Original Source: Hard AI

Image Source: Generated by Wujie AI
These days, Nvidia's "loophole" breakthrough in the US AI restrictions, launching a "special supply model" for the Chinese market, and preparing to continue selling high-performance GPUs to Chinese companies, has caused quite a stir.
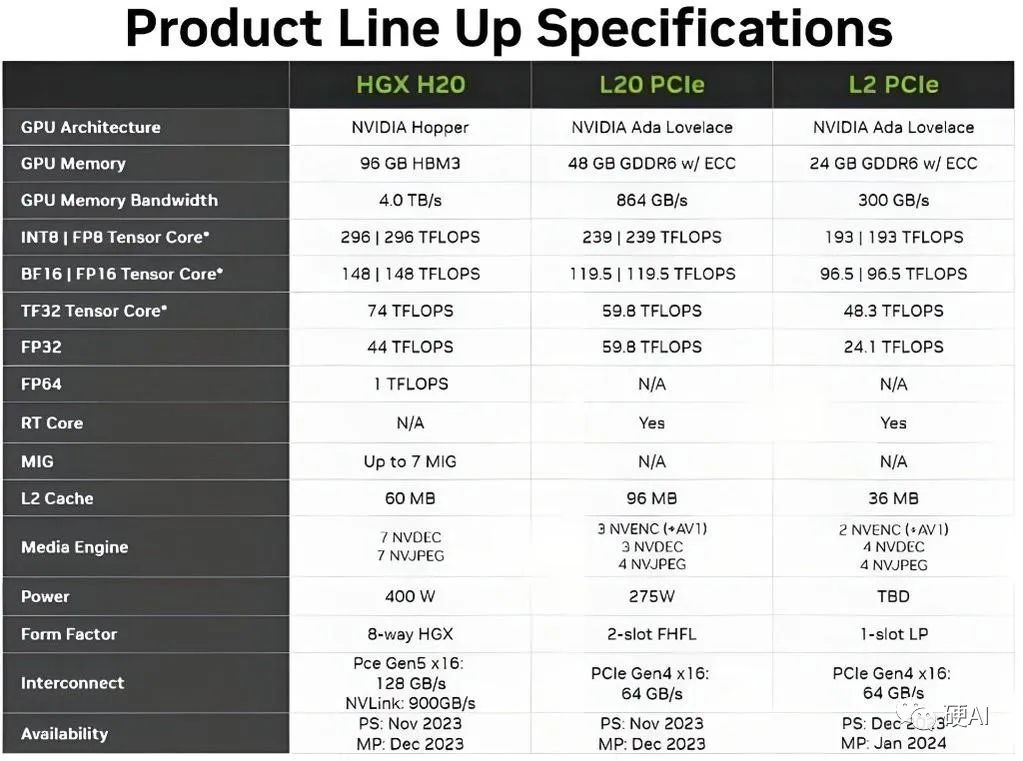
According to the latest reports from the media, Nvidia is about to launch at least three new AI chips, including H20 SXM, PCIe L20, and PCIe L2, to replace the previously export-restricted H100. These three chips are all based on the Hopper GPU architecture, with a theoretical peak performance of up to 296 TFLOPS (trillions of floating-point operations per second).
So, how does the performance of the three "special supply model" chips H20, L20, and L2 compare to the H100?
Theoretically, the speed of H100 is 6.68 times faster than H20. According to analyst Dylan Petal's latest blog post, even if the actual utilization of H20 can reach 90%, its performance in actual multi-card interconnection environments can only approach 50% of H100.
Some media also claim that the comprehensive computing power of H20 is only equivalent to 20% of H100, and the cost of computing power will significantly increase due to the addition of HBM memory and NVLink interconnection modules.
However, the advantages of H20 are also quite obvious, as it is more than 20% faster than H100 in large language model (LLM) inference. The reason is that in some aspects, H20 is similar to the next-generation super AI chip H200, which is set to be released next year.
Nvidia has already produced samples of these three chips, and H20 and L20 are expected to be released in December this year, while L2 will be released in January next year. Product sampling will begin one month before the release.
