Author: LINDABELL
At the recent Devcon conference, Ethereum Foundation core member Justin Drake proposed the Beam Chain initiative, which aims to upgrade Ethereum's consensus layer through zkSNARK and zkVM technologies to enhance the network's scalability, security, and efficiency. This vision has also brought renewed attention to the importance of zkVM. As a general-purpose zero-knowledge virtual machine, zkVM can handle complex computations in a more flexible and efficient manner while freeing itself from reliance on traditional smart contract logic.
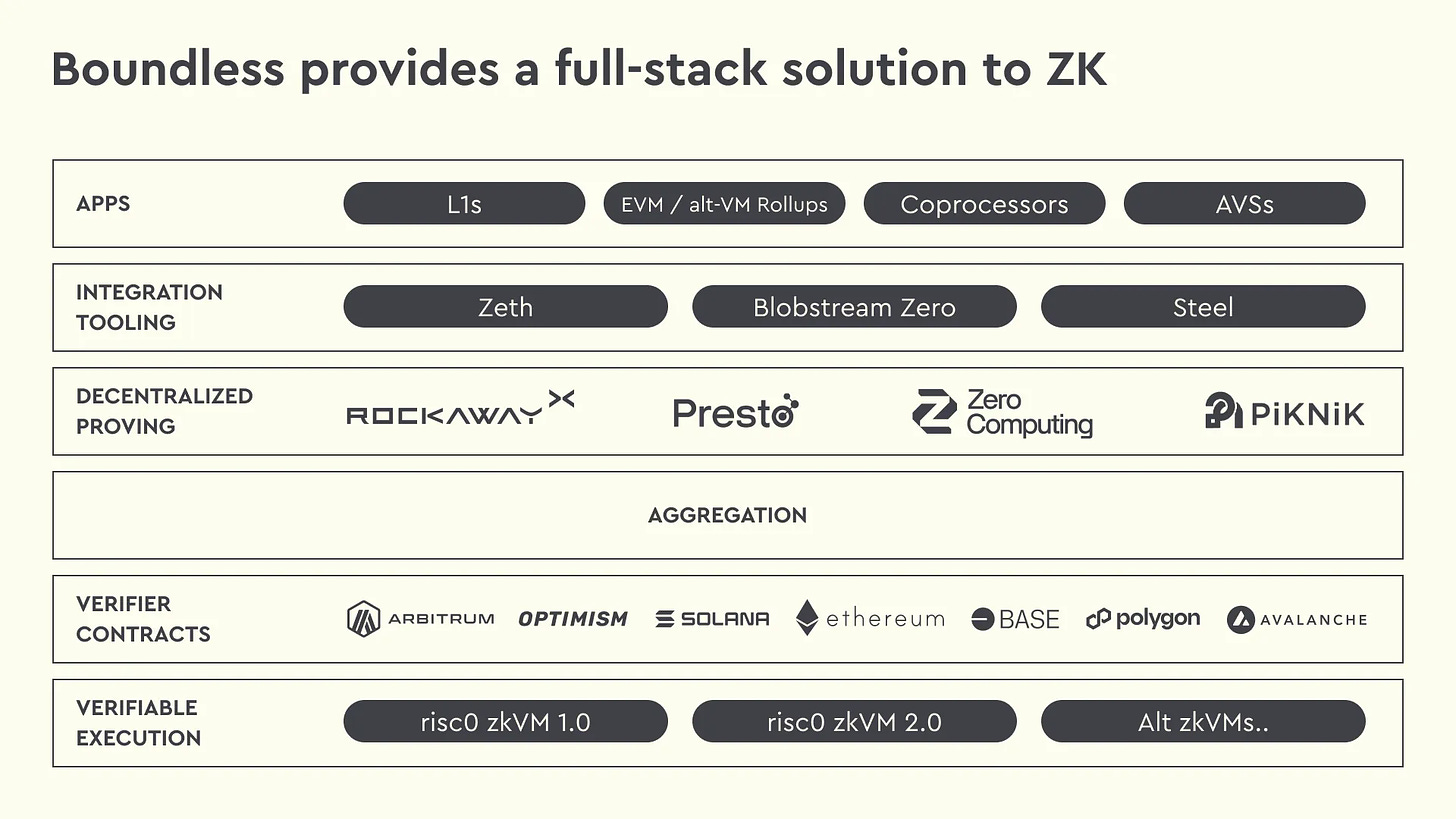
Driven by this trend, projects such as RISC Zero, Succinct, and Cysic are seen as important participants in driving innovation in this field. Among them, RISC Zero has developed a series of open-source tools, including Zeth, Kailua, and Bonsai, based on its RISC-V architecture zkVM, which not only enhances block validation and Rollup performance but also provides technical support for Ethereum's ZK upgrade.

