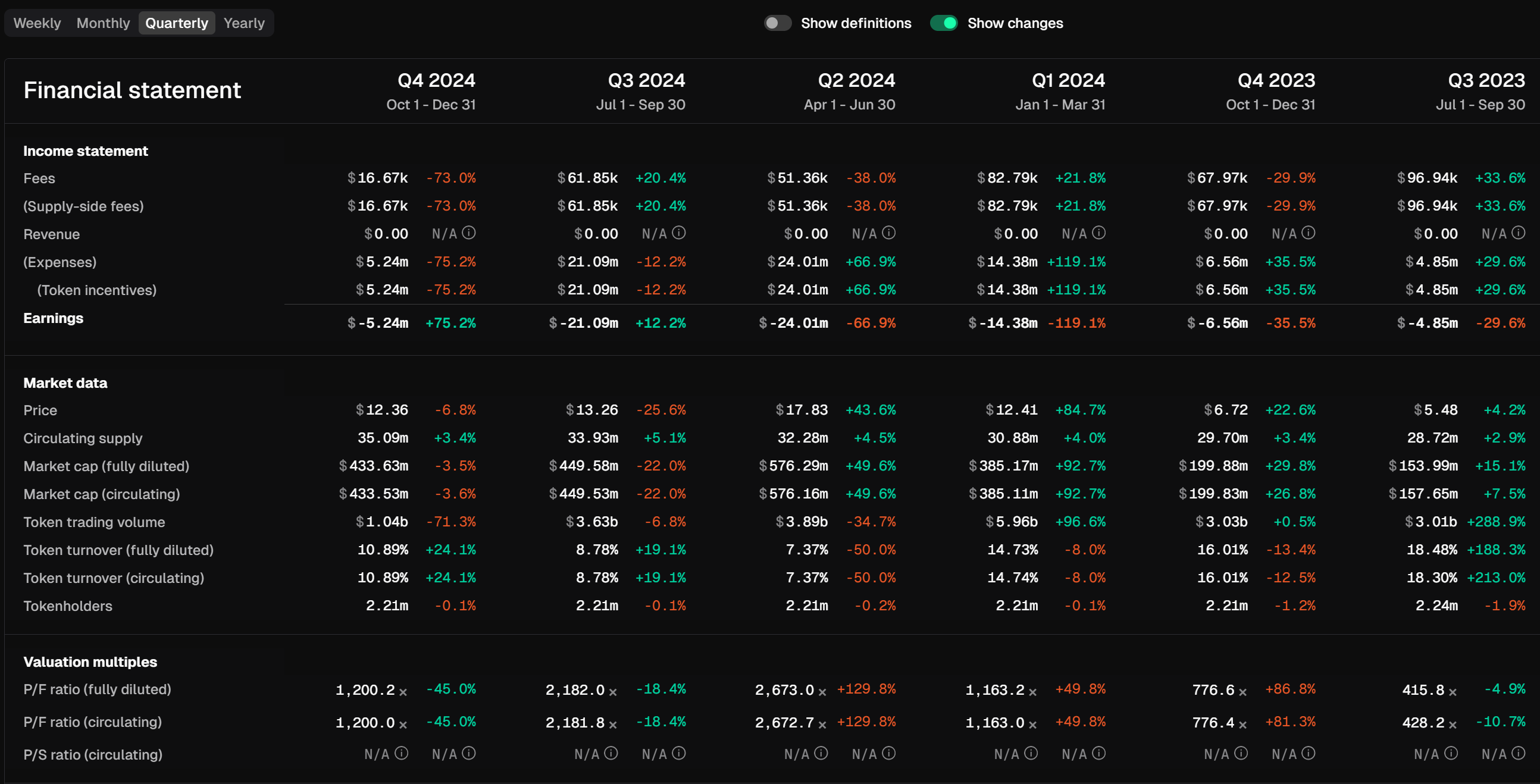
Livepeer's financial statements
To address the growing demand for generative AI technologies, such as those supported by ChatGPT and Sora, Livepeer has launched Livepeer AI. This project aims to provide computing power for video developers, helping them integrate generative AI features such as text-to-image, image-to-image, and image-to-video. Livepeer AI is currently in the testing phase, requiring Orchestrators to pre-download models to improve response times. In the future, Orchestrators will be able to load any diffusion model from platforms like Hugging Face based on demand and optimize GPU resources as needed.
