According to reports from Wu Shuo Blockchain, some users in mainland China recently received promotional advertisements for cryptocurrency funds on the homepage of Alipay's fund section. The content read, "Global investment, cryptocurrency soaring, starting from 10 yuan, get on board immediately." Upon verification, the fund in question is the Huabao Overseas Technology C (QDII-FOF-LOF), which has a purchase limit mechanism, allowing each person to buy only up to 1,000 yuan per day.
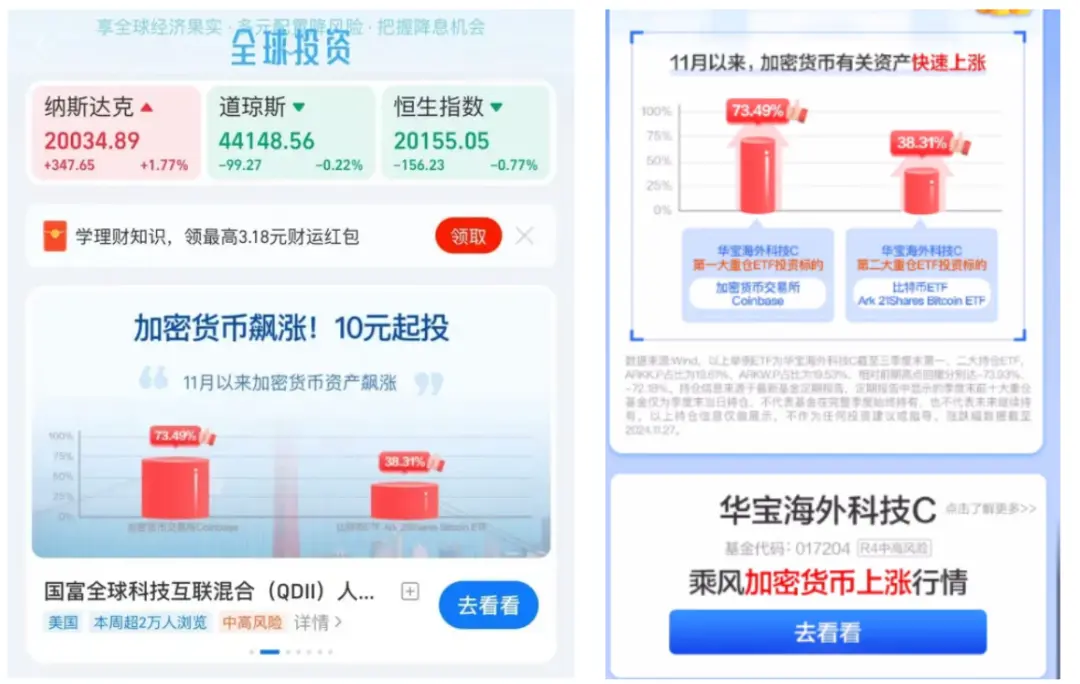
Given Alipay's significant position in China's internet industry, many friends in the circle have shared this news, speculating whether this is a sign that mainland China is relaxing its restrictions on cryptocurrency policies. Previously, Liu Honglin and Bai Zhen from the Mankun Law Firm analyzed “Web3 Lawyers: Can Chinese Investors Legally Invest in Crypto Assets through QDII?”, which may answer some concerns of industry practitioners.
The following is the relevant content.
Under Currents
The booming development of the cryptocurrency market has had a tremendous impact on traditional financial markets. As the most highly regarded cryptocurrency globally, the surge in Bitcoin's price has not only attracted the attention of individual investors but has also gradually become an asset allocation option for institutional investors. In the European and American markets, financial derivatives related to Bitcoin, such as ETFs and trust funds, have been launched and widely welcomed.
However, in China, the policy direction is entirely different. Since the national policy was issued in 2021 to comprehensively ban virtual currency mining and trading, investing in cryptocurrency has become almost an "impossible task." This policy is driven by considerations of financial risk prevention, social stability maintenance, and the management of the renminbi's foreign exchange. Domestic regulatory agencies are concerned that virtual currencies may lead to money laundering, illegal fundraising, and other issues, while also worrying about their negative impact on energy consumption and environmental protection. This has led to a complete blockade of any channels for direct contact with cryptocurrency, with increasingly strict legality reviews of related links, from banking services to payment interfaces.