RISC zkVM Ecosystem Product Matrix: From Core Technology to Application Scenarios
RISC Zero is a zkVM implementation based on the RISC-V instruction set architecture. As a general-purpose zero-knowledge computing platform, it supports various mainstream programming languages, such as Rust and C++, and can run almost any computational task. Compared to other zero-knowledge technology platforms, RISC Zero's provers and verifiers are completely open-source, allowing developers to generate and verify proofs locally. Additionally, RISC Zero's verifiers are compatible with multiple platforms, adapting to different blockchain ecosystems and simplifying the development process of decentralized applications.
In June of this year, RISC Zero released zkVM 1.0. This version not only supports multiple languages and complex computational tasks but also utilizes Continuations technology to break down large-scale computations into smaller segments, achieving efficient parallel computation and verification. According to the roadmap, RISC Zero plans to achieve a 20-fold improvement in zkVM performance and cost by the end of 2024, with optimizations including fully migrating the proof process to GPUs (80% completed), introducing new RISC-V v2 circuit designs, and conducting specialized optimizations for recursive circuits. At the same time, RISC Zero is integrating a series of acceleration modules for algorithms such as RSA, Keccak, and ECDSA to enhance the performance of Ethereum-related tasks and cryptographic operations.
Around the core capabilities of zkVM, RISC Zero has also developed a series of open-source tools and products. For example, through the Bonsai network, developers can generate zero-knowledge proofs without the need for dedicated hardware; the Steel tool allows complex EVM computations to be offloaded to an off-chain environment while maintaining verifiable results, reducing on-chain execution costs; and Blobstream Zero bridges the Celestia data availability layer, providing more possibilities for data sharing and verification in modular blockchain ecosystems.
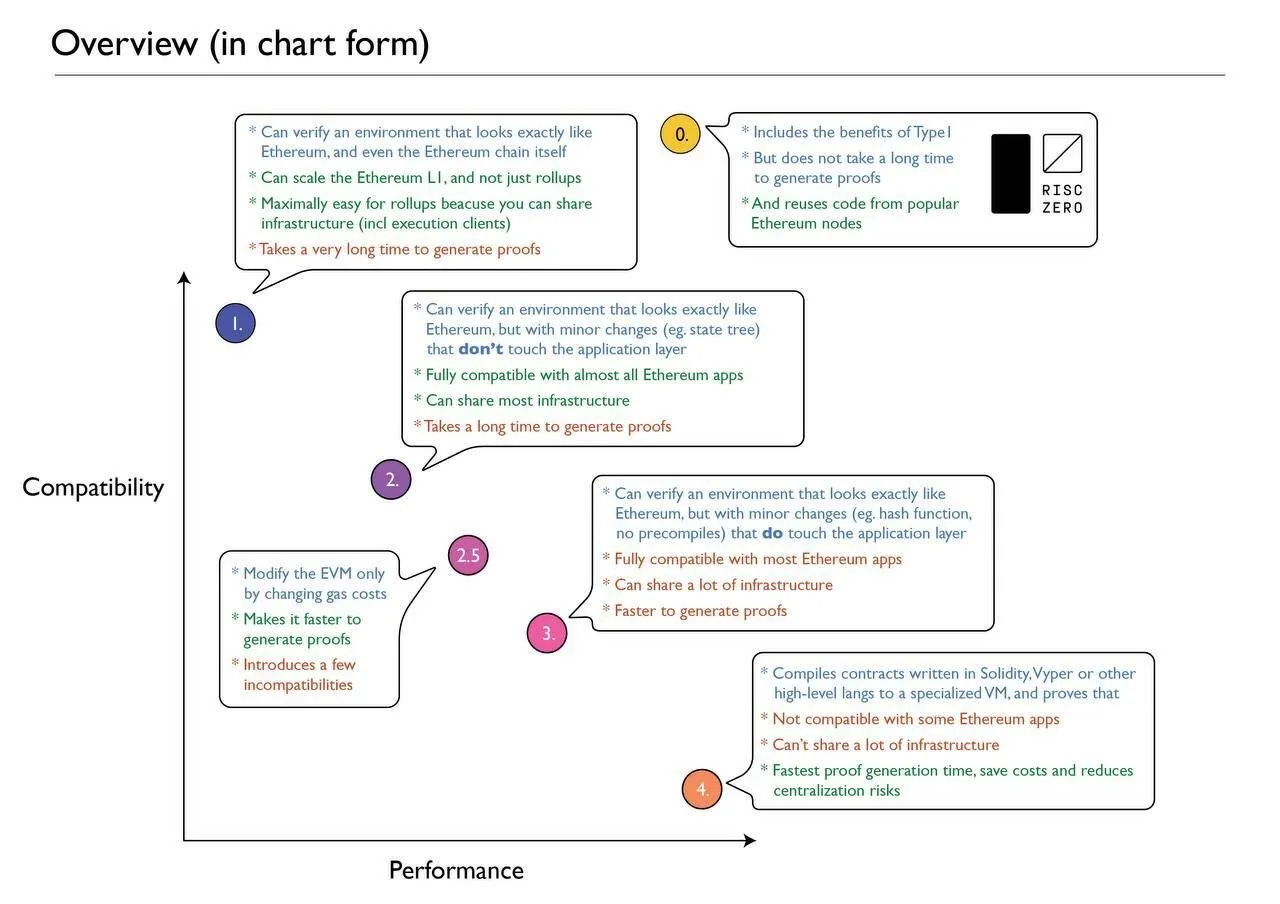
Zeth: Proving the Correct Construction of Entire Ethereum Blocks
Zeth is an open-source Ethereum zero-knowledge block prover developed by RISC Zero based on its zkVM technology, which can verify the validity of Ethereum blocks through zero-knowledge proofs without relying on traditional validators or synchronization committees. RISC Zero defines Zeth as a Type-0 zkEVM, which is fully compatible with the Ethereum protocol and improves development efficiency through code reuse.
Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin categorized zkEVMs into four types in his article "Different types of zk-EVMs": Type-1 seeks complete and uncompromising equivalence to Ethereum; Type-2 aims for complete equivalence to the EVM but not fully equivalent to Ethereum; Type-3 is almost equivalent to the EVM; and Type-4 is completely incompatible with Ethereum.
Thanks to the high performance of RISC Zero's zkVM, Zeth can complete the verification of Ethereum blocks in just a few minutes. Test data shows that Zeth can generate block proofs at a speed of 1.1 MHz and, by utilizing the "continuations" feature to scale GPU clusters, increase the speed to between 4.7 MHz and 6.3 MHz. This performance optimization also reduces the cost of proof generation. According to tests, the proof generation cost for a block containing 182 transactions is only $21.72, with a cost of about $0.11 per transaction.
During the development of Zeth, the RISC Zero team made full use of components from the Rust ecosystem, such as revm, ethers, and alloy, enabling developers to quickly implement block proof functionality and apply it to different scenarios. This design provides developers with more flexibility to adjust block construction logic as needed and adapt to future Ethereum improvement proposals.
At the application level, Zeth provides efficient solutions for zk Rollups, light clients, and cross-chain bridges. The construction of traditional zk Rollups and zkEVMs requires significant time and funding, making it daunting for small teams. However, Zeth, based on a modular zkVM architecture, allows developers to easily customize block validation logic. For example:
- zk Rollup: Zeth can quickly implement block proofs, shortening the development cycle and reducing funding requirements for ZK Rollups.
- Light Client: Validating block validity without needing to reconstruct the block reduces operational costs.
- Cross-Chain Bridge: Zeth can verify the correctness of cross-chain data without leaking sensitive on-chain information through ZKP, reducing reliance on third-party trust and lowering the risk of cross-chain attacks.
In May of this year, Zeth successfully expanded to support extracting Optimism block data from the Ethereum mainnet and generating ZKP to verify block correctness, also supporting on-chain verification. This means that with Zeth, Optimism can verify transactions more efficiently and resolve transaction disputes.
