"We do not sell these Bitcoins" — because what is truly waiting for a price is not cryptocurrency, but the next fifty years of X Yuan hegemony.
Written by: Daii
As the global crypto community holds its breath for positive signals from the White House summit, an executive order issued on the evening of March 6, Washington time, caused Bitcoin to evaporate 3.5% of its market value within 24 hours.
The Trump administration announced with great fanfare that it would sequester 198,109 Bitcoins (worth approximately $17.8 billion at current market prices) in a strategic reserve called "Digital Fort Knox" — a name that directly parallels the ultimate vault of U.S. gold reserves, suggesting that Bitcoin will become the "digital gold" supporting the credit of the U.S. dollar. However, the cold reality of the market voting with its feet starkly contrasts with the White House's proclaimed vision of "digital gold":
Locking up $17.8 billion worth of Bitcoin led to a market cap shrinkage of over $6 billion.
The market is very dull and fragile, always waiting for good news. However, when good news suddenly arrives, the market still feels it is not good enough, resulting in a decline instead of a rise. No matter how much of a jerk the Trump administration has been regarding the Ukraine issue, it is clear that this time, Trump has been let down when it comes to Bitcoin.

The disappointment in the market mainly stems from the unmet expectations of large-scale government purchases of Bitcoin. Many investors, especially new participants in the cryptocurrency market, may feel confused: why does the market seem to "not buy" the U.S. government's high-profile announcement of holding Bitcoin as a "strategic reserve"? Is this merely a "big thunder but little rain" policy show?
Not at all. The market's underestimation of this initiative is not coincidental; it is the result of cognitive bias and information asymmetry working together.
In simple terms, the market's short-sightedness and lack of understanding of professional tools have jointly caused this $6 billion shrinkage in Bitcoin.
In fact, whether from a strategic or tactical perspective, the executive order to establish a strategic Bitcoin reserve is a historic event, far surpassing the president and first lady's "disgraceful" meme coin launch. To put it in more academic terms, this is a very important "institutional positioning." This is also the key point I want to convey to you today.
Now, let's discuss them one by one.
1. Short-term Market Illusion
In financial markets, especially in highly volatile markets like Bitcoin, short-term trading and speculative behavior often dominate. Investors are more focused on short-term price fluctuations and "hot spots" that can yield quick profits.
For example, 56% of Bitcoin ETF shares are held by hedge funds, and when arbitrage strategies are no longer profitable, they will sell off. The recent sharp decline in Bitcoin is partly due to this. If you are interested in this topic, I recommend reading "Bitcoin Falls Below 90,000 Because Smart Money is Exiting?"
Therefore, when the U.S. government announced the establishment of a strategic Bitcoin reserve, the market expected Bitcoin prices to soar immediately. However, since the policy statement did not mention plans for "immediate purchases of Bitcoin," short-term traders did not see direct "positive" stimuli, and thus market enthusiasm was not ignited.
The market is like a moth drawn to a candle flame, attracted by short-term price fluctuations while ignoring the strategic chess game behind it. The U.S. government's definition of Bitcoin as a "strategic reserve" is by no means a simple symbolic gesture; it is an ultimate confirmation of Bitcoin's status as "digital gold." The value of this confirmation, as well as its profound impact on the future landscape of the Bitcoin market, is something that short-term price fluctuations cannot easily reflect.
