Source: New Smart Element
McKinsey AI report released, generative AI is progressing rapidly, with huge economic benefits, and cannot be underestimated in the future.
McKinsey's heavyweight report is out!
The core conclusion can be summed up in one sentence: the time for AI to reach human level will be faster than imagined, with the median prediction being before 2030.
It's worth noting that compared to the predictions in 2017, the new report stands out for its optimism.
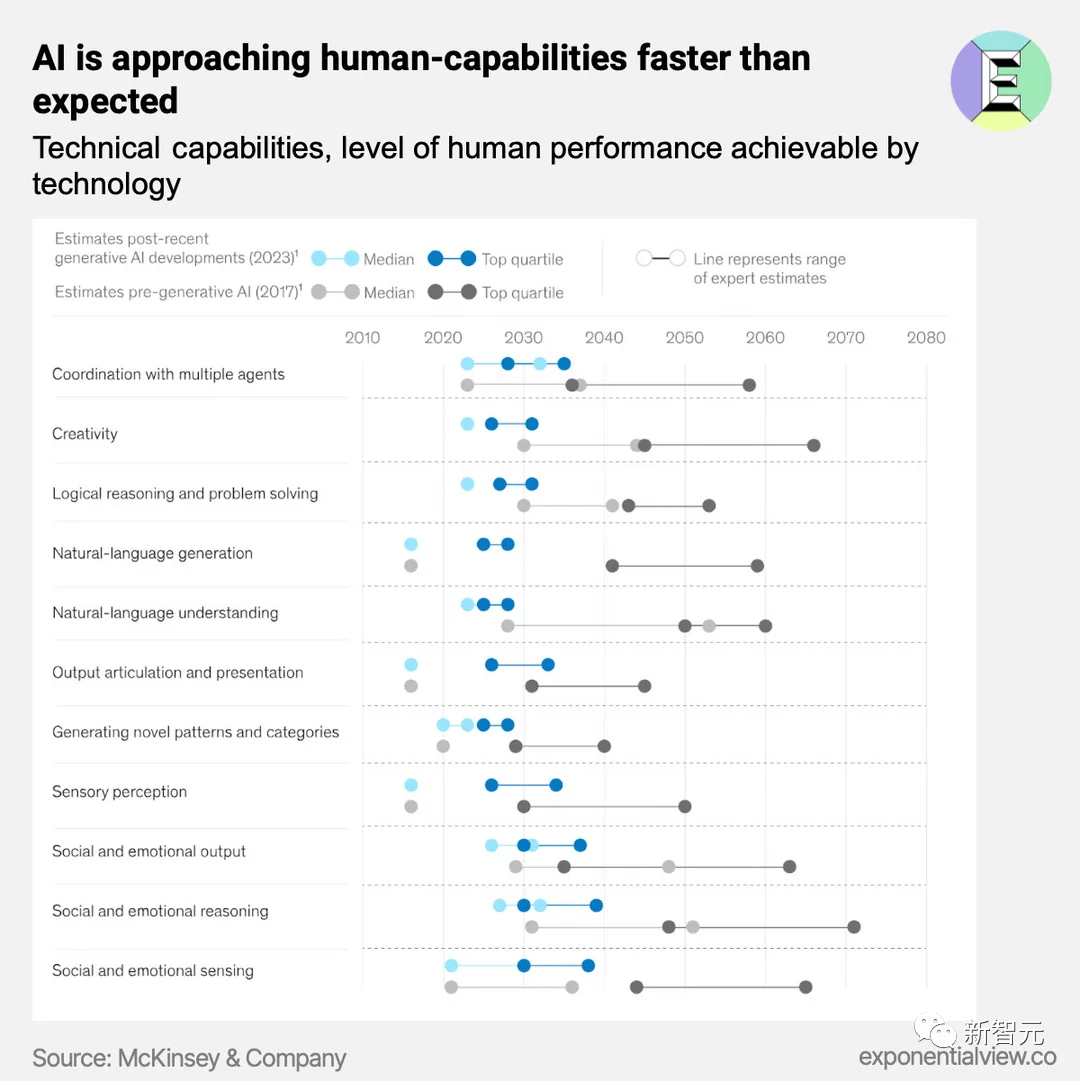
The above image is the final result chart of the report, which we will discuss in detail later.
