Authors: Climber, Jessy, cryptonaitive, Golden Finance
Note: This article was first published on April 20, 2024
In the cryptocurrency world, a day is like a year in the human world. Bitcoin has completed its fourth halving in its historical process, and in a sense, one cycle is like a hundred years.
Bitcoin evolves in four-year cycles, each stage refreshing people's understanding. From its initial use as a payment currency to being a store of value and digital gold, as well as its subversion and impact on sovereign currencies and mainstream financial systems, each time it has faced questioning, it has soared to the moon and achieved mythical gains.
Just like how science arrived in medieval Europe, shrouded in theology and ignorance, it ultimately could not stop the footsteps of truth. Adam Back, Nick Szabo, Satoshi Nakamoto, Hal Finney, Vitalik… one after another, these evangelists have forged ahead, with pioneers benefiting and believers living on.
Bitcoin is a virtual currency and a digital currency, but it is also like Noah's Ark when the financial tsunami strikes. For this giant ship, we might as well take a closer look at how it was built from scratch.
I. What is Bitcoin Halving? Why Halve?
1. Halving
Bitcoin halving, also known as "Halving," refers to a pre-coded event in the Bitcoin protocol that occurs every 210,000 blocks (approximately every four years). Halving is the process of reducing the amount of digital currency produced within a unit of time, mainly achieved by reducing block rewards.
The supply of Bitcoin is limited to 21 million units, and once this total is reached, the production of new BTC will stop. Bitcoin halving ensures that the amount of Bitcoin that can be mined per block will decrease over time. By 2140, it is estimated that all bitcoins will have been mined, with the total slightly less than 21 million.
This process aims to control the issuance of new bitcoins and maintain their scarcity, thereby ensuring a limited supply of Bitcoin. Essentially, halving involves reducing the rewards given to miners by half.
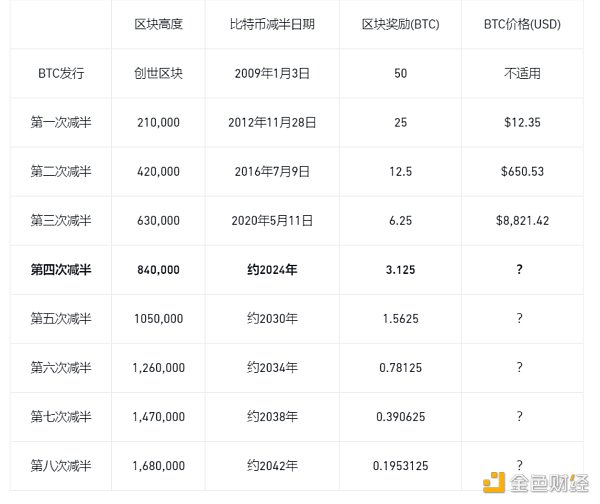
On April 20th, when Bitcoin reached block height 840,000, halving occurred, reducing the block reward from 6.25 bitcoins to 3.125 bitcoins.
Public data shows that miners currently bring approximately 900 bitcoins to the market every day. After halving, this number will decrease to around 450 BTC.
Halving has a significant impact, mainly because this event usually leads to market fluctuations and increased speculation in the cryptocurrency field; it reshapes the mining industry, lowering miners' profit points; and it stimulates technological innovation and community development within the blockchain ecosystem. However, the halving event may also act as a hedge against inflation, enhancing Bitcoin's attractiveness as a long-term investment asset.
2. Why Halve?
Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin white paper on October 31, 2008, and the first Bitcoin block was created on January 3, 2009. Halving is intended to control the circulating supply of Bitcoin. By reducing block rewards, the speed at which new bitcoins enter the market slows down, which helps prevent inflation and ensures the stability of Bitcoin's value.
After the halving on April 20, 2024, Bitcoin's inflation rate is expected to decrease from approximately 1.75% to just 0.85%.
