This report analyzes the current state of the stablecoin market, exploring the main participants, innovative solutions, and the challenges faced in this field. By studying the use cases, technical implementations, and market dynamics of stablecoins, the report aims to provide a comprehensive overview of stablecoins and their role in the future of digital finance.
Written by: Aiying Payment
Stablecoins have become a crucial part of the Web3 ecosystem, serving as a bridge between traditional finance and the digital asset space. These digital tokens are designed to maintain a stable value relative to a reference asset, most commonly the US dollar. As the cryptocurrency market grows and matures, stablecoins have emerged as essential tools for trading, remittances, and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, providing users with a way to avoid the inherent volatility of other cryptocurrencies.
Since the inception of the earliest stablecoins, the field has undergone significant changes, with various models emerging to address the challenge of maintaining price stability in a decentralized environment. These models include fiat-backed stablecoins issued by centralized entities, as well as algorithmic stablecoins that rely on complex mechanisms to maintain their price peg. Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages, forming a diverse ecosystem that continues to adapt to market demands and regulatory pressures.
This report analyzes the current state of the stablecoin market, exploring the main participants, innovative solutions, and the challenges faced in this field. By studying the use cases, technical implementations, and market dynamics of stablecoins, the report aims to provide a comprehensive overview of stablecoins and their role in the future of digital finance. The analysis will cover different categories of stablecoins, including fiat-backed, crypto-asset-backed, and algorithmic stablecoins, providing insights into their operational mechanisms, market acceptance, and potential impacts on the broader financial system.
I. Use Cases
The uses of stablecoins have far exceeded their initial role as trading tools in the cryptocurrency market. Castle Island Ventures conducted an in-depth investigation into the various uses of these digital assets in their report "Stablecoins: The Story of Emerging Markets." The study surveyed 2,541 adults from five major emerging market countries—Brazil, India, Indonesia, Nigeria, and Turkey—focusing on those who have used cryptocurrencies or blockchain networks in the past 12 months.
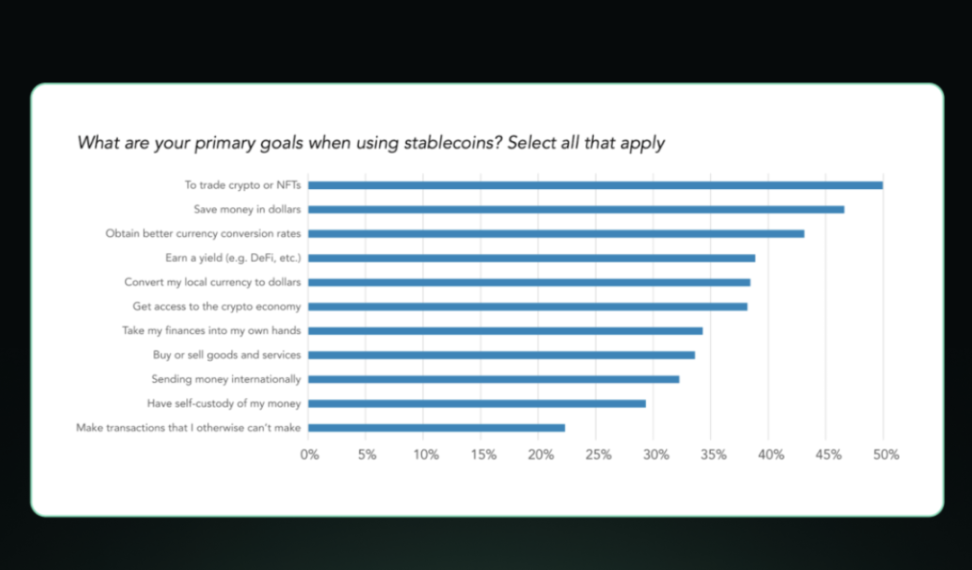
The report presents an insightful chart outlining the primary purposes for which users utilize stablecoins. While "trading cryptocurrencies or NFTs" remains the most common goal (selected by 50% of respondents), it is closely followed by several non-trading uses. For instance, saving in US dollars (47%) and obtaining better currency exchange rates (43%) are the next main objectives, indicating that stablecoins play an important role in preserving value and enhancing currency exchange efficiency, particularly in countries plagued by high inflation or currency volatility.
Interestingly, 39% of users indicated that they use mechanisms like DeFi platforms to "earn yields," showing that people increasingly view stablecoins as an investment tool. Additionally, 38% of users chose to convert their local currency to US dollars, and another 38% expressed a desire to enter the broader crypto economy through stablecoins, further indicating that stablecoins are acting as a bridge between traditional finance and crypto finance. These use cases suggest that stablecoins are meeting needs that the traditional financial system has not adequately addressed in certain regions.
The chart also shows that stablecoins are increasingly being used for everyday financial activities, with 34% of respondents using stablecoins to buy and sell goods and services, while 32% used them for international remittances, indicating a growing role for stablecoins in commerce and remittances. Furthermore, 34% of users stated that "wanting to take control of their finances" is one of their goals, while 29% of users value the self-custody features of stablecoins, reflecting a pursuit of financial independence.
In addition to these primary uses, the report also notes that stablecoins are beginning to gain recognition in commercial applications. Some businesses are using stablecoins for B2B payments and corporate treasury management, particularly in emerging markets where stablecoins can help combat local currency volatility. Moreover, in the employment sector, 23% of respondents reported that they have been paid or received salaries in stablecoins, indicating a gradual increase in the acceptance of stablecoins as a medium of compensation.
- Tether completes its first USDT-based oil trade in the Middle East, exploring the new role of stablecoins in traditional trade
- Tokenized payment innovation: Amazon tackles cross-border payment compliance challenges with tokenization solutions
- Tether launches Dirham stablecoin: Compliance pathways and localized cooperation models under UAE payment token regulations
II. History of Stablecoins - The Earliest Stablecoins
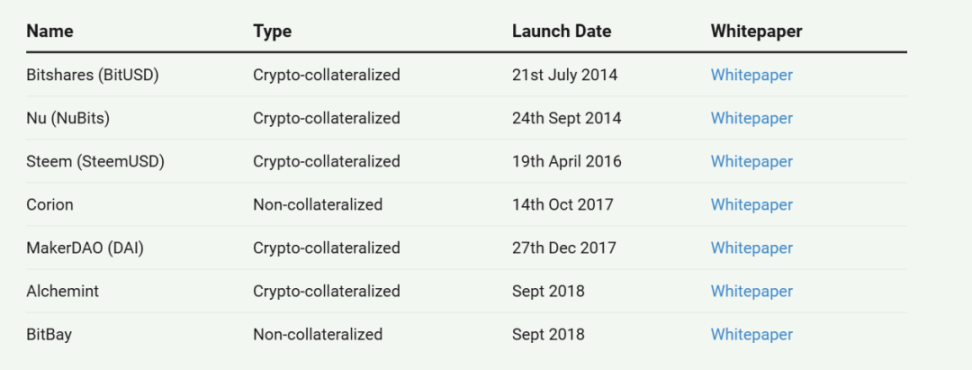
1. BitUSD
BitUSD was launched in July 2014 on the BitShares platform and is one of the earliest attempts in the decentralized stablecoin space. It was developed by Daniel Larimer, who later founded EOS. BitUSD was designed as an algorithmic stablecoin, collateralized by the volatile BitShares cryptocurrency rather than being based on traditional US dollar reserves. Users could create BitUSD by collateralizing BitShares, with an initial maintenance margin of 150% to prevent liquidation risks. The value of BitUSD relative to BitShares was determined within the decentralized exchange of the BitShares ecosystem.
However, this system lacked an adequate price stabilization mechanism, relying more on a kind of circular logic, with its price being self-referential and not directly pegged to the real-world value of the US dollar. Supporters of BitUSD argued that the design of this system could naturally maintain price anchoring through market forces and participant behavior, claiming that automatic margin call notifications and rational participants trading based on future expectations would achieve self-reinforcing price stability. According to this view, market participants had no reason to trade BitUSD at prices deviating from the target of $1, as any deviation would create arbitrage opportunities or indicate a loss of confidence in the entire system.
Despite appearing theoretically feasible, BitUSD faced significant challenges in practice. The lack of price oracles providing external US dollar price information was a contentious point in its design. Additionally, the system struggled to gain widespread adoption in reality, with the circulating amount of BitUSD at one point being only about $40,000, leading to insufficient liquidity and difficulty in achieving price stability. While BitUSD was an interesting early experiment in the decentralized stablecoin space, it ultimately failed to meet its intended goals.
The experience of BitUSD reveals the complexities and potential vulnerabilities of algorithmic stablecoins, particularly their susceptibility to manipulation and price volatility during market turmoil. Although its design was highly innovative, it also proved overly naive and difficult to scale effectively. The potential instability during financial fluctuations and the possibility that savvy trading firms could profit from attacking the peg highlight the challenges of maintaining stable value without traditional backing. Despite its many limitations, BitUSD provided valuable lessons for later decentralized stablecoin projects, paving the way for more complex designs in the years to come.
2. NuBits
NuBits was launched in September 2014 and was another early attempt to create a decentralized stablecoin, being one of the first projects to use a collateralized asset, in this case, Bitcoin. The NuBits project introduced a dual-token system, where NuBits (USNBT) is the stablecoin pegged to $1, while NuShares (NSR) serves as the governance token. This model, which uses cryptocurrency as collateral, aimed to provide a more stable value than BitUSD by using Bitcoin as a reserve asset. NuBits maintained its peg through a series of mechanisms, including adjusting supply based on demand, offering interest rates to incentivize users to hold NuBits during low demand, and utilizing Bitcoin reserves to support the peg.
The NuBits system relied on NuShare holders voting to increase the supply of USNBT when demand rose or to provide "parking" incentives when the price fell below $1. The so-called "parking" mechanism allowed users to temporarily withdraw their NuBits from circulation in exchange for interest payments, effectively reducing the available supply. However, this system lacked a direct method for reducing the overall supply of NuBits, a problem that later became very apparent.
Despite some initial successes, NuBits experienced its first major crisis in 2016 when the price of Bitcoin surged dramatically. Many NuBits holders sold their stablecoins to profit from the appreciation of Bitcoin. This sudden drop in demand rendered the system's stabilization mechanisms ineffective, leading to a de-pegging of the stablecoin, with NuBits' price falling below $1 and taking about three months to gradually recover. This event highlighted the system's vulnerability during rapid changes in market sentiment and the challenges of maintaining a peg during periods of high cryptocurrency volatility.
Although NuBits later successfully re-pegged to $1 and even experienced significant growth during the Bitcoin price crash in 2017, as crypto investors sought safe-haven tools, its market cap surged from $950,000 to $14 million in a short time. However, this growth did not last long. In March 2018, NuBits faced an even more severe crash, which it never fully recovered from. Due to insufficient reserves and a lack of collateral diversity (primarily relying on volatile cryptocurrencies), the system was unable to defend its peg when demand slightly decreased. The price of NuBits plummeted, reaching as low as $0.25, effectively marking its failure as a stablecoin.
II. Challenges of Stablecoins: The Collapse of Terra UST and the Delisting of BUSD
In recent years, the cryptocurrency market has faced numerous challenges, with some major stablecoins experiencing vastly different fates. The design goal of stablecoins is to peg their value to a reserve asset (such as the US dollar) to maintain stable value, making them an indispensable part of the crypto ecosystem. However, the sudden collapse of Terra's UST in 2022 and the orderly delisting of Binance's BUSD in 2023 revealed various risks and regulatory pressures within the stablecoin space.
The collapse of UST was a catastrophic event triggered by inherent design flaws and market pressures, while the delisting of BUSD was a more controlled process driven by regulatory actions. By comparing these two starkly different situations, we can better understand the range of issues faced by stablecoin issuers, from algorithmic stabilization mechanisms to compliance regulations. The lessons from these events are crucial for investors, developers, and policymakers as the industry continues to explore the complex realm of digital assets while facing increasing regulatory scrutiny.
1. Binance
- Token: BUSD
- Peak Supply: $23,361,438,102
Binance's BUSD is a widely used US dollar-pegged stablecoin issued in partnership with Paxos Trust, with a supply second only to USDC and USDT. In February 2023, the New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) ordered Paxos to stop minting new BUSD tokens, citing "some unresolved issues related to Paxos' oversight of its relationship with Binance." This regulatory action effectively initiated the delisting process for BUSD.
Following the NYDFS order, Paxos announced it would terminate its partnership with Binance regarding the issuance of BUSD but would continue to support existing BUSD tokens at least until February 2024. Binance initially stated that BUSD would "gradually exit the market," but in August 2023, Binance announced plans to phase out support for BUSD-related products and urged users to convert their BUSD to other assets before February 2024.
By November 2023, Binance confirmed it would stop supporting BUSD on December 15, 2023. The exchange stated that users could still redeem their BUSD before February 2024, after which all remaining BUSD balances would be automatically converted to FDUSD, a stablecoin issued by First Digital Limited. This marked the final delisting phase of what was once the third-largest stablecoin by market cap.
The situation with BUSD offers several lessons for the crypto industry. First, it highlights the increasing regulatory scrutiny and the importance of compliance measures for stablecoins. Second, this case demonstrates the risks of over-reliance on a single stablecoin or exchange, as many users were affected by the sudden delisting. Additionally, it indicates that clear communication and transition plans are essential during significant changes in the crypto ecosystem. Finally, the delisting of BUSD emphasizes the importance of diversification in the stablecoin market and the potential benefits of choosing compliant stablecoin alternatives.
2. Terra
- Token: UST
- Peak Supply: $18,708,520,935
The collapse of Terra's algorithmic stablecoin UST in May 2022 was one of the most significant events in the crypto industry, evaporating $50 billion in market value within three days. At the core of this ecosystem was the Anchor protocol, a lending protocol offering deposit rates of up to 20%, which was clearly unsustainable. This high yield attracted a massive influx of funds, driving up demand for UST and its sister token LUNA. However, the subsidies required to maintain these high rates gradually became untenable.
The Collapse of Terra UST Stablecoin
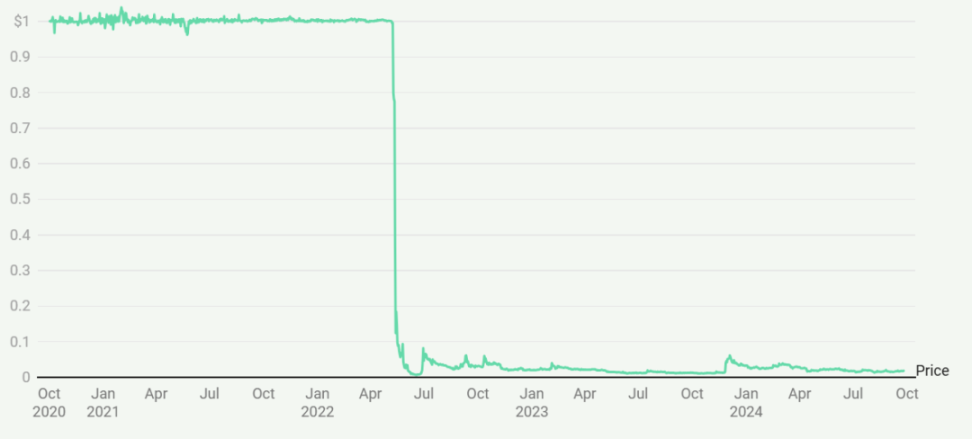
The crisis for Terra began on May 7, 2022, when a large number of depositors started withdrawing from the Anchor protocol and selling UST. Despite Terraform Labs' attempts to maintain the price peg of UST, as withdrawals accelerated, the price of UST fell to $0.75 on May 9. Since UST's design allowed holders to exchange UST for LUNA at a value of $1, this led to a so-called "death spiral," where a large amount of new LUNA was rapidly minted, causing its price to plummet. By May 13, the price of UST had fallen below $0.20, and LUNA had become nearly worthless.