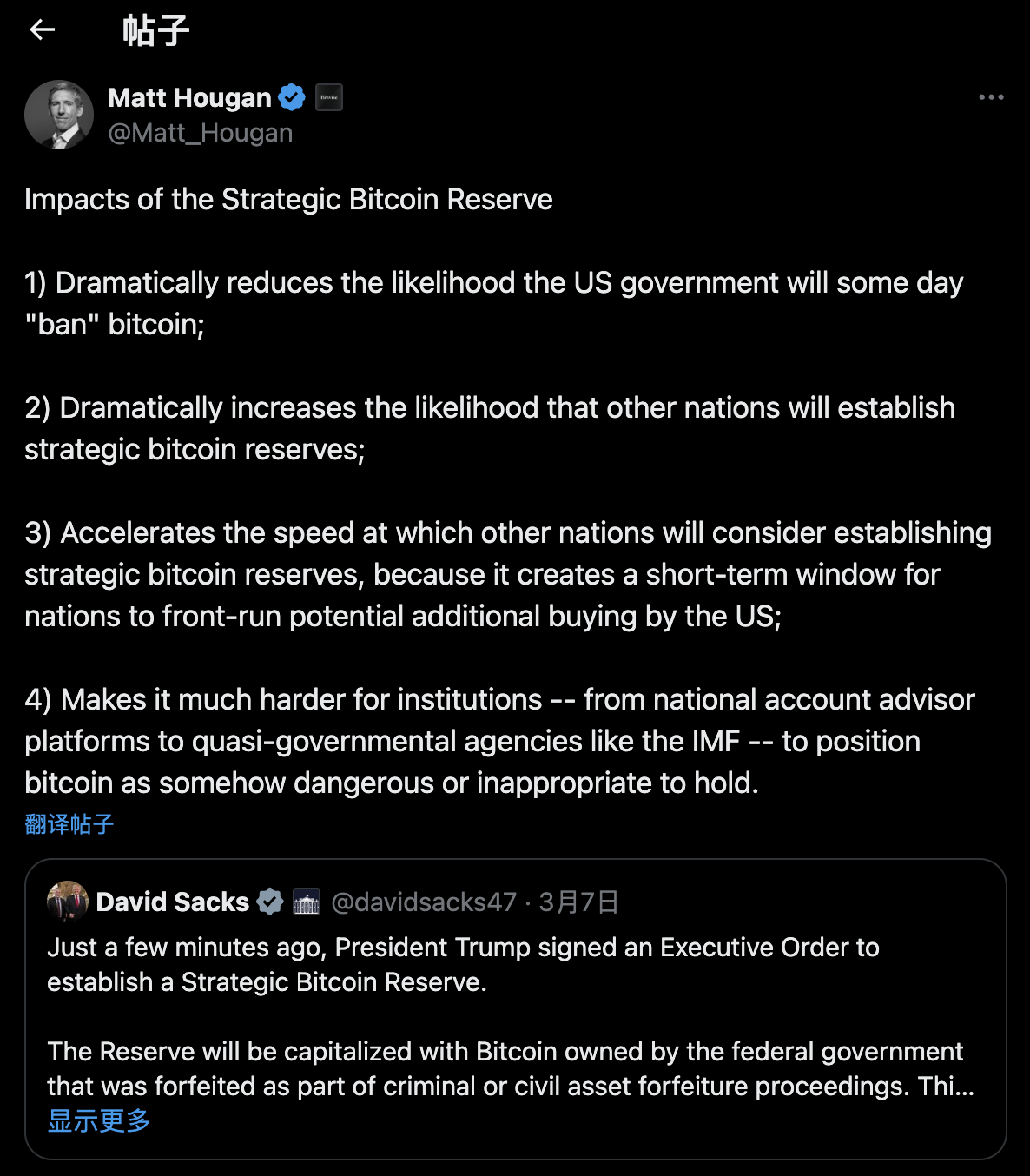
Matt Hougan, Chief Investment Officer of Bitwise, stated that in the long run, this is extremely beneficial for Bitcoin. He pointed out that a strategic Bitcoin reserve will:
- Greatly reduce the likelihood that the U.S. government will "ban" Bitcoin one day;
- Increase the likelihood that other countries will establish strategic Bitcoin reserves;
- Accelerate the pace at which other countries consider establishing strategic Bitcoin reserves, as it creates a brief window for them to seize potential additional purchases from the U.S.
Moreover, this initiative will silence many critics. From now on, it will be more difficult for quasi-governmental institutions like the International Monetary Fund to position Bitcoin as a dangerous or unsuitable asset.
