The latest developments in various fields of crypto assets indicate that the strategic direction behind the shift in the positions of the U.S. political and business sectors is likely to construct a "trinity" digital dollar hegemony system in the digital age.
Source: Tsinghua University Service Economy and Digital Governance Research Institute
On February 22, 2025, the Academic Annual Conference on the Development and Governance of China's Digital Economy was held at Nankai University. This conference, themed "Artificial Intelligence, Digital Economy, and New Quality Productivity," actively responded to the strategic call in the report of the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China regarding "accelerating the construction of a strong networked country and digital China." It gathered the wisdom of academia and industry to jointly explore the future development direction of the digital economy. The conference invited over 40 experts, scholars, and institutional representatives to engage in in-depth discussions on core topics such as digital economy, digital finance, digital trade, data elements, and the innovative development of artificial intelligence. Nankai University President Chen Yulu delivered a keynote speech titled "The Rise and Challenges of Cryptocurrency."

Chen Yulu delivered the keynote speech
The theme I want to share today is "The Rise and Challenges of Cryptocurrency." Cryptocurrency is a type of digital currency that operates through computer networks, with ownership of each unit of cryptocurrency recorded and stored in a digital ledger or blockchain. The blockchain is the underlying technology of cryptocurrency, with its core being consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW). Cryptocurrencies mainly include three major types: first, payment cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum; second, stablecoins, the most famous being the U.S. dollar stablecoins USDT and USDC; third, central bank digital currencies, also known as sovereign digital currencies, with larger-scale representatives like China's digital yuan. Cryptocurrencies have seven main characteristics: distributed; secure; scarce; anonymous; high volatility in price trading; significant energy consumption generated during the mining process; and global instant trading without considering currency exchange costs and international transfer time costs.
Since Satoshi Nakamoto (team) mined the first block of Bitcoin (Genesis Block) in January 2009, cryptocurrency has gradually occupied a place in the financial ecosystem from a niche virtual currency experiment. Currently, over 130 countries and regions have begun to include different forms of cryptocurrency in discussions within the mainstream financial system. Against the backdrop of increasing global geopolitical turmoil, high U.S. fiscal deficits, and a sharp rise in U.S. national debt, cryptocurrency assets represented by Bitcoin are receiving widespread attention. Recent trends indicate that the U.S. government is accelerating the construction of a trinity "digital dollar hegemony system" from three aspects: national strategic reserves, cryptocurrency legislation, and crypto financial infrastructure, attempting to extend its global hegemony in traditional finance into the digital economy era. In light of the above context, I will focus on elaborating on the global situation of cryptocurrency development and the associated risks and challenges.
The cryptocurrency market is experiencing breakthrough progress
In January 2024, Bitcoin spot trading platform ETFs were officially approved for launch, marking a significant event in the integration of crypto assets with traditional financial assets. In December of the same year, Bitcoin's price broke through $100,000, driving the total market value of cryptocurrencies to surge from $800 billion to $3.4 trillion in just two years. At the same time, the total market value of crypto assets relative to the liquidity of the six major central banks (G6) has risen sharply from less than 1% in 2009 to 12% by the end of 2024. In the mainstream market, Bitcoin's investment attributes are shifting from a niche risk asset to a mainstream asset class. The strategic Bitcoin reserve plan (SBR) proposed by the new Trump administration further stimulated and reinforced this transition process.
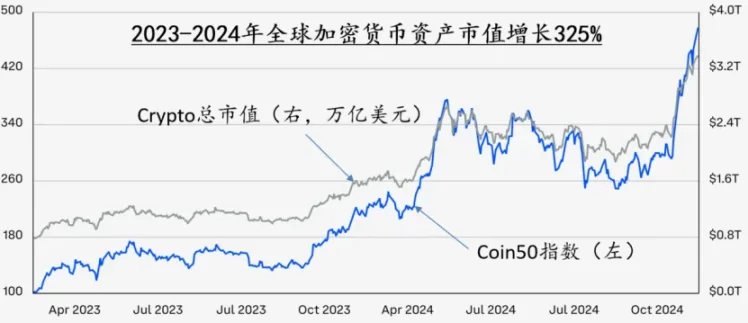
Figure 1: After the second half of 2023, global funds began to flood into the cryptocurrency market. Data source: Coinbase: Crypto Market Outlook 2025.
