This will not be the last Chinese AI model threatening the dominance of Silicon Valley giants.
Author: Carl Franzen
Translation: Deep Tide TechFlow
Just a few days ago, only the most specialized geeks (as one of them, I say this) had heard of DeepSeek, a Chinese AI company that is a subsidiary of the uniquely named High-Flyer Capital Management (a quantitative analysis firm established in 2015). However, in the past few days, it may have become the most talked-about company in Silicon Valley.
This is mainly due to the release of DeepSeek-R1, a new large language model (LLM) capable of performing "reasoning" similar to OpenAI's current best model, o1—taking seconds or minutes to reflect on its own analysis in a step-by-step or "thinking chain" manner when answering difficult questions and solving complex problems.
Not only that, but DeepSeek-R1's scores in various third-party benchmark tests (used to measure AI's performance in answering questions on various topics) are on par with or higher than OpenAI's o1, and it is reported that its training cost is only about $5 million, with far fewer graphics processing units (GPUs) used than the strict embargoed amount in the U.S. (OpenAI's home base).
However, unlike o1, which is only available to paid ChatGPT Plus subscribers ($20 per month) and higher-tier subscribers (such as the $200 per month Pro level), DeepSeek-R1 is released as a fully open-source model, which also explains why it quickly rose to the top of the most popular and active models in the AI code-sharing community, Hugging Face.
Moreover, because it is fully open-source, people have already fine-tuned and trained the model for various specific tasks, such as making it small enough to run on mobile devices or combining it with other open-source models. Even if you want to use it for development purposes, DeepSeek's API costs over 90% less than OpenAI's equivalent o1 model.
Most impressively, you don't even need to be a software engineer to use it: DeepSeek offers a free website and mobile app for U.S. users, and its R1-powered chatbot interface is very similar to OpenAI's ChatGPT. However, DeepSeek has once again surpassed OpenAI by connecting this powerful reasoning model with web search—a feature that OpenAI has not yet implemented (web search is currently only available on the weaker GPT series models).
An Obvious Irony
Given that OpenAI was originally committed to democratizing AI for the masses, there is a rather interesting, or rather unsettling, irony here. As Nvidia's senior research manager Jim Fan said on X: "We are living in a timeline where a non-U.S. company is continuing OpenAI's original mission—truly open frontier research, empowering everyone. It doesn't make sense. But the most interesting outcomes are often the most likely to happen."
As X user @SuspendedRobot noted (citing reports that DeepSeek seems to have been trained on ChatGPT-generated Q&A outputs and other data): "OpenAI steals data from the entire internet to make itself richer, while DeepSeek steals from them and gives it back to the public for free, which reminds me of a British folk tale."
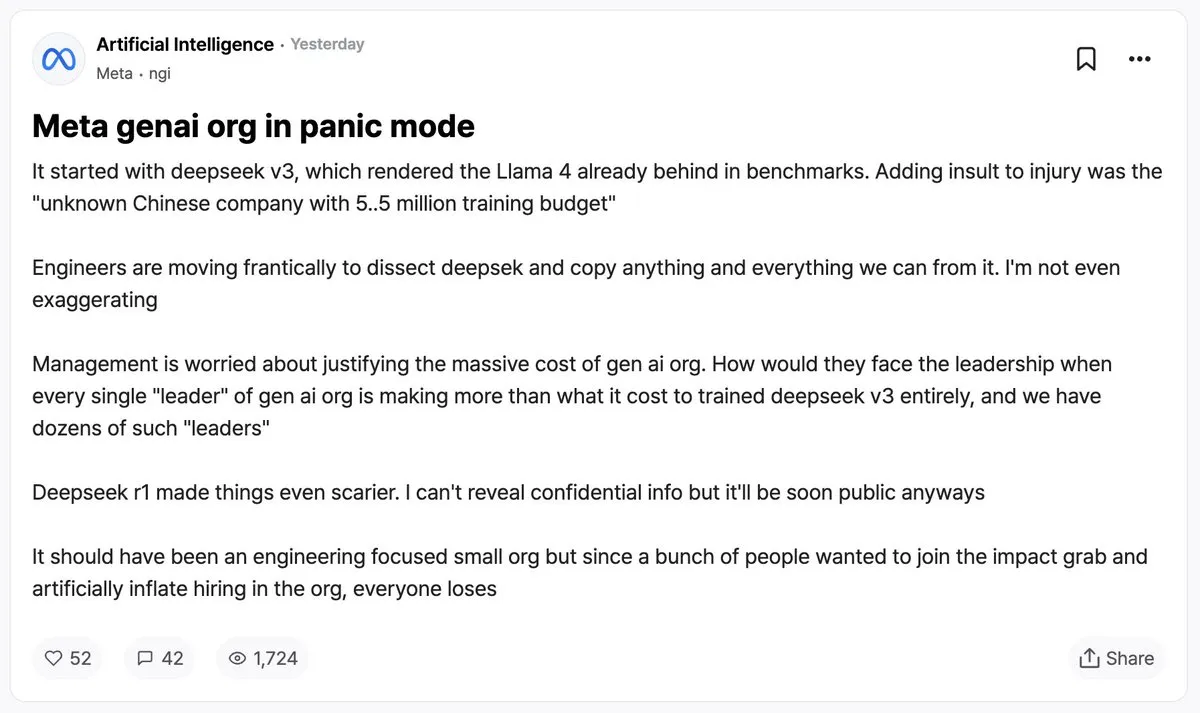
Meta in Crisis, Falling Behind Open Source Llama?
