Inscription ecology is booming, and technological innovation continues to enrich application scenarios.
Author: Kernel Ventures Stanley
Source: Kernel Ventures: The New Narrative of Inscription under the Support of Different Ecosystems
Translation: Plain Blockchain

I. Background of Inscription Market
1.1 Market Overview
Since the launch of the Bitcoin Ordinals protocol in January 2023, protocols such as BRC20 and Ordinals assets (commonly referred to as "Ordinals") have swept through the entire Bitcoin chain. It is hailed as "the world of retail investors." This can be attributed to the fair distribution model of inscriptions such as BRC20, where chips are completely minted by individual retail investors, without institutions, project teams, or insider trading. The minting cost of Ordi is about $1 per inscription, but after being listed on the Gate.io trading platform, the price soared to $20,000 per inscription. The astonishing increase in value has driven the continued popularity of the BRC20 protocol, attracting numerous Ordinals players and leading to a continuous surge in Gas fees on the Bitcoin chain. At its peak, the lowest confirmed Gas even reached 400 s/vb, exceeding the highest level of Gas in the past three years.
Based on this, this article will delve into the exploration of various inscription ecologies on different chains, discuss the current situation of various protocols, and predict the development trends of inscriptions under the empowerment of the ecosystem.
1.2 Data Overview
The Bitcoin block fee rate chart vividly illustrates the sharp rise in fees during May-June and November. This surge reflects users' enthusiasm for inscription protocols, not limited to the BRC20 protocol alone. During this period, various protocols developed on the Bitcoin network were introduced, triggering a wave called "Bitcoin summer."
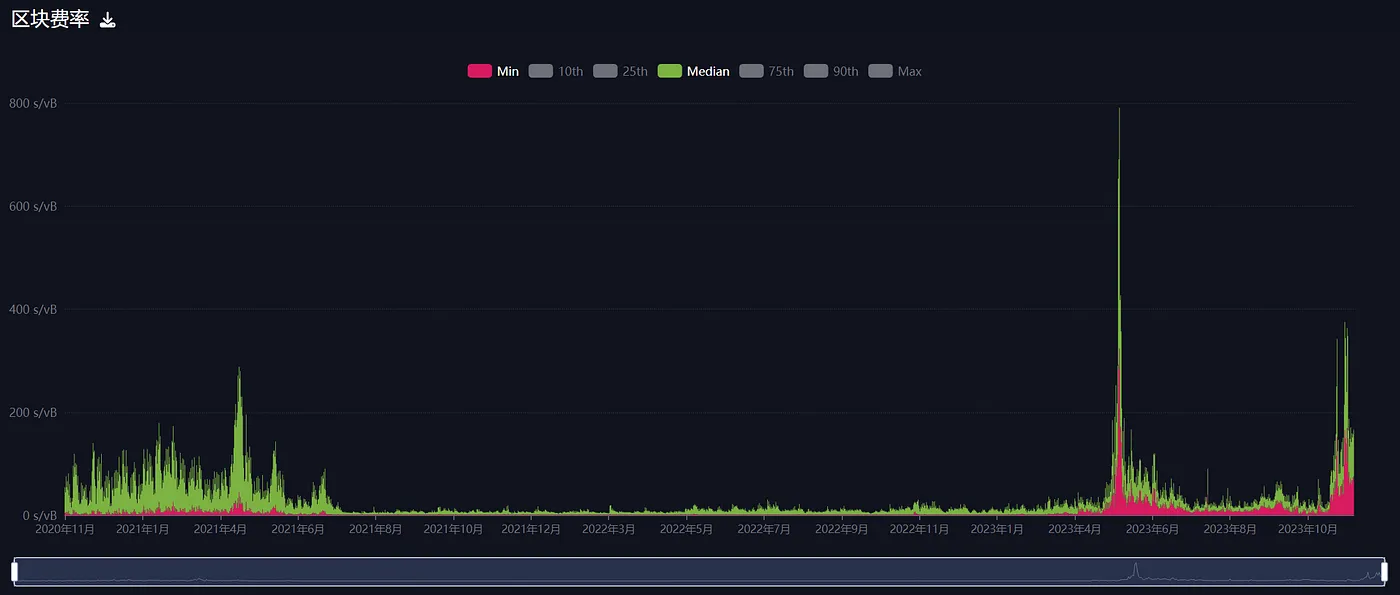
Bitcoin exchange rate over the past three years, image source: Mempool.space
From the data of inscription minting, the minting volume has stabilized and remained at a high level.