The Collapse of Terra Luna provided several important lessons for the crypto industry:
- It highlighted the inherent risks of algorithmic stablecoins, especially those without sufficient reserve backing;
- It demonstrated the dangers of unrealistic high-yield products, which can create fragile ecosystems that collapse rapidly when market conditions change;
- This event also emphasized the importance of transparency and clear risk communication, as many investors did not fully understand the complex mechanisms behind Terra.
Analysis of this collapse indicates that wealthier and more savvy investors were able to exit earlier with smaller losses, while retail investors reacted more slowly and suffered greater losses. The complexity of the Terra system made it difficult for many participants to fully grasp the risks involved. Although blockchain technology allows investors to monitor large transactions, this information asymmetry exacerbated rather than alleviated inequalities during the collapse.

III. Current Market Overview
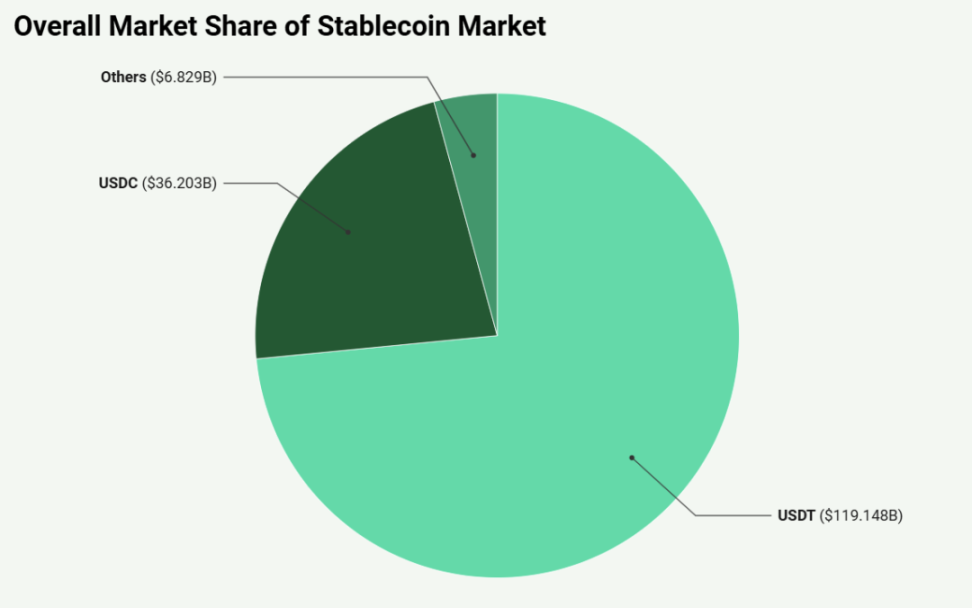
The stablecoin market exhibits a highly concentrated landscape, with Tether's USDT and Circle's USDC accounting for 95.8% of the total market cap. This "dual oligopoly" phenomenon underscores the significant role these centralized, fiat-backed stablecoins play in providing liquidity and stability to the crypto market. Their widespread use and perceived stability make them core assets in the crypto ecosystem, used for trading, as a store of value, and to support various DeFi applications.
However, the centralized nature of these dominant stablecoins and the enormous profits accrued by their issuers are increasingly coming under scrutiny. For instance, Tether reported a net profit of up to $5.2 billion in the first half of 2024, all of which was retained by the issuing company. Such concentration of wealth and control has sparked interest in alternative stablecoin models. A wave of new stablecoins is emerging in the market, aiming to return profits to users, while new products like "synthetic dollars" are also on the rise, such as Ethena's USDe. These innovations reflect a broader trend in the crypto space towards more decentralized, user-centric financial products, which may challenge the current dual oligopoly status in the future.
Overall market share of stablecoins excluding USDC and USDT
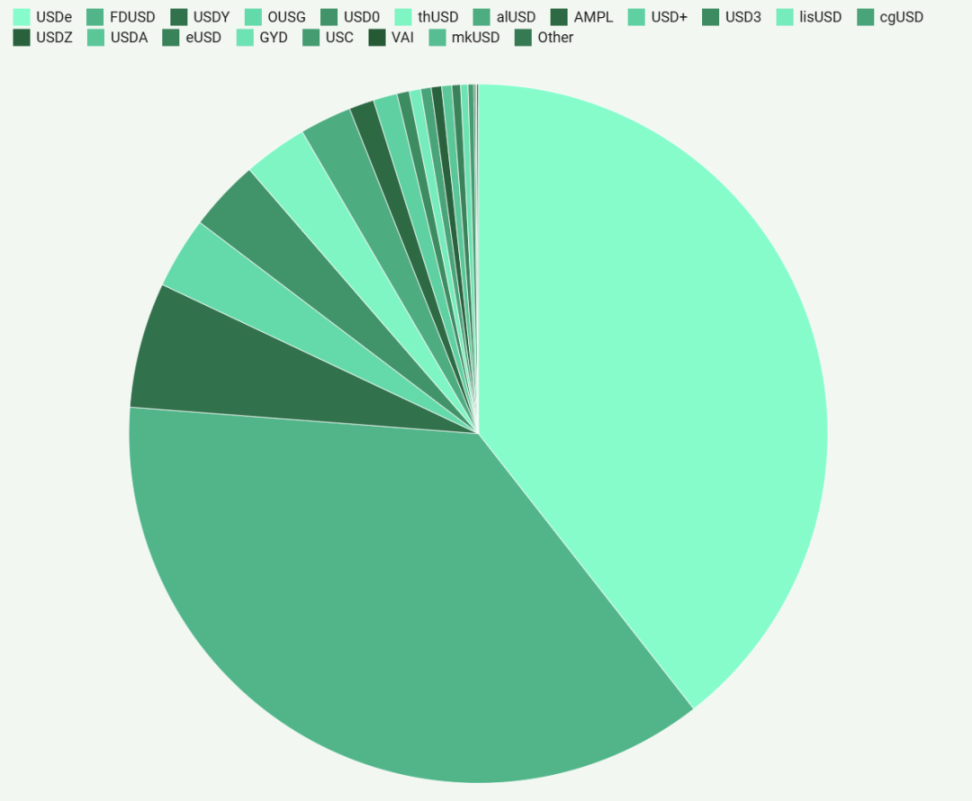
Beyond the dominance of USDT and USDC, a diverse ecosystem of smaller stablecoins is gradually forming, with a total market cap of $6.8 billion. These diverse stablecoins showcase various designs, each striving to find its niche in the rapidly evolving digital asset space, from fiat-backed tokens (like FDUSD) to more complex algorithmic models (like FRAX).
These smaller stablecoin participants are not merely imitating the big players but are actively innovating in areas such as collateralization methods, blockchain interoperability, and governance structures. For example, some projects are exploring cross-chain compatibility to enhance liquidity and accessibility, while others are implementing new stabilization mechanisms that combine algorithmic control with collateral backing. These experiments are crucial for the long-term development of the stablecoin space, as they stress-test different models and may uncover more efficient or resilient designs. As the stablecoin market matures, these innovations could play a significant role in shaping regulatory frameworks and user acceptance, thereby influencing the trajectory of the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem.
1. Cross-Chain Distribution
Distribution of stablecoins across different blockchains

The distribution of stablecoins across different blockchain networks reveals some interesting trends in user preferences and technology adoption. Ethereum remains far ahead, hosting the majority of stablecoin value. This dominance may stem from Ethereum's first-mover advantage in the smart contract space and its robust DeFi ecosystem.
Tron ranks second, clearly surpassing other alternative networks. This position is primarily due to the fact that a large amount of USDT is issued on the Tron blockchain, with a supply exceeding $61.8 billion. Tether's decision to issue a significant amount of stablecoins on the Tron network has allowed Tron to quickly occupy an important position. This strategic decision by Tether, combined with Tron's lower transaction fees, makes it an attractive option for USDT transactions, especially suitable for small transactions or in regions sensitive to transaction costs.
The distribution on other chains, such as BSC (Binance Smart Chain), Arbitrum, Solana, etc., indicates that the stablecoin ecosystem is gradually diversifying. This trend of decentralization across multiple chains reflects a broader multi-chain strategy in the crypto space, with projects and users seeking to optimize speed, cost, and the specific advantages of various ecosystems.
2. Growth Trends
Stablecoin Market Growth
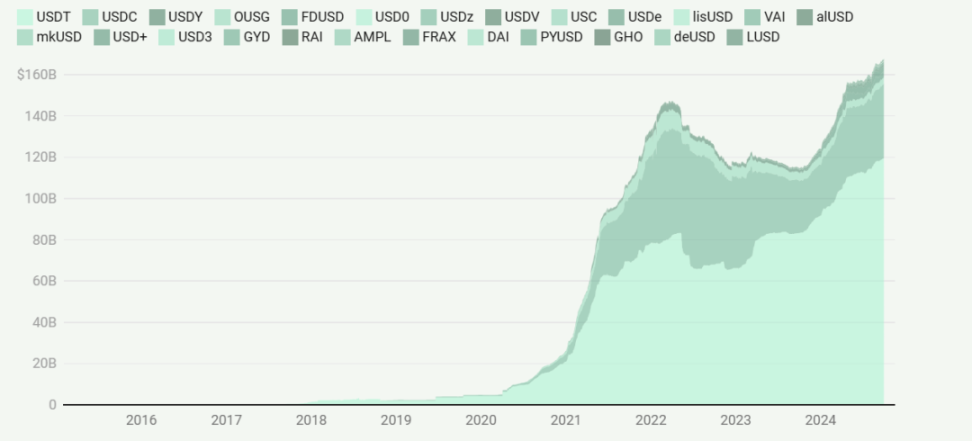
The stablecoin market has shown significant growth, especially since 2020. The market cap chart illustrates a transition from a relatively obscure state from 2016 to 2019 to explosive growth starting in 2020. This growth aligns with the broader DeFi boom and increased institutional interest in cryptocurrencies.
This growth can be divided into several key phases:
- Initial Slow Growth (2016-2019): Limited adoption and use cases for stablecoins.
- Rapid Expansion (2020-2021): The market rapidly expanded in sync with the DeFi boom and bull market.
- Peak and Adjustment (2022): Reflecting the dynamics of the entire crypto market and the impact of specific events like the Terra/LUNA collapse.
- Recovery and Continued Growth (2023-2024): Indicating the market's resilience and ongoing demand for stablecoins.
This growth pattern suggests that stablecoins have transformed from a niche product into a crucial component of the crypto ecosystem, playing a key role in transactions, yield generation, and serving as a store of value during market volatility.
3. Transaction Volume Compared to Web2 Solutions
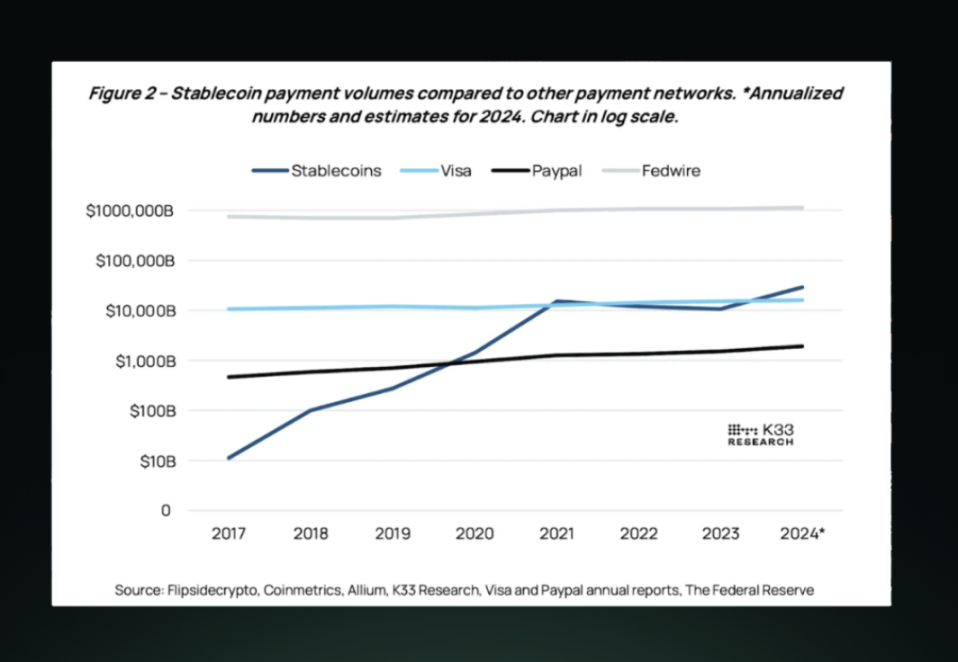
Perhaps the most indicative metric of the growing importance of stablecoins is their transaction volume compared to traditional payment networks. The comparison of stablecoin transaction volumes with Visa, PayPal, and Fedwire shows a rapid increase in stablecoin usage.
Starting from a relatively low base in 2017, stablecoin transaction volumes have exhibited exponential growth, surpassing PayPal's transaction volume by 2020 and beginning to approach Visa's transaction volume in 2021. Predictions for 2024 suggest that stablecoin transaction volumes could even exceed Visa's, though still below the massive interbank transfer volumes of Fedwire.
This comparison highlights the disruptive potential of stablecoins in the global payments landscape. However, it is important to note that these transaction volumes likely represent different types of transactions—stablecoin volumes may include more trading and DeFi activities, while Visa's volumes primarily represent consumer spending.
IV. Case Study: Real Asset-Backed Stablecoins
Real asset (RWA) backed stablecoins have become the dominant form over the past eight years, gradually surpassing the initial fiat-backed versions. While many stablecoins still maintain a 1:1 collateral relationship with dollars in bank accounts, the entire ecosystem has expanded to include a more diverse range of asset backing. For example, Paxos Gold (PAXG) provides investors with exposure to physical gold through the crypto ecosystem, demonstrating the flexibility of the RWA model in meeting diverse store of value needs.
Despite the diversification of asset types, fiat-backed tokens like Tether's USDT remain the most widely adopted, playing a critical role in trading and hedging against crypto market volatility. The success of USDT has incentivized other major players, such as Circle's USDC and Binance's BUSD, which also support their own pools of real assets.
Stability Anchoring of Real Asset-Backed Stablecoins
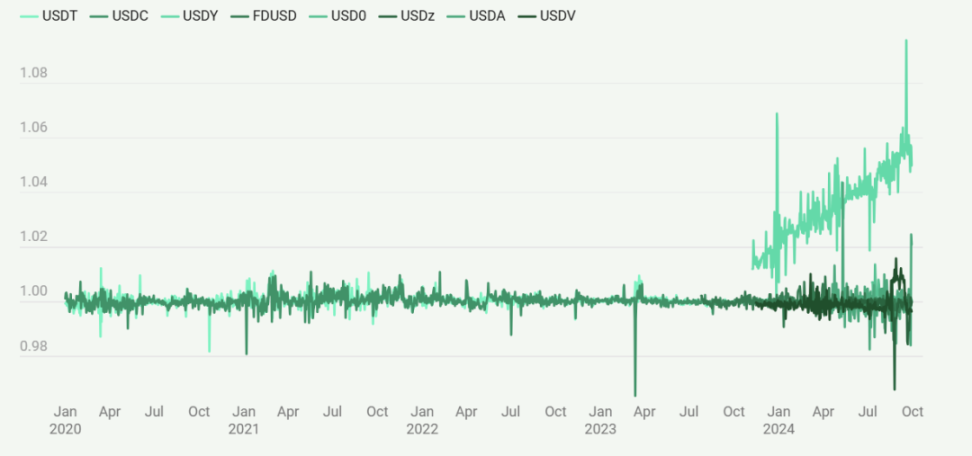
The stability anchoring of these real asset (RWA) backed stablecoins shows their relative success in maintaining a value close to $1. However, the chart above also reveals some volatility, particularly in recent years. This volatility indicates that even with real asset backing, maintaining a stable price peg remains challenging. It is important to note that USDY is a non-rebalancing token, and the apparent price increase does not represent a deviation from its peg but rather reflects the accumulation of yields for USDY holders.