Therefore, although the market did not respond positively to this policy in the short term, the establishment of this strategic reserve may have far-reaching implications for the Bitcoin market in the long run. Investors should look beyond the "smoke and mirrors" of short-term games and focus on the long-term strategic significance behind this policy.
2. Cognitive Barriers of "Professional Tools"
The U.S. government's establishment of a strategic Bitcoin reserve is not a spur-of-the-moment decision but a well-considered strategic move. To achieve this goal, the government cleverly employed several professional policy tools.
This time, in addition to the explicitly mentioned "budget neutrality" principle, the U.S. government's "toolbox" may also include the ESF fund (Exchange Stabilization Fund) and amendments to the Gold Reserve Act. Although the executive order itself may not directly mention these professional terms, understanding the operational mechanisms behind them is crucial for grasping the U.S. government's move.
2.1 "Budget Neutrality": Not a Ban on Purchases
The executive order explicitly emphasizes that the strategy for acquiring more Bitcoin must be "budget neutral," meaning "it will not increase the cost to U.S. taxpayers." At first glance, this seems to limit the government's ability to purchase Bitcoin and may be one reason for market disappointment — if no money is spent, how much can be bought?
But does "budget neutrality" really mean "not buying"?
The answer is clearly no. "Budget neutrality" is more like a "cost-saving" strategy, or more vividly, a high-level play of "making something out of nothing." It means the government can accumulate Bitcoin reserves through other means without directly using taxpayer budgets.
So, where is the government's "magic"? This brings us to the ESF fund, the "secret weapon."
2.2 ESF Fund: The Treasury's "Swiss Army Knife"
The ESF fund, or Exchange Stabilization Fund, is a special account under the U.S. Treasury. Its original purpose was to maintain the stability of the U.S. dollar's exchange rate, but over time, the functions of the ESF fund have far exceeded its initial design, becoming a flexible and powerful policy tool in the hands of the U.S. government.
Flexibility of funding sources: The funds for the ESF fund mainly come from the returns on U.S. dollar assets, such as the investment returns from foreign exchange reserves. This means the government can sell a portion of its foreign exchange reserves (like euros, yen, etc.), allocate the proceeds to the ESF fund, and then use the ESF fund's money to purchase Bitcoin. In this way, the funds for purchasing Bitcoin do not directly come from taxpayer budgets, cleverly achieving the goal of "budget neutrality."
High autonomy in operational authority: The use of the ESF fund is largely at the discretion of the U.S. Treasury Secretary, without the need for extensive congressional approval. This high degree of autonomy grants the government significant flexibility and discretion in operations. The government can adjust the scale of Bitcoin reserves based on market conditions and strategic needs without publicly disclosing details.
Successful historical applications: The ESF fund has not been entrusted with important tasks for the first time. Historically, the ESF fund has played a crucial role at key moments, such as:
- The 1994 Mexican financial crisis: The ESF fund was used to provide emergency loan assistance to Mexico, helping stabilize the peso's exchange rate and prevent the crisis from spreading.
- During the subprime mortgage crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic: The ESF fund was also used to support liquidity in financial markets and stabilize market sentiment.
These historical cases demonstrate that the ESF fund is a powerful and versatile policy tool, and the U.S. government could very well utilize the ESF fund to secretly and continuously accumulate Bitcoin reserves within the framework of "budget neutrality."
2.3 Gold Reserve Act: Providing a "Legal Veil" for Bitcoin Reserves
First of all, if you view the executive order's reference to Bitcoin as "digital gold" as a simple metaphor, you are gravely mistaken. Due to the existence of the Gold Reserve Act, "digital gold" may become a "policy bridge," allowing the government the opportunity to manage Bitcoin in a manner similar to how it manages gold.
The Gold Reserve Act, as the name suggests, is a law that originally regulated the management of U.S. gold reserves. It explicitly grants the Treasury the authority to safeguard and dispose of gold reserves and intervene in the foreign exchange market through the ESF.