Report Overview
To begin with, the report first provides a perfect summary of the extent to which our lives are currently influenced by technology.
In short, AI has already permeated every aspect of our lives.
In 2016, when DeepMind created AlphaGo, and defeated world champion Lee Sedol, AI once again entered our field of vision on a large scale. However, because it was limited to the game of Go, it gradually faded from the spotlight after the initial hype.
But this year is different.
Not to mention the skyrocketing number of users for ChatGPT, just products like Copilot, Stable Diffusion, and other generative AI have swept through our lives like a whirlwind.
The difference this time is that these AI tools are accessible to everyone. Anyone can use ChatGPT for creation, Midjourney for drawing, and Copilot for making presentations.
ChatGPT, equipped with GPT-4, has directly taken off in all aspects of performance from GPT-3.5. And then there's Anthropic's Claude, which can process 100,000 tokens (roughly the length of a short novel) in just one minute. In comparison, the first generation of Claude in March this year had a performance roughly one-tenth of the current one.
The report focuses on the speed of AI development, which has risen in just a few months.
In this report, generative AI is defined as applications built on basic models. The basic models have gained a wealth of new features in areas such as images, videos, audio, and code, and the performance of existing features has also seen significant improvements.
The report states that our understanding of the capabilities of generative AI is still in its infancy.
This is why McKinsey has produced this report, in order to gain a more thorough understanding of the future of generative AI.
Impact on the Economy and Society
Currently, major enterprises are all trying to apply generative AI and quickly adjust their workflows to adapt to the changes brought about by new technology.
The report points out that it is necessary for us to thoroughly understand what generative AI will bring to the overall social and economic development.
In the figure below, the report uses two complementary perspectives to determine where generative AI's capabilities can bring the greatest value in which areas, and how significant these values are.
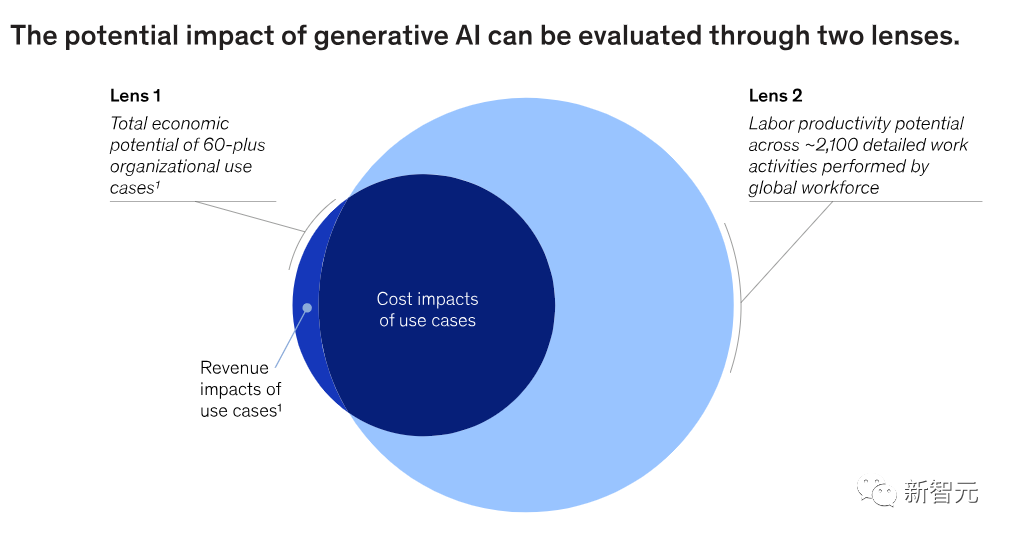
Lens 1 in the above figure is a comprehensive scan of enterprises that can use generative AI. These are called "use cases."