Since the second half of 2023, the U.S. government's regulatory stance on the cryptocurrency sector has undergone a significant shift, with its strategic intent likely aimed at extending U.S. traditional financial hegemony into the digital financial realm. Against the backdrop of soaring U.S. debt and persistent high inflation, this strategy can ensure the centralized position of the dollar in the wave of digital financial transformation while also supporting and alleviating the increasingly severe federal debt situation. This strategy may include short, medium, and long-term goals: in the short term, the U.S. government is attempting to construct a preliminary framework for global digital currency hegemony through three major means: cryptocurrency strategic reserves, encouraging the expansion of dollar stablecoins, and controlling the core infrastructure of crypto asset trading; in the medium term, it will continue to attract (or coerce) leading global crypto enterprises to migrate to the U.S. or fall under U.S. government regulatory systems through a loose regulatory environment, tax incentives, and long-arm financial sanctions, promoting industrial agglomeration, employment, and economic growth, while maintaining U.S. leadership in blockchain technology research and development; in the long term, the U.S. will ensure that it always holds centralized power in the wave of decentralization in the digital economy by dominating the formulation of global digital financial infrastructure and rules, ensuring that the dollar maintains a centralized position in global investment and trading in the digital economy era.
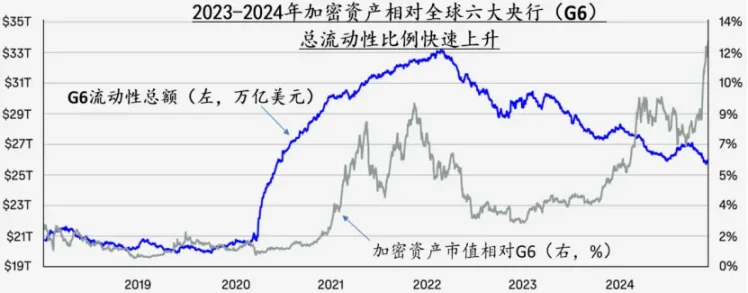
Figure 2: After the second half of 2023, the scale of cryptocurrencies surged and entered the mainstream asset market. Data source: Coinbase: Crypto Market Outlook 2025.
The shift in the positions of the U.S. political and business sectors on cryptocurrency and its strategic intent
1. Since the second half of 2023, there have been five significant shifts in the U.S. government and industry regarding cryptocurrency.
First, the stance of U.S. financial regulatory authorities has shifted from "harsh crackdown" to "guiding regulation." The new chair of the Trump administration, Paul Atkins, is a long-time supporter of cryptocurrency and has actively promoted the compliance path for crypto assets since taking office. Coupled with his close relationship with the new Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, this reflects the new U.S. government's active support for crypto assets and a trend of seeking a new balance between financial innovation and financial investor protection. In December 2024, the SEC approved Franklin Templeton's crypto index ETF (EZPZ) for trading on Nasdaq, marking a significant turning point in the U.S. financial regulatory stance.
Second, there has been a shift from legislative suppression to legislative support. The U.S. Congress is actively advancing a "dual pillar" regulatory framework for cryptocurrency— the "21st Century Financial Innovation and Technology Act" (FIT21) and the "Guidance and Establishment of a National Stablecoin Innovation Act" (GENIUS). The FIT21 Act will comprehensively establish the foundational framework for crypto regulation, addressing various classification and jurisdiction issues, clarifying the regulatory boundaries between the SEC and CFTC (U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission), setting standards for identifying the commodity and security attributes of digital assets, and establishing a legal framework for institutional digital asset custody. GENIUS aims to create a comprehensive regulatory framework for stablecoins, bringing the two major currencies—USDT and USDC, which account for 90% of the global stablecoin market value—under regulatory oversight. FIT21 passed the House of Representatives with bipartisan support in May 2024, and is expected to pass the Senate and be signed into law in 2025. GENIUS is scheduled for a Senate vote in March this year. Once these two bills are passed, the U.S. will form the most comprehensive crypto regulatory system globally, significantly influencing the innovation direction and market landscape of the cryptocurrency industry.
Third, there has been a policy shift from a harsh crackdown to strategic assetization. The Trump administration plans to launch a strategic Bitcoin reserve of 1 million BTC, to be included in the Treasury's foreign exchange stabilization fund. In January of this year, Trump signed an executive order titled "Strengthening U.S. Leadership in Digital Financial Technology," which primarily includes preparations to establish a Bitcoin strategic reserve (SBR) and prohibits the establishment, issuance, or promotion of any form of central bank digital currency within or outside the U.S., thereby targeting any potential competitors to dollar stablecoins.
