Stablecoins have a huge appeal to Nigeria, as they can reform the remittance system, expand financial inclusion, and provide new investment opportunities, but they also face significant challenges.
Author: Titilola Shittu
Translated by: Plain Blockchain
As the country with the largest population in Africa, Nigeria is a global leader in cryptocurrency trading volume. Despite some restrictions, young Nigerians view cryptocurrencies as a way to combat inflation and earn money online.
In early 2023, the situation was unstable as the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) banned banks from collaborating with cryptocurrency companies. However, in December 2023, the CBN lifted the ban, indicating a potential move towards a more regulated cryptocurrency market.
Recently, in May 2024, the situation changed again. The government classified cryptocurrencies as a national security risk, and some fintech companies are now blocking cryptocurrency trading.
According to CBN regulations, we will close any accounts involved in cryptocurrency or other virtual asset transactions and share their details with the relevant authorities - notice issued by Moniepoint on May 2, 2024.
This article will delve into the uses and challenges of stablecoins in Nigeria. So, let's start with the importance of stablecoins.

Table of Contents
∘ Why Do We Need Stablecoins?
∘ Types of Stablecoins
∘ CBN and Stablecoins in Nigeria
∘ Five Major Use Cases of Stablecoins in Nigeria
∘ Challenges Faced by Stablecoin Adoption
∘ Future Outlook
∘ Key Points
∘ References
1. Why Do We Need Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are designed to maintain a stable price and are typically pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar. Unlike volatile traditional cryptocurrencies, stablecoins aim to maintain a stable value relative to their pegged currency.

Different stablecoins achieve stability through various methods, such as holding reserves of the pegged currency (based on fiat currency) or other crypto assets (based on cryptocurrencies). Like other cryptocurrencies, stablecoins can be used for digital transactions, offering potential advantages in speed and cost.
The Nigerian currency, the Naira, has long been plagued by inflation, with prices typically rising over time, leading to a decrease in purchasing power. In contrast, stablecoins are designed to maintain relatively stable prices. Due to their peg to reserve assets like the US dollar, their value fluctuates much less than the Naira, making them a more attractive store of value.
For example, if you buy a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar today, its value should theoretically remain close to $1 even if the Naira depreciates. This allows you to maintain purchasing power over time, unlike the Naira, which may depreciate due to inflation.
2. Types of Stablecoins
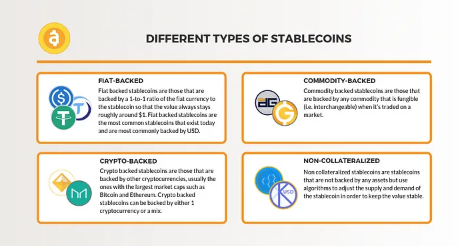
Stablecoins achieve stability through different mechanisms and can be divided into four main types:
Fiat-collateralized stablecoins: This is the most common type, backed by reserves of real-world currencies typically held in bank accounts. Each circulating stablecoin has a corresponding amount of reserve currency stored. For example, Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) are pegged to the US dollar.
Commodity-collateralized stablecoins: These stablecoins use commodities such as gold, silver, or even real estate as collateral. The value of stablecoins is pegged to the value of the underlying commodity. Due to the complexity of managing physical assets, there are fewer examples of this type of stablecoin, but Pax Gold (PAXG), backed by physical gold reserves, is a popular choice.
Types of Stablecoins
1) Cryptocurrency-collateralized stablecoins: These stablecoins are collateralized by other cryptocurrencies, typically well-established ones like Bitcoin or Ethereum. The value of stablecoins depends on the value of the supporting cryptocurrency. This method is complex because the underlying cryptocurrency itself may be unstable. DAI is a well-known example.
2) Algorithmic stablecoins: Also known as non-collateralized stablecoins, these are the most unique stablecoins. They do not rely on any external assets as collateral. Instead, they use smart contracts and algorithms to manage supply and demand. If the price of the stablecoin exceeds the pegged price, the algorithm increases the supply to lower the price. Conversely, if the price is below the pegged price, the supply decreases. TerraUSD (UST) is a popular algorithmic stablecoin, but it lost its peg in May 2022, highlighting the inherent risks of this approach.
While stablecoins offer more stable value compared to the Naira, they are not without risks. The pegging mechanism may sometimes break (unpeg), causing the value of stablecoins to fluctuate based on market conditions.
3. CBN and Stablecoins in Nigeria
Nigeria's adoption of stablecoins is driven by high inflation rates and faster transactions. Nigerians use stablecoins like Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) to hedge against Naira depreciation. Unlike traditional methods, stablecoins provide a faster and cheaper way to send and receive funds.