The reason Bitcoin was created is mainly due to the consideration that some countries may issue currency without restrictions. Nakamoto hoped to have a currency that would not be controlled by anyone and could transfer value between any two nodes at will, thus designing this peer-to-peer transaction system.
The market's supply and demand laws in economic theory indicate that if the circulation of a commodity is not restricted, it is easy to experience severe inflation, leading to a significant decrease in commodity prices. Conversely, when supply decreases while demand remains constant or increases, the value of assets may rise.
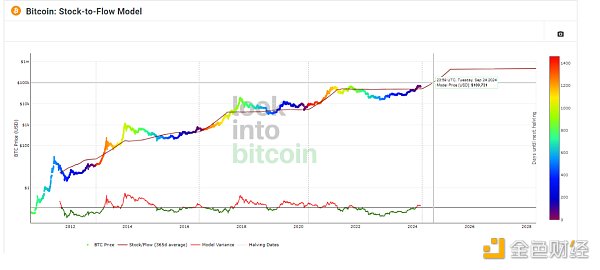
This halving mechanism has also been studied by institutions. The above image shows the Bitcoin stock-to-flow ratio model, which studies the annual mining volume and total inventory, attempting to predict the future value of Bitcoin. Backtesting has proven that it can accurately simulate past price trends.
According to the conclusions drawn from the model, Bitcoin's scarcity is the main driver of its price. After understanding the potential relationship between price and scarcity, holders will realize the value of Bitcoin as a store of value.
In terms of block time, the Bitcoin mining algorithm is programmed to find a new block every ten minutes. As more miners join the network and increase hashing power, the time required to find a block will decrease. To restore the 10-minute target, mining difficulty is recalculated approximately every two weeks. With the rapid growth of the Bitcoin network over the past decade, the average time to locate a block has remained at around 10 minutes (approximately 9.5 minutes).
In the Bitcoin network, a block is produced approximately every 10 minutes, and a certain amount of bitcoins will continue to be mined. By halving the Bitcoin reward every 210,000 blocks, the inflation rate of Bitcoin can be gradually reduced, thereby preventing severe inflation.
Nakamoto wrote in 2009, "From this perspective, Bitcoin is more like a precious metal. It does not maintain value by adjusting the supply, but rather sets a limit on the supply in advance, allowing the value to change accordingly. As the number of users grows, the value of each token will also increase. This can form a positive feedback loop; as the number of users increases, the value will gradually rise, thereby attracting more users to profit from the upward trend in price."
II. Bitcoin Halving and the Cycle of Bull Markets
Market participants often view Bitcoin halving as a precursor to a bull market, as the price of BTC has set new highs after each of the previous three halvings. Many investors also have similar expectations for the halving on April 20, 2024.
Basically, every time miners add a total of 210,000 blocks to the BTC blockchain, BTC will halve. After each BTC halving in the past, the price of BTC has experienced a sustained and substantial increase.
Halving timeline:
First halving (2012): The first Bitcoin halving occurred on November 28, 2012, reducing the mining reward from 50 bitcoins per block to 25 bitcoins.
Second halving (2016): The second halving, which took place on July 9, 2016, further reduced the block reward to 12.5 bitcoins.
Third halving (2020): During the third halving on May 11, 2020, the reward was reduced to 6.25 bitcoins per block.
Fourth halving (2024): During the fourth halving on April 20, 2024, the reward was reduced to 3.125 bitcoins per block. Future halvings will continue until the maximum supply of 21 million bitcoins is reached, expected to be around 2140.
As of today, Bitcoin has undergone four halvings, referred to as halving cycles within the industry. Historically, almost every time before and after a BTC halving, the price of BTC has sharply risen.
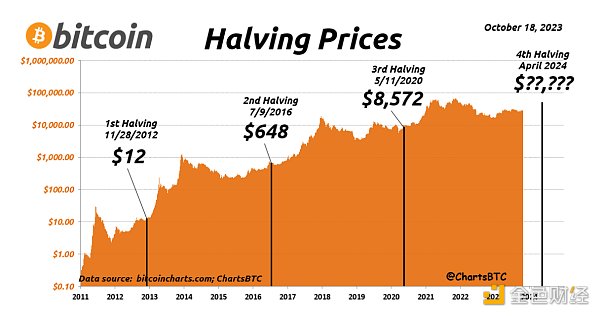
From the above image, it can be seen that the cycle of Bitcoin has been very stable since its inception.
