Mining and staking are two methods of earning passive income from cryptocurrencies. The former carries higher risks but offers greater potential returns, while the latter provides higher stability and is suitable for long-term investment.
Author: MrNouman / Source
Plain Blockchain
For years, there has been a debate on how to earn passive income from cryptocurrencies. Many investors have turned to mining and staking as two of the most profitable passive income strategies. However, there is significant confusion surrounding these terms.
Mining and staking are both viable ways to make money without being active in the market, but there are significant differences between them that may affect your investment returns. In this blog post, we will explore the pros and cons of each strategy to help you make informed decisions and find the best option for your goals.
1. Yield Farming
1) What is Yield Farming?
The process of providing liquidity to DeFi (decentralized finance) protocols, such as liquidity pools and cryptocurrency lending services, is called Yield Farming. It is likened to farming because it is a new way of "planting" your cryptocurrencies.

Liquidity Mining (also known as liquidity mining) is currently the most popular method of profiting from crypto assets. When liquidity providers offer liquidity, they receive a certain percentage of platform fees from decentralized exchange platforms (DEX) like Uniswap. These platform fees are paid by token swappers using the liquidity. It's a win-win situation: cryptocurrency holders gain more exposure, while the protocol benefits from increased liquidity and trading volume.
Some cryptocurrency enthusiasts consider Liquidity Mining and Yield Farming returns as two different investment strategies—mainly because users receive Liquidity Mining system's liquidity provider tokens (LP Tokens) as rewards for providing liquidity.
However, these terms are often used interchangeably. Cryptocurrency Yield Farming can also be referred to as DEX mining, DeFi mining, DeFi liquidity mining, or cryptocurrency liquidity mining.
2) How does Yield Farming work?
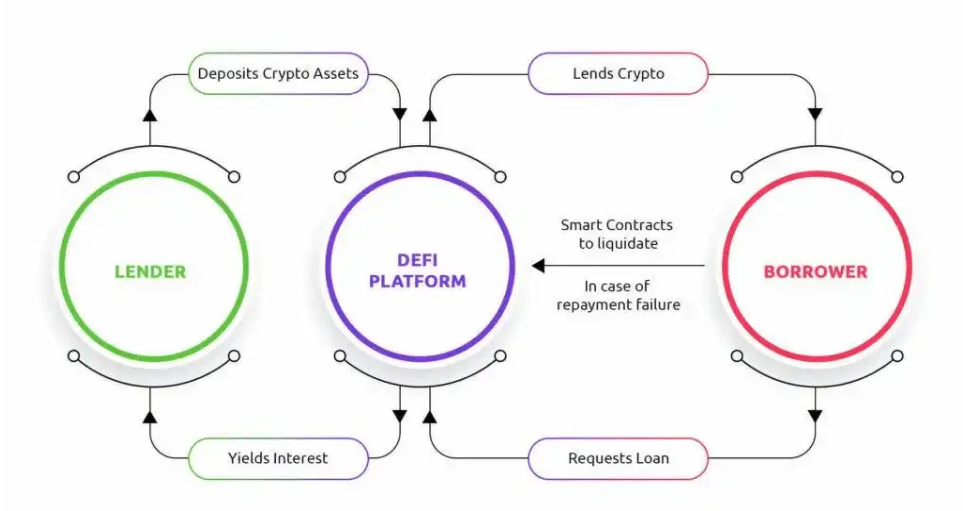
A key concept of Yield Farming is Automated Market Makers (AMMs), which are permissionless automated trading platforms that do not require users to submit orders like traditional platforms involving buyers and sellers. AMMs allow investors to trade more efficiently and conveniently without intermediaries or third parties. Additionally, due to automated market makers, trades are almost instant, further increasing the attractiveness of mining to many investors.
Liquidity Providers (LPs) and Liquidity Pools
Automated Market Maker (AMM) systems maintain order books, primarily composed of liquidity pools and liquidity providers (LPs).
Essentially, liquidity pools are smart contracts that pool funds to make it easier for cryptocurrency users to borrow, purchase, and trade digital currencies. Liquidity providers (LPs) contribute funds to the liquidity pool, leveraging these funds to drive the DeFi ecosystem. Liquidity pools incentivize them.
3) Advantages of Yield Farming
Mining allows many ordinary investors to earn returns from digital assets without needing a deep understanding of blockchain technology or devising complex trading strategies. The returns generated from mining enable investors to achieve returns that traditional investment tools cannot. With the continuous development and evolution of DeFi, it is clear that crypto mining will become a more mainstream method of generating online passive income.
4) Comparatively Good Yield Farming Platforms
Different forms of companies offer different financial services, most of which can generate astonishingly high interest. You might get an annual interest rate of 0.01% to 0.25% from major banks, but these low returns cannot compete with the 20% to 200% profits promised by some DeFi platforms. The higher the interest rate, the higher the risk of the staking pool—this is a crucial correlation. Beware of potential scams and unverified platforms that could lead to loss of funds.
