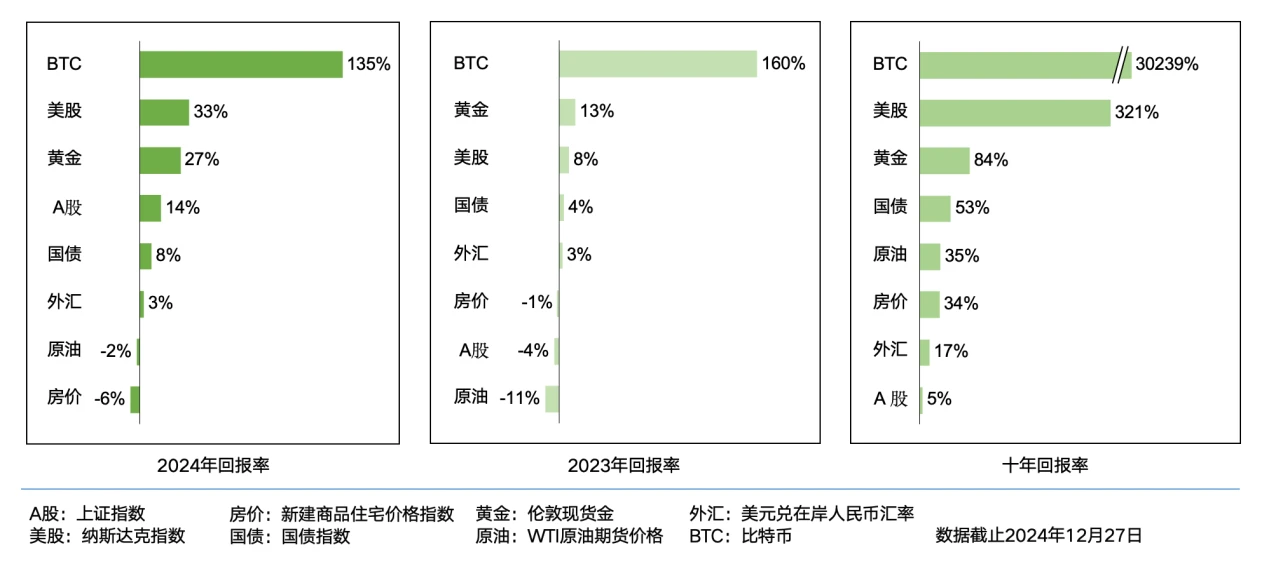
In 2024, the global economy demonstrated resilience amid numerous challenges, with a growth rate of 3.2%. Inflation eased, and central banks in multiple countries began a cycle of interest rate cuts. However, elections in over 70 countries led to increased internal divisions within governments and a rise in populism. Against the backdrop of easing inflation, many economies shifted their policies, such as the Federal Reserve cutting rates in September, Japan raising rates for the first time, and China strengthening stimulus policies after September. The global stock market returned over 20%, and the bond market also saw growth, with a diversified global asset investment portfolio achieving a total return of 12.5% based on a 16.5% performance in 2023.
I. Performance of Major Economies
(1) United States
The U.S. economy remained strong in 2024, with GDP growth of 2.7%, easing inflation, a cooling labor market, and a real estate market resembling stagflation. Corporate earnings performed well, but there was significant industry differentiation, with continued fiscal expansion and relaxed credit standards. In 2025, attention should be paid to the policies of the Trump administration, geopolitical conflicts, overvalued asset prices, and government debt risks.