First halving cycle: 2012.11.28-2016.07.10. This halving cycle led to two bull markets in April and November 2013, with the first bull market seeing the price of Bitcoin rise from $12 to $288, a 2300% increase, and the second bull market seeing the price rise from $66 to $1242, an 1782% increase.
Second halving cycle: 2016.07.10-2020.05.12. This halving cycle led to a bull market in December 2017, with the price of Bitcoin rising from $648 to $19800, a 4158% increase.
III. The Third Halving Cycle
The third halving cycle occurred from May 11, 2020, to April 20, 2024. This halving cycle led to two bull markets in April and November 2021. The first bull market saw the price of Bitcoin rise from $8572 to $69000, a 741% increase. The second bull market saw the price rise from $15476 to $737770, a 376% increase. Given the current price of Bitcoin, the crypto market is still in a bull market.
Historically, the price of Bitcoin has often experienced significant fluctuations before and after halving events. In the months leading up to halving, market expectations and speculation about the potential price increase due to reduced future supply often drive prices up. After the halving event, Bitcoin typically experiences a significant bull market.
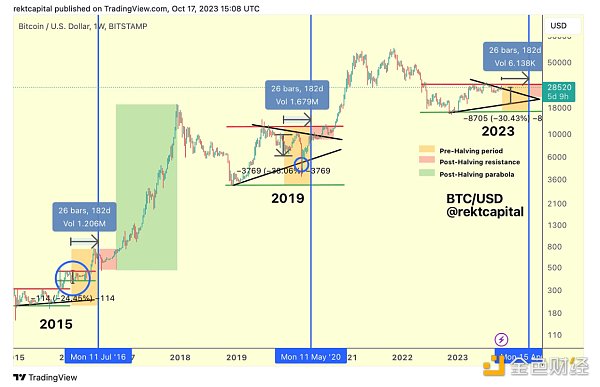
As shown in the above image, there is typically a bear market low of approximately 1.3 years before each BTC halving. Subsequently, it takes about 1.3 years for the market to reach its peak. Therefore, the entire market cycle fluctuates over approximately 2.6 years. Additionally, based on past BTC halving events, the price of BTC typically bottoms out around 477 days before the halving. Furthermore, from the halving day to the peak of the next bull market cycle, it typically takes an average of 480 days.
For example, after the 2012 halving, the price of BTC rose from $12.25 to $127 within 150 days. Similarly, after the 2016 halving, the price of BTC rose from $650.63 to $758.81 within 150 days. Finally, after the 2020 halving, the price of BTC rose significantly from $8821.42 to $10,943.00 within 150 days.
Looking back at previous halving events, Bitcoin has also experienced a period of retracement. In 2016, the market experienced a sharp sell-off from around $760 to $540 before and after the halving, representing a retracement of approximately 30%. The 2019 event saw an even larger retracement of about 38%.
This year is no exception, as of the time of writing, the price of Bitcoin has retraced by approximately 14%.
However, according to the Bitcoin stock-to-flow ratio model mentioned earlier, after the 2024 BTC halving, the price of BTC may rise to over $100,000. Crypto research institutions PlanB and Glassnode both predict that the price of BTC will rise and exceed $100,000 in 2024. Pantera Capital has even more specifically predicted that after the entire bull market cycle ends, the price of BTC will reach approximately $149,000 in 2025.
Historically, the Bitcoin cycle typically begins 12 to 18 months after the peak of the previous bull market, and new all-time highs appear a few months after the halving. However, unlike in the past, this halving event is accompanied by the development of a Bitcoin spot ETF in the United States, so the impact of this halving cycle may be weakened.