The most profitable DeFi platforms (such as Aave, Curve, Uniswap, etc.) are located on Ethereum, but the Binance Smart Chain (BSC) also has some substantial projects, such as PancakeSwap and Venus Protocol, which can compete with the Ethereum network.
Here is a list of some good platforms:
- Providing liquidity on Uniswap: Annual yield of about 20% to 50%
- Earning interest on Aave: Annual yield of about 0.01% to 15%
- Mining on PancakeSwap: Annual yield of about 8% to 250%
- Providing liquidity on Curve Finance: Annual yield of about 2.5% to 25%
- Yearn Finance: Annual yield of about 0.3% to 35%
The high interest rates (annualized yield) of mining pools make them fiercely competitive. Rates often fluctuate, forcing liquidity miners to switch between different platforms. The downside is that every time a miner enters or leaves a liquidity pool, they must pay gas fees.
2. Staking
1) What is Staking?
Staking is becoming increasingly popular in the cryptocurrency industry as it allows users to earn passive but high income while supporting their favorite networks or protocols. It involves holding a certain amount of coins or tokens in a secure wallet and participating in the validation of transactions on certain blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, Polkadot, BNB, Cardano, etc. In return, stakers receive more coins or tokens, which can generate a stable income stream. As rewards typically depend on the volatility of the network, staking can be very profitable if done correctly, making it an attractive choice for cryptocurrency enthusiasts looking to diversify their investment portfolios.
Proof of Work (PoW) vs. Proof of Stake (PoS)
In the cryptocurrency space, two core consensus mechanisms have garnered attention: Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). While PoW is currently the dominant protocol in the industry, PoS is also gaining popularity.
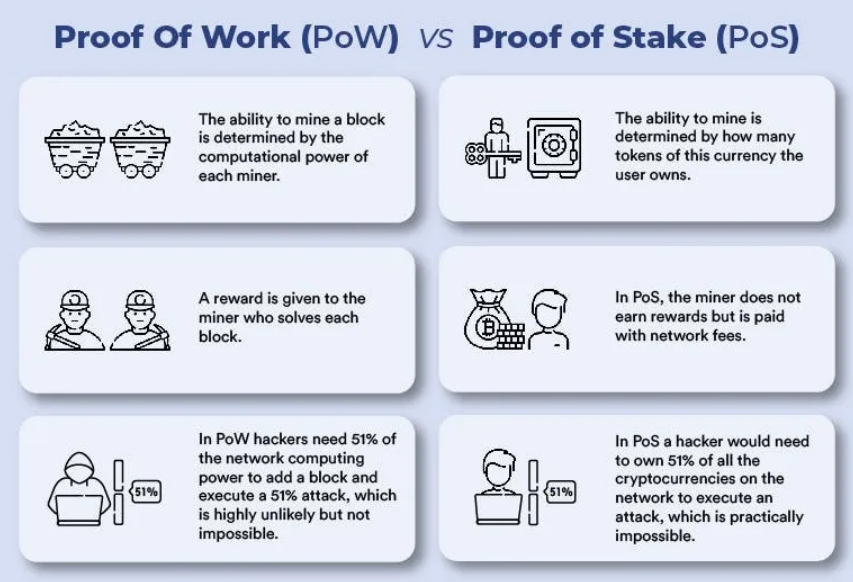
These protocols each have their own advantages and disadvantages. In PoW, miners invest computational power to process (validate) transactions—miners are rewarded for their efforts by receiving tokens. This makes it a secure system, but PoW is also associated with significant energy consumption.
In PoS, holders stake tokens from their balance and receive rewards. This offsets mining, reducing energy costs. However, since the protocol utilizes a validator selection algorithm for transaction validation, improper implementation could lead to centralization of control.
Therefore, these two protocols are not inherently superior or inferior; understanding the pros and cons of each protocol helps determine which protocol is best suited for specific situations.
2) How does Cryptocurrency Staking Work?