The centralized nature of RWA-backed stablecoins brings both advantages and disadvantages. On one hand, they provide high stability and attract large institutional investments, but on the other hand, this means that issuers need to maintain relationships with traditional banks and operate through regulated entities. This centralization raises concerns about transparency, trust, and potential scrutiny. Although issuers respond to these issues through voluntary audit reports and attestations, disputes regarding the composition and adequacy of reserves persist.
As the stablecoin space continues to evolve, RWA-backed tokens may be influenced by regulatory changes in major jurisdictions and ongoing innovations in support mechanisms. These stablecoins' ability to connect traditional finance with the crypto market remains unparalleled, although recent events regarding address blacklisting have highlighted potential risks of scrutiny. The future challenge will be how to balance the stability brought by RWA backing while maintaining the spirit of decentralization in the broader crypto ecosystem, all while navigating an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
1. Tether
- Token: USDT
- Supply: $119,147,677,308
- Yield: Not applicable
- Network Support: Ethereum, Tron, Solana, Optimism, and over 65 other chains
Tether's USDT is one of the largest stablecoins by market cap and one of the earliest stablecoins. Launched by Tether Limited in 2014, USDT aims to fill the gap between cryptocurrencies and traditional fiat currencies. It is designed to be pegged to the US dollar at a 1:1 ratio, aiming to minimize price volatility while enjoying the advantages of cryptocurrency trading.
As of September 2024, USDT's market cap is approximately $119 billion, making it the third-largest cryptocurrency by overall market cap and the dominant stablecoin. Its daily trading volume often exceeds that of Bitcoin, highlighting its significant role in the crypto ecosystem. USDT is widely supported across multiple blockchains, including Ethereum, Tron, and Solana, greatly enhancing its accessibility and utility.
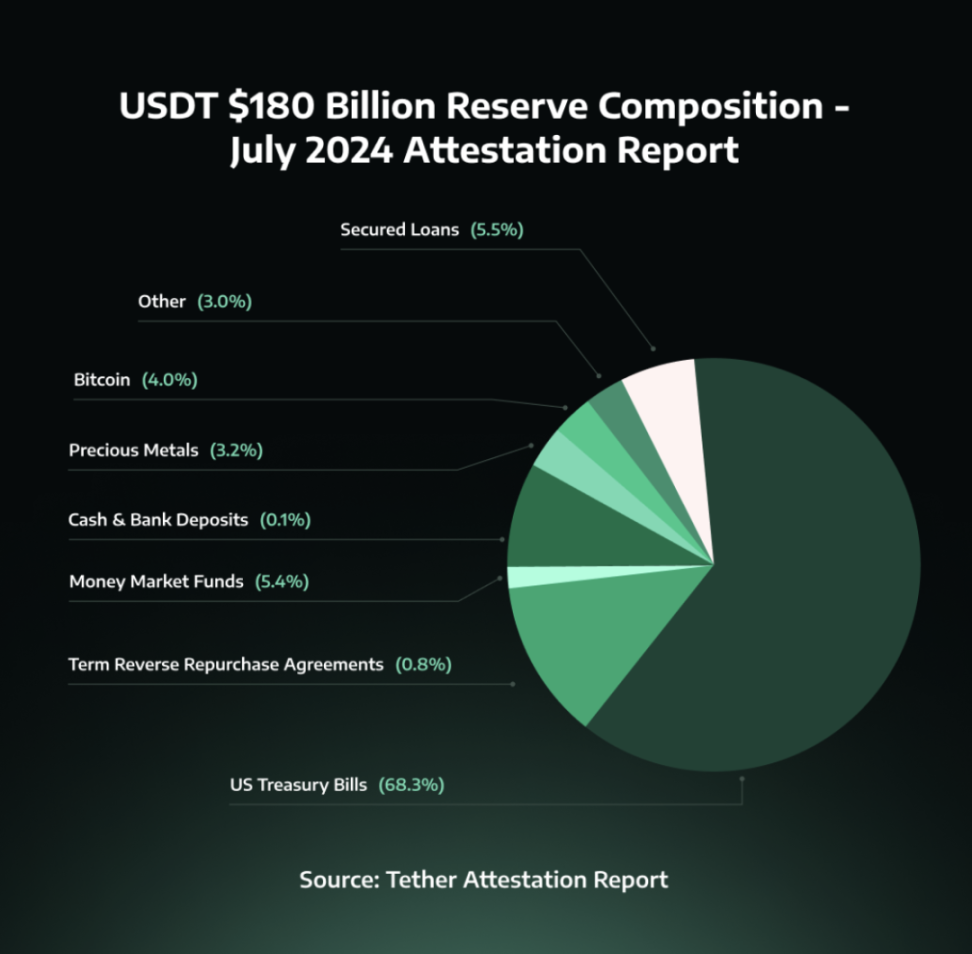
Tether's support mechanism has been a focal point of innovation and controversy. The company claims that each USDT token is backed by corresponding reserves, including cash, cash equivalents, and other assets. As of the latest audit report (June 2024), approximately 68% of Tether's reserves are in US Treasury bonds, with the remaining reserves diversified into secured loans (5.5%), Bitcoin (4%), and various other investments, including corporate bonds and precious metals.
This diversified reserve structure has drawn scrutiny from regulators and the crypto community. In response to these concerns, Tether has increased transparency by providing quarterly audit reports and daily updates on reserve holdings. However, some critics still demand more comprehensive audits.
Despite facing challenges, such as the market panic triggered by the UST collapse in 2022, which caused USDT to briefly de-peg to $0.95, Tether demonstrated resilience during this period, with the stablecoin quickly recovering to its pegged price, enhancing market confidence in its stability. The widespread use of USDT in cryptocurrency trading, its application in cross-border transactions, and its integration into various DeFi protocols all underscore its importance in the digital asset ecosystem.
Looking ahead, Tether faces both opportunities and challenges. The growing global demand for a digital dollar provides a solid foundation for the continued growth of USDT. However, the evolving regulations surrounding stablecoins, particularly in the US and Europe, may require Tether to adjust its operations and enhance compliance measures. As the stablecoin market matures, Tether's ability to address transparency issues while adapting to the regulatory environment will be key to its long-term success.
2. Circle
- Token: USDC
- Supply: $36,203,104,616
- Yield: Not applicable
- Network Support: Ethereum, Arbitrum, Base, Celo, NEAR, Solana, Hedera, and over 10 other chains
Circle's USD Coin (USDC) was launched in September 2018 in collaboration with Circle and Coinbase and is one of the major stablecoins in the crypto ecosystem. Circle was founded by Jeremy Allaire in 2013, with the initial goal of simplifying digital currency transactions. The launch of USDC marked an important step in addressing regulatory issues in the stablecoin space, with the Centre Consortium, jointly established by Circle and Coinbase, responsible for its governance and setting standards for fiat representation on the internet.
USDC distinguishes itself from other stablecoins through its commitment to compliance and transparency. At its core is a 1:1 support mechanism, with Circle maintaining an equivalent amount of cash and highly liquid, short-term US government securities as reserves for every circulating USDC.
Since its issuance, USDC's stability in anchoring
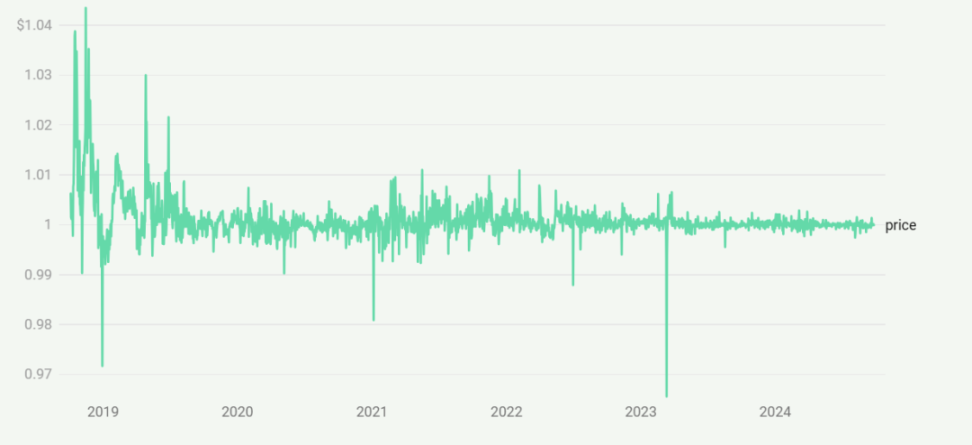
The price stability of USDC is one of its key features. Despite some minor fluctuations, USDC has maintained a very close peg to the US dollar, rarely deviating from $1 by more than 5-10 basis points. However, there have been instances of the peg being disrupted, the most recent occurring in 2023 when Silicon Valley Bank collapsed, and Circle held $3.3 billion in cash reserves at that bank. This de-pegging event also affected other stablecoins that rely on USDC for support, such as DAI, USDD, and USDP. Nevertheless, Circle's USDC quickly regained its peg, and there have been no similar occurrences since, but this also reveals the risks that centralized issuers may bring.
USDC's market position remains strong, currently available in over 180 countries and supporting 15 blockchain networks, with most of its supply on Ethereum. Key metrics also show its significant adoption level, including a monthly transfer volume of $4.4 billion, 2.9 million monthly active addresses, and 17 million holders.
The company aims to position USDC as a platform for building a new financial system, the preferred digital currency for institutional investors, and a tool for seamless, borderless value exchange. Circle has demonstrated its intent to diversify and adapt to regional regulatory frameworks by launching the euro-pegged stablecoin EURC, compliant with MiCA regulations. As the digital asset ecosystem continues to evolve, USDC's role in facilitating cross-border transactions and providing stable fiat digital representation will become increasingly important.
3. Ondo Finance
Ondo Finance is a DeFi platform designed to combine traditional finance with blockchain technology. The platform was founded with the intention of making institutional-grade financial products and services more widely accessible to the public. Ondo leverages blockchain technology to enhance the infrastructure and accessibility of financial products. The company's approach combines innovative blockchain solutions with best practices from traditional finance, including investor protection, transparent reporting, and regulatory compliance.
Ondo's core products are two: USDY (US Dollar Yield) and OUSG (Ondo Short-Term U.S. Government Bonds). These products provide unique solutions in the asset tokenization space, catering to different investor needs and regulatory requirements. Here is a brief comparison:
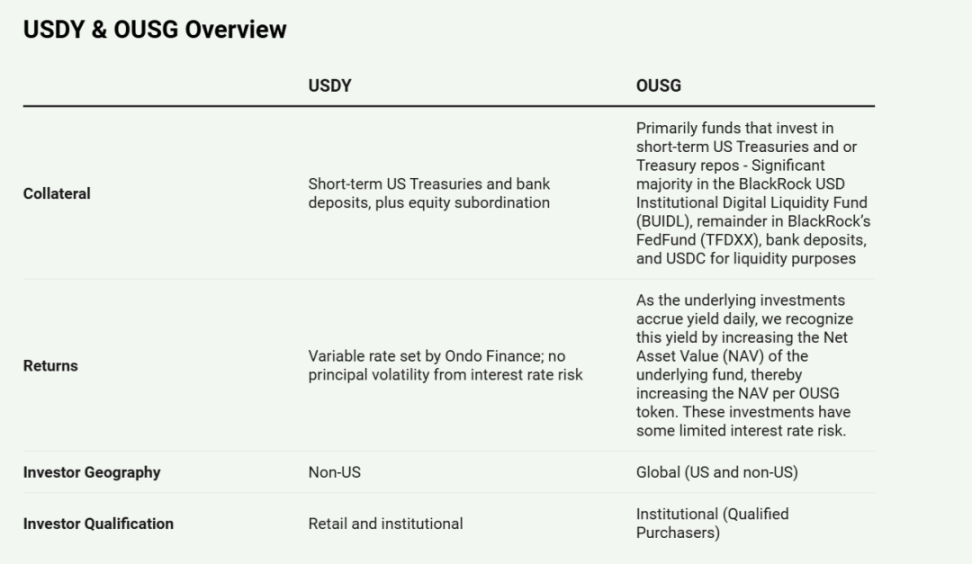
(1) USDY
- Token: USDY
- Supply: $396,396,512
- Yield: 5.35%
- Network Support: Ethereum, Solana, Sui, Aptos, Arbitrum, Mantle, Mantra, and Cosmos.
USDY is a decentralized, over-collateralized stablecoin launched by Ondo, designed to maintain a soft peg to the US dollar. By offering yields, it serves as a strong alternative to traditional stablecoins. The value of USDY is supported by a combination of short-term U.S. Treasury bonds and bank demand deposits, providing a stable and secure foundation.
A key feature of USDY is its dual-token structure. It has two versions: one is USDY, which appreciates in price as yields accumulate; the other is rUSDY, which maintains a constant price of $1 while reflecting yields through an increase in the number of tokens. This structure allows users to flexibly enjoy the yields generated by the underlying assets.
USDY introduces multiple institutional-level investor protection measures, distinguishing it from many other crypto assets. These measures include bankruptcy isolation, meaning the structure of the issuing entity is designed to protect token holders' interests in the event of bankruptcy of related entities, as well as oversight by a third-party collateral agent. Additionally, USDY employs a unique grouping system and has a 40-50 day lock-up period before token minting to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
The product is aimed at global non-U.S. individual and institutional investors, combining the utility of stablecoins with the yield potential of short-term U.S. Treasury bonds. For those looking to optimize idle capital in the crypto space while maintaining the stable value of the dollar, USDY is an attractive option.
(2) OUSG
- Token: OUSG
- Supply: $226,349,355
- Yield: 5.36%
- Network Support: Ethereum, Solana, Polygon
OUSG provides a more direct tokenized exposure to short-term U.S. Treasury bonds. Most of OUSG's portfolio is invested in BlackRock's USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund (BUIDL), while also allocating to other high-quality, liquid assets. The product aims to provide the safety and stability of U.S. Treasury investments while leveraging the advantages of blockchain technology.
A highlight of OUSG is its 24/7 instant minting and redemption feature, allowing qualified investors to quickly enter and exit positions, providing a level of liquidity that traditional Treasury investment products typically do not offer. Like USDY, OUSG also has two versions: accumulating (OUSG) and rebalancing (rOUSG) to cater to different investor preferences for yield accumulation.
Compared to USDY, OUSG's target investor group is more specific. It is aimed at qualified purchasers globally, typically including high-net-worth individuals and large institutional investors. This positioning allows OUSG to be exempt from certain U.S. securities regulations in some cases, thus providing features like instant trading that may be difficult to achieve in broader investment products.
4. First Digital
- Token: FDUSD
- Supply: $2,511,567,480
- Yield: Not applicable
- Network Support: Ethereum, Binance
First Digital Labs, a subsidiary of Hong Kong-based First Digital Group, launched First Digital USD (FDUSD) in June 2023, a new type of stablecoin aimed at restoring confidence in the crypto market. First Digital Labs quickly established FDUSD as a significant player in the stablecoin space. The launch of FDUSD came at a critical time following the collapse of several well-known stablecoins, while the crypto industry faced increasing regulatory scrutiny.