Investors should also note that the post-halving price increase of Bitcoin is also associated with significant macroeconomic events. For example, in 2012, the European debt crisis highlighted the potential of Bitcoin as an alternative store of value, leading to its price rising from $12 to $1100 in November 2013.
During the initial coin offering (ICO) boom in 2016, over $5.6 billion was injected into altcoins, indirectly benefiting Bitcoin and causing its price to rise from $650 to $20,000 in December 2017.
Of particular note is the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, where large-scale stimulus measures exacerbated inflation concerns, potentially driving investors towards Bitcoin as a hedge, leading to its price rising from $8600 to $69000 in November 2021.
The above information indicates that while halving helps reinforce the scarcity narrative of Bitcoin, macroeconomic factors also have a significant impact on the price of Bitcoin. The crypto market is already high-risk, so investors should approach it with caution.
III. The Epic of Bitcoin
To fully understand the crypto cycles triggered by each Bitcoin halving, it is necessary to review the epic history of Bitcoin.
Like many great things, Bitcoin did not come out of thin air; it also stood on the shoulders of predecessors.
Technological Foundations Before the Birth of Bitcoin
The birth of Bitcoin required breakthroughs in cryptography and digital currency.
1976: Birth of Asymmetric Encryption
In November 1976, cryptographers Whitfield Diffie and Martin E. Hellman published the paper "New Directions in Cryptography," which introduced cryptography from symmetric encryption (using the same key for encryption and decryption) to asymmetric encryption. This groundbreaking paper paved the way for secure digital signatures and the implementation of public and private key pairs, becoming an indispensable part of Bitcoin's functionality.
1977: RSA Algorithm
One of the earliest viable public-key cryptosystems, RSA, was named after its founders Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman.
1989: DigiCash
DigiCash, founded by David Chaum, was one of the first attempts at a completely anonymous and secure digital payment system. DigiCash was based on blind signature technology and built on the foundation of public and private key pairs. Despite its innovative approach, its centralized model led to its failure. However, DigiCash was an important precursor to the development of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw a period of innovation in digital currencies.
1996: e-gold (Digital Currency)
e-gold, created by Douglas Jackson and Barry Downey, allowed users to transfer ownership of gold electronically. Its centralized structure became the focus of legal challenges, especially in terms of money laundering. This, combined with security issues, led to its eventual dissolution.
1997: Hashcash (Proof of Work Mechanism)
Adam Back invented Hashcash in 1997, proposing a proof of work system. Hashcash is a proof of work mechanism used to prevent spam emails and denial-of-service attacks. The proof of work principle was later introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto into the Bitcoin consensus mechanism.
1998: B-money (Distributed Ledger)
Computer scientist Dai Wei proposed the B-Money electronic currency protocol, envisioned as a decentralized, anonymous electronic cash system. One of its methods involved all participants maintaining copies of all transactions to ensure collective and transparent verification. This protocol laid the groundwork for distributed ledgers, which Satoshi Nakamoto referenced when creating Bitcoin.
1998: BitGold
Nick Szabo invented BitGold, inspired by the gold mining process in the real world and incorporating a proof of work mechanism. BitGold required participants to demonstrate proof of work to create a new unit of currency called "bit." Once this work was verified, the new "bit" would be added to a chain, linking it to previous bits and forming a public, tamper-proof record. Szabo also proposed Byzantine fault tolerance to prevent double spending. This system was the first prototype of a structure similar to Bitcoin. Although Szabo detailed the principles of BitGold, a fully developed and operational model was never fully developed or launched.
2004: RPOW (Reusable Proof of Work)
Inspired by Hashcash, Hal Finney developed RPOW, believing it could serve as the basis for a payment system. RPOW would facilitate the transfer and exchange of tokens between individuals, promoting the use of proof of work tokens as a form of peer-to-peer electronic cash. This is why Hal Finney was initially interested in Bitcoin when Satoshi Nakamoto shared the Bitcoin white paper on the cypherpunks mailing list. Hal Finney was the first person to run a Bitcoin node, the first miner, and the first recipient of a Bitcoin transaction.