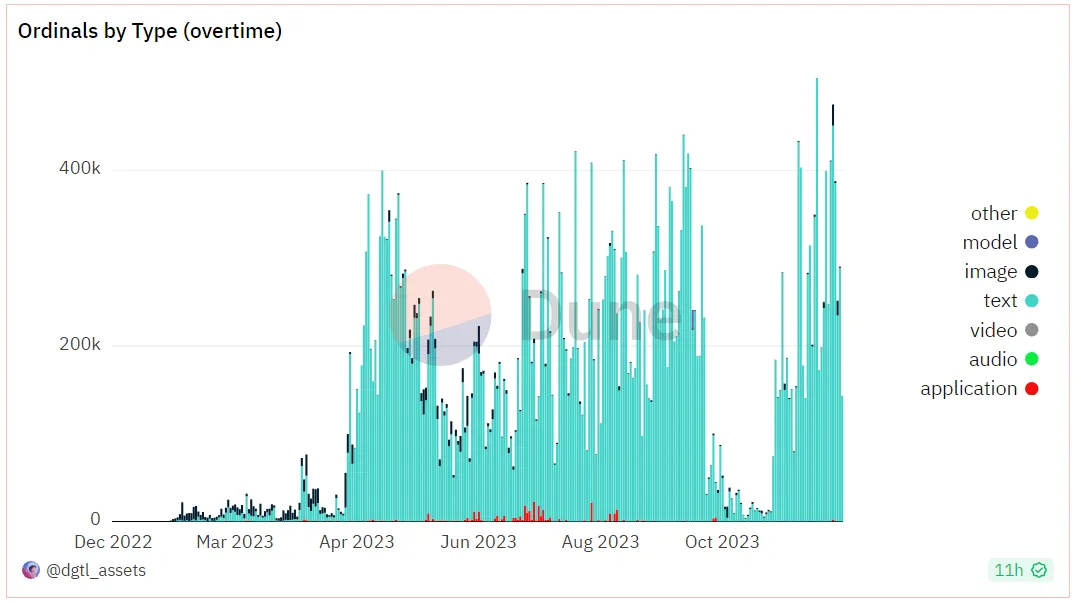
Ordinal inscription minting quantity, image source: Dune @dgtl_asserts
II. Vertical Analysis
This article will classify various chains and analyze the inscript protocols on each chain.
2.1 Bitcoin Chain
Ordinals / BRC20
On January 21, 2023, Bitcoin developer Casey Rodarmor launched the Ordinals protocol, allowing metadata to be engraved on the Bitcoin chain and assigning a script number. In March of the same year, Twitter user @domodata released the BRC20 protocol, evolving Token minting into on-chain strings. On November 7, Binance launched the flagship Token $ORDI of BRC20, causing a significant surge with a daily increase of nearly 100%.
As the first protocol in the inscription ecosystem, Ordinals encountered several issues:
BRC20 only supports four-letter Tokens, which poses significant limitations.
The selection of names is susceptible to front-running attacks, making token transactions prone to front-running.
The Ordinals protocol would lead to a large amount of redundant data on the Bitcoin network. For example, once a BRC20Token is minted, the original inscription becomes invalid once the Token transaction is sent. This would result in a large amount of data occupation, which is also a reason why some early Bitcoin enthusiasts are unwilling to support Ordinals.
Atomical Protocol
The ARC20 of the Atomical protocol uses a satoshi to represent the deployed Token and eliminates the four-character limit, allowing for more diverse gameplay. A unique project within this framework is "Realm," where each registered entity is a prefix text and ultimately has pricing rights to all suffixes. In terms of basic functionality, Realm can be used as a transfer and receipt address (payment name), and it also has various use cases, such as building communities/DAOs, identity verification, social profiles, seamlessly integrating with our envisioned DID development.
However, ARC20 and ATOM are still in a very early stage and require further development, including improvements to wallets and markets.
Rune
Casey, the founder of Ordinals, proposed a specific inscription implementation called Rune, aimed at issuing FT (fungible Tokens). This method allows Token data to be directly inserted into UTXO scripts, including the Token's ID, output, and quantity. Rune's implementation is very similar to ARC20, transferring Tokens directly to the BTC mainnet. The difference is that Rune includes the quantity of Tokens in the script data.
Although the concept of Rune is still in the conceptual stage, the founder of Trac developed the first functional protocol based on this idea, issuing PIPE Tokens. With high-profile publicity, PIPE quickly gained momentum, leveraging the speculative enthusiasm inherited from BRC20. Compared to BRC20, Rune has relatively stronger legitimacy, but gaining recognition from the BTC community still poses challenges.