$LPT is a governance token with governance rights, service rewards, fee payments, and staking income, with a market cap of $424 million, a circulation ratio of 100%, and a staking rate of 45.9%. $LPT has no circulation cap, and new $LPT is minted every round (5760 Ethereum blocks, approximately 22.4 hours). When the staking rate falls below 50%, Livepeer increases the inflation rate by 0.00005% each round, and when the staking rate exceeds 50%, it decreases by 0.00005% each round to balance network security and token liquidity.
Hivemapper
Hivemapper is a decentralized mapping platform built on Solana that provides accurate geographic data for various applications, including navigation, urban planning, and geospatial analysis. The platform allows participants to contribute data to the map by capturing high-quality street images using certified dashcams or smartphones, or by training the map AI through data annotation and editing. In return, contributors receive the native token $HONEY as a reward. For businesses and developers, Hivemapper offers access to map data through official map features/image APIs or monitoring tools like Scout. $HONEY also uses the BME mechanism to balance supply and demand, requiring users to burn $HONEY tokens to exchange for map credits.
The Hivemapper project is led by a senior professional team with expertise in software engineering, 3D technology, and mapping. This strong leadership has helped Hivemapper secure $21 million in funding from notable investors such as Spark Capital, Multicoin Capital, and Solana Ventures. To date, Hivemapper has achieved 28% global coverage, mapping over 371 million kilometers of roads, primarily concentrated in regions such as the United States, Canada, Europe, and East Asia.
$HONEY is a governance token with governance rights, service rewards, fee payments, and staking income, with a market cap of $334 million and a circulation ratio of 43%.
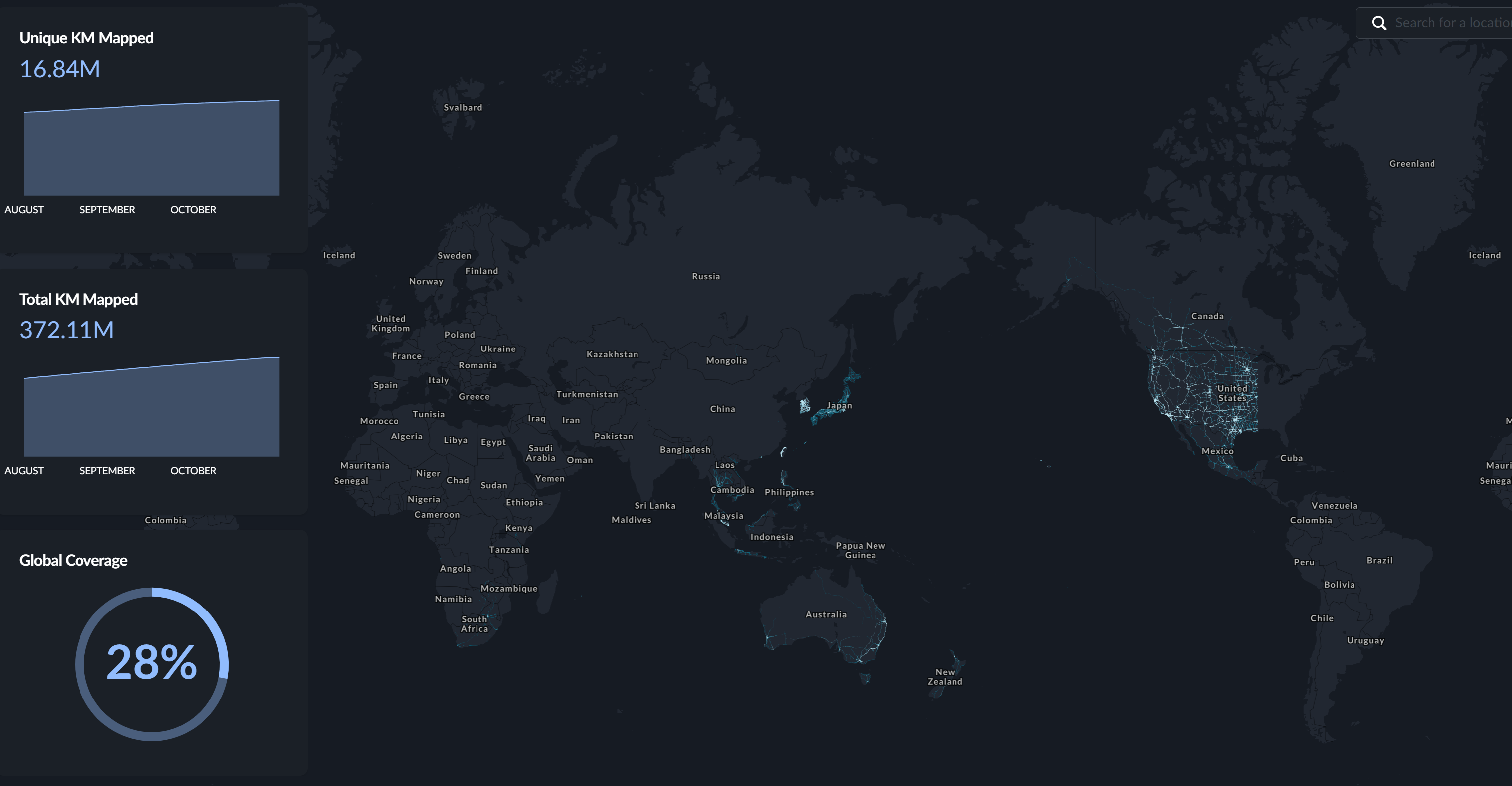
Coverage of Hivemapper
Which blockchain should DePIN projects be built on?
Since 2022, many projects have chosen to build on Solana (e.g., Grass, io.net) or migrate from Ethereum to Solana (e.g., Helium, Render). Several compelling factors drive this shift:
Integrated infrastructure, as opposed to Ethereum's complex modular design, reduces development difficulty. The Rust developer community and performance-oriented developers have also played a role in this push.
High throughput (TPS up to 65,000, stabilizing above 3,000, with a block confirmation time of 0.4 seconds) and low fees (0.00005 SOL per transaction). State compression technology is used to compress NFTs, following Rollup principles, reducing the cost of minting 1 million NFTs to just 5.35 SOL, and lowering the barrier for projects to identify devices through DID (decentralized identification).
Official guidance and support from Solana. Solana Labs' subsidiary Solana Mobile launched the Web3 phone Saga and collaborated with DePIN projects like Helium to promote ecosystem cooperation and prosperity.
However, Ethereum's layer two network solutions, such as Arbitrum, are also enhancing throughput and reducing costs. Arbitrum can achieve up to 40,000 TPS, while emerging DePIN projects like Aethir are beginning to adopt Ethereum's layer two network solutions to enhance scalability.
Other layer one networks are also focusing on the large-scale adoption of DePIN. IoTeX 2.0 has launched a new modular infrastructure for DePIN, providing a simplified tech stack that significantly shortens construction time, costs, and reduces the resources needed for market entry. This modular infrastructure consists of three main layers:
Modular Security Pool (MSP): This layer serves as a secure anchor, ensuring trust and stability between the DIM and Dapp/L2 layers. Service providers can participate in the MSP by staking IOTX, with the state being regularly anchored to IoTeX's L1 blockchain.
DePIN Infrastructure Module (DIM): Covering the entire tech stack, DIM provides hardware abstraction, connectivity, off-chain computing, and storage solutions.
DePIN Dapps and L2: This layer utilizes various DIMs to facilitate project development.
IoTeX also supports DePIN developers by providing open-source resources (public resources), making DePIN development more accessible and cost-effective.