Ideological Foundations and the Birth of Bitcoin
The issue of currency has always been thought-provoking. If currency is the crown of social science, then the business cycle is the gem on the crown of social science.
In classical times, numerous sociologists such as Cantillon, John Law, and David Hume have pondered the origins of inflation and the pursuit of sound money.
[End of Translation]
In modern times, in the pursuit of explaining the capitalist economic crises and business cycles, a group of economists emerged, known as the Austrian School. The Austrian School believes that inflation is primarily a monetary phenomenon, caused by the issuance of credit currency, which distorts market price signals and leads to widespread erroneous decisions by businesses in the market, ultimately resulting in market liquidation, i.e., economic crises.
Entering the 20th century, with the rise of the credit era, especially the gradual empowerment of central banks, fiat currency-induced inflation ultimately returned like a tiger to the mountain. Humanity witnessed numerous instances of hyperinflation, such as the German Mark and the Nationalist Party's Gold Yuan.
Notable infamous cases also occurred in the United States, starting with the economic Great Depression of 1929. This was due to the fear of competition from sound money by the central bank's fiat currency. During the Great Depression, on April 5, 1933, U.S. President Roosevelt issued Executive Order 6102, prohibiting the possession of gold by the American people. It was not until 1975 that Executive Order 6102 was repealed.
Surely, Satoshi Nakamoto must be quite familiar with this dark period in U.S. history. Perhaps this is why Satoshi Nakamoto entered April 5, 1975, as the date of birth when registering under the pseudonym for the P2P Foundation.
In 1974, Austrian School economist Hayek received the Nobel Prize in Economics, and in 1976, Hayek published "Denationalization of Money." Additionally, the criticism of inflation by the American monetarist Milton Friedman in the 1980s and 1990s, as well as the revival of the Austrian School in the United States driven by libertarians and the U.S. Libertarian Party, further contributed to the influence of the Austrian School.
Looking back, if Satoshi Nakamoto grew up in the 1980s and 1990s, he would undoubtedly have been deeply influenced by the Austrian School of economics and embraced its monetary proposition of "separation of money and state."
After the experiments of Adam Back, Dai Wei, Nick Szabo, Hal Finney, and others in the previous section, Satoshi Nakamoto began to stand on their shoulders, integrating the strengths of each and making original contributions.
In early 2007, Satoshi Nakamoto began writing code for Bitcoin. On November 17, 2008, in an article on the cryptography mailing list, Satoshi Nakamoto wrote, "I believe I have solved all these little details in the past year and a half while writing the code."
Then came 2008, the year of the shocking global financial crisis. The financial crisis prompted people around the world to rethink business cycles and inflation issues.
In this crisis, both Satoshi Nakamoto and humanity were ready.
Milestones in the Development of Bitcoin
- August 18, 2008: Registration of the Bitcoin.org domain
- October 31, 2008: Publication of the Bitcoin white paper "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" on the cryptography mailing list
- January 3, 2009: Mining of the first Bitcoin genesis block
- January 12, 2009: First BTC transaction
- February 2009: Launch of the first Bitcoin wallet, Bitcoin-Qt
- March 17, 2010: First recorded Bitcoin price
- May 22, 2010: First Bitcoin transaction for goods (10,000 BTC for two pizzas)
- July 18, 2010: Creation of the Bitcoin logo
- February 2011: Launch of the Silk Road
- June 2011: First Bitcoin bubble
- June 2011: First Bitcoin hack
- June 20, 2011: First major crisis at Mt. Gox
- April 18, 2011: Birth of the first altcoin, Namecoin
- November 18, 2012: First Bitcoin halving
- May 2, 2013: Installation of the first Bitcoin ATM in Vancouver, Canada
- March 18, 2013: Bitcoin market cap surpasses $1 billion
- July 3, 2013: First ICO (Mastercoin)
- December 18, 2013: Birth of "HODL"
- February 25, 2014: Mt. Gox files for bankruptcy protection
[End of Translation]
In 2015, throughout the year, there were discussions on Bitcoin scalability and block size issues, including two major conferences: the Scaling Bitcoin Montreal conference in September and the Scaling Bitcoin Hong Kong conference in December.