Fourth, the industry has shifted from hesitation and observation to a more proactive response. Many star companies, such as Apple, Tesla, and MicroStrategy, have already included or plan to include crypto assets in their corporate asset allocation. Traditional large financial institutions (such as the world's largest asset management financial group BlackRock) are also accelerating their accumulation of Bitcoin. The global Bitcoin ETF fund assets have surpassed 1.1 million BTC, with BlackRock's Bitcoin ETF (IBIT) accounting for 45% (approximately $153 billion in market value as of February 2025). The spot Bitcoin ETF attracted over $108 billion in funding in 2024, accelerating the integration of the crypto market with traditional financial markets.
Fifth, there has been an adjustment in tax policies. The U.S. Internal Revenue Service has allowed taxpayers to flexibly choose accounting methods for crypto assets in its temporary tax relief for 2025, temporarily alleviating the tax pressure on CEX users, but in the long term, it may drive crypto investments to concentrate on platforms controllable by U.S. regulatory authorities.
2. The latest dynamics in various fields of crypto assets indicate that the shift in positions of the U.S. political and business sectors is likely aimed at constructing a "trinity" digital dollar hegemony system in the digital age.
The three main pillars of this system are the Bitcoin strategic reserve (SBR), dollar (pegged) stablecoins, and U.S.-controlled digital financial infrastructure. In this system, the Bitcoin strategic reserve may play the role of gold reserves in the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. Bitcoin, as "digital gold," occupies a core value anchor position and will bring five potential strategic advantages to the U.S.
First, the first-mover advantage. As the most widely recognized cryptocurrency globally, Bitcoin's unique position makes it a safe haven for funds during periods of global geopolitical turmoil and high inflation. The U.S. is the first to include Bitcoin, which accounts for over 60% of the entire cryptocurrency market value, into its national strategic reserves. This first-mover advantage is conducive to attracting international capital to continue to converge on dollar-denominated on-chain and off-chain assets in the future.
Second, the role as a new tool for financial stability. During financial crises, Bitcoin's low correlation with traditional assets means that Bitcoin reserves can serve as a second financial stability tool for the U.S. government, assisting in supporting the balance sheets of systemic financial institutions in the U.S. and protecting the international status of the dollar.
Third, enhancing the competitiveness of the dollar system in the digital age. Stablecoins linked to the U.S. currently account for 95% of the global stablecoin market value, and combined with crypto asset trading that is not dollar-pegged but primarily settled in dollars, this will further consolidate the dollar's position as a central currency in the digital age, thereby helping to extend the dollar's dominance in the global monetary system from traditional finance to the digital financial realm.
Fourth, strengthening the United States' discourse power in the digital finance era. In the future, after occupying a dominant position in the crypto market through strategic reserves and dollar stablecoins, the U.S. will lead the formulation of global crypto asset rules and solidify the dual pillar U.S. standards based on GENIUS and FIT21 through international platforms such as the G7, IMF, and BIS, promoting a global regulatory framework for crypto assets that aligns with its own interests, thereby ensuring its top-level discourse power in the formulation of international digital asset rules.
Fifth, curbing the development of potential competitors' crypto assets. By imposing financial sanctions and legislative restrictions on the digital asset development of competitor countries, and through executive orders and legislation prohibiting any institution from establishing, issuing, or promoting CBDCs within the U.S., the U.S. aims to limit the internationalization space of competitor digital currencies by attracting emerging markets to adopt U.S.-led payment systems through technical assistance.
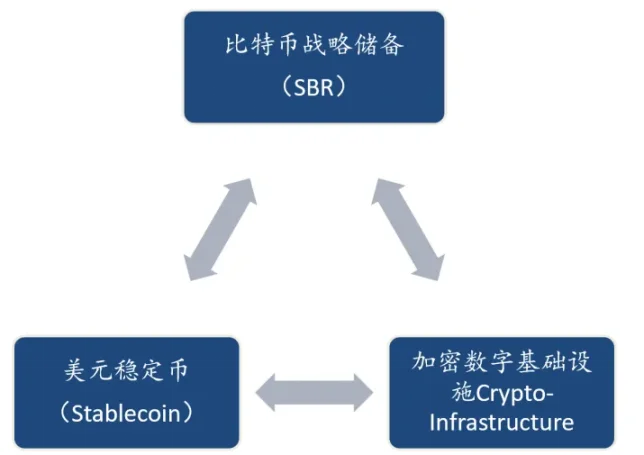
Figure 3: The "Trinity" U.S. Digital Currency Hegemony System
3. The EU's policy direction in the cryptocurrency field is to unify market regulation and promote green financial transformation.