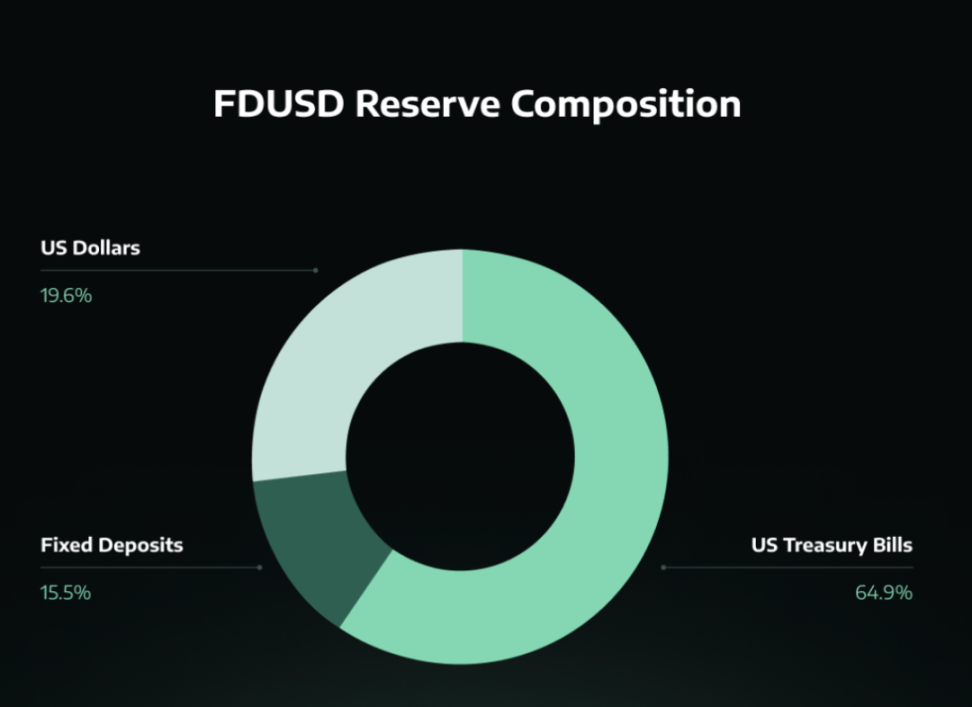
FDUSD Reserve Composition
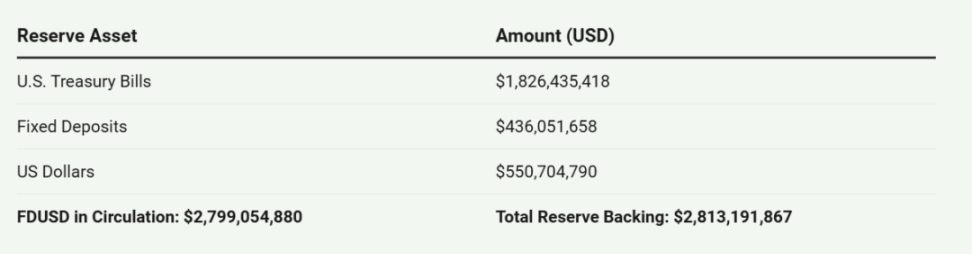
FDUSD is designed as a fully collateralized stablecoin, maintaining a 1:1 peg to the US dollar. Its stability is supported by a reserve of liquid assets, primarily composed of short-term U.S. Treasury bonds and a combination of time deposits and cash. These reserves are held by a public trust company registered in Hong Kong and various financial institutions across multiple countries, including Hong Kong, Singapore, Australia, Canada, Luxembourg, and the United States. This diverse geographical distribution aims to enhance the security and stability of FDUSD.
An important development for FDUSD is its integration with Binance, the world's largest cryptocurrency exchange. After Binance ceased support for BUSD due to regulatory pressure, FDUSD was adopted as the primary stablecoin. This partnership significantly boosted FDUSD's visibility and liquidity, rapidly increasing its market capitalization and trading volume. Binance's support, including a zero-fee policy for launching FDUSD trading pairs, has driven adoption of FDUSD among crypto traders and investors.
The stability mechanism of FDUSD relies on market arbitrage to maintain its peg. When the price of FDUSD deviates from its $1 peg, arbitrageurs can profit by minting or redeeming FDUSD directly from First Digital Labs, thereby pushing the market price back to the pegged position. However, it is worth noting that direct redemptions are currently limited to institutional clients that have completed the KYC process, while retail users must rely on secondary market liquidity for conversions.
Transparency and regular audits are key strategies for building trust in FDUSD. First Digital Labs publishes reserve reports monthly and is audited by the U.S. accounting firm Prescient Assurance. These reports aim to assure users that every FDUSD token is backed by corresponding reserves. However, some analysts have expressed concerns about the lack of information regarding the specific banks holding cash reserves in the reports, as well as the potential risks of asset isolation in the event of the issuer's bankruptcy.
5. Usual
Usual has introduced two main stablecoin products, USD0 and USD0++, designed for different uses within the DeFi ecosystem while maintaining a close connection to traditional financial assets. Usual's approach aims to address key issues in the current stablecoin market, including security, efficiency, and fairness, by leveraging the stability of U.S. Treasury bonds and overnight repos, while redistributing value to users through its governance token USUAL.
(1) USD0
- Token: USD0
- Supply: $225,651,265
- Yield: Not applicable
- Network Support: Ethereum
USD0 is Usual's primary stablecoin product, designed as a liquid deposit token (LDT), fully backed by real assets with ultra-short maturities, aiming to be a safer and more transparent alternative to traditional stablecoins like USDT and USDC. USD0 is backed 1:1 by real assets (primarily U.S. Treasury bonds and overnight repos), ensuring unparalleled stability and security. This support mechanism differentiates USD0 from many competitors, as it is not affected by the fractional reserve system of commercial banks, thereby reducing the systemic risks faced by other stablecoins in the past.
A key feature of USD0 is its transparency. The protocol maintains real-time transparent reserves, avoiding the fractional reserve practice that has been a concern among some centralized stablecoin issuers. This commitment to transparency instills greater confidence in users regarding the stability and backing of their holdings. Additionally, USD0 is designed to be permissionless and easily transferable, allowing for seamless integration into the broader DeFi ecosystem.
USD0 also serves as an aggregator of various U.S. Treasury bond tokens, enhancing liquidity and accessibility in the DeFi space. This feature allows Usual to bridge traditional finance and DeFi, providing users with exposure to the stability of government securities while retaining the flexibility and programmability of blockchain assets. Through this design, USD0 aims to create a more efficient and interconnected financial environment for individual users and the entire DeFi ecosystem.
(2) USD0++
- Token: USD0++
- Supply: $185,000,195
- Yield: Yes
- Network Support: Ethereum
USD0++ is an enhanced version of USD0, functioning as a liquid bond token (LBT) and can be viewed as an "enhanced 4-year DeFi Treasury bond." Its design goal is to provide users with higher yield potential while maintaining a close connection to the stability of USD0. The core mechanism of USD0++ includes locking USD0 for 4 years to ensure principal protection and lay the foundation for generating additional yields.**
A significant feature of USD0++ is its yield generation mechanism. It provides yields through USUAL tokens, aiming to exceed the risk-free rate while ensuring a risk-free return. This dual yield approach allows users to enjoy stable base returns while benefiting from the success and growth of the Usual protocol. To further enhance the appeal and security of USD0++, Usual has implemented a Base Interest Guarantee (BIG) mechanism, ensuring that the minimum yield equals the actual risk-free rate and is paid in USD0.
Despite the 4-year lock-up period of the underlying USD0, USD0++ maintains liquidity through secondary market trading. This liquidity feature allows users to exit their positions before maturity when needed, providing a solution for the flexibility often lacking in traditional fixed-term financial products. The trading of USD0++ in the secondary market also creates opportunities for price discovery and may allow users to gain additional value based on market dynamics and expectations of the Usual protocol's future success.
USD0++ is a unique attempt to combine the stability of stablecoins with the yield potential of more speculative DeFi assets. By offering USUAL token rewards, enabling users to participate in the protocol's success while maintaining a close connection to the stability of USD0, Usual aims to create a financial product that attracts both conservative and yield-seeking users. This balanced approach may draw a broader range of participants into the Usual ecosystem, driving its growth and liquidity.
6. Anzen
- Token: USDz
- Supply: $32,681,943
- Yield: 18.5%
- Network Support: Ethereum, Arbitrum, Base, Blast, Manta
Anzen Finance is a protocol aimed at bringing real asset yields on-chain. The core product of the platform is USDz, a stablecoin supported by a diversified portfolio of private credit assets. Unlike traditional stablecoins that are directly pegged to fiat currencies, USDz represents the tokenization of real-world assets, providing users with stable off-chain yield exposure in the DeFi space.
USDz is the native stablecoin of Anzen Finance, designed to provide users with yield generation potential while maintaining a stable value against the U.S. dollar. Each USDz token is backed at a 1:1 ratio using SPCT (secured private credit tokens), which are permissioned tokens representing real-world assets. This structure allows USDz to combine the stability of traditional finance with the efficiency and accessibility of DeFi.
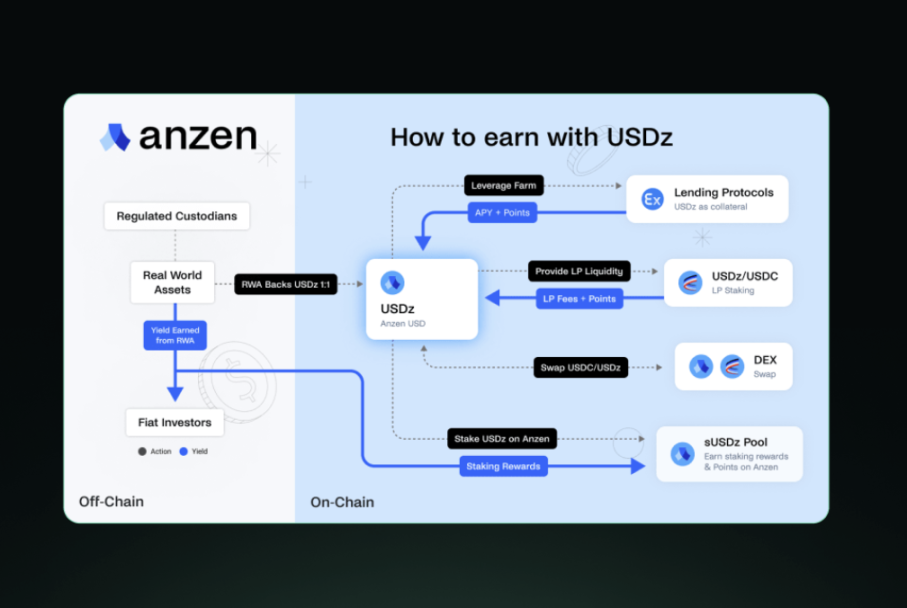
The protocol implements various mechanisms to maintain the stability and utility of USDz. Users can mint USDz by depositing accepted collateral assets (primarily USDC). The minted USDz can be staked to earn sUSDz, with rewards automatically accumulating during the staking period. This staking mechanism incentivizes users to hold USDz and participate in the protocol's ecosystem.
Anzen Finance also emphasizes the transparency of its operations. All transactions related to the issuance and redemption of USDz are recorded on the blockchain, allowing users to verify the stablecoin's solvency at any time. The protocol provides a transparent page where users can view the current status of the reserves supporting USDz.
"USDz is a multi-chain digital dollar backed by a diversified portfolio of credit assets. This real asset portfolio is designed to mitigate the volatility of the crypto market and provide sustainable yields across all market cycles. Anzen's uniquely differentiated platform serves as a core building block in DeFi, allowing all users to build upon it." — Ben Shyong, Founder of Anzen
7. Angle
- Token: USDA
- Supply: $31,637,004
- Yield: 7.7%
- Network Support: Ethereum, Polygon, Optimism, Arbitrum, Base, and over 10 other chains
Angle Finance is dedicated to creating stable and capital-efficient stablecoins pegged to various fiat currencies. The protocol's innovative approach combines features of over-collateralization and capital efficiency, allowing users to mint and burn stablecoins at oracle prices with extremely low fees. This design aims to provide complete convertibility between stable assets and collateral assets, making the protocol more liquid and efficient compared to traditional stablecoin models.
USDA is the stablecoin launched by Angle, pegged to the U.S. dollar, offering reliability, yield, liquidity, and transparency. It aims to address the main challenges faced by stablecoin users, including concerns about de-pegging, "frozen" assets in wallets, lack of yield-sharing on supporting assets, and opaque reserves. USDA is available on multiple blockchain networks, providing liquidity comparable to USDC while incorporating more features and advantages.
USDA Reserve Composition
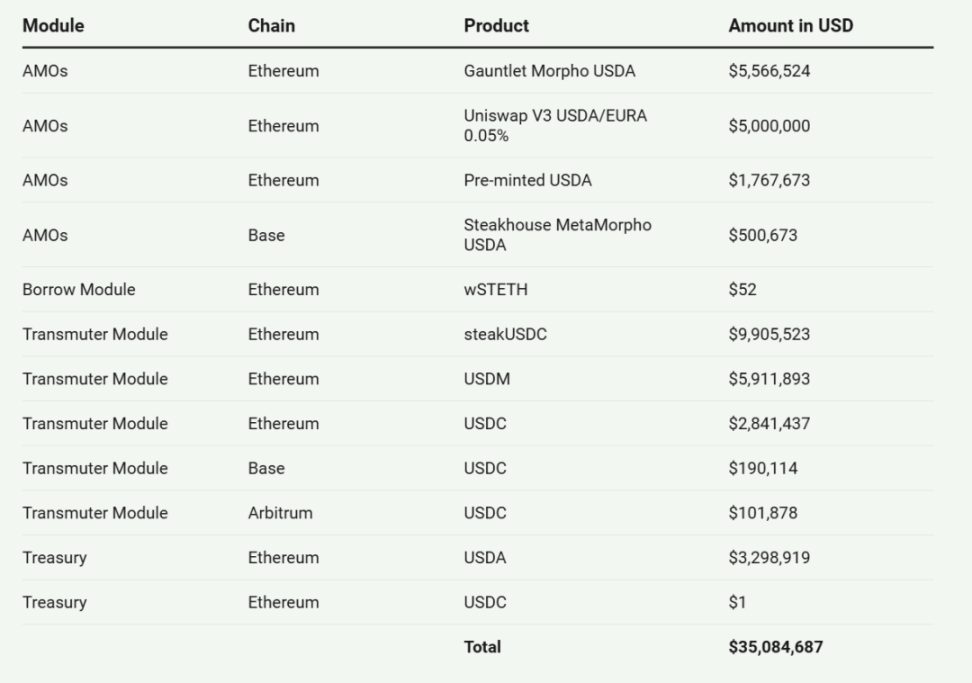
The stability and reliability of USDA are reinforced by its diversified collateral support, with total collateral assets exceeding $35 million, distributed across multiple blockchain networks and assets. This support includes significant allocations to several established DeFi protocols and stablecoins, such as stakeUSDC on Ethereum and USDC across multiple chains. This diversified approach combines on-chain DeFi assets with off-chain traditional financial instruments, providing a balanced risk profile that enhances USDA's resilience during de-pegging events.
A key feature of USDA is its native savings solution, allowing users to earn passive income by holding the stablecoin. Users can deposit USDA into Angle's savings solution (called stUSD), automatically earning rewards generated from the protocol's collateral and lending activities. These rewards come from returns on real assets (such as Treasury bills and tokenized securities), as well as interest paid by USDA borrowers.