On January 14, 2016, the Lightning Network white paper was released by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja. The Lightning Network aims to provide a scaling solution for Bitcoin by enabling off-chain payments through state channels, thereby speeding up transaction times.
On July 9, 2016, Bitcoin underwent its second halving at block height 420,000, reducing the block reward from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC.
On August 1, 2017, Bitcoin Cash (BCH) forked from Bitcoin due to differences in block size limits, with Bitcoin having a 1MB limit (increased to 4MB due to SegWit upgrade) and BCH having a 32MB limit.
On August 23, 2017, Segregated Witness (SegWit) was activated at block height 481,824 on the Bitcoin mainnet. SegWit aimed to address long-standing issues with Bitcoin, such as transaction malleability and scalability. It increased block size limits to 4MB by separating witness data from transactions, allowing more transactions per block and improving transaction security by addressing vulnerabilities.
In November 2017, the Lightning Network went live on the Bitcoin mainnet and completed its first transaction.
In November 2017, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) officially launched Bitcoin futures trading, and Bitcoin surged to a high of $19,000.
In January 2018, the legendary figure Lazlo Hanyecz successfully purchased pizza again using the Lightning Network.
In January 2019, the Lightning Torch event took place.
On March 12, 2020, due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the stock market, Bitcoin plummeted to below $3,800.
On May 25, 2020, Bitcoin underwent its third halving at block height 630,000, reducing the block reward from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC.
In January 2021, Stacks was launched, initially known as Blockstack, created by Muneeb Ali and Ryan Shea. It features its own programming language, Clarity, and a consensus mechanism called Proof of Transfer (PoX), allowing smart contracts to be executed on the Bitcoin blockchain.
On February 8, 2021, Tesla announced that it would accept Bitcoin as payment.
On February 19, 2021, the market capitalization of Bitcoin surpassed $1 trillion.
In April 2021, the price of Bitcoin reached $65,000.
In June 2021, China banned Bitcoin mining, causing Bitcoin to briefly drop below $30,000, and Bitcoin hash rate to migrate to the United States.
On September 7, 2021, Bitcoin became the legal tender in El Salvador.
On November 14, 2021, the Taproot upgrade was successfully activated, introducing Schnorr signatures and smart contract improvements to Bitcoin.
In November 2021, the price of Bitcoin reached $69,000, the previous all-time high.
In December 2022, the ICP mainnet integrated Bitcoin.
In 2023, the Bitcoin ecosystem experienced significant development, with new concepts such as Ordinals, Inscriptions, BRC20, Atomical, ARC20, Bitstamp, SRC20, Rune, TaprootAssets, and RGB emerging. The year 2023 saw more development than the previous few years.
In January 2024, the U.S. SEC approved the listing of 11 Bitcoin spot ETFs.
In March 2024, stimulated by the approval of Bitcoin spot ETFs, the price of Bitcoin rose to $73,000, breaking the previous high before the halving for the first time.
From 2024 to the present, the rise of Bitcoin layer 2 solutions. According to statistics from Jinse Finance, there are currently over 50 Bitcoin layer 2 solutions.
IV. New Leaders in the Crypto Industry
As Bitcoin has evolved and the crypto cycle has repeated, the leaders in the crypto industry have changed rapidly. Here are some of the key figures in the history of crypto development:
Satoshi Nakamoto: The creator of the Bitcoin protocol and the related software Bitcoin-Qt. His real identity is unknown, and he claimed to be a Japanese-American. In 2009, he released the first Bitcoin software and officially launched the Bitcoin financial system. He gradually faded out in 2010 and handed over the project to other members of the Bitcoin community.