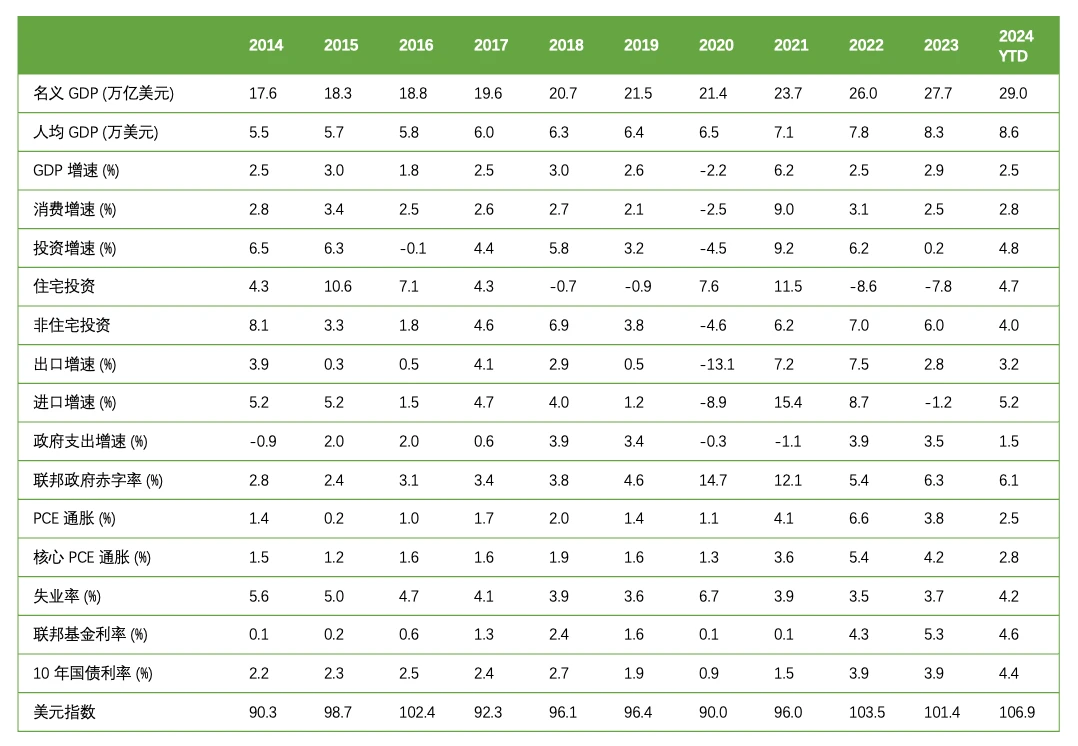
In 2024, the U.S. economy grew by 2.7%, primarily driven by household consumption, business investment, government spending, and exports. Household consumption, supported by a robust job market, wage growth, and low interest rates, is expected to grow by 2.6% for the year, contributing 1.7 percentage points to GDP. Business investment, bolstered by strong profits, the AI technology revolution, and fiscal subsidies, is expected to grow by 3.7% for the year. Government spending is projected to grow by 3.5% due to high fiscal deficits. Exports are expected to grow by 3.4% due to overseas demand and supply chain improvements.
Growth may slow in the next two years, facing high base effects, lagging monetary policy, and uncertainties surrounding Trump’s policies. Trump's tariffs and immigration policies may delay the disinflation process, reduce the extent of interest rate cuts, support a stronger dollar, thereby prolonging the effects of restrictive monetary policy, which could harm consumer demand and business confidence. Additionally, economic weakness in non-U.S. regions and trade wars may weaken the global economic outlook, dragging down the U.S. economy.
Regarding inflation, the core inflation rate has rebounded to 2%. Goods inflation has decreased due to supply chain recovery and a return to service demand, but service inflation has declined more slowly. It is expected that the PCE and core PCE inflation rates will drop from 2.4% and 2.7% in 2024 to 2.2% and 2.3% in 2025, with Trump’s policies potentially increasing uncertainty in the inflation outlook.
The labor market is gradually cooling but remains resilient, with non-farm employment growth slowing, the unemployment rate slightly rising to 4.2%, and wage growth declining to 3.9%. In 2025, the labor market is expected to continue its moderate slowdown, with new jobs primarily concentrated in healthcare, leisure and hospitality, and government sectors.
The real estate market is in a stagflation-like state, with sluggish home sales; new and existing home sales are expected to decline by 1% and 2.5%, respectively. New home supply is improving, with an increase in multi-family housing completions, but single-family homes remain in short supply. The commercial real estate vacancy rate is rising, but returns are steadily increasing. The real estate market may see moderate improvement in 2025, with new and existing home sales expected to grow by 7% and 4.5%, respectively, while home prices may continue to rise but at a slower pace.
In terms of corporate earnings, 2024 saw strong performance but significant differentiation across industries, with corporate profits growing by 10.5% year-on-year. Industries such as information services and machinery saw profit growth rates exceeding 17%, while sectors like energy and non-durable consumer goods experienced declines. In 2025, corporate profit growth may see a slight rebound, with market consensus predicting a 15% growth in S&P 500 index EPS, particularly in sectors like information technology and healthcare, where EPS growth is expected to exceed 15%, while sectors like real estate, consumer staples, and energy are expected to have relatively lower EPS growth.