For example, one use case in marketing is using generative AI to generate personalized email content, and the results include reducing the cost of generating such content, as well as increasing revenue by significantly improving the effectiveness of high-quality content on a large scale.
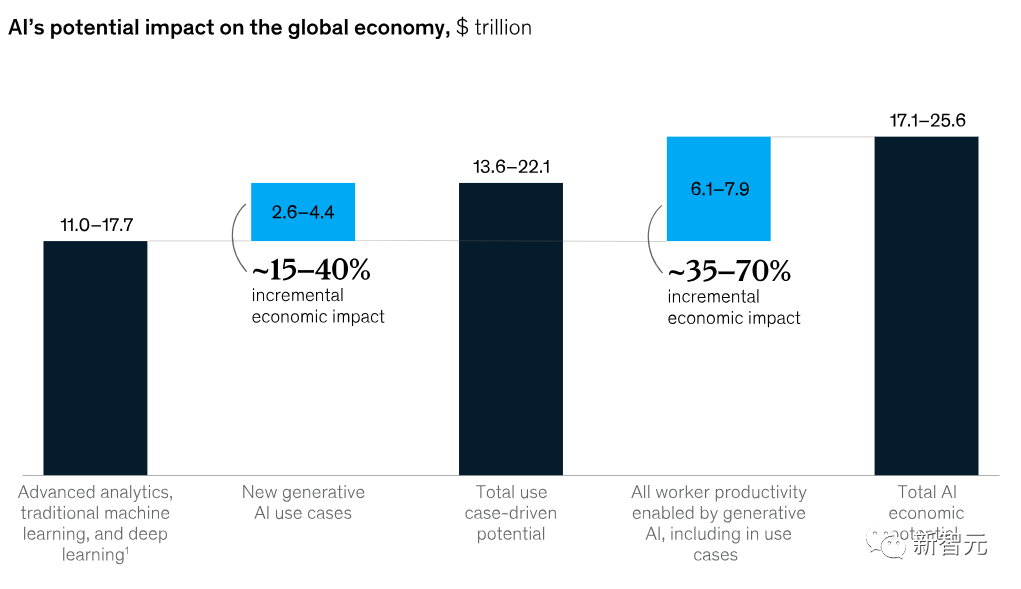
Based on this, the report identifies a total of 63 generative AI use cases covering 16 business functions, which, if applied across various industries, could bring annual economic benefits of $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion.
That's quite a lot.
This is an increase of 15% to 40% compared to the current estimated economic value of $11 trillion to $17.7 trillion, which was the prediction by McKinsey in 2017.
Lens 2 is a supplement to Lens 1, where the report analyzes the potential impact of generative AI on approximately 850 types of occupations.
Experts simulated various scenarios to estimate when generative AI could perform each of the more than 2,100 tasks that make up the global economy, which may include tasks such as communicating with others about operational plans or activities.
In this way, we can estimate how generative AI, with its current capabilities, will affect the labor productivity of all jobs performed by the global workforce, as shown in the figure below.
Future Potential
Although the current economic benefits are already considerable, the report states that there is much more to come.
Now let's talk about the potential.
Generative AI may have an impact on the functions of most businesses. However, if we measure the proportion of technical impact on the cost of functions, a few functions stand out, as shown in the figure below.
McKinsey analyzed 16 business functions and found that the annual value of only four functions—customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and research and development—accounts for approximately 75% of the total value of generative AI use cases.
In simple terms, not all businesses benefit significantly from AI from a technical perspective.