RGB
Lightning network capacity, image source: Mempool.space
As the Ordinals protocol has enhanced the Bitcoin network's ecosystem, more and more developers and projects are turning their attention to the Lightning network, as it has extremely low transaction fees and a TPS (transactions per second) of 40 million.
RGB is a smart contract system based on BTC and the Lightning network, representing the ultimate scaling solution. However, progress has been slow due to its complexity. RGB transforms the state of smart contracts into concise proofs and engraves these proofs into BTC UTXO output scripts. Users can verify the UTXO to check the determinate changes in the smart contract's state. When the smart contract state is updated, a new UTXO is created to store the proof of this state change.
All smart contract data is entirely on the BTC chain, operated by dedicated RGB nodes, recording the complete data of smart contracts and processing the computational workload of transactions. Users verify the deterministic changes in the contract state by scanning the entire UTXO on the BTC chain.
RGB can be seen as Layer 2 of BTC, a design that utilizes the security of BTC to ensure smart contracts. However, as the number of smart contracts increases, the demand for UTXO encapsulated data will inevitably lead to a large amount of redundancy on the BTC blockchain.
Since 2018, RGB has been in the development stage without speculative content. Tether Limited, the issuer of Tether, is an important supporter of RGB, aiming to issue a large amount of USDT on the BTC RGB.
From a product perspective, the mainstream wallet currently in use is Bitmask, which supports Bitcoin and Lightning Network deposits, as well as assets of RGB-20 and RGB-21. Bitlight Labs is also developing the RGB network, planning to establish its own wallet system and write smart contracts for DEX (decentralized exchange). The project has acquired BitSwap (bitswap-bifi.github.io) and is preparing to integrate it into the RGB network.
The biggest advantage of RGB is its low transaction fees and extremely high scalability. There was a time when smart contract development on the Bitcoin network was difficult and received little attention. However, with the increasing popularity of the Ordinals protocol in the ecosystem, more and more developers are experimenting with smart contracts on the RGB network. These smart contracts are written in the Rust language, incompatible with Ethereum, resulting in a steep learning curve and requiring further technical evaluation.
2.2 Other POW Chains
During the heyday of inscriptions on the Bitcoin chain, as other PoW chains are homologous and based on the UTXO spending model, Ordinals has migrated to some leading PoW public chains. In this article, we will analyze examples from the Dogecoin and Litecoin chains, as they have high market acceptance and development integrity.
Dogecoin:
The DRC-20 protocol on the Dogecoin chain is based on Ordinals, with functionality similar to the Bitcoin chain. However, it has gained popularity due to its low transaction fees and strong meme appeal.
Litecoin:
Similarly, the LTC-20 protocol on the Litecoin chain is also based on Ordinals. The protocol has received endorsements and attention from the Litecoin official team and its founder, Charlie Lee. It can be said to have a "noble lineage." The trading markets Unilit and Litescribe, as well as the wallet Litescribe, show a high level of development integrity, and the first Token $Lite has been listed on the Gate trading platform.
However, there were issues with the protocol before the introduction of indexing. A bug was discovered after the index was launched, leading to an increase in the issuance, but it has now been fixed and is worth noting. It is evident from the chart that after the LTC20 protocol was introduced, gas fees on the Litecoin chain surged significantly.