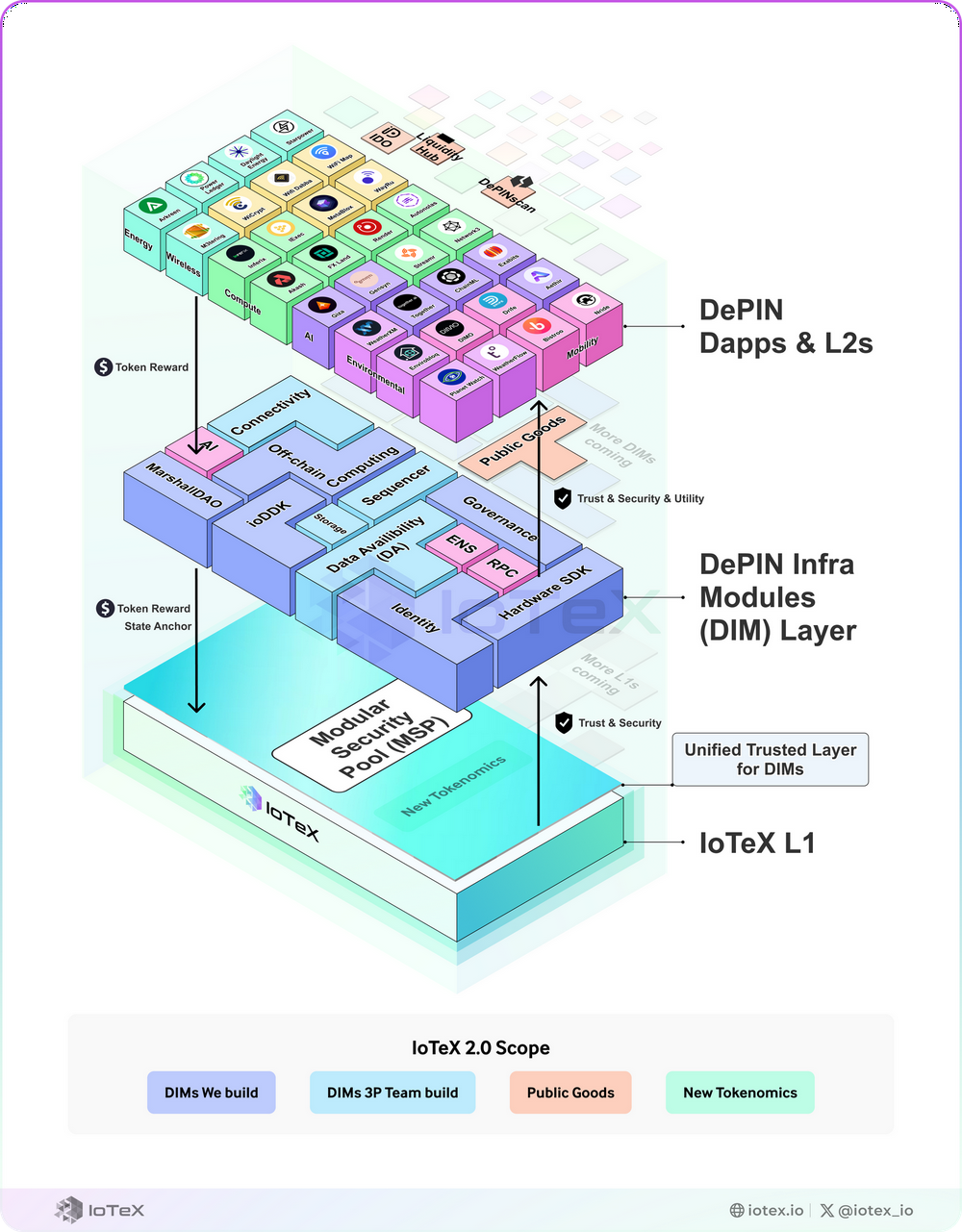
The modular design of IoTeX 2.0
Peaq is a layer one network specifically designed to support DePIN and is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Through parallel block production, asynchronous validation, and a flexible core timing mechanism, Peaq achieves a throughput of up to 10,000 TPS while maintaining low transaction costs of about $0.00025 per transaction. Peaq was founded in 2017 by EoT Labs, which focuses on advancing the Web3-based IoT economy and has raised $43 million from notable investors such as Borderless Capital, DWF Labs, and HashKey Capital.
Peaq's interoperability is supported by Wormhole, spanning multiple blockchain ecosystems, including Polkadot, Cosmos, Solana, and Binance. It also bridges to over 30 different blockchains, enhancing liquidity and cross-chain connectivity.
Conclusion
The large-scale adoption of DePIN is still in its early stages. Major challenges include a lack of organic demand and cash flow, poorly designed token economics, and significant selling pressure from unlocking events. However, the tokenization of physical assets is expected to lower costs and reduce barriers to entry, promoting the development of more permissionless markets and improving liquidity. Modular DePIN and innovations like DePINFi will enhance the efficiency of DePIN implementation, making the process cheaper, faster, and more accessible.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