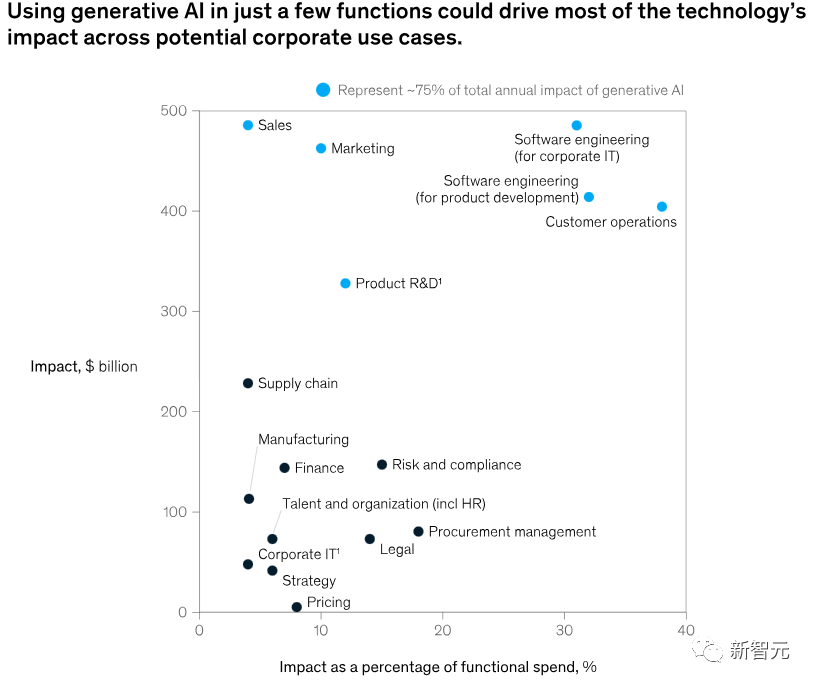
The report points out that in previous assessments of AI use cases, including several work areas such as manufacturing and supply chain, the potential value of generative AI is much lower.
The main reason for this is the nature of generative AI itself.
In addition to the potential value that generative AI can bring in specific use cases, it can also bring value to the entire company by fundamentally changing the company's internal knowledge management system.
We all know that generative AI has strong natural language processing capabilities, which can help employees easily search and retrieve internal knowledge stored by the company.
Clearly, this can enhance the team's ability to quickly access relevant information, enabling them to make wiser decisions and formulate effective strategies quickly.
Before the advent of generative AI, the same work might have taken a worker an entire day to complete, but after generative AI takes on these tasks, it is bound to generate huge benefits.
In addition, generative AI can also enhance value by collaborating with workers, speeding up their work efficiency, and enhancing their work capabilities.
I won't reveal whose DNA has been moved, but even this article was generated by the AI (not really).
In the 63 use cases analyzed in the report, generative AI has the potential to create a total value of $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion across various industries.
Of course, the specific impact depends on various factors, such as the combination of different functions, their respective importance, and more importantly—the industry's revenue scale, as shown in the figures below.
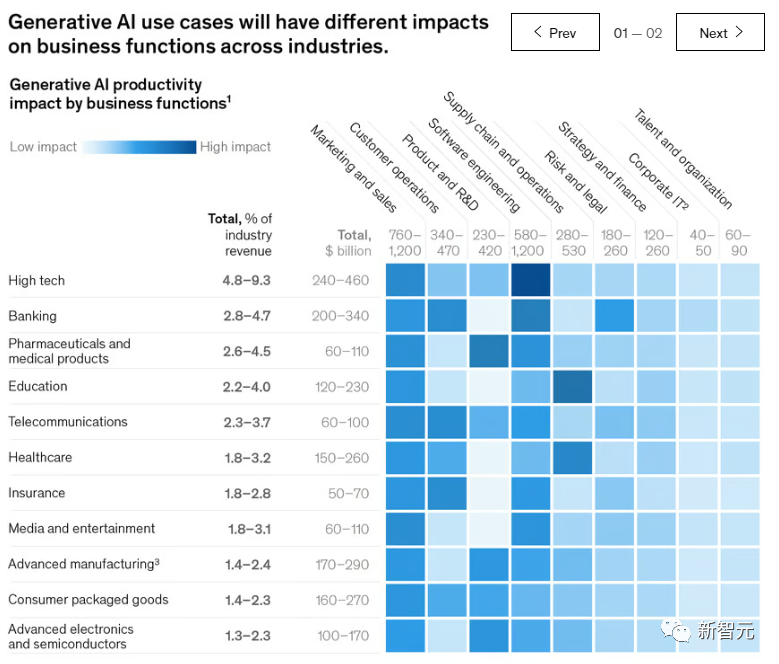
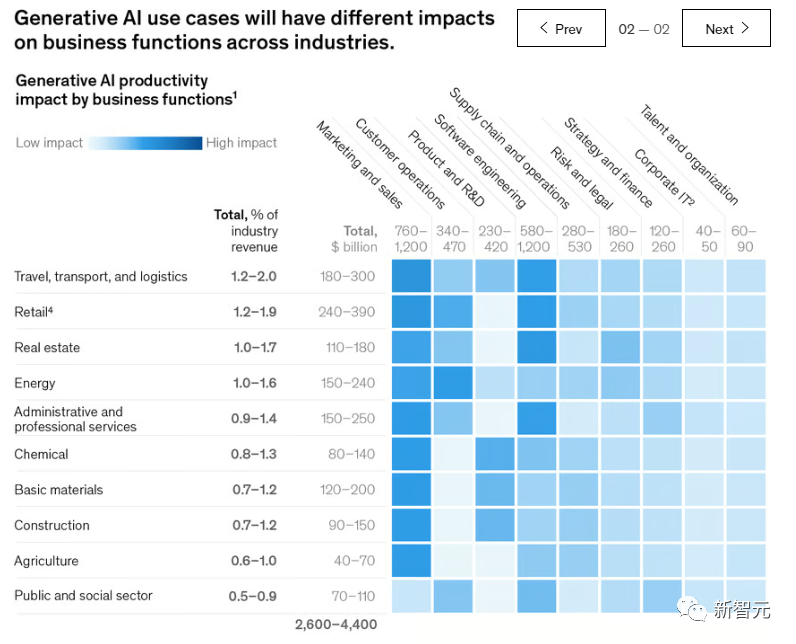
For example, according to the report, generative AI can bring about an additional value of approximately $310 billion to the retail industry (including automotive dealers) by enhancing functions such as marketing and customer operations.
In contrast, most of the potential value in the high-tech sector comes from the ability of generative AI to improve the speed and efficiency of software development, as shown in the figure below.

The report estimates that this number will become more impressive in the future, as the capabilities of AI are advancing rapidly.
Since 2017, the McKinsey Global Institute has been analyzing the impact of technological automation on different job activities and modeling various scenarios of technology adoption.
At that time, they estimated that workers spent at least half of their time adjusting existing technologies to automate processes, which is what we call the potential for technological automation.
Experts also simulated a range of possible scenarios to determine the adoption rate of these technologies and their impact on job activities in the global economy.
First, the widespread application of technology will not happen overnight. The transformation of technology from the laboratory to the automation of specific job activities takes time.
At the same time, if the cost of automation is higher than labor costs, then it is obviously not feasible.
Finally, even if it is feasible, it will take time to be implemented on a larger scale.
And this is the focus of the report. How much potential does generative AI have for automation in production and life, and how much can it improve work efficiency?
The report predicts that based on the current performance of generative AI, its capabilities will reach human performance faster than previously estimated, as shown in the figure below.
The institute previously believed that 2027 was the earliest year when technology could reach the intermediate level of human natural language understanding. However, in the latest report, this time has been brought forward to 2023.