A report by Chainalysis shows that Nigerians are among the highest adopters of stablecoins globally, using them to combat inflation and facilitate faster payments. Transactions are mainly peer-to-peer or international transfers. However, using stablecoins for everyday purchases is still uncommon.
Web3 envisions a future where stablecoins are integrated with DeFi applications. Nigerians can utilize stablecoins for borrowing, depositing, and earning interest. The goal is to create a more inclusive financial system, making stablecoins a tool for millions of Nigerians to access financial services.
The Central Bank of Nigeria takes a cautious stance on the cryptocurrency space, presenting significant challenges to the adoption of stablecoins in the country. In 2021, the CBN issued a directive prohibiting banks from facilitating cryptocurrency transactions, demonstrating a tough stance on cryptocurrencies, including stablecoins.
To prevent the devaluation of the Naira, the Nigerian government blocked access to cryptocurrency trading platforms operating in the country. How does the government block website access? Typically through telecommunications operators, which can be requested to blacklist specific IP addresses. In Nigeria's case, the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) instructed telecom companies to restrict consumer access to many cryptocurrency trading platform websites, including local operations, such as Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
Are these restrictions effective? They are somewhat effective, but individuals seeking to purchase crypto assets have ways to bypass IP restrictions. Binance confirmed that "some" Nigerian users encountered issues accessing the website. IP blocking is like a game of whack-a-mole, challenging to enforce and maintain.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms are particularly popular in Nigeria - according to data from blockchain analysis firm Chainalysis, Nigeria ranks first globally in P2P trading volume. While IPs of well-known P2P platforms can be blocked, many smaller platforms are unregistered and theoretically can evade IP freezes.
The Nigerian government has blamed these cryptocurrency trading platforms for the devaluation of the Naira. According to a report by Premium Times, the official reason for taking measures against IP addresses is "continued manipulation of the foreign exchange market," and the decision was made "based on reports that currency speculators and money launderers are using [cryptocurrency platforms] for criminal activities."
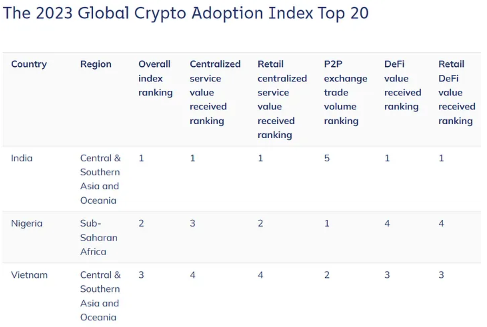
Global Cryptocurrency Adoption in 2023
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) has expressed concerns about the potential risks of money laundering, terrorist financing, and financial stability, which is why it takes a cautious stance on stablecoin adoption. Currently, Nigeria does not have a dedicated regulatory body for stablecoins. This lack of clarity creates uncertainty for businesses and individuals interested in using stablecoins. In the absence of clear regulations, businesses are reluctant to offer services related to stablecoins, hindering widespread adoption and potential benefits for Nigerians.
In Nigeria, several companies have expressed interest in developing stablecoins. One of them is the proposed compliant Nigerian Naira (cNGN). Let's explore the proposed cNGN stablecoin and the situation of the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) eNaira in Nigeria.
4. eNaira CBDC
The eNaira is a groundbreaking initiative in Africa and the continent's first official Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC). It is essentially the digital equivalent of the Nigerian Naira, issued and backed by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) like physical currency.

The eNaira operates on a private blockchain because the CBN wants to control user onboarding, know your customer (KYC) processes, and the creation of eNaira. This is why the CBN uses Hyperledger Fabric, a system that allows private organizations to create private blockchains.
This digital currency is stored in a secure eNaira wallet on your phone or other devices. Unlike cryptocurrencies, the value of eNaira is pegged to the physical Naira, meaning 1 eNaira = 1 Naira.
Despite its launch in October 2021, the initial reception of eNaira was slow. The CBN is devising strategies to increase the user base, such as partnering with financial institutions and providing incentives for eNaira transactions.
5. cNGN Stablecoin
The cNGN stablecoin is a proposed digital currency project in Nigeria that has garnered significant attention. Its goal is to reshape the country's financial landscape.

This project is developed by the Africa Stablecoin Consortium (ASC), which consists of Nigerian financial institutions, fintech companies, and blockchain experts. This collaboration aims to leverage the expertise of all parties to create a robust and reliable stablecoin.
Similar to Nigeria's digital currency eNaira, cNGN is expected to bring more Nigerians into the financial system, especially those who do not have access to traditional banks. Regulatory provisions regarding cryptocurrencies and stablecoins in Nigeria are still evolving. The eNaira, launched by the Central Bank of Nigeria, poses competition for cNGN.
