"Consortium chain" is the "favorite" of our country.
Author: Liu Honglin, Founder and Director of Shanghai Mancun Law Firm
01 Blockchain is not just a public chain
In the new pattern of the Web3 world, blockchain has always occupied an important position and is also an important part of our country's development strategy. In April 2020, the National Development and Reform Commission has clearly included "blockchain" in the new infrastructure. Overall, our country's attitude towards blockchain is very positive.
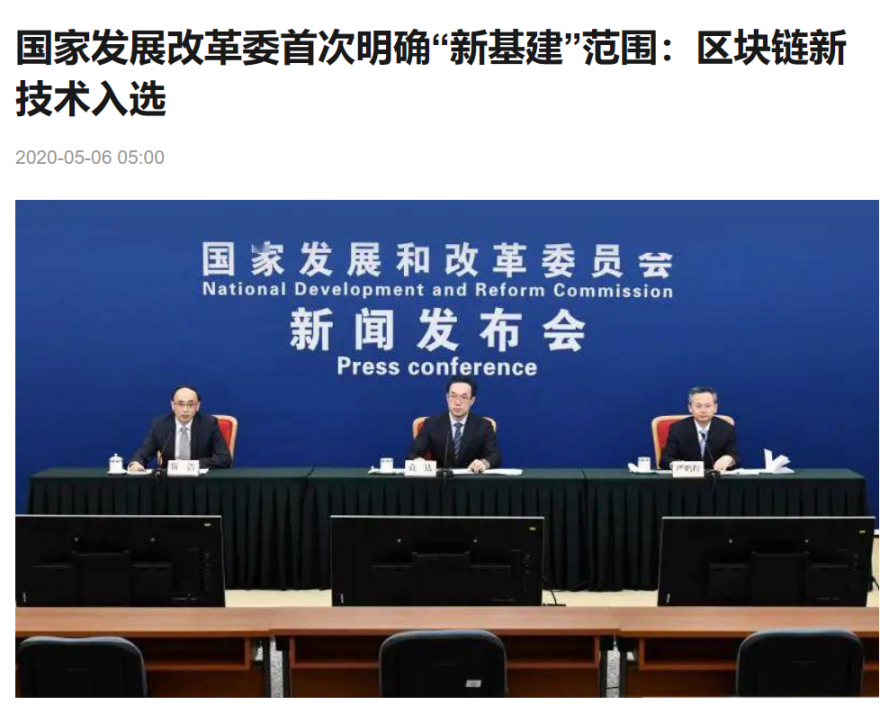
▲The above picture is from Sohu News
The country is clearly supporting the development of blockchain, so why do ordinary people like us always feel that blockchain is something "testing the illegal edge"? This is because most people only came to know about blockchain through virtual currencies such as "Bitcoin," "Ethereum," and "Tether," and our country has expressly prohibited "speculating on currency."
Indeed, blockchain is the core technology of virtual currency, but the virtual currency only uses one of its forms - "public chain." A public chain refers to a blockchain where anyone can read, send transactions, obtain valid confirmations, and participate in the consensus process. However, in addition to the public chain, blockchain also includes private chains and consortium chains.
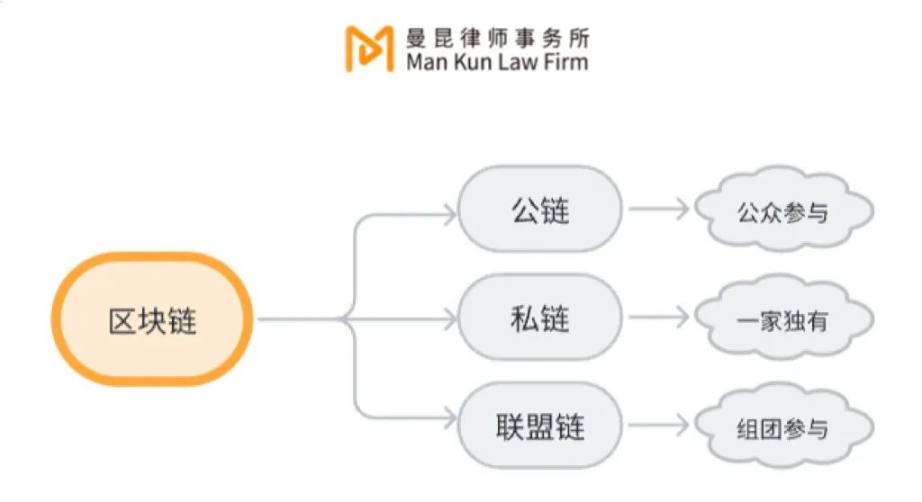
02 Consortium chain is China's "favorite"
According to the information released by the Cyberspace Administration of China in 2019, among the first 197 domestic blockchain information service filing numbers, the number of consortium chains was as high as 116, while there were only 25 public chain projects. It is not difficult to see where the "wind" of blockchain is blowing. It turns out that "consortium chain" is the "favorite" of our country. The reason why the country vigorously supports the consortium chain is naturally because it is more suitable for China's national conditions.