This is mainly reflected in three aspects: First, the EU's "Regulatory Framework for Crypto Asset Markets" (MiCA) will come into full effect on December 31, 2024, aiming to establish a unified and clear regulatory framework for crypto assets across the EU. It will categorize all crypto assets into three types and implement differentiated regulation while strengthening compliance requirements for stablecoin issuance and crypto asset exchange operations. This framework aims to manage risks while promoting innovation, ensuring consumer rights and financial stability. Second, the unified regulatory framework lays the foundation for the EU to gain initiative and discourse power in the global cryptocurrency market. Third, it guides the establishment of a green financial development path for cryptocurrencies, with MiCA imposing high carbon emission taxes on energy-intensive blockchains, promoting a shift from PoW mechanisms to low-carbon consensus mechanisms like PoS, thereby reshaping the regional landscape of the mining industry.
4. Other global economies face competitive dynamics between stablecoins and sovereign digital currencies.
This is mainly reflected in three aspects. First, the number of economies exploring and promoting CBDCs is continuously increasing. Currently, about 130 countries and regions worldwide are exploring and promoting CBDCs. China's digital yuan has been steadily expanding its domestic and cross-border pilot projects in recent years, making it the largest sovereign digital currency globally. Eighteen G20 member countries, including Japan, South Korea, India, and Russia, are also accelerating their layouts for CBDCs or Bitcoin strategic reserves, actively seeking digital financial sovereignty and rule discourse power. Second, there is a competitive dynamic between sovereign digital currencies and stablecoins. The CBDC model has sovereign advantages, but dollar stablecoins already have scale advantages. From 2020 to 2024, the market value of USDT surged 5.52 times, while USDC increased 11.35 times, together accounting for 90% of the total market value of global stablecoins. By 2024, the settlement volume reached $15.6 trillion. Third, future digital currencies face risks of regionalization and fragmentation. The U.S. is attempting to strengthen dollar digital financial hegemony through three major means: establishing SBR reserves, legislating stablecoins, and restricting the issuance and circulation of CBDCs. The EU's MiCA framework will objectively limit the development of non-euro stablecoins. Increased competition means that the future global digital financial payment system may face risks of market segmentation and fragmentation.
5. Stablecoins are becoming the frontier for the integration of crypto financial assets and traditional financial assets.
This is mainly presented in two typical facts. On one hand, stablecoins enhance the resilience of off-chain dollar assets. In the 2023-2024 period, the market value of stablecoins rapidly increased and surpassed the growth rate of the U.S. M2, strongly supporting the demand for dollars and U.S. Treasury bonds in the context of the U.S.'s ongoing high deficit and uncertain financial environment. On the other hand, stablecoins are gradually entering mainstream payment channels. In the first 11 months of 2024, the stablecoin market completed $27.1 trillion in transactions, including a large volume of P2P and cross-border B2B payments, indicating that businesses and individuals are increasingly utilizing stablecoins to achieve commercial value while meeting regulatory requirements, and are closely integrating with traditional payment platforms like VISA and Stripe.
New trends in cryptocurrency development pose risks and challenges for China
1. Objectively assessing China's current advantages and disadvantages in the blockchain and cryptocurrency fields.
There are three main advantages: First, the layout of the digital yuan and blockchain industry is leading. In the field of central bank digital currencies, the digital yuan is currently the largest CBDC project globally and has received national strategic support. Since its development began in 2014, it has steadily advanced, covering multiple areas such as retail, wholesale payments, and cross-border settlements. Since 2021, the development and practical progress of the cross-border digital currency bridge project (mBridge) have also been globally leading. These foundations make it likely that the digital yuan will become a financial transaction tool and asset carrier competing with dollar stablecoins in the future. In the blockchain industry, China has incorporated blockchain technology into its national strategy since the early stages of industrial emergence and has clearly proposed the development direction of integrating blockchain with the real economy. The market scale and growth potential of the industry are significant, with China's blockchain market expected to exceed 100 billion yuan by 2025, having achieved widespread application in finance, supply chain, government business services, and other fields, with a continuous increase in the number of registered enterprises, reaching 63,300 by the end of 2023.