Vitalik Buterin: Known as V God, the founder of Ethereum. When he first encountered cryptocurrencies, he was a Bitcoin enthusiast and founded "Bitcoin Magazine" in 2011. He also wrote the most comprehensive Bitcoin Python library, pybitcointools. Vitalik was a supporter of big blocks for Bitcoin and initially wanted to make Bitcoin scalable. He and his team worked on Colored Coins, which allowed users to issue tokens in the BTC ecosystem. Ethereum inherited the idea of big blocks and is different from Bitcoin as digital gold, as it is a "computer."
Craig Steven Wright, also known as Faketoshi: The founder of BSV, a fork of BCH. He is an Australian who claimed to be Satoshi Nakamoto. His fame came from claiming to be Satoshi Nakamoto in 2016 and even received confirmation from Gavin Anderson, a member of the Bitcoin Core team. However, Wright was unable to provide sufficient evidence, and he eventually gave up, but he was given the title "Australian Satoshi."
During the Bitcoin fork controversy, Wright was very active and even threatened to destroy Bitmain with money. He later forked BCH, giving rise to BSV.
Chang Jia: Also known as Liu Zhipeng, the founder of "8btc," China's largest blockchain forum and media outlet. He is also a science fiction writer. He has a significant influence in the Chinese blockchain community and has long been committed to promoting blockchain technology and theoretical research. He is the originator of the "impossible triangle" theory in blockchain and published the first book on Bitcoin in China, "Bitcoin: A Real and Illusory Financial World."
Kao Cat: Also known as Jiang Xinyu, another prominent figure in the development history of Bitcoin. He was the first person in the Chinese Bitcoin community to successfully launch an ICO project and was also one of the earliest geniuses in Asic mining machine technology in China. By the end of 2014 to early 2015, he suddenly disappeared and has not been seen since.
Wu Jihan: The founder of Bitmain, which at its peak controlled over 50% of Bitcoin's mining power. In 2017, during the Bitcoin block size debate, he supported big blocks and later forked Bitcoin, giving rise to BCH. He even attempted to take over BTC, but ultimately failed.
Li Xiaolai: A former New Oriental teacher, known as the richest Bitcoin holder in China. He first purchased Bitcoin in 2010 and made additional purchases during the bear market in 2014. By then, he had accumulated hundreds of thousands of Bitcoins. In 2017, Li Xiaolai cashed out all his Bitcoins, earning approximately 13.5 billion RMB, and publicly stated that Bitcoin is a scam.
Casey Rodarmor: The developer of the Ordinals protocol, which enabled the issuance of NFTs on Bitcoin, marking another attempt to issue NFTs on Bitcoin after Colored Coins in 2012 and the derivatives platform Counterparty in 2014. He later proposed the Rune protocol, which will be launched on the day of Bitcoin's fourth halving.
Larry Fink, CEO of BlackRock: As early as 2017, Fink declared himself a "faithful believer" in cryptocurrencies. In 2023, BlackRock submitted an application for a Bitcoin ETF, and Fink stated that cryptocurrencies are expected to surpass global currencies. This move by the global financial giant undoubtedly injected new vitality into the mainstream adoption of Bitcoin. Later, BlackRock did become one of the first in the United States to eat the crab of Bitcoin spot ETFs.
[End of Translation]
Salvadoran President Nayib Bukele: He is the world's first president to openly support Bitcoin and has made Bitcoin the legal tender of his country. Since then, the country has been buying one Bitcoin every day. This is undoubtedly an innovative attempt at the current financial system.
MicroStrategy CEO Michael Saylor: MicroStrategy holds the most Bitcoin, and Michael Saylor is also one of the influential figures in the cryptocurrency field. It is said that he holds over 120,000 Bitcoins.
Changpeng Zhao: The founder of Binance, who used the money from selling a house in 2014 to go all-in on Bitcoin at a price of $600. In 2017, he founded Binance, currently the largest exchange by trading volume. After the crackdown on exchanges in China, he decisively chose a global development direction. It has been proven that going global has indeed achieved success for Binance. However, this also led to legal disputes with the U.S. government.