Bonsai: Allowing Developers to Generate Proofs Without Using Their Own Hardware
Bonsai is a remote proof service designed for zkVM applications, allowing developers to generate proofs without using their own hardware, thus addressing the conflict between limited on-chain computing resources and high costs. Through Bonsai, developers only need to define the zkVM application and input data to be executed, and Bonsai can run the computation in the background and generate the corresponding zero-knowledge proof. This process requires no additional hardware deployment by the developer. Additionally, Bonsai utilizes a large number of GPU clusters to support parallel processing of multiple computational tasks. Furthermore, Bonsai provides a simple and user-friendly API and SDK interface, making it easy for developers to integrate it into existing systems, further reducing development difficulty.
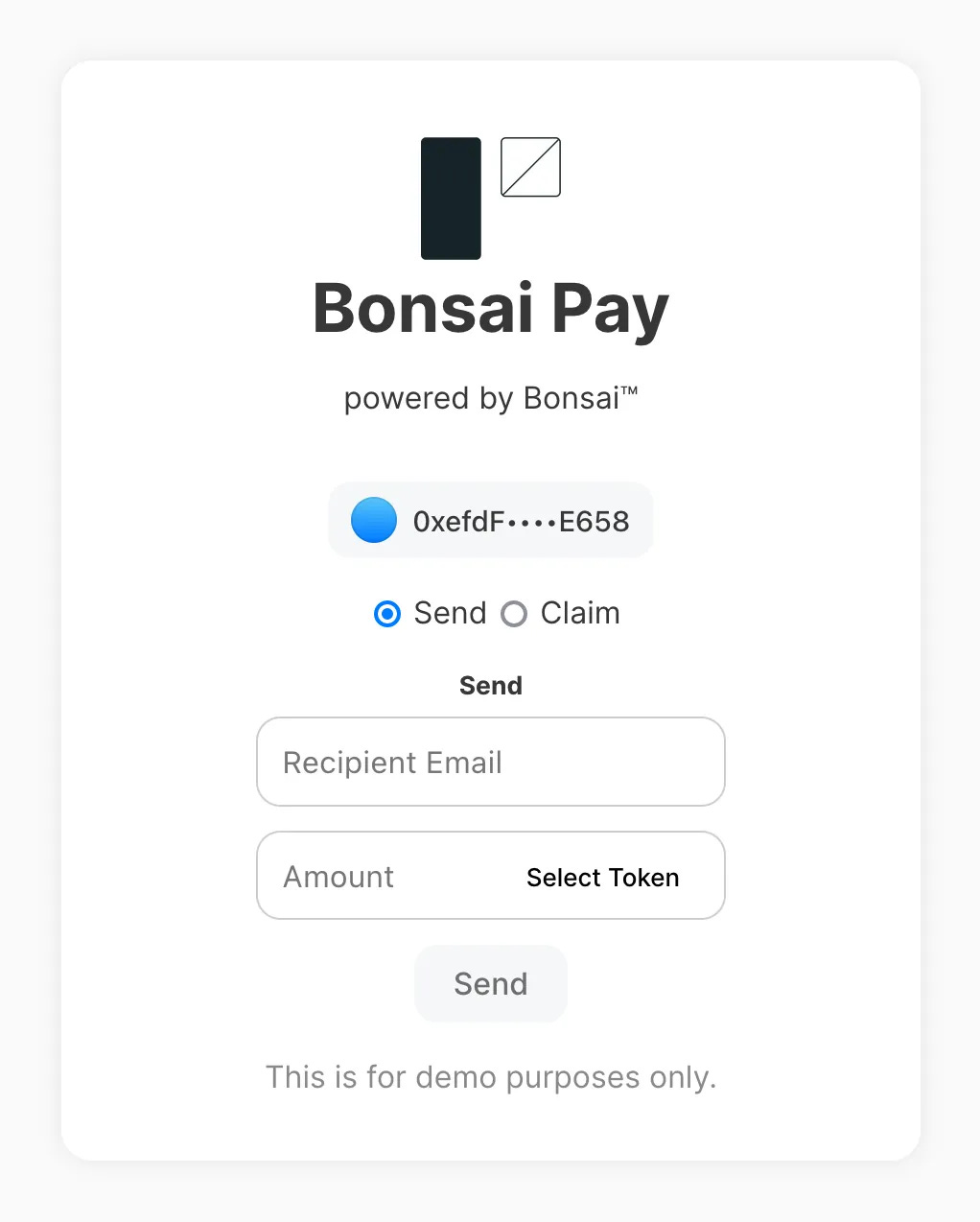
Based on this remote proof service, RISC Zero launched the open-source tool Bonsai Pay, which combines OAuth2.0 authentication and ZKP technology, allowing users to send or receive tokens on the Ethereum network using their Google accounts. For example, when Alice wants to transfer funds to Bob, she can use Bonsai Pay to input Bob's Google email and the transfer amount. Bob can then log into Bonsai Pay, input his email address, and complete Google account authentication. Bonsai Pay will use OAuth 2.0 to generate an authorization token, proving that Bob is indeed the holder of that email. Subsequently, Bonsai Pay calls the Bonsai proof service to generate a zero-knowledge proof, demonstrating that Bob's Google account is associated with his wallet address. After the smart contract verifies the proof, it will unlock the funds and transfer them to Bob's wallet address.