Why is it said that the "consortium chain" is more suitable for China's national conditions?
Blockchain is a decentralized distributed ledger technology. Simply put, it is like everyone having a ledger in their hands. Whenever there is a transaction, there will be a loudspeaker announcing "Zhang San has traded with Li Si," and then everyone will know about this transaction. Everyone records "Zhang San has traded with Li Si" in their own ledger. Everyone has a clear account, which makes blockchain technology able to solve problems such as centralized and opaque information, data tampering by intermediary institutions (such as banks, governments, etc.).
However, the public chain has the characteristics of decentralization, immutability, and transparency. This also means that the data on the public chain does not rely on centralized institutions and cannot control the data in the system. In addition, the public chain also has the characteristics of no access threshold and anonymity, allowing anyone to participate. This leads to a large number of blockchain projects based on the public chain facing issues such as KYC and anti-money laundering, especially those projects that issue tokens on the public chain often face questions about whether their token issuance constitutes illegal fundraising or illegal issuance of securities. It can be seen that the current regulatory mechanism in China is not very friendly to the public chain. Correspondingly, private chains operating under the name of blockchain are highly centralized and are not significantly different from traditional centralized servers, and obviously cannot solve the traditional problems in the industry. The consortium chain - this "compromise" - can solve traditional industry problems and is easy to regulate, naturally becoming the "seed player" for the development of blockchain in our country.
Consortium chains are jointly managed by multiple institutions, with each institution managing one or more nodes, and their data can only be read, written, and sent internally. Although the consortium chain sacrifices some "decentralization," it greatly enhances controllability and can largely meet the compliance and regulatory needs under Chinese law. While using blockchain technology to empower various industries, it also avoids the risks brought by the public chain.
Currently, China's consortium chains are steadily developing under policy support, growing like mushrooms after the rain. For example, AntChain, Baidu Super Chain, Tencent Cloud Blockchain… Among these influential domestic consortium chains are the China Blockchain Research Alliance (CBRA), China Distributed General Ledger Basic Protocol Alliance (ChinaLedger), and Financial Blockchain Cooperation Alliance (GoldenChain). These three alliances jointly drafted the "China Blockchain Technology and Application White Paper," setting industry standards for the development of consortium chains.
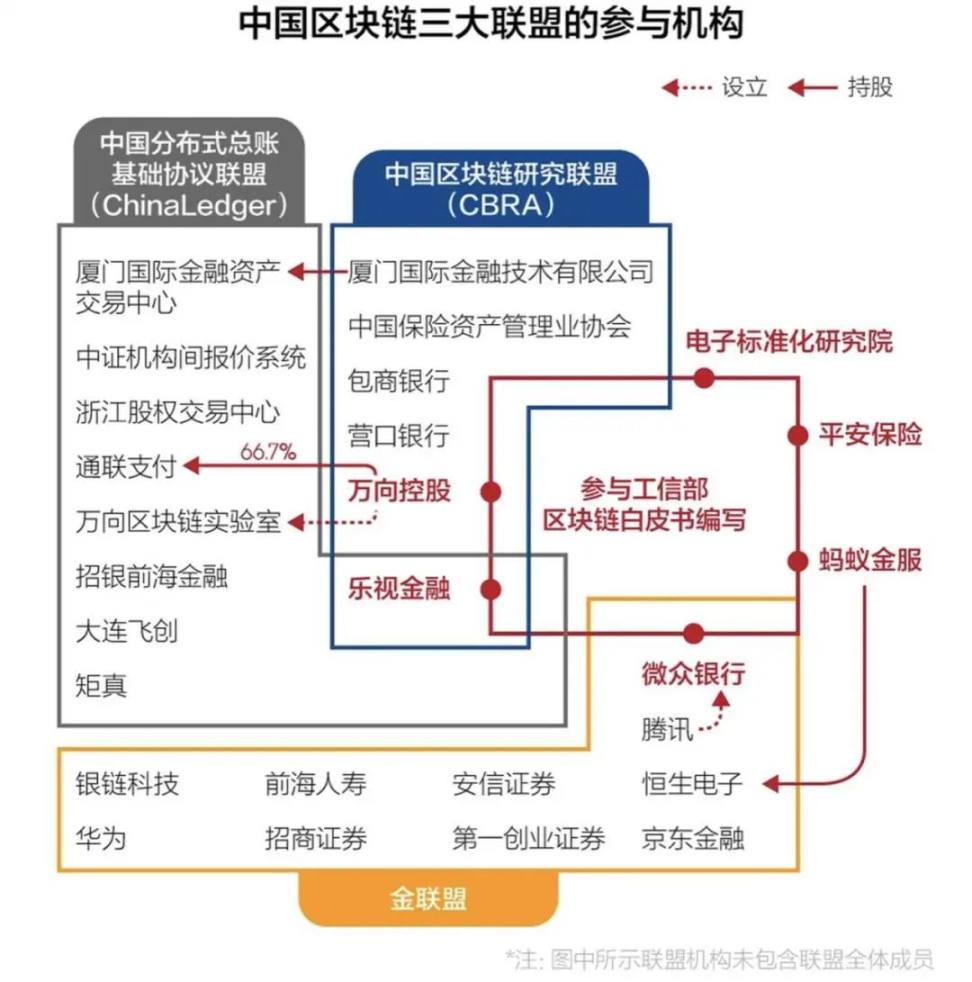
▲Information source: ChainCatcher website
03 What qualifications are needed for compliant operation of consortium chains in China
After understanding the advantages of consortium chains, many Web3.0 entrepreneurs must be curious: What qualifications are needed to operate consortium chains in China?