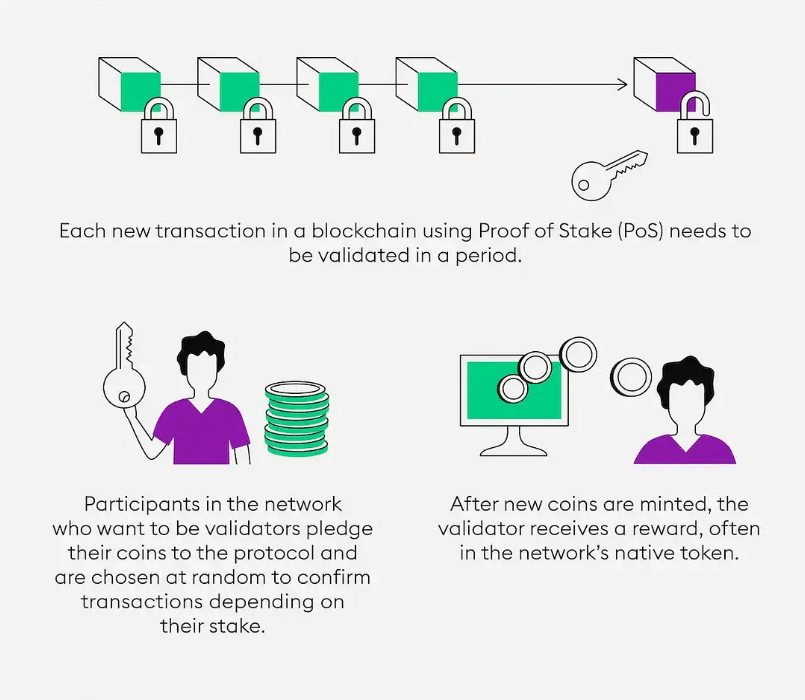
Source: Bitpanda
Staking is a popular way in the blockchain world to earn income by committing funds as collateral. It involves locking a certain amount of cryptocurrency and earning rewards through a validation process, similar to mining but with less work and risk. As a reward for staking their tokens, users can earn rewards for contributing to the security and stability of the ecosystem.
3) How to Stake PoS Cryptocurrencies
To stake cryptocurrencies, users must download and sync a wallet and transfer tokens. Users can set up staking configurations in their wallet, check statistics for staked tokens, and closely monitor blockchain rewards. Ensure all network security settings are up to date and enable the highest level of protection to avoid putting staked funds at risk. Additionally, data should be backed up as frequently as possible, as unforeseen events could lead to interruptions that jeopardize funds. Staking cryptocurrencies is a rewarding way to protect your wallet and support the network's consensus.
The following are the most commonly staked cryptocurrencies:
- Ethereum (ETH)
- Cardano (ADA)
- Tezos (XTZ)
- Polygon (MATIC)
- Theta (THETA)
These five cryptocurrencies offer high potential rewards for users willing to lock funds in the network for a period of time. While the rewards vary in each case, staking these five cryptocurrencies is considered more reliable compared to other coins.
4) The Impact of DeFi on Staking
Since DeFi platforms are decentralized, they are less susceptible to security vulnerabilities compared to traditional banking applications, making them generally more secure. DeFi setups also provide users with access to high annualized yields, additional governance privileges, or voting rights that other financial systems cannot offer.
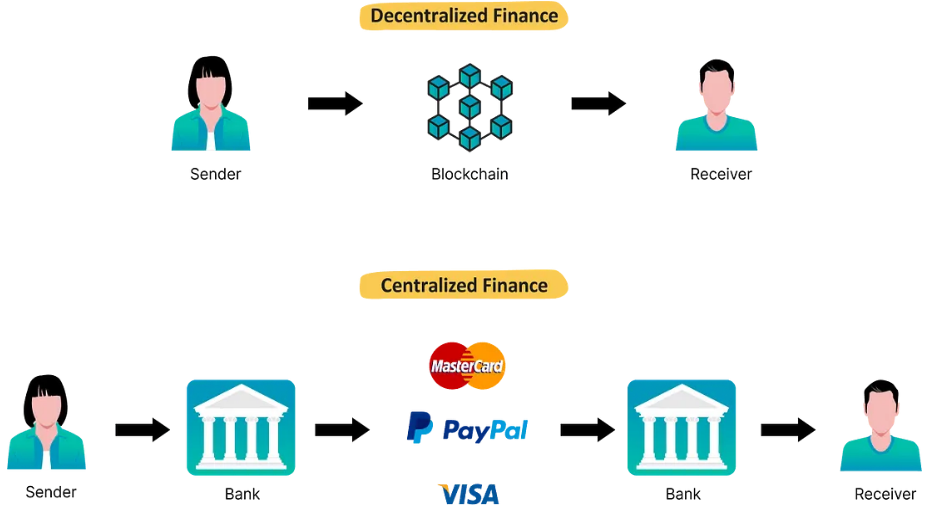
Investors participating in DeFi should take additional precautions when staking, including:
- Considering the security of the DeFi platform
- Determining the liquidity of staked tokens
- Investigating whether rewards could lead to inflation
- Diversifying through different staking platforms and initiatives.
3) What is the Difference Between Mining and Staking?
Choosing between mining and staking as an investment form can be tricky. While both offer the potential for additional income, it is important to understand which is suitable for your situation and goals.
Although the terms "mining" and "staking" are sometimes used interchangeably, there are some clear differences between them.
Profitability: The profits generated from mining and staking differ significantly, usually expressed in terms of "Annual Percentage Yield" (APY).