To ensure stability, USDA employs an advanced anti-de-pegging mechanism based on Angle's proprietary price stabilization module (also known as "Transmuter"). This risk management framework has been developed based on years of research and deep insights into recent stablecoin de-pegging events. In extreme cases, all holders of USDA or stUSD can exchange their tokens for any collateral asset of the protocol.
USDA also offers lending and leverage features, allowing users to obtain leverage based on Liquid Staking Tokens and Liquid Restaking Tokens through integrations with platforms like Morpho Blue. Additionally, the Angle protocol provides a fully transparent real-time balance sheet of USDA collateral reserves on its website, allowing users to verify the support of their stablecoins at any time.
By combining USDA with EURA, Angle Finance aims to become an efficient on-chain foreign exchange trading hub. The protocol has developed a system to reduce on-chain foreign exchange trading slippage, potentially providing users with cross-currency trading rates that compete with traditional foreign exchange markets. This development could open new opportunities for cross-border trading, remittances, and foreign exchange transactions in the DeFi space.
8. Verified
- Token: USDV
- Supply: $1,516,183
- Yield: Not applicable
- Network Support: Ethereum, Binance, Avalanche, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Viction
The Verified Foundation was launched in November 2023, aiming to create a fairer and more transparent stablecoin environment through its native token USDV. The foundation's approach combines the stability of real assets with innovative blockchain technology to address the limitations present in the current stablecoin market.
USDV is a community-driven stablecoin fully backed by tokenized U.S. Treasury bonds. As an ERC-20 compatible token based on the OFT standard (Omnichain Fungible Token), USDV can operate across multiple blockchain networks, including Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, Avalanche, Arbitrum, and Optimism. Each USDV token is pegged 1:1 to the U.S. dollar, providing a stable store of value and medium of exchange.
A key feature of USDV is its use of Matrixport's Short-Term Treasury Bond Token (STBT) as the initial base reserve asset. STBT is a token compliant with the ERC-1400 standard, pegged to a net asset value (NAV) of $1, fully backed by short-term Treasury bonds and secured reverse repurchase agreements. This collateral mechanism provides USDV with higher stability and transparency, with all transactions traceable on-chain and verifiable through Chainlink's reserve proof system.
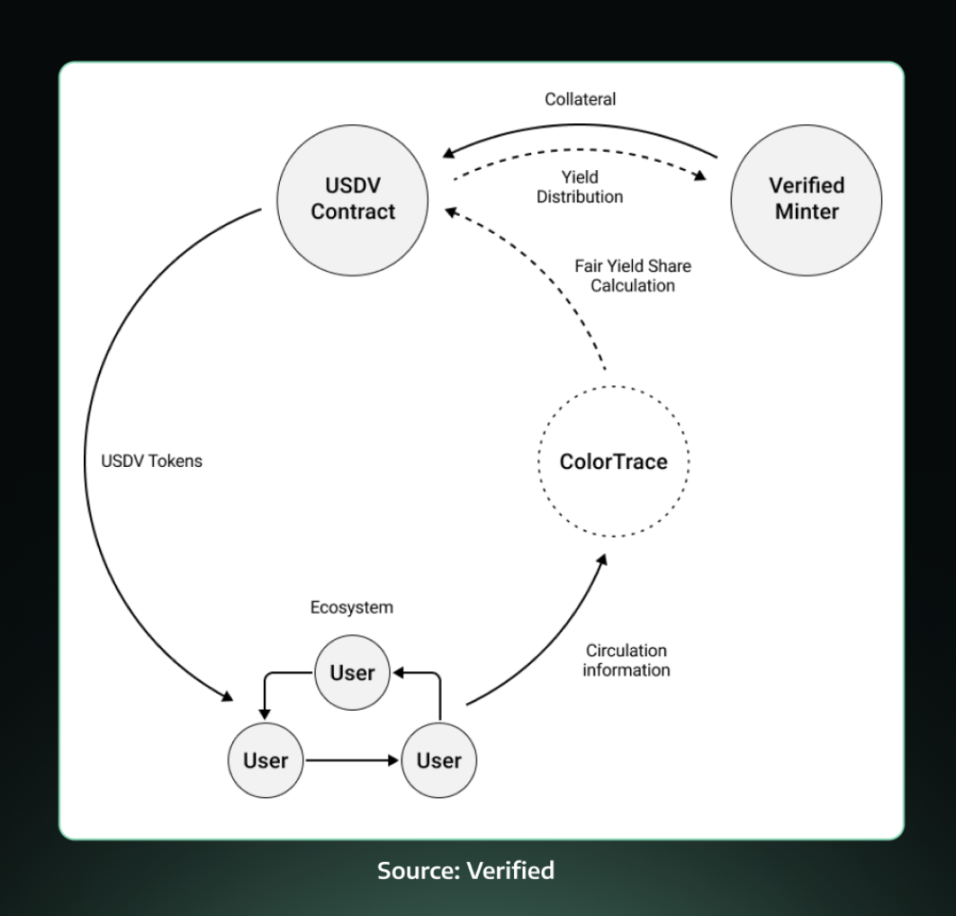
USDV employs the ColorTrace algorithm developed by LayerZero Labs to ensure that reward distribution among verified minters is fair and transparent. This system allows minters to tag their circulating tokens and unambiguously receive rewards sourced from on-chain reserves. The ColorTrace technology addresses the challenges of attribution for fungible tokens, creating a more equitable distribution of contributions to the success of the ecosystem for all contributors.
The USDV protocol incorporates various mechanisms to maintain stability and transparency. These include a reminting process that allows verified minters to increase their treasury shares without locking new assets, a redemption process for converting USDV back to underlying assets, and the management of the system's economy through various fees. Additionally, USDV integrates with LayerZero's OFT standard, enabling seamless operation across multiple blockchain networks, which may make it one of the most widely available cross-chain stablecoins.
### Case Study: Crypto-Collateralized Stablecoins

Crypto-collateralized stablecoins have emerged as a decentralized alternative to traditional fiat-backed stablecoins, aligning more closely with the core principles of "trustlessness" and decentralization in the crypto ecosystem. These stablecoins are backed by other digital assets, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other tokenized assets, and are typically issued and redeemed through decentralized protocols. This process involves locking digital assets as collateral in smart contracts to mint new stablecoins. A well-known example of this model is DAI, issued by MakerDAO.
Stability of Crypto-Collateralized Stablecoins
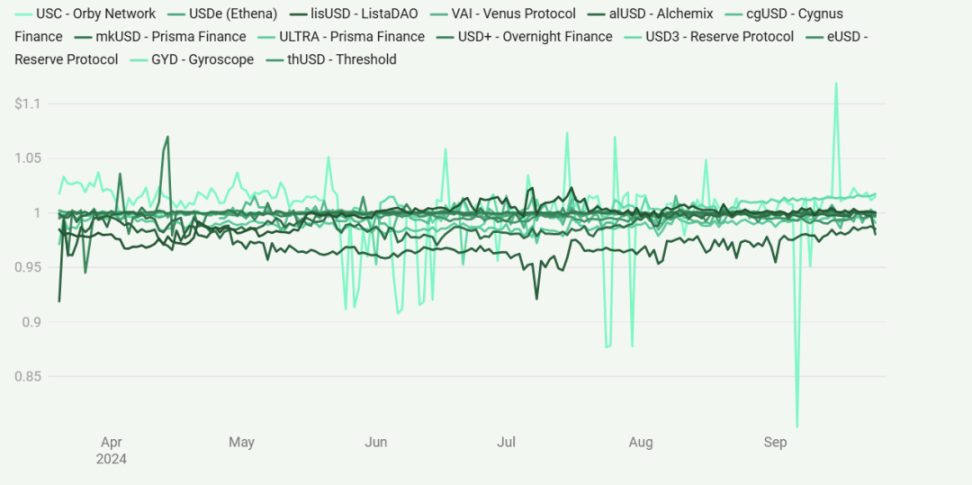
The price stability of these stablecoins reveals the differences in how various protocols maintain their pegs. For instance, USC (Orby Network) exhibits significant volatility, being one of the most price-volatile stablecoins shown in the chart. In contrast, USDe (Ethena) maintains excellent price anchoring, with minimal deviation from the $1 mark. Other stablecoins, such as USD+ (Overnight Finance) and VAI (Venus Protocol), show relatively stable performance, but their levels of stability vary.
The governance of these stablecoin protocols is typically managed through decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), using governance tokens for decision-making. While this approach enhances censorship resistance, it may lead to slower operations and lower efficiency compared to centralized models. A key challenge for crypto-collateralized stablecoins is managing the volatility of the supporting assets. To mitigate this risk, many protocols implement over-collateralization, requiring the value of the locked crypto assets to exceed the minted stablecoins. For example, the Maker protocol requires a collateralization ratio of 150% when borrowing DAI. While this method ensures stability, it results in capital inefficiency.
To address these challenges, some protocols have begun accepting other more stable cryptocurrencies as collateral, including centralized stablecoins like USDC. This strategy has been adopted by projects like DAI and FRAX, aiming to reduce volatility risk but also facing criticism for potentially reintroducing centralized risks. As the field evolves, new methods are being explored, including the use of neutralized derivative positions to maintain price stability. The price stability charts highlight the importance of these innovations, as protocols strive to achieve a delicate balance between decentralization and stability.
1. Orby Network
- Token: USC
- Supply: $18,300,000
- Yield: 18% through stable pools
- Network Support: Cronos
Orby Network is a decentralized lending protocol based on the Cronos blockchain, allowing users to borrow its native stablecoin USC without ongoing interest costs. The protocol enables users to deposit accepted collateral types into "pods" (similar to collateral debt positions) to create USC. Orby's approach replaces ongoing interest with a one-time borrowing fee and refundable liquidation reserves, aiming to provide borrowers with more predictable costs while maintaining the protocol's stability.
USC is an over-collateralized, soft-pegged stablecoin designed to maintain a 1:1 value with the U.S. dollar. It serves as a store of value, medium of exchange, and unit of account within the Orby ecosystem. The stability of USC is maintained through various mechanisms, including market operations, floating base interest rates, and redemption processes. The protocol allows users to always redeem 1 USC for collateral worth $1, which helps support the peg, especially when USC trades below $1. Although USC itself is not a native yield token, users can earn yields by depositing USC into stable pools, providing them with passive income opportunities.
To ensure the stability and security of USC, Orby implements a comprehensive risk management system. This includes a stable pool that serves as an immediate liquidity source for liquidation events. In the event of liquidation, the outstanding debt is offset by USC from the stable pool, and the collateral is distributed to the depositors of the stable pool. Additionally, Orby has implemented a "recovery mode" that activates when the total collateralization ratio (TCR) falls below a certain threshold, temporarily raising the liquidation threshold and preventing further trades that would lower the TCR.
The launch of USC as a borrowing option without ongoing interest marks a significant development in the DeFi space, particularly on the Cronos network. By eliminating ongoing interest costs, Orby aims to promote greater economic activity and capital efficiency. Users can borrow USC long-term without the pressure of compounding interest, potentially creating new opportunities for asset utilization and participation in other DeFi activities. As part of the Cronos Accelerator Program, Orby Network and its USC stablecoin are expected to play a key role in the evolving Cronos DeFi ecosystem, providing users with a unique financial tool that balances stability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness.
"Stablecoins are crucial for DeFi as they provide price stability and support broader financial activities like lending. With USC, Orby Network ensures an over-collateralized decentralized stablecoin that facilitates secure, seamless transactions while reducing volatility risks. We focus on creating a reliable, transparent stablecoin that helps DeFi users better manage volatility and participate in decentralized financial services with greater confidence." — Orby Team
2. Ethena
- Token: USDe
- Supply: $2,607,358,346
- Yield: 12%
- Network Support: Ethereum, Solana
Ethena is a protocol aimed at creating a censorship-resistant, scalable, and stable synthetic dollar called USDe. Ethena addresses the limitations of traditional stablecoins by adopting a unique "neutral hedging" strategy. The protocol uses crypto assets like Ethereum and Bitcoin as collateral, combined with short positions in perpetual futures contracts, to maintain the value stability of the collateral assets relative to the U.S. dollar. Ethena's approach aims to provide a solution independent of traditional banking infrastructure while offering attractive returns to users.
USDe is a synthetic dollar asset that maintains its peg to the U.S. dollar through "neutral hedging," meaning it hedges against the price risks of the supporting Ethereum and Bitcoin assets. Unlike traditional stablecoins backed by fiat reserves or over-collateralized crypto assets, USDe achieves its stability by combining long positions in crypto assets (primarily ETH, recently including BTC) with corresponding short positions in perpetual futures. This neutral hedging strategy ensures that USDe's value remains stable regardless of the price fluctuations of the underlying crypto assets.
When users who have undergone KYC verification and are whitelisted mint USDe directly through Ethena, they typically use USDT. Ethena then usually purchases BTC or ETH and hedges the corresponding price risk by shorting perpetual contracts, thereby creating a synthetic dollar position that is resistant to price fluctuations of the underlying assets. The protocol uses over-the-counter settlement (OES) service providers to custody collateral and manage exposure to centralized exchanges, significantly reducing counterparty risk.
The Anchoring Stability of Ethena's USDe Since Its Launch
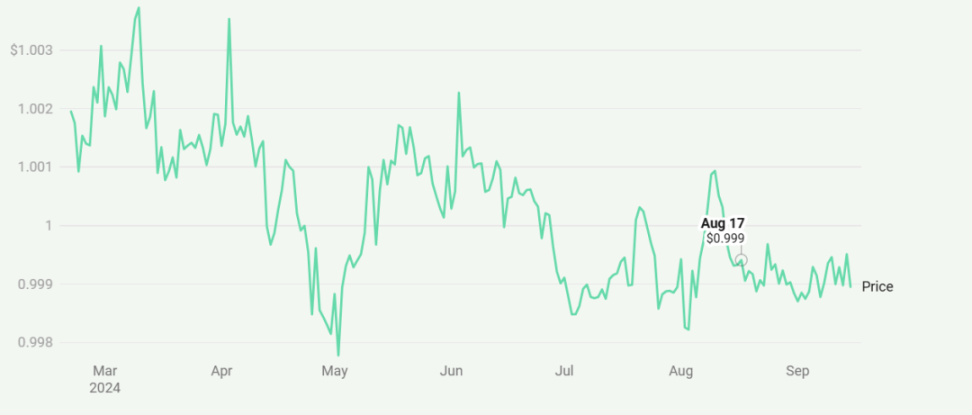
The anchoring stability of Ethena's USDe since its launch demonstrates the protocol's extraordinary ability to maintain a stable peg to the U.S. dollar, even performing well during market fluctuations in 2024. This stability addresses a major concern of initial critics who compared USDe to the failed Terra/UST. However, data shows that these concerns were largely unfounded, as the support mechanisms of the two projects are fundamentally different. Since its launch in early 2024, USDe has consistently traded within a narrow range close to $1, with a maximum deviation of only ±0.25%, which is quite impressive for a stable asset in the crypto market.
sUSDe is the staked version of USDe, representing one way Ethena implements "internet bonds." Users can stake their USDe tokens to receive sUSDe, which accumulates rewards over time. sUSDe follows the ERC-4626 token vault standard, ensuring compatibility with other DeFi protocols. As sUSDe accumulates rewards, its value relative to USDe also increases, allowing users to benefit from the yields generated by the protocol, which are distributed every eight hours.