01
"H20 Vs. H100"
First, let's look at the H100, which has 80GB of HBM3 memory, a memory bandwidth of 3.4Tb/s, and a theoretical performance of 1979 TFLOP, with a performance density (TFLOPs/Die size) as high as 19.4, making it the most powerful GPU in Nvidia's current product line.
The H20, with 96GB of HBM3 memory and a memory bandwidth of 4.0 Tb/s, both higher than the H100, but with a computing capability of only 296 TFLOP and a performance density of 2.9, far inferior to the H100.
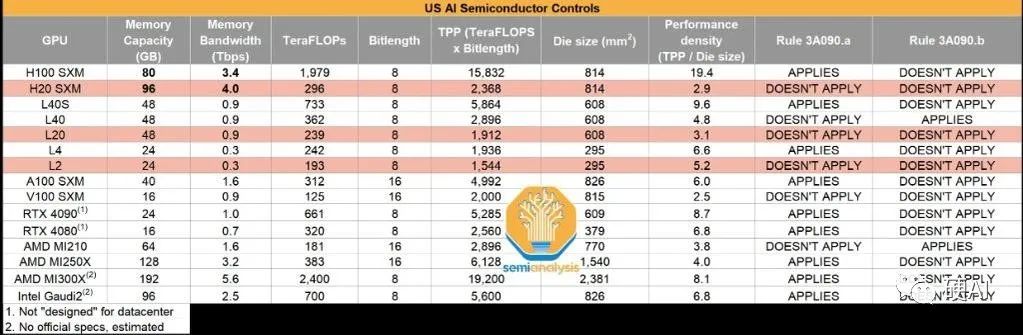
Theoretically, the speed of H100 is 6.68 times faster than H20. However, it is worth noting that this comparison is based on the floating-point calculation capability of FP16 Tensor Core (FP16 Tensor Core FLOPs), and sparse computing is enabled (greatly reducing the amount of computation, thus significantly improving speed), so it does not fully reflect all of its computing capabilities.
In addition, the GPU's thermal design power is 400W, lower than the H100's 700W, and can be configured with 8 GPUs in the HGX solution (Nvidia's GPU server solution). It also retains the high-speed NVLink interconnection function of 900 GB/s and provides 7 MIG (Multi-Instance GPU) functions.
H100 SXM TF16 (Sparsity) FLOPS = 1979
H20 SXM TF16 (Sparsity) FLOPS = 296
According to Peta's LLM performance comparison model, at moderate batch size, the peak token/second of H20 is 20% higher than H100, and the token-to-token latency at low batch size is 25% lower than H100. This is because the number of chips required for inference has been reduced from 2 to 1, and if 8-bit quantization is used again, the LLAMA 70B model can run effectively on a single H20, instead of needing 2 H100s.
It is worth mentioning that although the computing capability of H20 is only 296 TFLOPS, far less than the 1979 of H100, if the actual utilization rate of H20 MFU (currently H100's MFU is only 38.1%), this means that H20 can actually achieve 270 TFLOPS, so the performance of H20 in actual multi-card interconnection environments is close to 50% of H100.
From the perspective of traditional computing, H20 is somewhat downgraded compared to H100, but in terms of LLM inference, H20 is actually more than 20% faster than H100, as it is similar to the upcoming H200 in some aspects. Note that H200 is the successor to H100, a super chip for complex AI and HPC workloads.
02
"L20 and L2 have more streamlined configurations"
At the same time, L20 is equipped with 48GB of memory and a computing performance of 239 TFLOP, while L2 is configured with 24GB of memory and a computing performance of 193 TFLOP.
L20 is based on L40, and L2 is based on L4, but these two chips are not commonly used in LLM inference and training.
Both L20 and L2 adopt the PCIe form factor, using PCIe specifications suitable for workstations and servers. Compared to higher-spec models such as Hopper H800 and A800, their configurations are more streamlined.
L40 TF16 (Sparsity) FLOPs = 362
L20 TF16 (Sparsity) FLOPs = 239
L4 TF16 (Sparsity) FLOPs = 242
L2 TF16 (Sparsity) FLOPs = 193
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