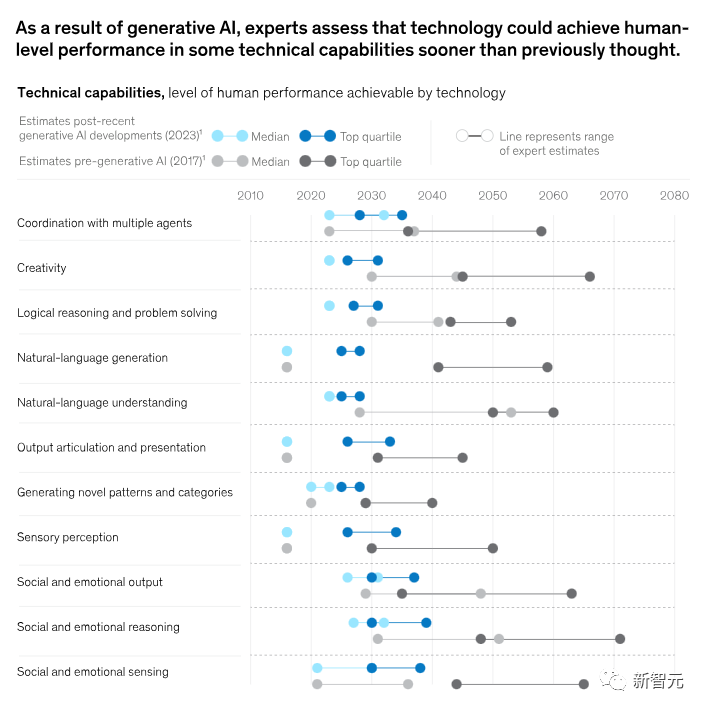
In theory, the current automation rate has increased from about 50% to 60-70% by integrating existing technologies.
Furthermore, due to the rapid development of generative AI's natural language capabilities, the curve of technological development potential is quite steep.
The figure below shows the 2017 forecast and the latest forecast, and from the curve, it is easy to see how "optimistic" it is.
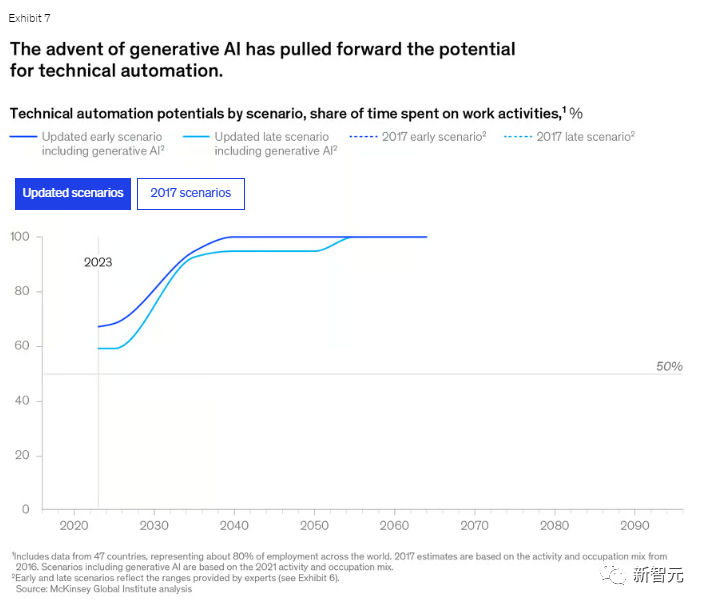
Latest forecast
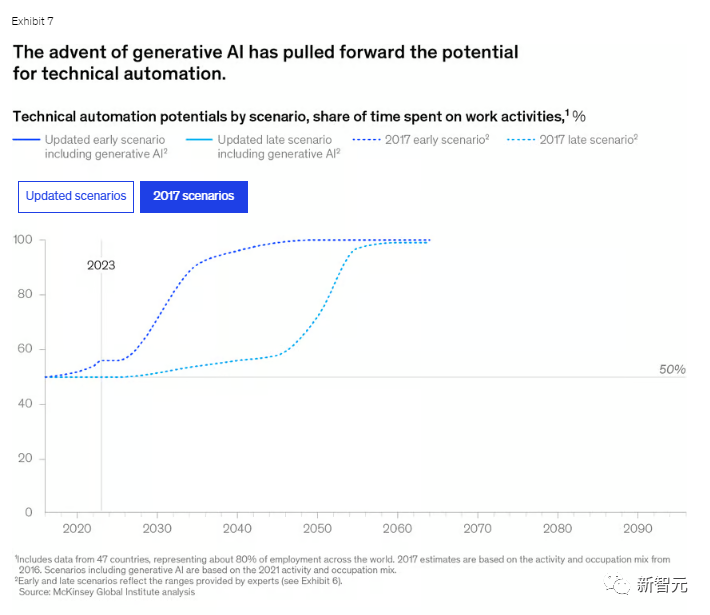
2017 forecast
The following figure is a curve chart from the report showing how the activities of workers will change daily, with the latest forecast at the top and the 2017 forecast at the bottom.