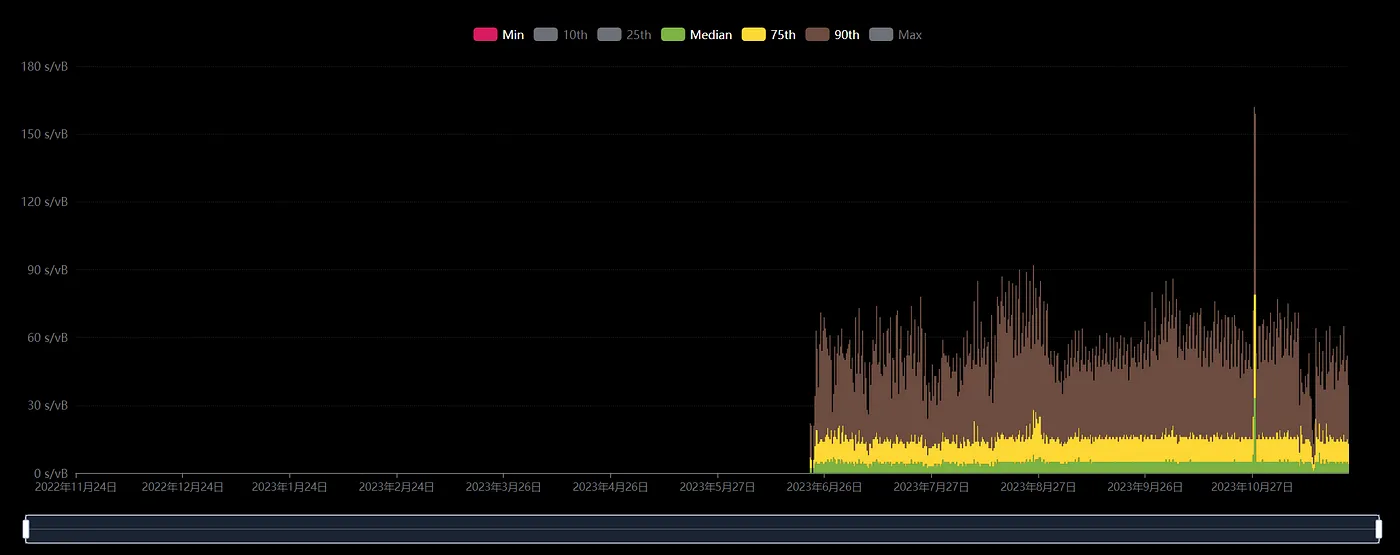 Litecoin exchange rate over the past year, image source: Litecoinspace
Litecoin exchange rate over the past year, image source: Litecoinspace
2.3 Ethereum Chain
Ethicality
As of now, the trading platform Etch on the Ethscriptions protocol has achieved a trading volume of 10,500 ETH. The initial price of the first Token Eths was $4,300. For those who held on from the beginning, the initial investment cost on June 18 was less than 1U. Those who persevered have now received a return of over 6,000 times the initial investment.
Eth's core is the Ethscriptions Virtual Machine (ESC VM), which can be likened to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The "dumb contracts" in the ESC virtual machine allow Eths to break free from the inscription limitations of NFT speculation and enter the realm of functionality and practicality. Eths has officially entered the competition in the base layer and L2 solution space.
The Eths community says, "Eths represents another approach to Ethereum Layer 2. Unlike typical Layer 2 solutions, which are independent chains and may have backdoors, Eths transacts on the Ethereum mainnet, with gas fees as cheap as on Layer 2. It supports various activities, such as exchanging on the Eths platform, DeFi, and GameFi. The key is that it runs on the mainnet, making it more secure and decentralized than Layer 2."
However, elucidating this new Layer 2 narrative is challenging. Firstly, token splitting is still in the development stage, and the current inscriptions are still non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that cannot be split into fungible tokens (FTs).
As of the latest news, FacetSwap (https://facetswap.com/) has introduced the splitting feature. But it is worth noting that mainstream trading markets currently do not support split inscriptions. Users can wait for future adjustments. Currently, split inscriptions can be used for activities such as exchanges and adding liquidity on Factswap. All operations are resolved through a virtual address (non-existent address) 0x000…Face7. Users can embed messages in IDM and send the hexadecimal data of the message to an address ending with Face7 for approval, transfers, and other operations. As it is still in the early stages, its development trajectory still needs to be observed.
2.4 Other EVM Chains
Evm.ink
Evm.ink has migrated the protocol standard of Ethscriptions to other EVM-compatible chains, allowing these chains to mint inscriptions and build indexes for other EVM chains. The recently popular projects POLS and AVAL use Evm.ink (essentially the standard of Ethscriptions) for index identification.
POLS character selection data, image source: Dune @satsx
AVAL character selection data, image source: Dune @helium1990_
POLS and AVAL have a total supply of 210 million inscriptions each. POLS has over 80,000 holders, while AVAL has over 23,000 holders. The minting progress for both is approximately 2-3 days. This indicates a strong community interest in low-cost Layer 2 inscriptions, as they offer high investment returns.
Due to their low cost, users from the long tail of the BTC and ETH chains have participated, leading to overflow. This trend is not limited to these two chains. Other chains like Heco and Fantom have also experienced a surge in gas fees, all related to inscriptions.
Daily transaction volume on EVM chains, image source: Kernel Ventures
2.5 Solana
SPL20
Solana inscriptions began at 4 am on November 17 and were completed by 8 am, with a total of 21,000 inscriptions. Unlike other networks, the main body of inscriptions is NFT, and the index content is the actual inscriptions. NFTs can be created on any platform, and the index is determined based on the hash of the image or file. The second point is embedded text; only inscriptions with matching hashes and embedded text are considered valid. Currently, major proxy platforms use IPFS, while other proxy platforms use AR.