For example, early adopters of new projects or methods in mining can earn quite substantial profits. According to CoinGecko's data, potential returns range from 1% to 1,000% APY. In contrast, staking rewards typically fluctuate between 5% and 14%.
Risk Level: Mining offers higher returns but also comes with greater risks. One reason is that crypto mining is often used in newer DeFi projects, leading to higher "rug pull" risks. Staking, on the other hand, is more common in established PoS networks with lower risk.
However, both mining and staking come with a certain level of risk due to volatility. If the value of tokens unexpectedly drops, both miners and stakers may incur losses. There is also the possibility of liquidation if your investment is not covered by your collateral.
Complexity: Staking is generally considered a simpler passive income technique, as it only requires investors to select a staking pool and lock their cryptocurrency. It also does not require a large initial investment. On the other hand, mining can be time-consuming as investors must decide which tokens to lend and on which platform, and may need to switch platforms or tokens repeatedly. Ultimately, how actively you manage your investment may determine whether you choose staking or mining.
Staking requires only one cryptocurrency to start, while mining allows you to earn from trading pairs.
Liquidity: When comparing mining and staking, the winning strategy is obvious for investors seeking liquidity. Both strategies require cryptocurrency investors to have a certain amount of cryptocurrency to profit. However, unlike staking, mining does not require locking up funds—investors have full control of the cryptocurrency and can withdraw at any time through this technique.
Inflation: PoS tokens are often affected by inflation, and any rewards to stakers are composed of newly created token supplies. Staking your tokens at least makes you eligible for interest proportional to the staked amount and synchronized with inflation. If you miss out on staking, the value of your current assets will decrease due to inflation.
Duration: Both require users to stake their funds for a period of time on different blockchain networks. Some also have minimum amount requirements.
Transaction Fees: Miners can switch pools frequently on a weekly basis. They constantly adjust their strategies to increase income and maximize returns. This is why gas fees are undoubtedly a major concern for miners who freely switch liquidity pools, but this cost may be overlooked when comparing mining and staking. Even if miners find higher returns on another network, they must consider any switching costs.
Security: Staking is generally considered more secure because stakers participate in the strict consensus process used by the underlying blockchain. On the other hand, mining (especially based on newer DeFi protocols) may be more susceptible to hacking attacks, especially if there are vulnerabilities in the smart contract code.
Impermanent Loss: Miners in a two-sided liquidity pool may incur impermanent losses due to cryptocurrency price fluctuations. Rising digital asset values do not benefit investors. For example, if an investor deposits funds into a mining pool and the cryptocurrency price surges, the investor is better off holding onto those cryptocurrencies rather than adding them to the pool. Investors may also incur impermanent losses if the value of their tokens decreases.
Staking does not result in impermanent losses.
The similarities between mining and staking are that they are the two most popular ways for cryptocurrency enthusiasts to earn passive income.

4) Conclusion: Which is Better?
Staking is an excellent choice for investors who are not concerned about short-term price fluctuations but care about long-term investment returns. If there is a need to quickly retrieve funds before the staking period expires, it is best to avoid locking funds for staking.
For investors who prefer short-term methods, mining is a good choice. It does not require fixed funds. You can switch between platforms to find higher annualized yields. When adopting a short-term approach, mining can generate more income. This is a high-risk endeavor compared to staking. Tokens with lower trading volumes often benefit the most from mining, as it is the only practical way to trade them.
Overall, mining and staking both have specific advantages. Staking typically has lower risk and does not require locking up funds, making it suitable for situations requiring quick operations. However, in the long term, mining offers greater flexibility and the ability to switch between different platforms and tokens to achieve higher yields. Mining helps diversify investment portfolios and allows reinvestment of earnings to earn more interest. Although mining may bring higher income, the cost of switching platforms and tokens should be considered. In general, staking is more secure and stable, making it suitable for long-term investment.

Staking and mining are still somewhat new concepts, and they are sometimes even used interchangeably. Both involve holding cryptocurrency assets to generate interest. Here are some common questions answered for both scenarios:
1) Is mining better than staking? In most cases, mining offers higher returns than staking. However, these returns are dynamic. On the other hand, with the fixed annualized return provided by staking strategies, users can ensure their earnings at the end of the staking period. Ultimately, it all depends on your own risk preference and investment style.
2) Is mining riskier than staking? Mining (especially leveraged mining) may carry risks due to the impact of price fluctuations associated with certain tokens; however, many miners have achieved positive returns through this strategy.
3) Is staking a form of mining? Sort of. Liquidity mining is a derivative form of mining, while mining is a derivative form of staking.
4) Is mining profitable? Yes, returns typically fluctuate between 5% and 30%, depending on the specific DeFi protocols and asset categories involved. While every investment strategy carries risks, staking provides an interesting option for traders seeking higher returns without taking on too much risk.
Source: Medium
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