But it’s not just Fan who has noticed DeepSeek's success. Based on my conversations and readings with various engineers, thinkers, and leaders, the open-source availability of DeepSeek-R1, its high-performance results, and the fact that it seems to have "suddenly emerged" to challenge the former generative AI leaders have sent shockwaves throughout Silicon Valley and beyond. If not "everyone" is going crazy over it as my exaggerated headline suggests, it is at least a hot topic in tech and business circles.
A post shared on Blind (Silicon Valley's anonymous gossip-sharing app) is circulating widely, suggesting that Meta is in crisis due to DeepSeek's success, as it has quickly surpassed Meta's own efforts to become the open-source AI king with its Llama model.
"This Changes the Entire Game"
X user @tphuang made a compelling point: "DeepSeek has commoditized AI beyond the top tier. The first image was an eye-opener for me. R1 is much cheaper than U.S. labor costs, which means many jobs will be automated in the next five years." He later pointed out why DeepSeek's R1 is more attractive to users than OpenAI's o1:
"o1 has three huge problems:
1) Too slow
2) Too expensive
3) End users lack control/over-reliance on OpenAI.
R1 solves all these problems. Companies can buy their own Nvidia GPUs to run these models without worrying about extra costs or slow/unresponsive OpenAI servers."
@tphuang also posed a thought-provoking analogy: "Will DeepSeek become the Android of the LLM space?"
Tech entrepreneur Arnaud Bertrand candidly discussed the astonishing impact of DeepSeek's success on X: "No matter how much you emphasize the extent of this game-changing shift, it’s not enough. This is not just about AI; it’s a huge irony against the U.S. attempt to stifle Chinese technological development. Without such restrictions, DeepSeek might not have emerged (as the saying goes, necessity is the mother of invention)."
Censorship Issues
However, some have raised warnings about DeepSeek's rapid rise, arguing that as a startup operating in China, it must comply with the country's laws and content censorship requirements. In fact, when I personally used the iOS version of DeepSeek in the U.S., I found that it would not answer certain questions.
As a member of the media, I certainly value freedom of speech and expression, which is one of the fundamental principles I staunchly support.
However, I must also point out that OpenAI's models and products (including ChatGPT) also refuse to answer a range of questions—especially those involving human sexual behavior and adult/NSFW content, even if those questions are quite ordinary.
Of course, this is not a completely equivalent comparison. For some, the aversion to relying on foreign technology may lead them to be skeptical about DeepSeek's ultimate value and practicality. But its performance and low cost are undeniable.
In an era where 16.5% of goods in the U.S. are imported from China, I find it hard to warn against using DeepSeek-R1 solely based on censorship concerns or security risks—especially when the model code can be downloaded for free, used offline, run on secure devices, and fine-tuned at will.
I do notice that the fervent discussions surrounding DeepSeek contain some existential crisis thinking about "Western decline" and "Chinese rise." Some have already linked this to the situation where U.S. users joined the Xiaohongshu app when TikTok was briefly banned, during which they were surprised by the quality of life in China showcased in the videos shared there. The emergence of DeepSeek-R1 occurs against this narrative backdrop—where China appears to be rising (and indeed is on many metrics), while the U.S. appears to be declining (and indeed is on many metrics as well).
The First but Not the Last Chinese AI Model Shocking the World
This will not be the last Chinese AI model threatening the dominance of Silicon Valley giants—even as these giants, like OpenAI, are raising more funds than ever for their development of artificial general intelligence (AGI, programs that surpass humans in most economically valuable tasks).
Just yesterday, another Chinese model from TikTok's parent company ByteDance—Doubao-1.5-pro—was released, performing comparably to OpenAI's non-reasoning GPT-4o model in third-party benchmark tests, but at a cost only 1/50th of the latter.
Chinese models are developing so quickly and so well that even those outside the tech industry are taking notice: The Economist just published an article about DeepSeek's success and other Chinese AI efforts, and political commentator Matt Bruenig posted on X: "I have been using Gemini, ChatGPT, and Claude for NLRB document summarization for nearly a year. DeepSeek is better than all of them in this regard. Its chatbot version is free. The price of using its API is 99.5% lower than OpenAI's API. [shrug emoji]"
How Will OpenAI Respond?
It's no wonder that OpenAI co-founder and CEO Sam Altman stated today that the company will introduce the yet-to-be-released second-generation reasoning model series, o3, into ChatGPT, even for free users. OpenAI seems to still be carving its own path with more proprietary and advanced models—setting industry standards.
But the question is: How long can OpenAI maintain its lead in producing and releasing new cutting-edge AI models with DeepSeek, ByteDance, and other Chinese AI companies hot on its heels? If it truly falls behind, how fast and severe will its decline be?
However, OpenAI does have another historical precedent to draw from. If DeepSeek and Chinese AI models indeed capture a significant market share like Google's open-source Android did in the mobile space for a time—you only need to look at how Apple's iPhone captured the high-end segment of the market through its closed, proprietary, all-internal approach and then steadily expanded downwards, especially in the U.S., to now hold nearly 60% of the domestic smartphone market share.
Nevertheless, for all those spending big bucks on leading lab AI models, DeepSeek shows that the same capabilities can be obtained at a lower price, with greater control. In a corporate environment, this may be enough to win.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