The reason why Changpeng Zhao has been praised in the industry is that he is not just running an exchange. Binance has invested in and incubated many projects, constantly working to expand the industry.
In the development history of Bitcoin, countless people have come and gone, while some have persisted, actively promoting Bitcoin in the early days and later participating in industry development. The history of crypto development will remember those who actively contributed, and their faith in Bitcoin has also brought them substantial financial returns.
V. From Payment Currency to Digital Gold, Anarchism Finally Embraced
Since 2008, Bitcoin has been around for almost sixteen years. Bitcoin was born after the 2008 financial crisis, when Satoshi Nakamoto, faced with currency over-issuance and resulting inflation, wanted to establish a financial system independent of any country. At its inception, Bitcoin was intended to be electronic cash, and Nakamoto hoped it would be used by people just like traditional currency.
However, in the first two years, Bitcoin was almost worthless. The price of one Bitcoin was less than half a cent, and there were no merchants willing to accept Bitcoin as payment. It wasn't until May 2010 that Bitcoin was used to purchase food. An early miner, Laszlo Hanyec, exchanged 10,000 Bitcoins for two pizzas.
Subsequently, Bitcoin truly gained widespread use as a payment method on the dark web. In 2011, the dark web marketplace Silk Road was established, and Bitcoin became the hard currency used on the platform. Apart from its anonymity, Bitcoin was highly sought after on the dark web due to its difficulty to trace.
Early data also shows that in the first three years of Bitcoin's existence, 30% of transactions were directed to the dark web. By 2014, the average daily Bitcoin transaction volume on the six major dark web markets reached $650,000. Money laundering, drug trafficking, and human trafficking became associated with Bitcoin. It was estimated that as of January 2018, approximately 25% of Bitcoin users and nearly half of Bitcoin transactions were related to illegal activities.
Some dark web markets disappeared, and the most commonly used virtual currency for money laundering shifted from Bitcoin to Tether due to its price stability. With the sharp rise in the price of Bitcoin and its high volatility, its function as an exchange currency gradually weakened, and it increasingly became a tool for storing value. After the block size debate in 2017, Bitcoin firmly established its position as digital gold, and in practice, it has continued to solidify this position.
As some sovereign national currency systems collapsed, Bitcoin became a choice for people in some countries to surpass fiat currency.
In September 2021, Bitcoin became the circulating legal tender in El Salvador. El Salvador has become a Bitcoin nation.
The new president of Argentina has also promoted the benefits of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies in various public forums. The people of inflation-ridden Argentina are actively buying Bitcoin. Argentina is one of the countries with the highest adoption rates of cryptocurrencies globally. Inflation data shows that the inflation rate in Argentina rose from 254.20% in January 2024 to 276.20% in February.
The examples of these countries show that Bitcoin is indeed playing the role Satoshi Nakamoto initially envisioned to resist inflation. However, some sovereign nations are actively embracing Bitcoin, and the original intention of being independent of the mainstream financial system can no longer be realized. Today, some governments are actively regulating and embracing Bitcoin, and Bitcoin has become part of the mainstream financial system. The most direct evidence is that some countries have approved Bitcoin spot ETFs, especially the approval in the United States, which has had a significant impact.
Looking back at the development of Bitcoin over the years, we can see that Bitcoin has gradually transitioned from a payment method to an investment similar to gold, and countries' attitudes towards it have shifted from crackdowns to having to study regulation, or actively embracing it.
Previously, Bitcoin was a plaything for a handful of geeks, but after nearly sixteen years of development, the narrative of Bitcoin has shifted from a payment currency to digital gold, from a form of resistance to the national financial system to finally being embraced by the mainstream financial system.
Bitcoin itself is also changing, from the block size debate to forks, and now the emergence of new concepts such as inscriptions and runes on it.
Various forces have staged all kinds of disputes for their own interests on Bitcoin, but none of these have truly shaken Bitcoin. Bitcoin remains great.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