Throughout the process, Bonsai Pay verifies the fact that "Bob's Google account is associated with his wallet address" through ZKP technology while avoiding the disclosure of any specific information about the Google account.
Another important application of Bonsai is the Bonsai ZK Co-processor. It uses zero-knowledge proof technology to transfer complex computational tasks off-chain while generating tamper-proof proofs to ensure the correctness of the results. Additionally, deploying the Bonsai co-processor is very simple; developers only need to write a zkVM application to handle the logic and call Bonsai through a simple Solidity contract to run the computation and verify the results. Throughout the process, the Bonsai proof service is responsible for generating the zero-knowledge proofs for off-chain computations, which can be verified on-chain.
The Bonsai ZK Co-processor is suitable for on-chain applications that require high performance and low costs. For example, in DAO governance, it can transfer complex voting calculations off-chain, significantly reducing on-chain gas fees. The Bonsai DAO Governor has reduced the gas cost per vote by over 50% through the co-processor, effectively improving governance efficiency and lowering participation barriers.
Boundless: A Verifiable Computing Layer
In traditional blockchain architecture, to ensure the validity of transactions, all nodes need to repeat the execution of all computations for each transaction. This "global re-execution" model, while ensuring security and consistency, also incurs extremely high computational costs. To address this issue, RISC Zero has launched Boundless, allowing a single node to complete the computation and generate a verifiable zero-knowledge proof, enabling other nodes to confirm the results by simply verifying the proof without needing to repeat the computation.
Boundless simplifies the verification process through recursive composition techniques. It combines multiple small zero-knowledge proofs into a single overall proof, allowing verifiers to check just one total proof instead of verifying all stage proofs individually. To further optimize the efficiency of zero-knowledge proof generation, Boundless includes dedicated cryptographic acceleration circuits that enhance the efficiency of common tasks such as hash calculations and digital signature verifications.
Moreover, developers using Boundless do not need to have an in-depth understanding of zero-knowledge technology; they can simply write applications in familiar programming languages (such as Rust or Solidity). Currently, Boundless is open for free access to developers. They can leverage the proving services provided by Boundless to quickly build and deploy zero-knowledge applications on any blockchain without needing to migrate existing systems or update verification contracts.
Blobstream Zero: A Cross-Chain Bridge for Simplifying Cross-Chain Data Verification with zkVM
Blobstream Zero is a zkVM-based cross-chain bridge launched in collaboration between RISC Zero and Celestia, aimed at seamlessly connecting Celestia's data availability layer to existing modular blockchain ecosystems. By sharing and verifying data on Celestia, Blobstream Zero facilitates more convenient data transfer and verification between chains.
As a fully open-source public product, Blobstream Zero allows any project or developer to run local instances and generate zero-knowledge proofs. Additionally, Blobstream Zero can support ZK co-processors. The ZK co-processor is essentially an off-chain computing tool that requires reliable data to perform computations. Blobstream Zero can obtain data from blockchains like Celestia and can generate ZK proofs to demonstrate that the transmitted data is reliable.
Steel: A New Paradigm for Smart Contract Execution with Off-Chain Execution and On-Chain Verification
Steel is an open-source tool launched by RISC Zero that utilizes zkVM technology to achieve off-chain verifiable smart contract execution. With Steel, developers can transfer EVM operations from on-chain to off-chain execution while generating zero-knowledge proofs to ensure the authenticity and verifiability of the computation results.