Originally planned for a "sandbox environment" launch in February 2024, indicating limited trial runs and not open to the general public. This indicates that ASC is taking a cautious approach to test and refine the cNGN system before broader promotion.
From my research, the success of cNGN and eNaira will depend on various factors, including:
Clear guidelines set by Nigerian authorities to build user confidence.
Collaboration between ASC, the Central Bank of Nigeria, and other stakeholders for successful rollout.
Educating Nigerians about the associated benefits to drive adoption.
The cNGN stablecoin shares similar use cases and challenges with other stablecoins backed by fiat and cryptocurrencies.
6. Five Major Use Cases of Stablecoins in Nigeria
Stablecoins are a novel financial tool with the potential to reshape transactions and financial inclusion. Here are its major use cases broken down from the perspectives of users and businesses:
1) Hedging Against Inflation
In countries with high inflation rates like Nigeria, stablecoins offer a more stable store of value than the local currency. Users can hold stablecoins to maintain purchasing power over time. Inflation gradually erodes the value of savings. This means that spending 500 Naira on a loaf of bread today might require spending 1000 Naira next year due to inflation.
Unlike fiat currencies, the value of many stablecoins is pegged to more stable assets (such as the US dollar). This means their prices should be relatively stable compared to the local currency experiencing high inflation.
The data below shows an increased interest in Bitcoin and stablecoins when the Naira depreciates.
2) Secure Cross-Border Transfers
Stablecoins can be used as a fast, cost-effective tool for cross-border transfers. Traditional bank transfers may involve high fees and longer processing times, while stablecoins can complete transfers in minutes with relatively lower fees. This is particularly useful for Nigerians who need to make frequent fund transfers to overseas family and friends.
3) Financial Inclusion
Stablecoins can provide financial inclusion for those who cannot access traditional banks. Many Nigerians do not have bank accounts, but they can engage in digital payments, store value, and participate in economic activities by using stablecoins.
4) Business Payment Solutions
For Nigerian businesses, stablecoins can serve as a more convenient, efficient, and low-cost payment solution. They can be used for online commerce, cross-border transactions, and supply chain payments, providing businesses with a more flexible and reliable means of payment.
5) Investment and Trading
Stablecoins can also be used as an investment tool for cryptocurrency trading, portfolio diversification, and long-term store of value. For those seeking returns in the digital asset space, stablecoins offer a relatively stable choice.
Overall, stablecoins have broad application prospects in Nigeria, offering many potential benefits for individuals, businesses, and the entire economy.
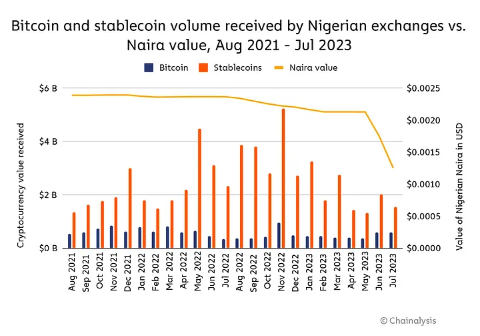
Comparison of Stablecoin Trading Volume Received by Nigerian Trading Platforms and Naira Value
Some platforms offer interest when holding stablecoins. While not guaranteed, the interest earned may exceed the inflation rate, allowing your assets to maintain or increase purchasing power. The effectiveness of stablecoins as a hedge against inflation depends on the extent to which they maintain their peg. If the peg breaks, stablecoins will not be able to protect against the effects of inflation.
6) Faster and Cheaper Remittances
Nigerians working in other countries and remitting income back home to their families or communities typically send their earnings through channels such as banks, remittance services, or online platforms. These remittances are an important source of economic support for many Nigerian families, contributing to their livelihoods, education expenses, and healthcare.
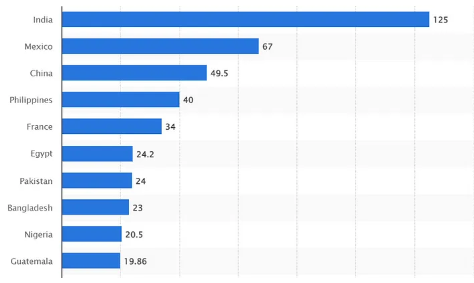
Top Ten Countries with the Highest Remittance Receipts in 2023
Traditional remittance methods, such as remittance services, can be slow and involve multiple intermediaries, leading to delays and fees. Stablecoin transactions occur on blockchain networks known for their fast processing times. This significantly reduces the time needed for Nigerians working abroad to remit money back home.