Ethena Generates Yields Through Three Main Mechanisms
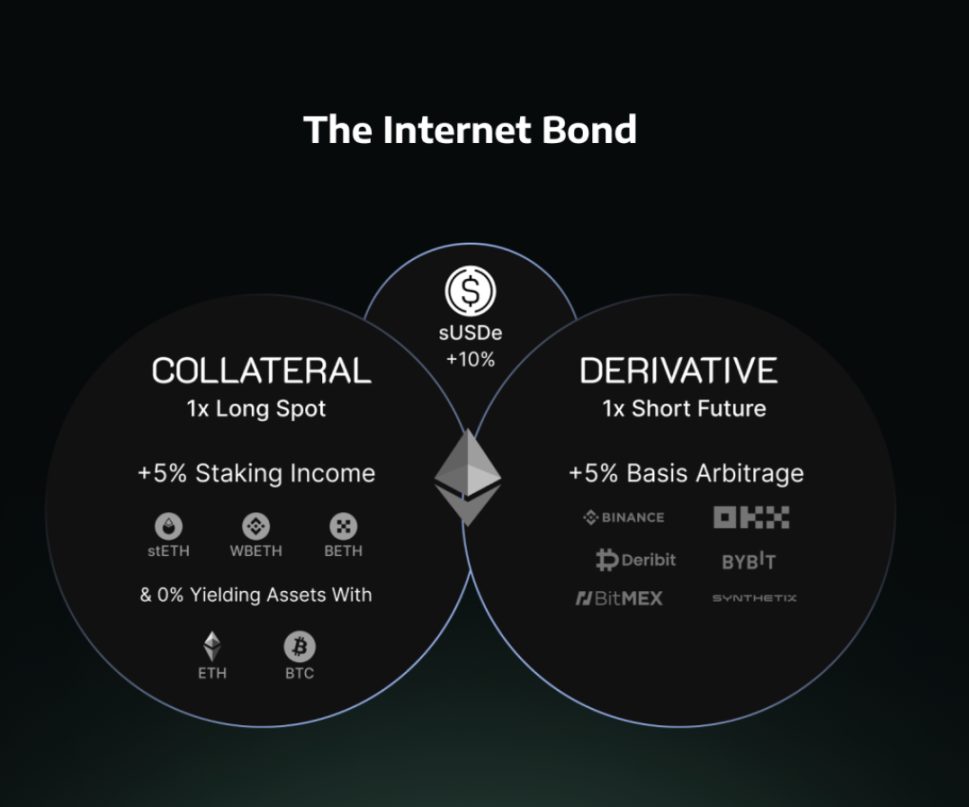
- Staking Rewards: Part of the yield comes from staking the collateral assets. For example, when ETH or liquid staking tokens like stETH are used as collateral, they generate staking rewards from the Ethereum network. These rewards include inflation from the consensus layer, fees from the execution layer, and the capture of MEV (Miner Extractable Value).
- Funding Rates of Perpetual Futures: The majority of the yield comes from the short positions in perpetual futures contracts. In the crypto market, due to widespread bullish sentiment and leverage demand, holding long positions typically requires paying funding fees to shorts. Ethena collects these funding fees by maintaining short positions. Historically, the funding rates for ETH and BTC have been positive, providing a stable source of yield for the protocol.
- Real-World Asset (RWA) Rewards: A portion of Ethena's collateral assets earns rewards by holding U.S. Treasury bonds. This combination of yield sources allows Ethena to offer attractive returns to USDe stakers. The protocol automatically manages these positions and adjusts as needed to optimize yield generation.
It is important to note that while Ethena is committed to providing sustainable returns, actual yields may fluctuate due to market conditions, funding rates, and staking rewards. The protocol has implemented risk management strategies, including the establishment of a reserve fund to help protect against potential negative funding rate scenarios, and dynamically allocates more RWA assets beforehand.
Through this innovative synthetic dollar and yield generation approach, Ethena has rapidly made progress in the DeFi space, attracting a significant total locked value (TVL) and establishing its important position in the stablecoin market.
3. Lista DAO
- Token: lisUSD
- Supply: $36,032,408
- Yield: 5.16%
- Network Support: Binance
Lista DAO combines liquid staking and collateral debt positions to provide users with a unique yield generation and lending platform. Launched in 2023, Lista DAO aims to address the capital efficiency issues faced by over-collateralized stablecoins while leveraging the advantages of Proof-of-Stake rewards and yield-generating assets. The protocol employs a dual-token model, including the decentralized stablecoin lisUSD and the governance token LISTA.
lisUSD is a decentralized stablecoin, referred to by the protocol as a "destablecoin." Unlike traditional stablecoins that pursue absolute price parity with fiat currencies, lisUSD is designed to maintain a relatively stable value while allowing for some price fluctuations. This approach makes lisUSD more capital-efficient in its usage and better able to respond to market conditions. The stability of lisUSD is maintained through a combination of over-collateralization and algorithmic mechanisms, including dynamically adjusted lending rates based on market prices.
When users deposit supported collateral assets (such as BNB, ETH, stablecoins, and other cryptocurrencies) into the protocol, lisUSD is generated. Compared to other decentralized stablecoins, lisUSD typically has a lower collateralization ratio, thereby improving capital efficiency for borrowers. A unique feature of lisUSD is its integration with Lista DAO's liquid staking functionality. The protocol can generate yields on the deposited collateral through staking rewards and other DeFi strategies, which helps enhance the overall sustainability of the system and potentially reduce borrowing costs for users.

A key innovation of lisUSD is its price stability mechanism. When the trading price of lisUSD exceeds the target price, the protocol incentivizes users to borrow more lisUSD by lowering lending rates and reducing mining rewards for lisUSD. Conversely, when the trading price of lisUSD falls below the target price, the protocol raises lending rates and increases mining rewards for lisUSD to encourage users to purchase lisUSD from the market to repay debts. This dynamic approach enables more organic price stability compared to traditional algorithmic stablecoins.
Lista DAO also introduces an algorithmic market operation (AMO) system for lisUSD, similar to the monetary policy contracts used by Curve Finance for crvUSD. This system introduces dynamically adjusted lending rates based on market conditions, further enhancing the price stability of lisUSD. The AMO system considers factors such as the current price of lisUSD determined by oracle data and preset parameters to calculate appropriate rates. This mechanism allows the protocol to respond more effectively to market pressures and maintain the price peg of lisUSD without solely relying on user arbitrage activities.
4. Venus Protocol
- Token: VAI
- Supply: $4,765,896
- Yield: 9.83%
- Network Support: Binance
Venus Protocol is an algorithmic money market system built on the BNB Chain. Launched in 2020, it allows users to provide collateral, borrow assets, and mint synthetic stablecoins within a decentralized platform. Venus combines elements from successful protocols like Maker and Compound to offer lending and stablecoin minting functionalities.
The protocol aims to enhance performance in key areas such as risk management, decentralization, and user experience. Venus introduces several new features, such as isolation pools for securely introducing niche assets, multi-source price oracles to reduce single point of failure risks, and mechanisms to maintain the stability of its native stablecoin. Additionally, Venus has implemented an innovative governance model that employs different proposal tracks to balance the need for rapid parameter adjustments with the need for thorough reviews of significant changes.
VAI is the primary stablecoin of Venus Protocol, designed to maintain a peg to the U.S. dollar. Users can mint VAI using vTokens generated from previously provided collateral assets, allowing them to maximize the capital efficiency of their collateral. The stability of VAI is maintained through a stability fee system, which users must pay when repaying minted VAI.
The stability fee is calculated per block and added to the user's minted VAI balance. It consists of a base rate that users must always pay and a variable rate that depends on the current price of VAI. This mechanism encourages users to choose to mint or burn VAI during price fluctuations, thereby promoting price stability. When the price of VAI falls below $1, the stability fee increases, encouraging borrowers to repay loans and reduce circulating supply; conversely, when the price of VAI exceeds $1, the fee remains at the base rate, potentially encouraging more minting.
Venus has also implemented other measures to support the stability of VAI, including providing liquidity for the VAI/USDT trading pair on PancakeSwap to facilitate smooth trading and mitigate market volatility. Additionally, the protocol sets a cap on the global minting volume of VAI to reduce the likelihood of de-pegging and unnecessary liquidations. Furthermore, Venus mandates that liquidators must first liquidate VAI before liquidating other assets in cases of insufficient account holdings, helping to reduce bad debt associated with VAI.
5. Alchemix
- Token: alUSD
- Supply: $163,764,914
- Yield: Not applicable
- Network Support: Binance
Alchemix was launched in 2021 and operates on the Ethereum blockchain, aiming to provide users with a self-repaying loan mechanism through yield farming strategies. The protocol allows users to deposit collateral, typically in the form of stablecoins like DAI, while they can borrow against their collateral, with the initial deposit generating yields to automatically repay the loan.
The core product of Alchemix is its synthetic token alUSD, which represents the user's future yield. When users deposit DAI into the Alchemix vault, they can borrow alUSD equivalent to 50% of the value of their collateral. The deposited DAI is then used to generate yields, primarily through Yearn Finance's vaults. As yields accumulate, they are automatically used to repay the user's debt, effectively creating a self-repaying loan system. This innovative approach eliminates the need for users to manually manage loan repayments and reduces the liquidation risks commonly found in other DeFi lending platforms.
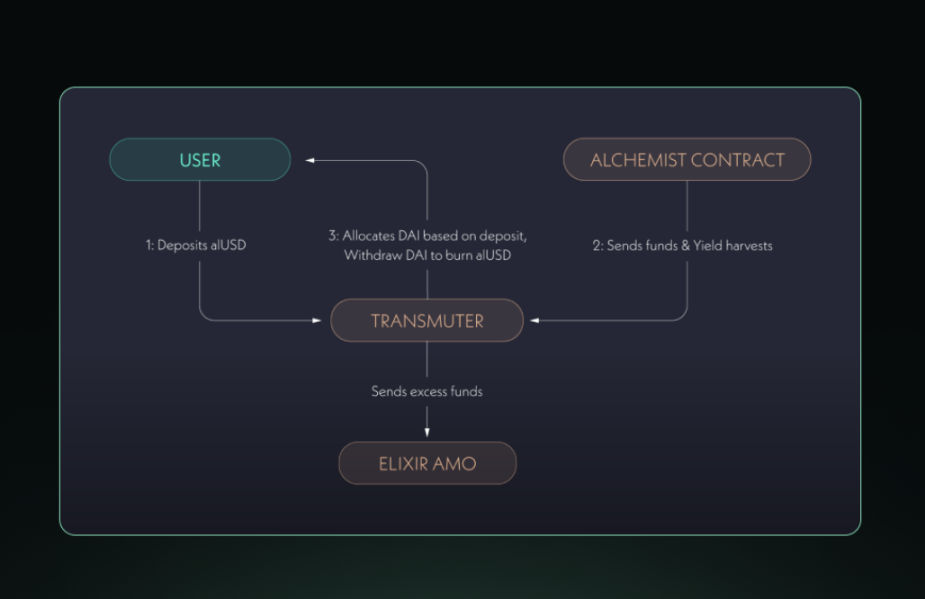
A key component of the Alchemix ecosystem is the Transmuter, a mechanism designed to maintain the peg of alUSD to the U.S. dollar. The Transmuter allows users to convert alUSD back to DAI at a 1:1 ratio, ensuring the stability and liquidity of the synthetic asset. Additionally, the yields generated by the protocol's strategies also flow into the Transmuter, further supporting the conversion process and the overall stability of the system.
The native governance token of Alchemix, ALCX, plays a crucial role in the protocol's decentralized governance model. ALCX holders can participate in voting to decide on important protocol decisions, such as adjusting parameters, introducing new features, and allocating funds for development and ecosystem growth. The token was initially distributed through a fair launch mechanism, with no pre-mining or team allocation, aimed at achieving a more equitable distribution between users and stakeholders.
Price Stability of Alchemix's alUSD Since Its Launch
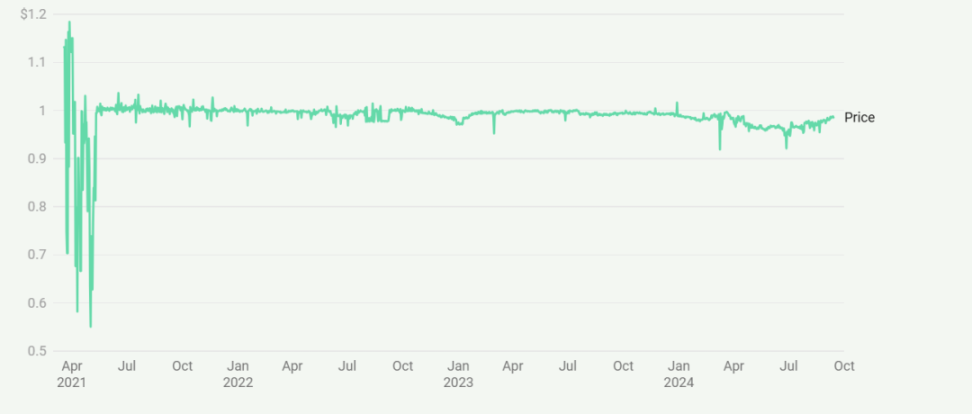
The protocol faces several challenges, including maintaining the stability of its synthetic assets and managing the complexities of integrating various yield strategies. However, Alchemix continues to evolve, exploring new collateral types and yield sources to expand its offerings and improve capital efficiency. As the DeFi space matures, Alchemix stands out as an example of innovative financial engineering, providing users with a unique way to leverage their assets while minimizing active management and risk.
The protocol faces several challenges, including maintaining the stability of its synthetic assets and managing the complexities of integrating various yield strategies. However, Alchemix continues to evolve, exploring new collateral types and yield sources to expand its offerings and improve capital efficiency. As the DeFi space matures, Alchemix stands out as an example of innovative financial engineering, providing users with a unique way to leverage their assets while minimizing active management and risk.
6. Cygnus Finance
- Token: cgUSD
- Supply: $33,351,937
- Yield: 15.3%
- Network Support: Base
Cygnus Finance operates on the Base blockchain, aiming to bridge traditional finance and DeFi through its native stablecoin cgUSD. The project's core product is a yield-bearing stablecoin backed by short-term U.S. Treasury bonds, allowing users to earn interest while maintaining stability. By enabling the minting of cgUSD using assets from multiple chains, Cygnus seeks to enhance cross-chain liquidity and accessibility within the DeFi ecosystem.
Cygnus Finance employs a re-benchmarking mechanism that directly allocates the interest from U.S. Treasury bonds to cgUSD holders. This system automatically increases users' cgUSD balances as interest accumulates, effectively creating a self-growing stablecoin. The protocol maintains a balance between the total supply of cgUSD and its underlying asset portfolio, which includes on-chain stablecoins and off-chain Treasury bonds, to ensure a 1:1 exchange rate with USDC on every New York banking day.
cgUSD is an ERC20 re-benchmark token designed to maintain a stable value of $1 while allowing holders' balances to grow with accumulated interest. This daily re-benchmarking aligns with U.S. banking hours, creating a unique combination of traditional financial cycles and blockchain technology. Users can mint cgUSD at a 1:1 ratio (excluding fees) with USDC and redeem at the same ratio, providing flexibility and yield generation potential within the stablecoin framework.
To enhance compatibility with various DeFi protocols, Cygnus has launched wcgUSD, a wrapped version of cgUSD. While wcgUSD maintains a constant token supply, its price reflects the accumulated interest growth over time. This non-re-benchmark design makes wcgUSD more suitable for integration with DeFi platforms that may not support re-benchmark tokens, expanding Cygnus's application within a broader ecosystem.
Cygnus employs various mechanisms to maintain the stability and peg of cgUSD. These mechanisms include the "Transmuter" tool, which enables a 1:1 conversion between cgUSD and USDC, and the "Elixir AMO" (Automated Market Operator) to manage liquidity and price stability. The protocol also implements a 5-7 day withdrawal process to balance users' liquidity needs with the management of the underlying Treasury bond portfolio.