The policies and advantages of consortium chains are "manageable and controllable," so how exactly are they "managed and controlled"? Here, I have also compiled related qualifications and filings for everyone, so that you can be "well-prepared" in the race of consortium chains:
1. ICP Filing/License
According to Article 7 and Article 8 of China's "Regulations on the Administration of Internet Information Services," if domestic servers are used for Internet business, an ICP filing is required. If there are further business needs involving "charges," such as membership fees, advertising fees, recharge services, transaction services, etc., further application for an ICP license is required.
For example, Baidu Super Chain's website shows that it has obtained an ICP license:
While AntChain has completed ICP filing:
2. Network Security Filing
According to Article 11 of the "Regulations on the Security Protection of Computer Information Systems of the People's Republic of China," computer information systems that are connected to the international network need to be filed with the public security organs at or above the provincial level.
In general, the qualifications of top Internet companies for consortium chains are relatively complete. For example, Tencent's TrustSQL and Bilibili's High Energy Chain have both completed network security filings.

3. Blockchain Filing
According to Article 11 of the "Regulations on the Management of Blockchain Information Services," blockchain information service providers should fill in information in the blockchain information service filing management system within ten working days from the date of providing services and complete the filing procedures. It should be noted that when the project name or website changes, changes must be made within five working days from the date of the change. As a part of blockchain, consortium chain filing is naturally indispensable.
The above images show that these consortium chains have also completed blockchain filings. For example, AntChain has complete blockchain filings:
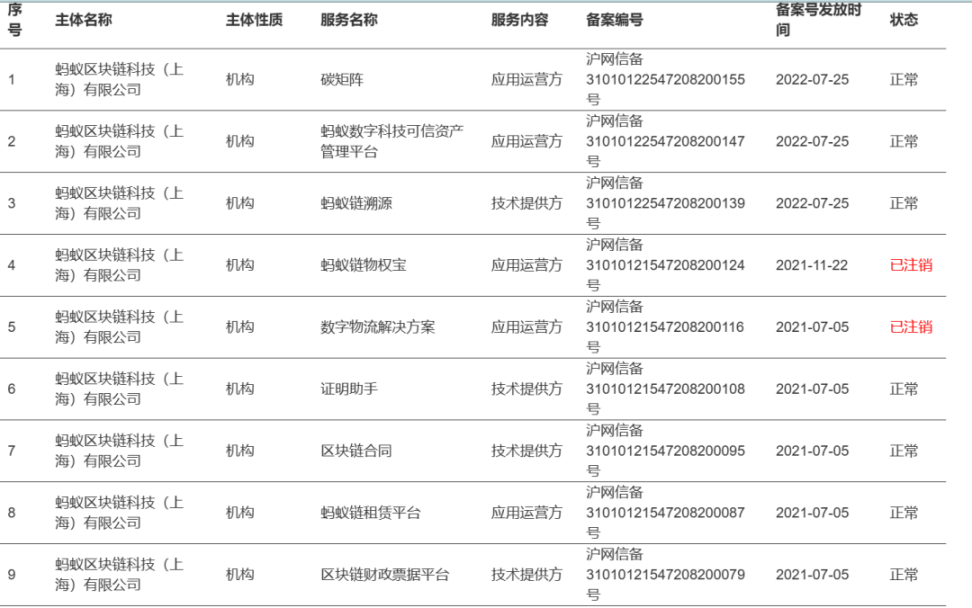
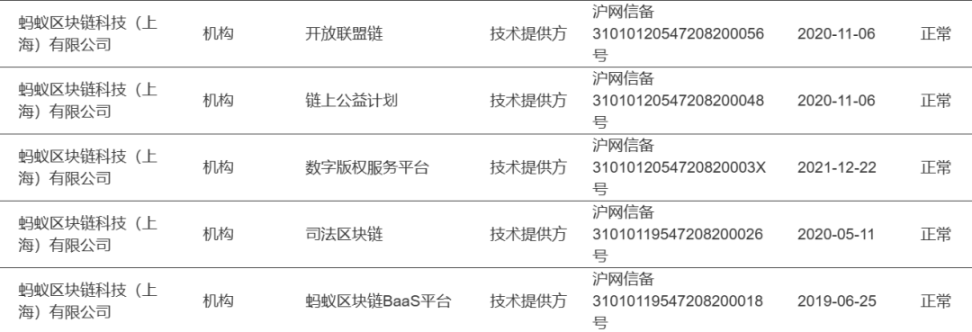
4. EDI License
According to Article 4 of the "Regulations on the Administration of Telecommunications Business Operation Permits," operators of telecommunications businesses should obtain a business operation permit issued by the telecommunications management agency in accordance with the law. EDI belongs to the second category of value-added telecommunications services, which includes "online data trading and processing services," including transaction processing services, electronic data exchange services, and network/electronic equipment data processing services. For example, e-commerce, take-out, and second-hand trading platforms like Tmall, Taobao, Meituan, and Xianyu all need EDI licenses. If the consortium chain involves such "transaction services," an additional EDI license is required.
For example, the Blockchain Service Network (BSN) website shows that it has obtained an EDI license:

04 Legal risks of lacking qualifications
Correspondingly, those who should have the above qualifications or filings but fail to apply for them will face corresponding penalties. Here, I have listed the risks of lacking qualifications:
1. Without ICP, no illegal gains will be confiscated/fined/ordered to close
According to Article 19 of the "Regulations on the Administration of Internet Information Services," if there is no ICP filing, the operator will be ordered to rectify within a time limit, and if they refuse to rectify, there is a risk of website closure.
If there is no ICP license for operating Internet services, or if services provided exceed the scope of the license, the operator will be ordered to rectify within a time limit, any illegal gains will be confiscated, and a fine of 3 to 5 times the illegal gains will be imposed. If there are no illegal gains or the illegal gains are less than 50,000 yuan, a fine of 10,000 to 100,000 yuan will be imposed. In serious cases, the website will be ordered to close.
In addition, a fine will be imposed for not displaying the ICP filing number on the website! Failure to indicate the business license number or filing number on the homepage of the website will result in a fine of 5,000 to 50,000 yuan.
2. Without network security filing, a warning or suspension for rectification
According to Article 12 of the "Regulations on the Security Protection of Computer Information Systems for International Networking," those who violate the filing system for international networking of computer information systems will be given a warning or ordered to suspend operations for rectification.
In recent days, a network technology company in Guilin, Guangxi, was warned and penalized for not completing network security filing.

3. Without blockchain information service filing, warning/fine
According to Article 22 of the "Regulations on the Management of Blockchain Information Services," those who fail to complete the filing procedures according to this regulation or provide false filing information will be ordered to rectify within a time limit. Refusal to rectify or serious circumstances will result in a warning and a fine of no less than 10,000 yuan and no more than 30,000 yuan.
4. Without EDI, confiscation of illegal gains/fine/suspension of business/reputation on the list of dishonest operators
According to Article 46 of the "Regulations on the Administration of Telecommunications Business Operation Permits" and Article 69 of the "Telecommunications Regulations of the People's Republic of China," those who operate telecommunications businesses without authorization or beyond the scope of authorization will be ordered to rectify, have their illegal gains confiscated, and be fined 3 to 5 times the illegal gains. If there are no illegal gains or the illegal gains are less than 50,000 yuan, a fine of 100,000 to 1,000,000 yuan will be imposed. In cases of serious circumstances, those who are ordered to suspend business operations will be directly included in the list of dishonest operators in the telecommunications business.
05 Conclusion
The wind of the consortium chain is still blowing strong, and "technology" + "policies" is the pathway to success. A wise person seizes the opportunity and acts accordingly. While everyone is riding the waves in the consortium chain industry and setting sail for the clouds, complete qualifications and filings will also "safeguard" everyone's journey.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