These traditional remittance services often charge high fees, reducing the amount received by the beneficiaries in Nigeria. Stablecoin transactions reduce some intermediaries, thereby lowering overall costs. While there are transaction fees on the blockchain, they are often lower than traditional remittance services for smaller transactions.
With blockchain technology providing transparency, Nigerians working abroad can track their remittances in real-time, providing them with peace of mind about the destination of their funds.
7) Cross-Border Payments
Stablecoins facilitate seamless cross-border payments, eliminating the need for currency conversion and related fees. This benefits freelancers, online shoppers, and individuals conducting international business.
Cross-border payments often face obstacles such as slow processing times, high fees, and currency fluctuations. Stablecoins address these issues and offer several advantages for international transactions.
Nigeria received over $56 billion in cryptocurrency between July 2022 and June 2023.
Traditional cross-border payments involve multiple intermediaries, each extracting a portion of the fees. Stablecoin transactions on blockchain networks bypass these intermediaries, significantly reducing costs. Unlike traditional systems with waiting and cutoff times, stablecoin transactions settle almost instantly using blockchain technology. This means recipients can access funds more quickly.
Many stablecoins are pegged to stable assets like the US dollar, providing predictability and protection against fluctuations in the local currency for both senders and recipients. Blockchain transactions are publicly recorded, ensuring transparency and immutability. This reduces the risk of fraud and errors compared to traditional systems.
Additionally, traditional systems often have operational time constraints, while blockchain transactions using stablecoins can occur at any time and place.
8) Opening New Markets
Stablecoins open doors for businesses to enter new markets, especially for companies selling digital products or services globally. Customers can use stablecoins for payments, eliminating the barrier of currency conversion.
In many developing countries, a significant portion of the population lacks access to traditional banking services. Through stablecoins provided by cryptocurrency wallets, businesses can tap into new customer bases, facilitating more convenient online payments.
Establishing traditional payment infrastructure to enter new markets is complex and expensive for businesses. Stablecoins offer a faster and more cost-effective way to start accepting payments from new customers.
Furthermore, for businesses operating in areas with currency instability, stablecoins pegged to assets like the US dollar provide more price stability and predictability, especially in international transactions.
Not everyone in every new market is familiar with or willing to use cryptocurrencies. Building awareness in promoting the adoption of stablecoins is crucial to facilitate their adoption.
9) Fundraising and Investment
Businesses raise funds through stablecoin issuance, attracting a broader global investor base. Compared to traditional fundraising methods involving banks and intermediaries, stablecoins leverage blockchain technology for faster settlement times and potentially lower fees. This benefits both startups raising funds and investors participating in fundraising.
Traditional financial markets have operational time constraints, but fundraising using stablecoins can occur at any time and place on the global blockchain network. This higher accessibility presents new opportunities for startups and investors.
Stablecoins can be subdivided into small units, enabling fractional ownership of assets. This allows more investors to participate in fundraising, making investment more accessible to a wider investor base, including those with limited funds.
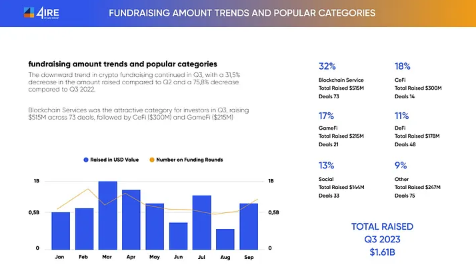
Cryptocurrency Fundraising Trends
The rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), supported by stablecoins, has opened the door to innovative fundraising models. For example, using stablecoins for Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) can simplify the process and reach a broader investor base. Blockchain transactions involving stablecoins are publicly recorded, ensuring transparency and immutability. This reduces the risk of fraud or errors, increasing investor confidence.
7. Challenges of Stablecoin Adoption
While Nigeria has a high adoption rate of cryptocurrencies, there are concerns about the potential impact of widespread stablecoin adoption. Despite the unique advantages of stablecoins, their adoption faces a range of complex challenges that need to be addressed, including:
1) Financial Stability Risks
The Central Bank of Nigeria is concerned that widespread stablecoin adoption may weaken its control over monetary policy. If not carefully regulated, stablecoins could disrupt currency supply and capital outflows.
If Nigerians use stablecoins as their primary store of value, the effectiveness of traditional monetary policy tools of the Central Bank of Nigeria may be diminished. Nigerians may convert their Naira reserves into stablecoins, leading to capital outflows and further weakening the value of the Naira.
While some stablecoins are anchored to stable assets like the US dollar, they are not immune to price fluctuations. If the anchoring relationship weakens or breaks, it could cause instability in the Nigerian financial system, especially if stablecoins are widely used for transactions or savings.