Solana inscriptions, like Eths, have a significant limitation - they cannot be split. Due to the lack of splitting capability, they are essentially NFTs, lacking the liquidity and operational convenience equivalent to tokens, not to mention the vision of future Dex Swap.
The protocol's founder is also the founder of TapPunk on the Tap protocol. The team behind the largest proxy platform, Liberplex (https://www.libreplex.io/), has been very proactive since its launch. The team has made rapid progress in development, completing operations such as hash indexing and changing inscription properties (invariability). They also host live coding and Q&A sessions on the official Discord. The first inscription "Sols" has a minting cost of approximately $5. The highest price in the secondary market is 14 SOL, with a floor price of 7.4 SOL, equivalent to $428. Daily trading volume exceeds 20,000 SOL, equivalent to approximately $1.2 million, with active turnover.
3. Core Comparison
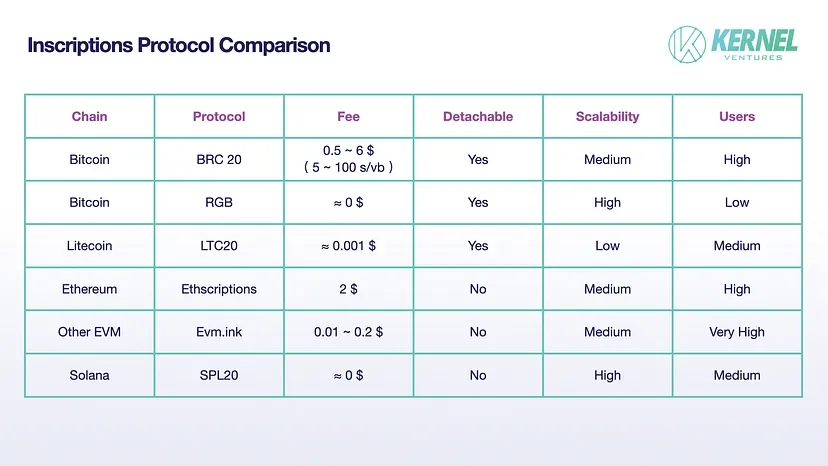
Comparison of mainstream inscription protocols, image source: Kernel Ventures
The chart compares several major inscription protocols based on four dimensions: cost, divisibility, scalability, and user base.
- Cost: The RGB protocol stands out with the best fee rates, achieving almost zero-cost transactions using the Lightning Network.
- Divisibility: Solana and recent EVM protocols lack the ability to split, and future developments in this area are worth looking forward to.
- Scalability: The smart contract functionality of the RGB protocol provides significant scalability. Solana's scalability is still under discussion, but the team and the Solana Foundation express support, indicating that it may not lack scalability.
- User base: EVM chains naturally have lower gas costs, attracting a larger user base due to the lower cost of trial and error. BRC20, as the first inscription token, ranks first in orthodoxy and has accumulated a large user base.
3.2 Protocol Token Data Comparison
Comparison of protocol tokens, image source: Kernel Ventures
Analyzing the mainstream tokens of various protocols, it is evident that the current market value of these tokens is approximately $6 billion, not including small-cap currencies. In addition, Ordi accounts for 80% of the total market value, indicating significant development opportunities for other protocols. It is worth noting that protocols like RGB are still in the process of improvement and have not yet issued tokens.
In terms of the number of holders, Pols and Ordi dominate, while holders of other protocols are fewer. Eths and Solana inscriptions have not been split, so a comprehensive analysis of holder distribution is still under development.
3.3 Innovation and Risk Analysis
Currently, the main use of inscriptions is fair distribution, allowing users to fairly participate in projects. However, the development of the inscription space is not limited to fair launches.
The latest developments in the inscription space show significant vitality and innovation. The industry's growth is largely attributed to key technological advancements in Bitcoin, such as SegWit, Bech32 encoding, Taproot upgrade, and Schnorr signatures. These technologies not only improve the transaction efficiency and scalability of the Bitcoin network but also enhance its programmability.
For example, in the RGB protocol, smart contracts built on the Bitcoin Lightning Network not only exhibit extremely high transaction volume (40 million per second) but also benefit from being part of the largest blockchain ecosystem, Bitcoin.