7. Prisma Finance
Prisma Finance allows users to use LST (Liquid Staking Tokens) as collateral to mint stablecoin mkUSD and use LRT (Liquid Re-staking Tokens) as collateral to mint ULTRA, creating opportunities for improved capital efficiency and yield generation. Prisma's codebase is based on Liquity and is fully immutable, enhancing the protocol's security and decentralization.
The governance of the protocol is managed by Prisma DAO, responsible for controlling parameters, token issuance, and protocol fees. This structure allows the protocol to respond flexibly to market conditions while maintaining decentralized control. Prisma integrates with other DeFi protocols, particularly Curve and Convex Finance, to create a capital-efficient system where users can earn from multiple sources of yield.
Price Stability of mkUSD and ULTRA Since Their Launch
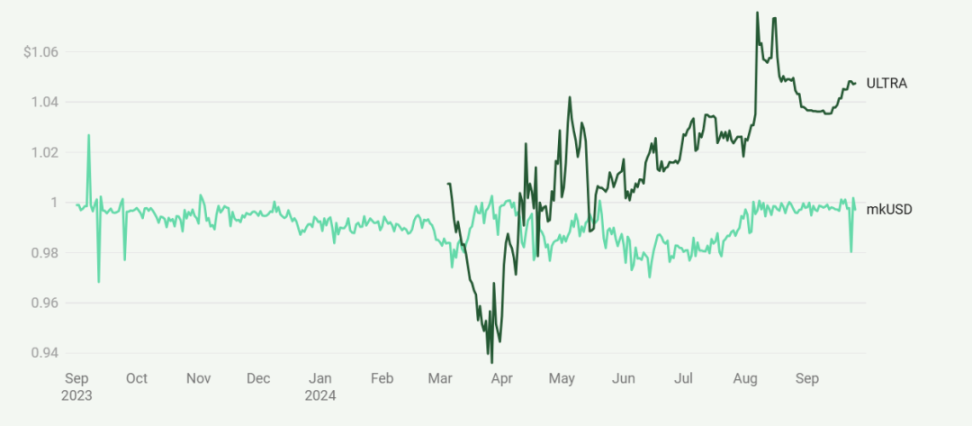
Prisma employs a risk management framework that includes asset analysis before introducing new collateral types. The protocol uses mechanisms such as minimum collateral ratios, liquidation, and stability pools to maintain solvency. These features are designed to support the peg stability of both stablecoins. However, the actual effects vary. As shown, mkUSD exhibits less volatility and is generally closer to its target value, while ULTRA shows more significant price fluctuations, often deviating from the $1 target. This indicates that maintaining sustained price stability remains a challenge, especially for ULTRA.
8. mkUSD
- Token: mkUSD
- Supply: $3,893,866
- Yield: 6.45%
- Network Support: Ethereum
mkUSD is the primary stablecoin issued by the Prisma protocol. Users can mint mkUSD by depositing supported LST (Liquid Staking Tokens) as collateral. The protocol requires each vault to have at least $2,000 mkUSD in debt, which includes a $200 liquidation reserve. These reserves are used to cover potential liquidation costs.
The stability of mkUSD is maintained through various mechanisms, including a redemption mechanism that allows users to exchange mkUSD for collateral at face value, and a dynamic fee system adjusted based on market conditions. The protocol also utilizes a stability pool as the primary line of defense against solvency crises, allowing mkUSD holders to deposit tokens and profit through liquidation.
9. ULTRA
- Token: ULTRA
- Supply: $221,065
- Yield: 14.09%
- Network Support: Ethereum
ULTRA aims to meet the growing demand for LRT (Liquid Re-staking Tokens), similar to Prisma's initial approach to LST. ULTRA allows users to gain additional liquidity while retaining the yield benefits of LRT ownership. PrismaLRT is integrated into the main Prisma interface, allowing users to use LRT as collateral to borrow ULTRA. This setup enables LRT holders to unlock capital in the form of stablecoins while still maintaining their rewards and potential earnings.
10. Overnight
- Token: USD+
- Supply: $75,580,596
- Yield: 10.3%
- Network Support: Optimism, Arbitrum, ZkSync, Linea, Base, Binance, Blast, Polygon
Overnight Finance is a protocol focused on asset management, particularly specializing in neutral risk strategies. The platform aims to simplify cash management for stablecoins and maximize users' yield generation. Initially launched on the Polygon network, Overnight Finance has since expanded to other EVM chains, offering a range of products centered around its flagship stablecoin USD+. The protocol's approach combines the stability of traditional financial instruments with the advantages of blockchain technology, providing users with innovative solutions to enhance yield potential in the DeFi space.
USD+ is the main token of the Overnight Finance protocol, designed as a fully collateralized, re-benchmarked stablecoin pegged 1:1 to USDC. Unlike algorithmic stablecoins, USD+ is fully backed by highly liquid and reliable stablecoins (such as USDC, USDT, and DAI). The token employs a unique minting and burning mechanism: when users purchase USD+, new tokens are minted; when they exchange USD+ for USDC, the tokens are burned. This method ensures that the supply of USD+ is proportional to the collateral, maintaining its peg and stability.
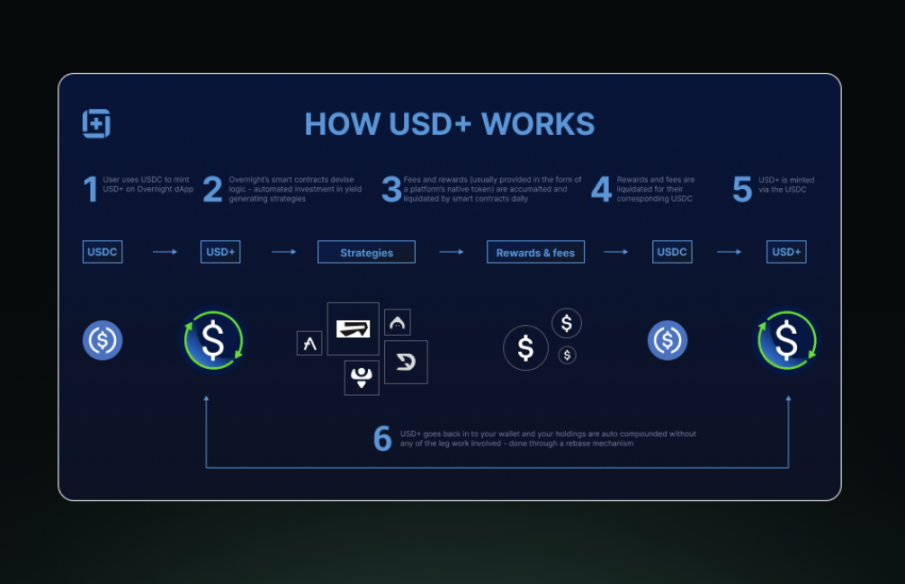
The uniqueness of USD+ lies in its yield generation capability. The collateral supporting USD+ is deployed in a diversified array of low-risk DeFi strategies, including lending protocols, stable liquidity pools, and other conservative yield farming opportunities. These strategies generate yields daily, which are then passed on to USD+ holders through the re-benchmarking mechanism. Each day, rewards and fees from these strategies are collected, converted into USDC, and used to mint new USD+ tokens. These newly minted tokens are then proportionally distributed to all USD+ holders, effectively increasing their token balances without requiring any action from users.
This daily re-benchmarking feature allows USD+ to function both as a stablecoin and as a yield-bearing asset. Users enjoy the stability of a token pegged to USDC while also earning passive income. Yields may vary daily based on the performance of the underlying strategies, but Overnight Finance reports an average annual percentage yield (APY) ranging from 5% to 15%. Additionally, USD+ can be used in liquidity pools and other DeFi applications, allowing users to potentially stack yields and further maximize their returns while still maintaining exposure to stable assets.
11. Reserve Protocol
Reserve Protocol is a platform that allows for the permissionless creation of asset-backed, yield-bearing, over-collateralized stablecoins on Ethereum. The platform aims to provide a scalable decentralized alternative to address the volatility of cryptocurrencies. Reserve Protocol enables anyone to deploy their own Reserve stablecoin (RToken) and manage it through a customized collateral basket, governance system, and yield distribution model. This open approach is designed to promote exploration and competition in on-chain currency design to find optimal solutions.
The protocol utilizes a unique system where RToken is fully backed by a basket of ERC-20 tokens, which can be minted or redeemed for its underlying collateral at any time. To enhance stability and security, RToken can be over-collateralized using Reserve Rights (RSR, the native token of the protocol). RSR holders can stake their tokens on specific RTokens, providing additional collateral default protection and earning a share of the income generated by the RToken.
12. USD3
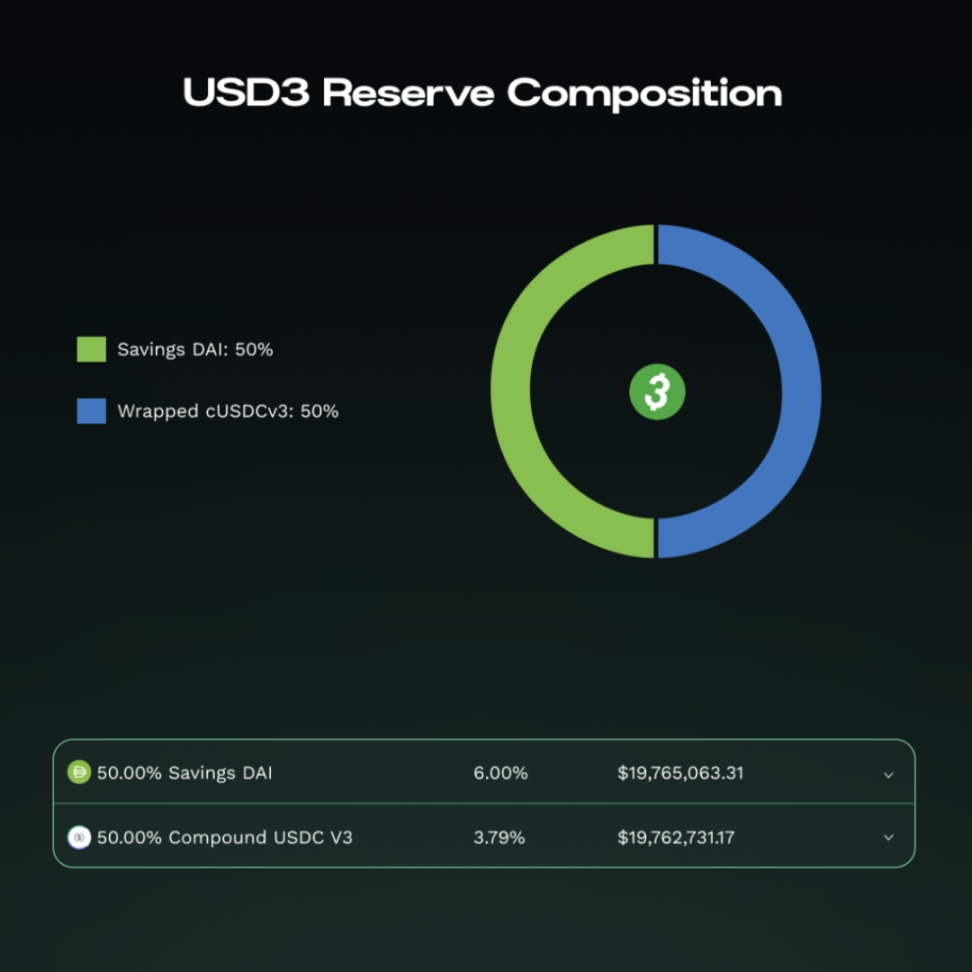
USD3, also known as Web 3 Dollar, is the newest stablecoin added to the Reserve Protocol ecosystem. It aims to become the native currency of Web3, backed by a basket of high-rated stablecoins, including sDAI and Compound's V3 USDC. This collateral composition is designed to provide a balance between stability and yield generation, with USD3 targeting an annual percentage yield (APY) of up to 10%.
The governance structure of USD3 allocates 85% of the generated income to USD3 holders, 12% to RSR stakers, and 3% to the treasury for growth initiatives. This model incentivizes holding and staking behavior, potentially attracting a broad user base. USD3 also emphasizes transparency and security, achieved through on-chain reserve proofs and the over-collateralization of RSR. As a new member of the Reserve Protocol ecosystem, USD3 aims to position itself as an attractive option for DeFi users, DAO organizations, and others seeking stable, yield-bearing assets in the Web3 space.
13. eUSD
- Token: eUSD
- Supply: $27,498,534
- Yield: 4.18%
- Network Support: Ethereum
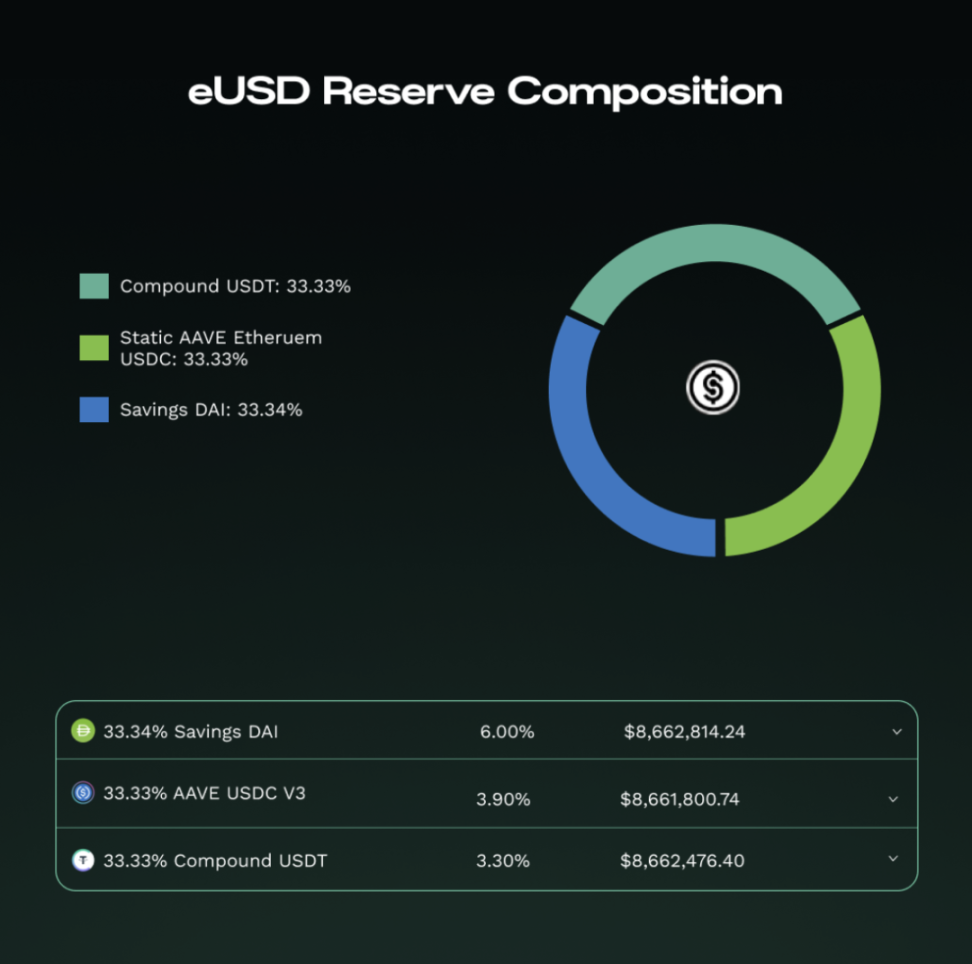
eUSD (Electronic Dollar) is one of the flagship stablecoins created by the Reserve Protocol. Launched in February 2023, it is designed as a fully collateralized stablecoin pegged to the U.S. dollar. The collateral basket of eUSD consists of yield-bearing stablecoins, including Aave's USDC and USDT deposits (saUSDC and saUSDT), as well as Compound's USDC and USDT deposits (cUSDC and cUSDT), each accounting for 25% of the collateral basket. This composition allows eUSD to maintain stability while also providing yields to holders.