On the fiscal front, the federal government’s budget deficit for the 2024 fiscal year reached $1.8 trillion, with a deficit rate close to 7%. The student loan forgiveness policy implemented by the Biden administration helps reduce the debt burden on young people, releasing consumption potential. As concerns about economic recession diminish, bank credit standards are loosening; if the Federal Reserve continues to cut rates, credit standards will further relax, helping to lower financing costs and promote credit expansion.
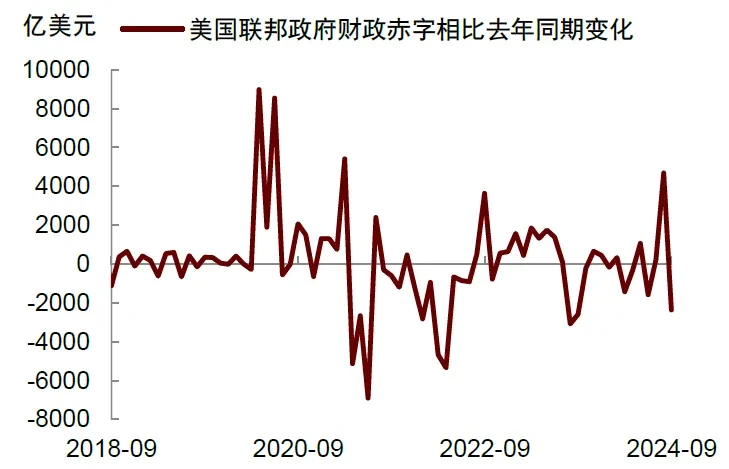
In 2025, risks will largely depend on the policies of the new U.S. government, with Trump potentially implementing domestic tax cuts, external tariffs, immigration expulsions, and encouragement of fossil fuels. These measures may sustain economic growth but could also push inflation higher. Geopolitical conflicts may lead to a sharp rise in oil prices, triggering "stagflation." Overvalued asset prices may decline significantly, weakening the wealth effect for U.S. residents and leading to reduced consumer spending. Concerns over U.S. government debt may intensify, causing U.S. Treasury yields to rise, which would suppress valuations of risk assets and negatively impact U.S. financial stability.

(2) Japan
In 2024, Japan's economy stagnated at the beginning of the year but showed signs of weak recovery in the middle of the year as consumption rebounded and inbound demand increased. However, factors such as yen depreciation, labor shortages, and weak exports are expected to lead to a negative growth of 0.3% for the year. In the first quarter, GDP fell by 0.6% quarter-on-quarter and 2.2% year-on-year, but in the second and third quarters, it grew by 0.5% and 0.3% quarter-on-quarter, respectively. Yen depreciation and labor shortages are the main obstacles to economic recovery.
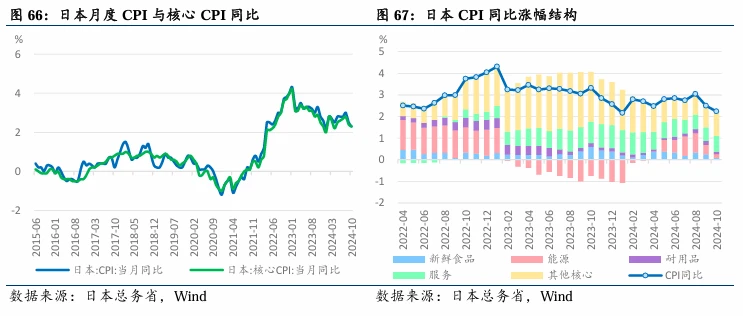
On the inflation front, Japan is gradually emerging from deflation, with the overall CPI and core CPI excluding fresh food both exceeding 2% from January to October. The CPI and core CPI peaked in August, rising by 3% and 2.8% year-on-year, respectively, while in October, Japan's CPI and core CPI rose by 2.3% and 2.2% year-on-year. Several factors are driving Japan's gradual exit from deflation, including wage growth, with a 5.1% increase in wages during this year's spring labor negotiations (with a basic wage increase of 3.56%); price pass-through increases, with corporate prices significantly rising from 2022 to 2023, and although the growth rate has slowed in 2024, it continues to rise, with service prices also significantly increasing following wage hikes after 2023; and rising price expectations, with the Bank of Japan's December survey indicating that "overall price expectations" are expected to grow by 2.4% year-on-year after one year, 2.3% after three years, and 2.2% after five years, showing a stable upward trend.