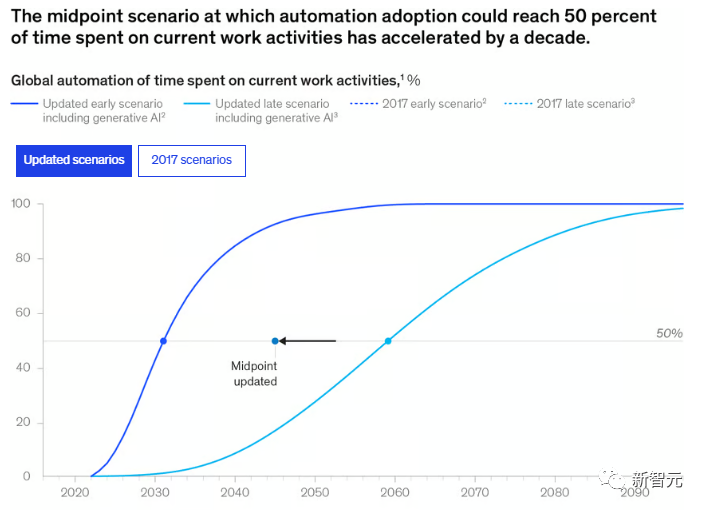
Latest forecast
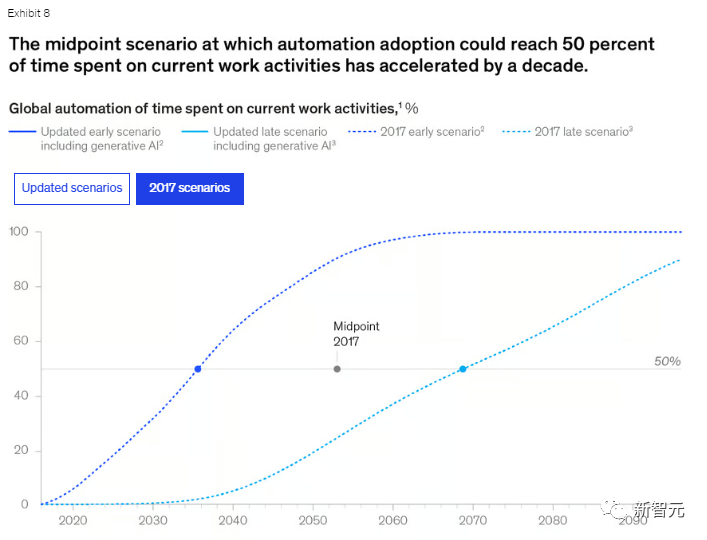
2017 forecast
Experts predict that generative AI may have the greatest impact on knowledge work, especially activities involving decision-making and collaboration, which previously had the lowest potential for automation, as shown in the figure below.
The report estimates that the potential for automating professional knowledge has increased by 34 percentage points, while the potential for automating management and talent development has increased from 16% in 2017 to 49% in 2023.