Traditional smart contracts require complete execution of all logic on-chain, which not only incurs high gas costs but also limits the development of complex applications. Steel's off-chain computation and on-chain verification mechanism addresses this issue. For example, in a simple smart contract that checks if an account's ERC20 balance is greater than 1 and increments a counter variable, traditional methods require complete on-chain execution of the logic, while Steel performs the computation off-chain and generates a zero-knowledge proof, requiring only the verification of the proof on-chain without repeating the contract logic.
Currently, RISC Zero has released Steel 1.0, and partners have already utilized this tool to develop applications. For instance, in a contract call involving approximately 400,000 SLOAD operations, the computation was transferred to off-chain execution via Steel, followed by on-chain verification of the generated zero-knowledge proof. The proof generation cost was less than $10, and the on-chain verification cost was below 300,000 gas.
Kailua: A Hybrid ZK Solution Driving Innovation in Rollup Architecture
Following the release of Zeth, RISC Zero introduced Kailua, which provides an upgrade solution for optimistic Rollups through a hybrid ZK Rollup approach. Traditional optimistic Rollups typically require a 7-day challenge period, leading to slower transaction finality, while ZK Rollups can achieve rapid finality but incur high ongoing costs for generating zero-knowledge proofs. Kailua combines the advantages of both, achieving a balance between cost and efficiency through a hybrid architecture. As an extension of the Optimism Kona framework, Kailua not only supports unmodified Kona running on zkVM but also introduces an innovative dispute resolution mechanism that reduces staking requirements and minimizes finality delays, thereby enhancing system efficiency and usability.
In Kailua's architecture, the dispute mechanism features a new design. Firstly, its dispute resolution mechanism eliminates time limits, allowing verifiers ample time to generate proofs in the event of network interruptions or other special circumstances, thereby enhancing system resilience. Even in extreme cases, RISC Zero's zkVM's scalable architecture can complete proofs within an hour. Additionally, Kailua's on-demand verification feature allows developers to flexibly configure verification frequency, enabling a gradual transition to a fully verified Rollup model at a lower cost.
Unlike ZK Rollups, Kailua's design does not require continuous proof generation. For low-frequency empty blocks or Rollups with special contract requirements, Kailua offers a more cost-effective option. Furthermore, Kailua significantly reduces the staking cost requirements for Rollups. The staking amount for traditional optimistic Rollups increases linearly with longer finality periods, while Kailua's optimized design fixes the staking requirements, allowing the system to maintain security and activity at a lower cost even over long periods.
Currently, Kailua is fully open-source. Developers can use its command-line tools to deploy a local Optimism test network and quickly upgrade to a network that supports ZK fault proofs. Kailua also supports simulating fault proposals, helping developers understand how verifiers challenge erroneous states through zkVM, thereby gaining deeper insights into its dispute resolution mechanism. In the future, Kailua will further optimize cost and performance and expand support for more Rollup frameworks.
Summary
As seen from the above, RISC Zero's zkVM product matrix is driving the development of zero-knowledge proof technology across multiple domains. Zeth and Kailua focus on optimizing Rollup architecture, enhancing block verification efficiency and dispute resolution speed. Bonsai provides remote proof services, reducing hardware dependencies and operational costs, enabling developers to build applications more efficiently. Meanwhile, Blobstream Zero offers reliable support for modular blockchain ecosystems through efficient verification of cross-chain data. Additionally, Steel lowers the gas costs of smart contract execution through its model of off-chain computation and on-chain verification.
Of course, while continuously improving the zkVM product matrix, RISC Zero is also pushing for innovation in the underlying zkVM technology. Recently, RISC Zero zkVM released version 1.2, introducing a new precompilation method that allows developers to deploy precompilation logic alongside applications without needing to embed it within the zkVM itself. This means developers can add new precompilation logic without modifying on-chain verification contracts or coordinating prover configurations, and without forking or making significant changes to the zkVM to achieve performance optimizations. Furthermore, by defining precompilations through applications, the computational costs of proof generation can be reduced. For example, after integrating RSA precompilation, Automata reduced the execution cycle from 39 million to 217,000, lowering costs by approximately 180 times.
As zkVM technology continues to optimize, its development potential will gradually be reflected in various application scenarios. However, to better unleash this potential, it still relies on ecological collaboration and the actual performance of technological implementation.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