Providing a legal framework for strategic asset reserves: The core significance of the amendments to the Gold Reserve Act is that it provides a legal framework for the U.S. government to establish and manage "strategic asset reserves." Although this law was initially aimed at gold, the interpretation and applicability of its legal provisions are flexible. If the U.S. government intends to include Bitcoin in the category of "strategic assets," the amendments to the Gold Reserve Act could become a strong legal support.
The analogy between "digital gold" and "gold reserves": The executive order's definition of Bitcoin as "digital gold" is by no means a simple metaphor. The positioning of "digital gold" actually draws a comparison between Bitcoin and traditional "gold reserves," suggesting that the government may manage Bitcoin reserves in a manner similar to how it manages gold reserves. The Gold Reserve Act is precisely the key law regulating the management of "gold reserves."
The "flexibility" of legal interpretation: The vitality of law lies in its interpretation and application. The U.S. legal system possesses a certain degree of "flexibility," and the interpretation of the Gold Reserve Act may adjust with the development of the times and technological advancements. If the government intends to promote the legalization and institutionalization of Bitcoin reserves, the legal community could very well interpret the Gold Reserve Act in a manner favorable to Bitcoin, providing a more solid legal foundation for its strategic reserve status.
2.4 Summary
Through the principle of "budget neutrality," leveraging professional tools such as the ESF fund and the Gold Reserve Act, the U.S. government attempts to quietly position "digital gold" without alarming Congress or sparking controversy, seizing the strategic high ground of "crypto dollars."
However, due to the complexity of the U.S. legal system, if the courts ultimately determine that "gold" in current laws specifically refers to tangible assets, directly extending this to Bitcoin would require breaking the boundaries of legal interpretation. Therefore, relying solely on an executive order may face judicial challenges, and explicit authorization from Congress may still be needed.
Additionally, there is another path to consider. According to the Strategic and Critical Materials Stockpiling Act, Bitcoin could be classified as a "non-sovereign asset for hedging macroeconomic risks," which may also require explicit authorization from Congress.
Considering the current Republican advantage in both houses of Congress, obtaining authorization may not be as difficult as imagined. The key question is how high the priority of strategic Bitcoin reserves is for the current government. Is it worth the effort to push this forward?
If the Trump team realizes that this is another historic opportunity to achieve dollar hegemony following "gold dollars" and "petrodollars," then the U.S. strategic Bitcoin reserve would represent another successful "institutional positioning" that is well worth the effort to promote.

3. Institutional Positioning: A Strategic Game Concerning Future Monetary Dominance
Having understood why the market underestimates the value of strategic Bitcoin reserves, let us now clear the fog and examine the U.S. government's actions from a more macro and long-term perspective to understand its true strategic significance.
3.1 What is "Institutional Positioning"?
"Institutional Positioning" refers, in simple terms, to the act of establishing the status of a certain entity or concept at the institutional level in order to occupy a favorable position in future developments and to gain the power to set rules and discourse.
You can think of "Institutional Positioning" as a chess game. A skilled player not only focuses on immediate "captures" but also emphasizes "positioning" — seizing key positions on the board, constructing advantageous formations, thereby taking the initiative in the entire game and ultimately achieving victory.
Competition between nations, especially in emerging technologies and strategic fields, is often a game of "Institutional Positioning." The country that can first complete institutional arrangements in new fields and new tracks will gain a first-mover advantage in future developments and may even control the power to set rules, thus winning strategic initiative.
The core of institutional positioning lies in "seizing the runway" and "setting standards."
Seizing the runway: In the early stages of development in emerging fields, rules and institutions are often not yet perfected, creating a significant "institutional vacuum." Countries that take the lead in institutional arrangements can seize the development runway, laying the foundation for their future development and potentially leaving other competitors behind.
Setting standards: Institutions themselves contain standards and rules. Whoever can dominate the construction of institutions can largely define future industry standards and competitive rules. In global competition, mastering the power to set standards often means holding the initiative and advantageous position in competition.