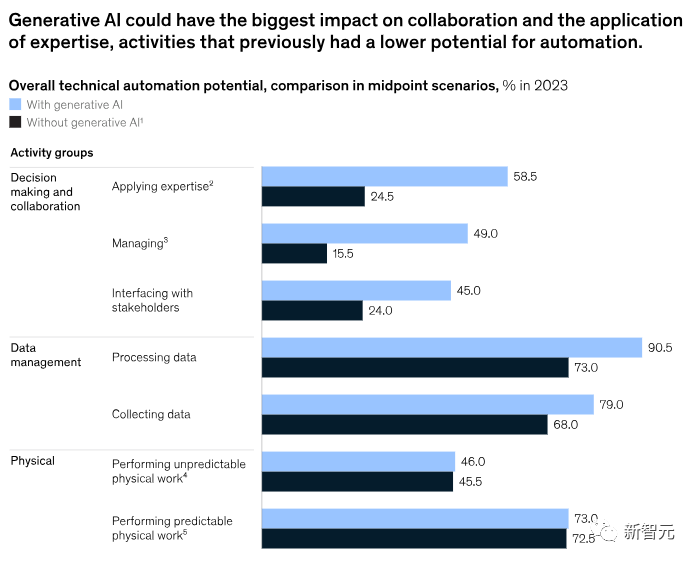
In addition, generative AI can understand natural language and apply it to various activities and tasks, which largely explains why the potential for automation is so great.
In the economic field, about 40% of the activities performed by workers require at least reaching the intermediate level of human understanding of natural language.
Therefore, many work activities involving communication, supervision, recording, and interaction with others are likely to be automated through generative AI, accelerating the transformation of professions such as education and technology, which were previously expected to be automated later, as shown in the figure below.
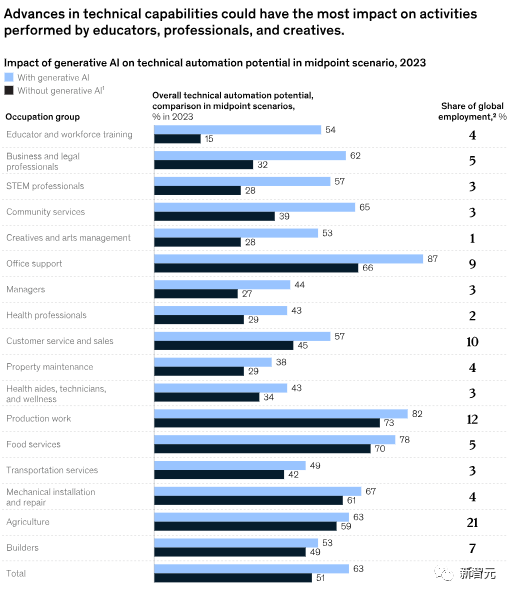
In addition to the above, the McKinsey report also provides analysis from other dimensions.
Due to space limitations, they are not listed one by one.
Where to go from here?
All of the above analyses can be said to focus on the overall picture of the industry.
To reflect the down-to-earth nature of the report, the final section focuses on the impact of generative AI on individuals and how each of us should respond.
The report states that with the development of new technologies, stakeholders must take action to prepare for opportunities and risks.
The main focus of concern is what we have always talked about, such as the problem of illusions, and the issue of knowledge copyright in the selection of training data.
The report predicts that, based on the median forecast, at least a quarter to a third of jobs will change in the next decade. For different roles of different people, the responses we need to make are completely different.
For leaders of companies and enterprises, what they need to consider is how to harness the potential value of generative AI while managing the risks it brings.
In the coming years, how will generative AI and other AI technologies change the mix of professions and skills required by companies? How will companies achieve these transformations in recruitment plans, retraining programs, and other aspects of human resources?
Can companies play a role in ensuring that technology is not used for negative purposes that could harm society?
How can companies transparently share their experiences in promoting the use of generative AI within and across industries with the government and society?
These are the questions that managers need to explore.
For decision-makers in government departments, what does generative AI mean for future workforce planning?
How can they provide necessary policy support as workers' activities change over time?
Can new policies be formulated or existing policies revised to enable AI to achieve greater social value?
Finally, as individuals, consumers, and citizens, how should we pay attention to the development of new technologies? Where can we obtain correct and fair information?
How can individuals balance the convenience and impact brought by generative AI?
As individuals, how can we express our demands in the decision-making process?
Many questions urgently require our deep consideration.
In short, this report comprehensively observes the significant impact of the explosion of generative AI on our society (especially in the economic aspect).
Reference:
https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/the-economic-potential-of-generative-ai-the-next-productivity-frontier?#business-value
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