Regarding risks, caution is advised, especially for certain launchpads. For example, the recent Rug project Ordstater case, following the success of MUBI and TURT, led to a surge in launchpads. Some platforms may execute a Rug Pull directly after the initial DEX offering (IDO). It is crucial to carefully read the whitepaper and research the background before participating in any project, to avoid blindly following KOLs due to FOMO.
4. Future Potential of the Inscription Ecosystem
4.1 Market Potential
Galaxy Research and Mining predicts that by 2025, the market value of Ordinals will reach $50 billion, while the estimated number of inscriptions at that time will be only 260,000. Currently, the number of inscriptions has reached 33 million, growing 126 times in just six months. The market value of Ordi has reached $400 million, and Sats has reached $300 million. This indicates that the forecast for the entire inscription market has been greatly underestimated.
4.2 Product Potential
Currently, BRC20 trading activities are mainly concentrated on OKX and Unisat. The Web3 wallet launched by OKX this year provides a good experience for trading BRC20 assets. The improvement of wallet-side infrastructure further simplifies and shortens the entry path for "retail investors," allowing them to smoothly enter this new market. With the emergence of various protocols, different protocols have launched their own trading markets and wallets, such as Atomicals, Dogechain, Litecoin, and more. However, the wallets currently available on the market are modified versions of Unisat, built on the open-source foundation of Unisat.
In comparison to Bitcoin (POW) and Ethereum, we can analogize various protocols as different chains, with the fundamental difference being the Chain ID. Therefore, future products may involve Unisat integrating different protocols, allowing users to switch between protocols within the wallet as needed, similar to the chain-switching feature in wallets like Metamask.
Vertical Potential
As funds continue to pour into the inscription market, users are no longer satisfied with meme-driven speculation and are shifting their focus to inscription-based applications. Unisat has brought innovation to BRC20 by introducing BRC20-Swap, allowing users to easily exchange BRC20 Tokens similar to AMM DEX. As the first liquidity-enhancing product in the Ordinals ecosystem, Unisat is poised to unleash the potential of the Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem, potentially leading to the development of lending and derivative products. Recently, Unisat has also opened its API interface, making it convenient for small developers to call various functions, such as automatic batch order scanning, monitoring of inscription minting, and more. This can lead to the creation of many utility projects.
While transaction fees on the Bitcoin network are relatively high, for Layer2 solutions like Stacks and RIF, the fees are lower, but they lack a user base and sufficient infrastructure. This makes Bitcoin's EVM an intriguing story. For example, BEVM is a project based on the Ethereum network, providing a Layer2 solution for the Bitcoin ecosystem, with native on-chain BTC tokens. Users can use the official cross-chain bridge to move Bitcoin from the mainnet to BEVM. BEVM's EVM compatibility makes it easy to build applications on EVM chains, and the barriers to entry for migrating DeFi, exchanges, and more from other chains are lower.
However, Bitcoin's EVM has several issues to consider. Issues include whether cross-chain assets can maintain decentralization and immutability, consensus issues with EVM chain nodes, and how to synchronize transactions with the Bitcoin network (or decentralized storage). Due to the relatively low barriers to entry for Ethereum Layer2, security may be compromised, which is the primary concern for those currently interested in Bitcoin EVM.
Summary
This article analyzes various inscription protocols on the Bitcoin chain, such as Ordinals (BRC20), Atomical, RGB, Pipe, and compares them with other Pow chains, Ethereum's Ethscriptions, Evm.ink, and Solana's SPL20 protocol, exploring differences in cost, divisibility, scalability, and user aspects. In the context of the inscription market, starting with the Ordinals protocol, a wave of inscription protocols like BRC20 is referred to as the "retail world." This analysis provides an overview of data such as Bitcoin block fees and the number of forged inscriptions, offering insights into the development trends of the inscription ecosystem.
In the analysis of the inscription market, the core elements of mainstream inscription protocols, such as cost, divisibility, scalability, and user count, are compared to demonstrate their similarities and differences. Finally, through the comparison of protocol token data and core protocol comparison, a comprehensive analysis of the market value and user distribution of various mainstream protocols is summarized, emphasizing innovation points and risk analysis, highlighting the vitality and innovation in the inscription field.
Looking ahead, the inscription field is expected to continue technological innovation, driving the practical application of more complex functionalities. The strong market development is expected to maintain stable growth, providing more opportunities for investors and participants. Additionally, more creative projects and protocols are expected to emerge, further enriching the inscription ecosystem of public chains like Bitcoin. As the inscription domain provides new income opportunities for miners, their income may also increase.**
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