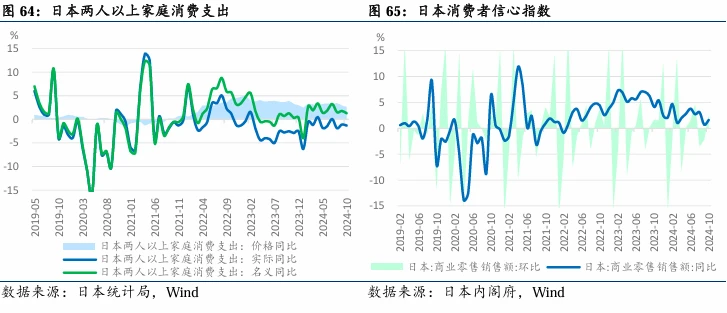
In terms of consumption, the year-on-year growth rate of real household consumption expenditure remains negative, with household consumption lagging behind price increases, and retail growth slowing, leading to low consumer confidence.
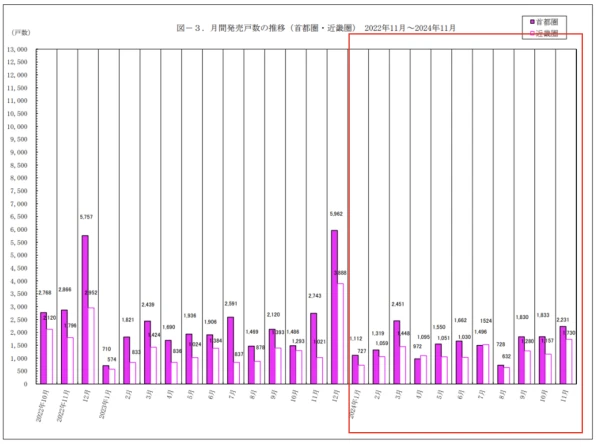
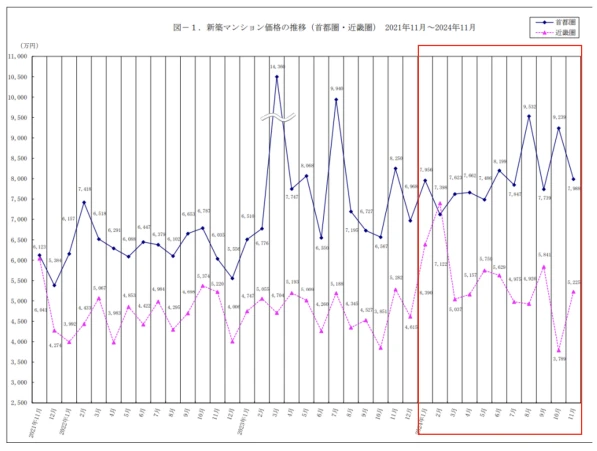
In the real estate sector, housing prices in the capital region maintain an upward trend, with new apartment prices in November declining by 5.2% and 3.2% year-on-year, but overall still on an upward trajectory.
In terms of exports, Japan's exports to major economies have all declined, with a year-on-year decrease of 1.8% in the first ten months. Exports to Russia plummeted by 27.9%, while exports to the U.S., China, ASEAN, the EU, South Korea, and Oceania also fell, although exports to India and the Middle East saw some growth. The decline in exports from traditional competitive industries has led to a trade deficit.
Regarding exchange rates, the yen depreciated overall in 2024, with the USD/JPY exchange rate reaching the 157 range. In the first half of the year, the yen rose to a historical high of 161.9, but subsequently began a second round of depreciation starting in October due to expectations of Federal Reserve rate cuts and the impact of Trump’s policies.
(3) Europe
Overall economic growth in Europe is weak, estimated at about 0.9% in 2024, with a similar forecast for 2025. Germany is a relatively solid part of Europe but is experiencing economic contraction, continuing to shrink from 2023 to 2024, with cumulative real growth at zero since before the pandemic. Germany is affected by the energy crisis, with conservative fiscal policies and the debt brake law limiting fiscal deficits, leading to internal disagreements within the ruling party and the dismissal of the finance minister, with early elections scheduled for February 2025. Germany faces significant demographic challenges, with a peak in the population around 60 years old leading to a large number of retirements, reducing the labor force, increasing wages but declining productivity, and difficulties in industrial transformation.