For ordinary investors, it has become nearly impossible to invest in cryptocurrency through legitimate channels, and attempting to open overseas accounts is not an easy task either. This operation not only requires overcoming the technical and informational barriers of opening accounts abroad but also faces China's strict foreign exchange controls and potential compliance and tax risks that may arise during cross-border capital flows. These restrictions mean that while there is a demand for domestic investors to invest in cryptocurrency, they often have to resort to "gray" or even illegal means, further increasing legal and financial uncertainties.
Even so, market demand still exists. For many Chinese investors, allocating cryptocurrency is not just about pursuing short-term gains but also a need for global asset diversification. So, can one legally invest in cryptocurrency through the officially recognized QDII mechanism? This not only concerns the feasibility of investment but also touches on the struggle between policy bottom lines and market realities.
The Mechanism and Limitations of QDII: It Allows You to Go Abroad, But Not Necessarily "Freely"
The Qualified Domestic Institutional Investor (QDII) mechanism has been an important tool for Chinese investors to legally participate in overseas markets since its launch in 2006. This mechanism is a significant attempt at gradually opening China's capital account, aiming to provide domestic investors with legal channels to invest in overseas markets through specific institutions while optimizing the use of foreign exchange reserves and managing cross-border capital flows in an orderly manner.
QDII allows qualified financial institutions, including banks, fund companies, securities companies, and insurance companies, to design and sell financial products that invest in overseas markets. Through these products, domestic investors can indirectly participate in investments across various asset classes, including overseas stocks, bonds, funds, and financial derivatives. The core operation of QDII is that investors do not need to directly contact overseas financial markets but can achieve global asset allocation through the specialized management of domestic institutions. This mechanism not only reduces the risks and costs for individual investors when directly investing abroad but also ensures the legality and compliance of capital flows.
However, QDII is not a "universal key"; its operational mechanism and restrictions determine that its investment scope and compliance are strictly controlled. It is a "window," but not a completely open "door."
The investment scope of QDII is jointly regulated by the State Administration of Foreign Exchange and the China Securities Regulatory Commission, and all investment targets must meet the requirements of legitimate overseas markets. Traditional QDII products mainly involve stocks, bonds, and traditional funds, which have certain risk control attributes. However, for emerging market assets, especially cryptocurrency, QDII has not explicitly allowed it at present. Particularly for cryptocurrency-related ETFs or trust funds, even if they are legal in European and American markets, they may still be rejected by domestic regulatory agencies from being included in the QDII investment scope due to the "policy sensitivity" of the underlying assets. This uncertainty means that QDII cannot fully meet investors' demands for cryptocurrency.
QDII implements a total quota management system, with the foreign exchange administration allocating quotas to specific institutions each year based on market and foreign exchange reserve conditions. In recent years, due to the slow pace of capital account opening, the demand for QDII quotas has consistently exceeded supply. Financial institutions tend to use these precious quotas for lower-risk, stable-return traditional asset classes rather than for cryptocurrency, which has high policy uncertainty and significant market risks.
Moreover, the core design concept of QDII is to provide a stable overseas investment channel, which is clearly at odds with the high volatility of cryptocurrency. The cryptocurrency market is known for its extreme price fluctuations and significant market manipulation risks, with instances of price changes exceeding 20% in a short period not being uncommon. For QDII investment products that are oriented towards stability, this risk characteristic is not compatible.
The launch of QDII products requires multiple rounds of approval, and from product design to final launch, they must comply with various regulatory requirements. Especially in the current context of strict domestic regulation against virtual currencies, whether financial institutions have the motivation to develop QDII products related to cryptocurrency remains a significant question.
The fund product mentioned in the Alipay advertisement in this news event is indeed a QDII. In simple terms, domestic retail investors can indirectly participate in overseas asset investments by investing in the aforementioned QDII fund and then using the QDII fund as the main body for overseas layout. According to the Q3 2024 report of the Huabao Overseas Technology Equity Securities Investment Fund (QDII-LOF), it states in the investment strategy section, "This fund mainly invests in overseas technology-themed related funds (including ETFs), ultimately investing in stocks that support long-term development through technology."