3.2 Strategic Bitcoin Reserves: The U.S. "Crypto Dollar" Strategy's "Institutional Positioning"
The establishment of "Strategic Bitcoin Reserves" by the U.S. is a key move in its "Institutional Positioning" within the digital currency field and even the future global monetary system. Its strategic intent and positioning methods can be described as "killing three birds with one stone," showcasing remarkable ingenuity:
Legal positioning: Through an executive order rather than a legislative process, the U.S. government cleverly anchors Bitcoin as a "strategic asset," establishing its legal status at the national strategic level. This "legal positioning" lays the foundation for the future compliance and institutionalization of Bitcoin within the U.S. financial system and sets an example for other governments to follow.
Discourse power positioning: By defining Bitcoin as "digital gold" and including it in the category of "strategic reserves," the U.S. government has seized global discourse power over "crypto assets." Through "official endorsement," it enhances the legitimacy and authority of Bitcoin and may guide the "value recognition" and "classification standards" of crypto assets globally, thus mastering the "rule-setting power" in the crypto asset arena.
Operational positioning: Through the principle of "budget neutrality" and tools like the ESF fund, the U.S. government has also achieved "Institutional Positioning" at the operational level. The "budget neutrality" principle can reduce resistance to policy implementation while reserving institutional interfaces for future flexible increases in Bitcoin reserves; the use of the ESF fund provides the government with operational space and institutional guarantees for secretly and continuously accumulating Bitcoin.
It can be said that the establishment of "Strategic Bitcoin Reserves" by the U.S. is not merely about "holding" some Bitcoin; it is a "well-thought-out, meticulously arranged" act of "Institutional Positioning." Its strategic goal is not limited to "hedging risks" or "value storage," but rather focuses on the transformation of the future global monetary system, constructing a "crypto dollar" strategy, and competing for "dominance" in the "digital currency era." I have provided a more detailed interpretation of these contents in "Dollar Hegemony 3.0: Trump's 'Decentralized' Conspiracy."
3.3 Historical Reflection: Successful Cases of Institutional Positioning
To better understand the strategic value and far-reaching impact of "Institutional Positioning," we can review some successful historical cases of institutional positioning, which may provide us with insights and references.
Case 1: The Federal Reserve's Gradual Institutional Positioning (1913-1933)

Initial "weak" positioning as "strategic lurking": Established in 1913, the Federal Reserve was initially designed as a "clearing platform for banks," with its powers strictly limited, even deliberately avoiding direct monetary control. This "weak" positioning seemed to limit the Federal Reserve's development prospects at the time. However, from the perspective of "Institutional Positioning," this was a form of "strategic lurking," laying the groundwork for the future expansion of the Federal Reserve's powers and institutional evolution.
Seizing "key positioning" opportunities during crises: In 1932, as the U.S. economy was mired in the Great Depression, the "Federal Reserve Act" Section 13(3) was activated, allowing the Federal Reserve to provide credit to non-bank institutions in "special and emergency circumstances." This seemingly "insignificant" clause became the "institutional breakthrough" for the Federal Reserve's power expansion. The Federal Reserve cleverly seized the "institutional positioning" opportunity during the "crisis moment," laying the foundation for its future rise.
"Gradual" power expansion leading to becoming the "Central Bank of Central Banks": It was through Section 13(3) and a series of subsequent institutional evolutions and power expansions that the Federal Reserve ultimately transformed from a "weak" clearing platform into a "gradual" core hub controlling global monetary policy, becoming the true "Central Bank of Central Banks." The rise of the Federal Reserve illustrates that the value of "Institutional Positioning" often needs to be fully realized over a long-term evolution.
Case 2: The Nested Institutional Positioning of the Petrodollar System (1974)

The "Petrodollar" agreement did not directly challenge the "gold standard": After the oil crisis in 1973, the U.S. reached a secret agreement with Saudi Arabia regarding "Petrodollars," stipulating that Saudi oil transactions must be settled in dollars. This agreement, on the surface, appeared to be merely a "commercial transaction," seemingly unrelated to "Institutional Positioning." However, from a strategic height, the "Petrodollar" agreement was an extremely clever form of "nested institutional positioning." The U.S. cleverly chose "oil" as a "breakthrough point," "curving to save the country," deeply binding the dollar to the pricing power of the global commodity — oil, rather than directly challenging the still-dominant "gold standard," thus avoiding direct conflict while achieving more far-reaching strategic goals.