(4) Other Countries
India's GDP growth is at 7.0%, primarily driven by domestic demand; Russia's growth is at 3.6%, relying on energy prices and government stimulus under sanctions; the UK’s growth is at 1.1%, returning to a normal development model; and South Korea's growth is at 2.5%, mainly driven by exports. In 2025, attention should be paid to the sustainability of India's domestic demand growth, particularly whether government infrastructure investment can continue to drive economic development; for Russia, the impact of sanctions on energy price fluctuations on the economy should be monitored; for the UK, the stability of economic recovery is a concern; and for South Korea, the impact of changes in export markets on its economic growth should be observed.
II. Performance of Various Assets and the Cryptocurrency Industry in 2024
(1) Stock Market
In 2024, the global stock market performed exceptionally well, with a return rate exceeding 20%. This growth was primarily due to the resilience of the global economy, easing inflation, and the initiation of interest rate cuts by multiple central banks. Specifically:
U.S. Stock Market: The S&P 500 index achieved significant growth in 2024, with an annual return rate close to 27%, outperforming most years in the past two decades. This growth was primarily driven by strong corporate earnings, a low-interest-rate environment, and investor optimism about economic growth. Notably, technology and growth stocks performed exceptionally well, propelling the overall market upward.
Emerging Markets Stock Market: Despite facing numerous uncertainties, emerging markets also performed well, with an annual return rate of 18%. This growth was mainly due to the recovery of the Chinese economy, strong domestic demand growth in India, and economic reforms in countries like Brazil. The stock markets in China and India, in particular, stood out, attracting significant international capital inflows.
European Stock Market: The European stock market also achieved a return rate of 15% in 2024. Although economic growth was relatively weak, policy adjustments and economic reforms in major economies like Germany and France provided support for the market. Additionally, the economic stability following Brexit also contributed to the recovery of the European stock market.
(2) Bond Market
The bond market also experienced steady growth in 2024, with an annual return rate of 8%. This growth was primarily due to the interest rate cut cycle initiated by global central banks, which lowered bond yields and increased bond prices. Specifically:
U.S. Treasuries: The U.S. Treasury market performed robustly, with the 10-year Treasury yield declining from 4.5% at the beginning of the year to 3.8% at the end of the year, driving up Treasury prices. The annual return rate reached 10%, attracting significant safe-haven capital inflows.
European Bonds: The European bond market also performed well, with the yield on German 10-year government bonds falling from 2.5% at the beginning of the year to 2.0% at the end of the year, boosting bond prices. The annual return rate reached 9%, reflecting cautious optimism in the market regarding the recovery of the European economy.
Emerging Market Bonds: The emerging market bond market showed strong performance, with an annual return rate of 12%. This growth was mainly driven by the recovery of the Chinese economy and economic reforms in countries like Brazil, attracting significant international capital inflows.
(3) Real Estate Market
The real estate market exhibited a mixed performance in 2024, with an overall return rate of about 5%. Specifically:
U.S. Real Estate: The U.S. real estate market experienced a stagflation-like state in 2024, with sluggish home sales; new and existing home sales declined by 1% and 2.5%, respectively. Despite this, home prices continued to rise in 2024, with an average annual increase of about 3%. In the commercial real estate sector, vacancy rates for offices and apartments increased, but returns remained at a high level.
Chinese Real Estate: The Chinese real estate market faced significant adjustments in 2024, with sales area of commercial housing, new construction area, and residential land transaction area declining by 51%, 69%, and 68%, respectively. Nevertheless, policy adjustments and improved market expectations brought some signs of recovery in the fourth quarter, with home prices remaining stable in first-tier cities and some second-tier cities.
Japanese Real Estate: Housing prices in the Tokyo metropolitan area maintained an upward trend in 2024. Although sales of new and existing homes declined, the average annual increase in home prices was about 2%. In the commercial real estate sector, vacancy rates for offices and apartments increased, but returns remained at a high level.
(4) Commodity Market
The commodity market performed steadily in 2024, with an annual return rate of about 3%. Specifically:
Oil: Despite ongoing geopolitical conflicts, the oil market performed relatively steadily in 2024, with an average price of about $75 per barrel for the year, yielding a return rate of about 2%. This price level reflects the market's cautious expectations for global economic growth.