A unique feature of eUSD is its integration with MobileCoin's privacy blockchain. This integration enables eUSD to operate as a privacy-focused digital dollar on the MobileCoin network, facilitating transfers between Ethereum and MobileCoin through a permissioned bridge. eUSD employs a governance model where users holding eusdRSR (staked RSR) can participate in decision-making processes, including adjustments to the collateral composition and protocol parameters. The stablecoin has demonstrated strong resilience, successfully navigating challenges such as the USDC de-pegging event in March 2023.
14. Gyroscope
- Token: GYD
- Supply: $23,203,354
- Yield: 11.98%
- Network Support: Ethereum
Gyroscope is a project dedicated to developing an "all-weather" stablecoin, Gyro Dollar (GYD). Their goal is to create a fully collateralized, decentralized stablecoin capable of withstanding various risks in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.

15. Gyroscope
The key innovation behind GYD lies in its "all-weather" reserve design. Unlike many existing stablecoins that are supported by a single asset or a small number of assets, GYD is backed by a diversified portfolio of crypto assets spread across multiple independent "vaults." This layered reserve structure is designed to isolate different types of risks—including price, counterparty, regulatory, and technological risks. If a particular vault or asset fails, the entire reserve remains unaffected.
GYD utilizes an algorithmic pricing mechanism called Dynamic Stability Mechanism (DSM) to maintain its peg. DSM automatically adjusts the minting and redemption rates based on market conditions and reserve health. Under normal circumstances, GYD can be minted or redeemed close to $1. If the reserves come under pressure, DSM can impose redemption fees or restrictions to prevent a run while still allowing for orderly exits. This mechanism aims to instill confidence in users that GYD can return to its peg even during crises.
The project continuously improves and refines its mechanisms based on real market conditions. While the long-term resilience of Gyroscope's approach requires time to validate, the project demonstrates a commitment to combining academic research with practical applications, providing a unique all-weather stablecoin design to address market challenges.
16. Threshold
- Token: thUSD
- Supply: $202,423,989
- Yield: Through Stability Pools
- Network Support: Ethereum
Threshold is a decentralized network that provides cryptographic services and infrastructure for blockchain applications. The network was formed in 2023 through the merger of NuCypher and Keep Network, offering solutions such as tBTC—a decentralized bridge from Bitcoin to Ethereum—and Threshold access control for conditional and private data sharing. The network is governed by T token holders, who can support various cryptographic services by staking and running nodes.
Threshold USD (thUSD) is a stablecoin soft-pegged to the U.S. dollar, backed by ETH and tBTC as collateral. It has a minimum collateralization ratio of 110%, allowing users to borrow thUSD against their holdings of ETH or tBTC. thUSD is designed as an improved fork of the Liquity protocol, with the main differences being multi-collateral support and a Protocol Controlled Value (PCV) model.
The stability of thUSD is maintained through various mechanisms, including the Dynamic Stability Mechanism (DSM) and Concentrated Liquidity Pools (CLPs). DSM adjusts the minting and redemption rates based on market conditions and reserve health, while CLPs support efficient trading around the target price of $1.
Price Stability of Threshold thUSD
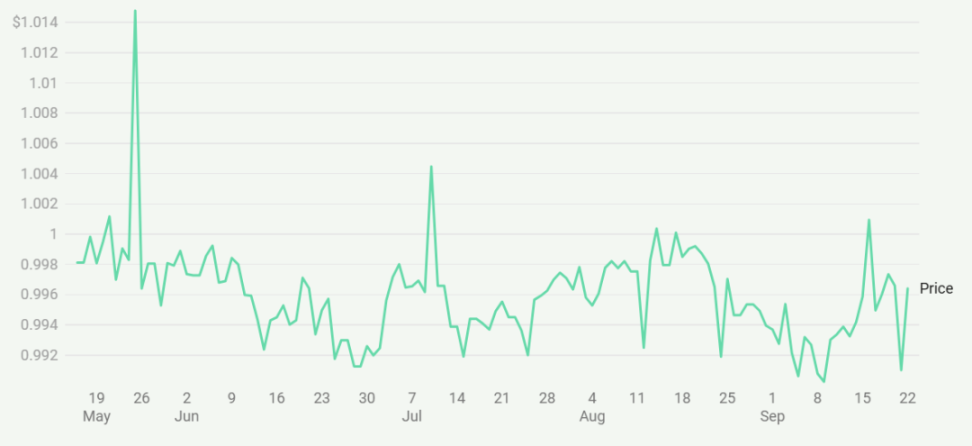
From the price stability chart of thUSD, the current mechanisms appear to be functioning well, despite the project being in its early stages. Data shows that thUSD's price has remained relatively stable, with the largest deviation reaching 1.014771343. This is a deviation of 14.77 basis points, or 1.477% above the target of $1. Such a small deviation indicates that Threshold's method of maintaining price stability is currently quite successful. However, continued observation is needed to see if it can maintain this stability in the long term.
### Case Study: Algorithmic Stablecoins and Hybrid Stablecoins
Algorithmic Stablecoins and Hybrid Stablecoins
Algorithmic stablecoins attempt to solve the trilemma of stablecoins, aiming to achieve price stability, decentralization, and capital efficiency simultaneously. Unlike fiat-backed or over-collateralized crypto stablecoins, algorithmic stablecoins utilize smart contracts to balance supply and demand, maintaining price stability without traditional collateral. Generally, this system employs a two-token model, one being the stablecoin and the other a floating price token. The protocol ensures that users can always exchange a stablecoin for an equivalent floating token worth $1, providing an incentive for arbitrageurs to stabilize the price through market actions. When demand for the stablecoin fluctuates, the protocol adjusts the supply of the two tokens to stabilize the price.
However, the collapse of TerraUSD (UST) in May 2022 exposed the vulnerabilities of algorithmic stablecoins. UST was a stablecoin pegged to the U.S. dollar and backed by the LUNA token, but it experienced a severe de-pegging event, ultimately falling into what is known as a "death spiral." This event revealed the risks inherent in systems that rely solely on market incentives and algorithmic mechanisms to maintain stability. When UST's value plummeted, the system accelerated the minting of LUNA tokens in an attempt to restore the price peg, leading to severe inflation of LUNA and further undermining confidence in the system. Despite attempts by the Luna Foundation to stabilize UST through its crypto reserves, the system ultimately collapsed, resulting in significant losses and damaging confidence in the entire stablecoin market.
Following the collapse of UST, the stablecoin market began to shift towards a hybrid model, combining algorithmic mechanisms with partial collateralization. These hybrid stablecoins aim to leverage the capital efficiency of algorithmic models while reducing risk through partial backing by crypto assets. Frax Finance's FRAX is an example of this model, utilizing algorithmic mechanisms and crypto collateral to maintain its peg. This shift in model reflects the ongoing exploration of balance between stability, efficiency, and decentralization in the stablecoin space. As the market matures, more innovations are expected to emerge, attempting to address the vulnerabilities exposed by past failures while retaining the advantages of algorithmic models.
1. Reflexer
- Token: RAI
- Supply: $3,561,999
- Yield: Not Applicable
- Networks: Ethereum, Fantom, Polygon, Solana, Avalanche, Arbitrum, Optimism
Reflexer Labs is driving innovation in the stablecoin market by developing non-pegged stable assets, with RAI (Reflex Index) being their flagship product. Founded in 2020 by Stefan Ionescu and Ameen Soleimani, Reflexer draws inspiration from the DAI concept in the MakerDAO whitepaper. The core idea of Reflexer is to achieve price stability without relying on a fixed peg, thereby providing more flexible and resilient financial tools within the decentralized finance ecosystem. Reflexer employs advanced control theory and automation mechanisms to manage assets, minimizing manual management and intervention.
RAI was launched in February 2021 as Reflexer’s first and primary product—a stable asset collateralized by ETH and not pegged to a fixed price. Unlike traditional stablecoins that target a fixed value (usually $1), RAI's price fluctuates with market forces while still maintaining relative stability. The stability of RAI hinges on its redemption price, which acts as a floating target that the system strives to guide RAI's market price towards. The redemption price is dynamically adjusted by an on-chain automatic controller using a proportional-integral (PI) feedback mechanism. When RAI's market price deviates from the redemption price, the controller adjusts the interest rate (referred to as the redemption rate), incentivizing users to mint more RAI when the price is too high or repay their debts when the price is too low.
Price Stability of RAI Since Its Launch
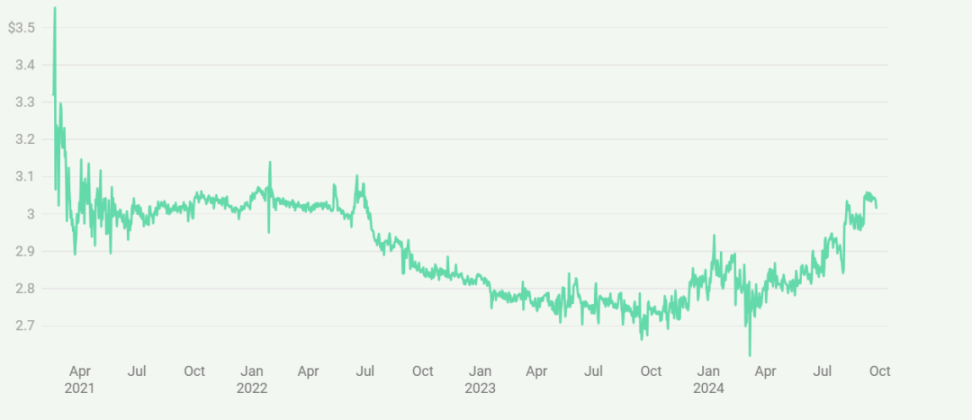
Although RAI is an algorithmic stablecoin not pegged to a specific value, its price has remained relatively stable since its launch. The chart above shows the price history of RAI, indicating that it has maintained relative stability even in the face of significant market events. Since its inception, RAI has experienced several market upheavals that negatively impacted the overall crypto market environment, such as the collapse of FTX in November 2022. The chart shows that while RAI's price has fluctuated, it has generally remained between approximately $2.75 and $3.25. RAI's performance demonstrates that its stability mechanism, which relies on market incentives rather than a fixed peg, can provide stability even during periods of significant market pressure, serving as a good example for the design of algorithmic stablecoins.
Reflexer positions RAI as a potential solution to broader economic challenges, such as the Triffin Dilemma. The Triffin Dilemma refers to the conflict of interest faced by countries whose currencies serve as global reserve currencies, balancing short-term domestic goals with long-term international objectives. By creating a stable asset that is not pegged to any national currency and governed by transparent, algorithmic rules, RAI aims to provide a truly neutral global reserve asset for the DeFi ecosystem and the broader economic environment. While the adoption and long-term success of RAI will take time to validate, its design of stability without relying on a fixed peg represents a significant advancement in the evolution of decentralized finance and monetary systems.
"RAI is the first collateralized debt asset to use a market feedback mechanism to reprice the face value of stable assets. It is a milestone in the evolution of DeFi towards more resilient, automated, and liberated finance. Reflexer continues to explore decentralized stable assets in this field." — Bert Kellerman, Research Director
2. Ampleforth
- Token: AMPL
- Supply: $78,835,736
- Yield: Not Applicable
- Network: Ethereum
Ampleforth is a protocol dedicated to creating a more stable and flexible digital currency. Since its launch in 2019, Ampleforth's AMPL has adopted a unique price stabilization method by adjusting the token supply rather than pegging it to external assets.
The core mechanism behind AMPL is the elastic supply model. Unlike Bitcoin, which maintains a fixed supply, or most stablecoins that maintain a fixed peg, the Ampleforth protocol algorithmically increases or decreases the total supply of AMPL based on demand. When demand increases and the price of AMPL rises above $1, the protocol mints new tokens and distributes them proportionally to all holders, increasing supply to pull the price back down. Conversely, when demand decreases and the price falls below $1, the protocol destroys tokens from all wallets to reduce supply, thereby pushing the price back up. Importantly, these supply adjustments keep each holder's relative share in the network unchanged.
The goal of this elastic supply approach is to create a digital asset that can maintain purchasing power while also serving as a stable unit of account, allowing for free price fluctuations. The target price for AMPL is not a precise $1, but rather equivalent to the purchasing power of $1 in 2019 (adjusted for inflation). By expanding supply in bull markets and contracting supply in bear markets, AMPL seeks to reduce volatility compared to fixed-supply cryptocurrencies without relying on fiat reserves or centralized control.
Ampleforth's design offers several unique advantages. As an uncollateralized asset not pegged to a fixed value, it avoids the centralization risks of fiat-backed stablecoins and the complex collateral requirements of crypto-collateralized stablecoins. The elastic supply means that AMPL can expand according to demand without being limited by an artificial supply cap. Moreover, by maintaining purchasing power, AMPL aims to serve as a unit of account for contracts and lending, a key monetary attribute that most cryptocurrencies lack due to high volatility. However, AMPL also faces challenges regarding user acceptance and understanding of its innovative supply adjustment mechanism. For users accustomed to fixed supply amounts, the daily changes in token supply and individual wallet balances can be confusing. Additionally, despite being designed for stability, AMPL may still experience significant short-term price fluctuations in situations where demand changes rapidly, outpacing supply adjustments.
Conclusion
Since its inception, the stablecoin ecosystem has demonstrated significant growth and innovation, evolving from simple fiat-backed tokens to a diverse array of models that include crypto-collateralized, algorithmic stablecoins, and hybrid models. This report explores various stablecoin projects, each with its unique mechanisms for maintaining price stability and providing utility. From established players like Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) to emerging projects like Ethena's USDe and Usual's USD0, the market continues to expand in response to the demand for stable assets in trading, remittances, and decentralized finance applications.
Fiat-backed stablecoins, such as USDC and USDT, still dominate the market as they are considered stable and user-friendly. However, there is growing interest in more decentralized alternatives. Crypto-collateralized stablecoins like DAI and innovative projects like Reflexer’s RAI are gaining attention for their censorship-resistant features and reduced reliance on traditional financial systems. Meanwhile, algorithmic and hybrid models like Frax and Ampleforth are attempting to achieve stability through partial collateralization, although they still face challenges in maintaining user confidence and peg stability.
The collapse of TerraUSD (UST) in 2022 was a significant event in the development of stablecoins, exposing the potential risks of purely algorithmic models and prompting the market to shift towards more robust partially collateralized designs. This event, along with regulatory scrutiny surrounding Binance USD (BUSD), highlighted the ongoing challenges faced by the stablecoin industry, including the need for compliance, transparency, and effective risk management.
As the stablecoin market matures, several trends are becoming apparent. There is an increasing focus on transparency and compliance, with many projects beginning to regularly publish their reserve proofs. Yield-bearing stablecoins, such as Aave's GHO and Ethena's USDe, are becoming increasingly popular, providing users with opportunities for passive income. Additionally, the expansion of stablecoins across multiple blockchain networks is enhancing interoperability and accessibility. Looking ahead, the stablecoin ecosystem is likely to continue evolving, with regulatory frameworks, technological innovations, and potential new application scenarios shaping its future direction.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