Many stablecoins rely on underlying asset reserves (such as the US dollar) to maintain their anchoring relationship. If these reserves are not properly managed or become inaccessible, it could threaten the stability of stablecoins and potentially trigger financial panic.
The anonymity associated with certain cryptocurrencies may be attractive to criminal activities. If stablecoins are widely adopted, they could be used for money laundering or funding illegal transactions, affecting financial stability and security.
2) Security and Operational Risks
Cryptocurrencies, including stablecoins, operate on decentralized networks. While this provides transparency, it also makes them vulnerable to hacking. If a trading platform or a wallet holding stablecoins is attacked, users may lose their funds. For example, in 2020, Tether was hacked, resulting in the theft of 300,000 USDT, highlighting potential vulnerabilities.
Despite being designed for stability, especially those backed by crypto assets, stablecoins may experience price fluctuations during market downturns. These fluctuations may offset their stability advantage.
Unlike traditional bank accounts, access to stablecoins depends on private keys. Losing these private keys means losing access to the funds. Secure storage and management of private keys are crucial but may be challenging for some users.
Some stablecoins rely on centralized entities holding reserve assets. If these custodians are attacked or face financial difficulties, it could threaten the stability of the anchoring relationship and lead to financial losses for users.
3) Limited Infrastructure
With population growth and demand for internet services, Nigeria has one of the largest smartphone markets in Africa. The market is growing rapidly, with smartphone penetration expected to reach 66% by 2025.
Despite high smartphone penetration, many Nigerians do not fully understand the underlying technology and risks of stablecoins. Lack of financial literacy may lead to impulsive investment decisions and financial losses.
For widespread adoption, stablecoins need seamless integration with traditional banking systems. However, a significant portion of Nigeria's population either does not have bank accounts or has limited access to banking services. This lack of integration makes it difficult for people to easily exchange between fiat and stablecoins.
Additionally, Nigeria has relatively few cryptocurrency exchanges. This limited infrastructure makes it difficult for people to use stablecoins for buying, selling, or cashing out.
4) Social Concerns
The anonymity associated with some crypto transactions raises concerns about financing criminal activities. Social engineering scams, phishing attacks, and fraudulent investment schemes targeting stablecoins may disproportionately affect novices.
Many Nigerians, especially those residing in non-urban areas or with limited exposure to technology, may not be familiar with stablecoins or cryptocurrencies in general. This lack of awareness may hinder adoption and make them susceptible to fraud or misinformation.
Understanding how stablecoins work, their risks and benefits, and how to use them securely requires a certain level of financial literacy. If a significant portion of the population lacks this knowledge, it may exacerbate social inequality and prevent them from accessing potential financial benefits.
Even stablecoins pegged to fiat currencies may experience some degree of price fluctuation. This inherent volatility may raise concerns for potential users, especially those unfamiliar with the crypto market or with limited financial resources.
8. Future Outlook
The challenges facing the widespread adoption of stablecoins in Nigeria can be addressed. Most importantly, the government must be willing to demonstrate support and acceptance.
First, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) can establish clear regulatory guidelines for stablecoins. This will mitigate risks such as money laundering and ensure proper reserve management by stablecoin providers. Independent audits of stablecoin reserves can increase trust and confidence in the anchoring mechanism.
"Global cryptocurrency exchanges should be registered or licensed in Nigeria and comply with the same regulatory requirements applicable to financial intermediaries, following the same activities, the same risks, and the same principles of regulation," emphasized a recent International Monetary Fund report.
Second, trading platforms and wallet providers should invest in robust security measures and educate users on secure storage practices to prevent hacking and fraud. Promoting the use of mature and secure blockchain protocols can reduce vulnerabilities in the smart contracts used by stablecoins.
Collaboration between the government and the private sector can expand and promote affordable smartphones to increase digital inclusion. Cooperation between cryptocurrency companies and banks can facilitate easier exchange between fiat and stablecoins. Establishing more cryptocurrency exchanges in Nigeria can improve accessibility.
Finally, educational institutions can conduct financial literacy campaigns to introduce Nigerians to stablecoins and their risks and benefits. The Central Bank of Nigeria can enact consumer protection-focused regulatory guidelines to protect users from fraud and promote transparency in the stablecoin market.
I believe Nigeria can create a more stable, secure, and inclusive environment for the adoption of stablecoins. Such an environment can enable Nigerians to fully leverage the potential advantages of stablecoins, such as faster, cheaper transactions, new investment opportunities, and financial inclusion for the unbanked population.
Original article link: here
Source: Medium
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