Binding "commodity pricing power" to the dollar, laying the foundation for "dollar hegemony": The establishment of the "Petrodollar" agreement not only enhanced the dollar's position in oil transaction settlements but, more importantly, through "commodity pricing power," deeply bound the dollar to the "lifeblood" of the global economy — energy, thus laying the "institutional foundation" for the dollar's "global hegemony" over the next 50 years. Even after the collapse of the "gold standard," the dollar was still able to maintain its position as the world's reserve currency, largely thanks to the "Petrodollar" system. The strategic wisdom of "nested institutional positioning" is thus evident.
3.4 Summary: Institutional Positioning, Awaiting Value Reassessment
Historical reflections tell us that the value of "Institutional Positioning" often requires time to validate, and it takes strategic patience and long-term vision to truly understand. The U.S. strategic Bitcoin reserves may currently be in the "lurking period" of "Institutional Positioning," and its true strategic value has not yet been fully recognized and priced in by the market.
However, it is foreseeable that once the strategic intent of "Institutional Positioning" is widely understood by the market, and once the "institutional dividends" begin to be gradually released, the reassessment of Bitcoin's value may experience explosive growth.
Conclusion: Algorithms Shake the Printing Press, Code Restructures Bretton Woods
The establishment of the U.S. strategic Bitcoin reserves is by no means a simple asset allocation game; it is a "dimensionality reduction strike" of digital civilization against the traditional monetary order. When Trump's signature was affixed, we witnessed not only the "locking up" of 200,000 Bitcoins but also a silent financial coup — algorithms began to compete with the printing press for the definition of the global monetary system.
History often rhymes: In 1971, Nixon closed the gold window, freeing the dollar from the shackles of the gold standard and ushering in the era of fiat currency hegemony; in 2025, Trump included Bitcoin in the national reserves, effectively implanting "digital genes" into dollar hegemony, attempting to replicate the "Petrodollar" logic of dominance in the world of code. The brilliance of this "crypto dollar" strategy lies in its dual acknowledgment of the impending twilight of centralized monetary systems while attempting to extend the twilight of hegemony through decentralized technology.
The market's short-sighted reaction is akin to the bankers who questioned Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) at the Bretton Woods Conference in 1944 — they only saw the exchange rate between gold and dollars but failed to recognize that institutional positioning would reshape financial rules for half a century. Today, the algorithmic code of Bitcoin is writing a new monetary constitution: when state machinery begins to hoard censorship-resistant assets, it is essentially pre-installing an "escape pod" for the ultimate crisis of sovereign currency. If you also want to have your own escape pod, I have two beginner-friendly tutorials: one on how to buy Bitcoin and another on how to send Bitcoin to a cold wallet, which should be sufficient for you.
In the future currency wars, victory may not depend on whose central bank balance sheet is larger, but on who can incorporate "digital gold" into a more sophisticated strategic nesting. Just as the Petrodollar once transformed black gold into a medium of credit, the crypto dollar is attempting to convert hash values into levers of power. The outcome of this game may validate Hayek's prophecy: "The denationalization of money will ultimately bury the ghost of Keynesianism" — only this time, the pickaxe is wielded not only by the free market but also by awakening sovereign states.
When the White House deposits Bitcoin into "Digital Fort Knox," it is not just the soft sound of encrypted cold wallets but the sound of the old financial order's foundations cracking. Algorithms are competing with the printing press for the power to define currency; the future "dollar" may be shaped by code and hash values.
Who will become the next "dollar"?
The answer may lie in Sachs' statement: "We do not sell these Bitcoins" — because what is truly waiting for a price is not cryptocurrency, but the next fifty years of X Yuan hegemony.
Currently, it is just that the odds are slightly more in favor of the "dollar."
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