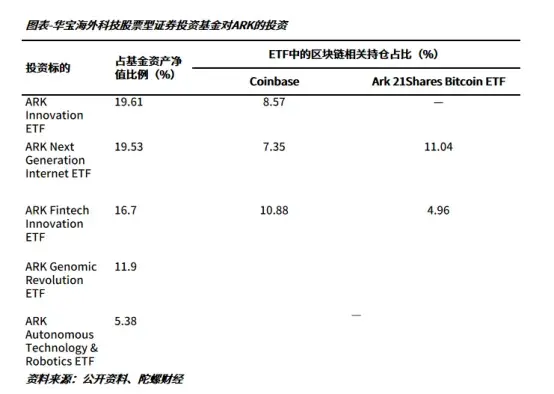
What is the proportion of cryptocurrency investment in the fund? According to professional media analysis, Huabao Overseas Technology has approximately 4.93% of Coinbase stock and 2.98% of Ark 21Shares Bitcoin ETF, totaling 7.92%. Considering the latest scale of Huabao Overseas Technology C is 406 million yuan, cryptocurrency does not dominate either in amount or proportion. Therefore, whether this fund can be considered a cryptocurrency fund may still need time to verify.
Feasibility and Risks: Theoretical Possibility, Real-World Difficulties
Although theoretically, it is not entirely impossible to allocate cryptocurrency through QDII, the practical operation of this path is fraught with complex policy restrictions, institutional concerns, and investment risks.
In China, the legal status of cryptocurrency has long been in a "policy gray area." Although the government has banned trading and mining activities of virtual currencies, its specific attitude towards indirect investment in cryptocurrency is not clear. Especially participating in the cryptocurrency market through a legitimate mechanism like QDII, its legal nature remains highly controversial.
On one hand, Chinese regulatory agencies have very strict risk management for financial products, and cryptocurrency is considered a high-risk category due to its high volatility and potential for market manipulation. Even indirectly participating in cryptocurrency investment in the form of ETFs or trust funds, the underlying asset attributes of these products may still be deemed "not compliant with domestic policy requirements," leading to rejection from the QDII investment scope.
Additionally, the stability of domestic regulatory policies is also a potential hidden danger. Even if a certain QDII product is approved, subsequent policy changes may lead to product suspension or even liquidation, which poses uncontrollable significant risks for investors. The instability of policy direction makes allocating cryptocurrency through QDII more like a "high-risk policy probe."
Even if policies are relaxed, whether financial institutions are willing to develop QDII products related to cryptocurrency remains a major challenge. This mainly involves the high compliance costs. Designing a compliant QDII product requires a significant amount of time and resources, including multiple rounds of communication with regulatory authorities, strict screening of investment targets, and designing risk control plans. For high-volatility and high-policy-sensitive investment directions like cryptocurrency, compliance costs will further increase.
Moreover, financial institutions also need to bear reputational risks and legal responsibilities. If the cryptocurrency market experiences severe fluctuations, leading to significant losses for investors, financial institutions may face investor complaints or even legal lawsuits. Additionally, institutional reputation may be affected by product design issues, especially in an unclear policy environment, making this risk even more pronounced.
The cryptocurrency market has long been known for its extreme volatility. For example, Bitcoin's price once fell over 30% in a month, only to rebound over 40% shortly thereafter. This market characteristic places extremely high demands on the design of QDII products. The extreme distribution of returns and risks means that the investment returns of cryptocurrency are highly uncertain; even if prices rise during a certain period, a subsequent rapid decline may cause investors' gains to "evaporate." This extreme risk distribution makes it difficult for institutions to design products that can attract investors while controlling risks. Furthermore, the cryptocurrency market is a highly complex and information-asymmetric field for ordinary investors. Many investors generally lack sufficient understanding of this market, and this information gap may lead to blind investment risks.
Summary by Mankun Lawyers: Compliance Path is Promising, but Difficult to Achieve in the Short Term
Allocating cryptocurrency through QDII is theoretically a compliance method worth exploring, but under the current policy and market conditions, the possibility of implementation remains low. Whether it is policy ambiguity, institutional concerns, or the immaturity of market risks and investor awareness, all make this path seem far from smooth.
For ordinary investors, a more practical strategy is to gradually understand and participate in the cryptocurrency market through other compliant means before regulatory clarity is achieved. At the same time, it is essential to promote the further improvement of relevant policies to create conditions for the future possibility of QDII investing in cryptocurrency. In the future, when policies are clear and the market is mature, QDII may become an important tool for Chinese investors to enter the cryptocurrency market, but for now, all of this still needs to wait.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