Second, there are rich application scenarios. The scenarios for digital currency have expanded from the initial areas of retail, transportation, and government affairs to broader fields such as wholesale, catering, entertainment, education, healthcare, social governance, public services, rural revitalization, and green finance. The blockchain industry has numerous mature cases in many areas, including supply chain finance, cross-border trade, and e-government.
Third, there is strict risk prevention and control. China implements strict regulation on cryptocurrency trading and initial coin offerings (ICOs), effectively preventing risks in the virtual economy and providing a more controllable and stable industrial environment for the compliant development of digital currencies.
China's current disadvantages mainly reflect insufficient international competitiveness in certain areas. First, the influence of technical standards is relatively lagging. Due to differences in regulatory laws, the U.S. currently dominates underlying technologies such as ZKP and Layer 2 scaling, while the EU has also set technical barriers through the MiCA framework, resulting in insufficient discourse power for China in core protocols and global standard formulation. Second, the development of public chain ecosystems is relatively lagging. China's blockchain industry is primarily based on consortium chains and private chains, and the lack of public chains leads to a gap in innovation capabilities in decentralized finance (DeFi) and Web 3.0 compared to Europe and the U.S.
2. The U.S.-led hegemony strategy in crypto assets poses multiple threats to China's financial security.
First, there is capital outflow and exchange rate pressure. The long-term appreciation trend of crypto assets represented by Bitcoin against the dollar and other international currencies, along with the rapid expansion of dollar stablecoin trading volume, further strengthens the dollar's dominant position in the global monetary system through the convenience of cross-border payments and value storage functions, which will undoubtedly squeeze the valuation and internationalization space of the renminbi. In addition, dollar-dominated crypto channels have become a new path for capital flight. In recent years, leading U.S. companies have massively allocated Bitcoin, and the large-scale financing wave of on-exchange crypto ETFs has created a strong "demonstration effect," potentially attracting some domestic capital to flow out through gray channels.
Second, regulatory arbitrage in DeFi creates cumulative industrial competitive advantages. The relatively loose regulatory and tax policies in the U.S. attract global DeFi innovation resources, thereby reaping more technological dividends from the entire chain, from underlying standards to application layers. After long-term accumulation, this will form a competitive advantage over China's digital financial infrastructure technology.
Third, there is a competition for underlying technology standards and innovation resources. On one hand, the U.S. currently leads in innovation in areas such as ZKP and Layer 2, while the EU is also gaining network effects from a unified large market through the integration of regulation via MiCA, while setting technical barriers. China needs to be vigilant against the risk of losing the right to formulate industry standards for crypto assets. On the other hand, China faces pressure from the outflow of blockchain industry innovation resources: the EU's carbon emission policies for the crypto industry and the U.S. tax incentives for mining operations are leading Chinese mining companies and blockchain venture capital firms to consider relocating to Central Asia, the Middle East, and the U.S., which objectively undermines the innovation capabilities and computational power security of the domestic blockchain industry.
Fourth, the threat of U.S. crypto asset hegemony. First, the U.S. is accelerating the gradual incorporation of mainstream crypto assets into its financial hegemony system. Once this trend is established, it will inevitably squeeze China's strategic development space in the digital finance field. Second, after the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the U.S. government, in collaboration with countries like the UK and UAE, has implemented large-scale long-arm financial sanctions against the Russian government, institutions, and individuals in the cryptocurrency field, seizing a large amount of crypto assets and arresting relevant personnel, demonstrating the initial power of its digital financial hegemony. Finally, the Trump administration's promotion of the Bitcoin strategic reserve plan and resistance to foreign sovereign digital currencies has also intensified the confrontation between China and the U.S. in the digital currency field.
Of course, crypto assets represented by Bitcoin are currently exhibiting a severe market bubble state, and continued appreciation is difficult to sustain. Once the bubble bursts, it will be a significant blow to the U.S. crypto asset hegemony strategy. In this regard, we must maintain a clear understanding and strategic resolve, adhere to the value concept of financial services for the real economy, and firmly pursue the path of building a financial powerhouse with Chinese characteristics.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