Gold: The gold market performed strongly in 2024, with prices rising from about $1,800 per ounce at the beginning of the year to $2,000 per ounce by the end of December, resulting in a return rate of about 11%. This growth was primarily driven by the interest rate cut cycle of global central banks and increased demand for safe-haven assets from investors.
Other Metals: Basic metals such as copper and aluminum performed steadily in 2024, with an annual return rate of about 3%. This growth was mainly due to the recovery of the Chinese economy and increased demand from emerging markets.
(5) Cryptocurrency Industry
2024 was a year of transformation and recovery for the cryptocurrency industry. After experiencing a bear market in 2023, the industry gradually regained confidence, accelerated innovation, and saw significant increases in institutional participation. The launch of Bitcoin ETFs, major changes in the policy environment, the policy expectations brought by Trump's election, and the resurgence of Solana became key factors driving the industry's development.
The price of Bitcoin (BTC) rose from about $40,000 at the beginning of the year to over $100,000 by December, an increase of over 150%. The launch of Bitcoin ETFs and substantial purchases by institutional investors were the main drivers of its price increase. Many other cryptocurrencies also performed well, with Memecoins and AI+Crypto standing out in this market cycle.
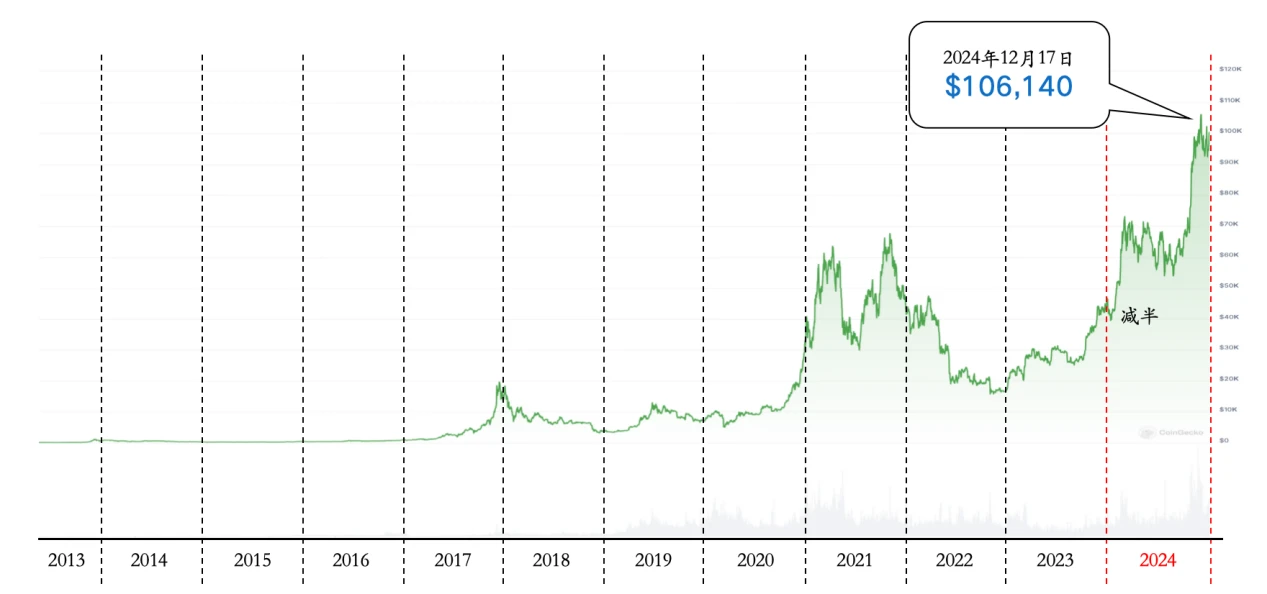
In terms of user growth, the number of cryptocurrency users continued to rise, especially in emerging markets. The widespread adoption of stablecoins became an important factor driving user growth, as many users in emerging markets bypassed traditional banking systems through stablecoins, achieving more efficient and lower-cost financial transactions.
III. Conclusion
In 2024, the global economy maintained relatively stable growth amid numerous challenges, while the cryptocurrency industry welcomed new development opportunities driven by improved policy environments, technological innovations, and expanded applications. The market performance of mainstream cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin was strong, and the rise of emerging blockchains injected new vitality into the industry. With significant inflows from institutional investors and a continuous increase in user numbers, the cryptocurrency industry is gradually maturing and is expected to play a more important role in the global economy in the future.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



