In the past year, AI narratives have developed rapidly in the Crypto market, with leading VCs like a16z, Sequoia, Lightspeed, and Polychain making significant investments of millions of dollars. Many high-quality teams with research backgrounds and prestigious school affiliations have also entered Web3, moving towards decentralized AI. In the next 12 months, we will witness these quality projects gradually coming to fruition.
In October this year, OpenAI raised another $6.6 billion, marking an unprecedented height in the arms race of the AI sector. Retail investors have few opportunities to profit outside of direct investments in Nvidia and hardware, and this enthusiasm is bound to spread into Crypto, especially with the recent nationwide craze for AI Memes. It is foreseeable that Crypto x AI, whether in existing listed tokens or emerging star projects, will continue to gain momentum.
With the leading decentralized AI project Hyperbolic recently receiving additional funding from Polychain and Lightspeed, we analyze the development trajectory of Crypto x AI infrastructure projects based on six projects that have recently secured significant financing from top institutions, looking ahead to how decentralized technology can safeguard humanity in the future of AI.
Hyperbolic: Recently announced the completion of a $12 million Series A financing round led by Variant and Polychain, with total funding exceeding $20 million, with participation from well-known VCs such as Bankless Ventures, Chapter One, Lightspeed Faction, IOSG, Blockchain Builders Fund, Alumni Ventures, and Samsung Next.
PIN AI: Completed a $10 million pre-seed financing round, with investments from notable VCs including a16z CSX, Hack VC, and Blockchain Builders Fund (Stanford Blockchain Accelerator).
Vana: Completed an $18 million Series A financing and a $5 million strategic financing, with investments from well-known VCs such as Paradigm, Polychain, and Coinbase.
Sahara: Completed a $43 million Series A financing, with investments from well-known VCs such as Binance Labs, Pantera Capital, and Polychain.
Aethir: In 2023, completed a $9 million Pre-A financing round at a valuation of $150 million, and in 2024, completed approximately $120 million in node sales.
IO.NET: Completed a $30 million Series A financing, with investments from notable VCs such as Hack VC, Delphi Digital, and Foresight Ventures.
Three Elements of AI: Data, Computing Power, and Algorithms
Marx told us in "Capital" that the key elements in social production are means of production, productive forces, and production relations. If we draw an analogy, we can find similar key elements in the world of artificial intelligence.
In the AI era, computing power, data, and algorithms are key.
In AI, data is the means of production. For example, the text and images you generate while chatting on your phone or posting photos on social media are data; they are like the "ingredients" for AI, forming the foundation for its operation.
This data includes various forms, from structured numerical information to unstructured images, audio, video, and text. Without data, AI algorithms cannot learn and optimize. The quality, quantity, coverage, and diversity of data directly affect the performance of AI models, determining whether they can efficiently complete specific tasks.
In AI, computing power is the productive force. Computing power is the underlying computational resource required to execute AI algorithms. The stronger the computing power, the faster the data processing and the better the results. The strength of computing power directly determines the efficiency and capability of AI systems.
Powerful computing power not only shortens model training time but also supports more complex model architectures, thereby enhancing the intelligence level of AI. Large language models like OpenAI's ChatGPT require months of training on powerful computing clusters.
In AI, algorithms are the production relations. Algorithms are the core of AI, and their design determines how data and computing power work together, serving as the key to transforming data into intelligent decisions. With strong computing power, algorithms can better learn patterns in data and apply them to real-world problems.
Thus, data is akin to fuel for AI, computing power is the engine, and algorithms are the soul. AI = data + computing power + algorithms; any startup wanting to stand out in the AI sector must have all three elements or demonstrate a unique leading advantage in one of them.
As AI develops towards multimodal (models based on various forms of information that can simultaneously process text, images, and audio), the demand for computing power and data will only grow exponentially.
In the Era of Computing Power Scarcity, Crypto Empowers AI
The emergence of ChatGPT has not only sparked a revolution in artificial intelligence but has also inadvertently pushed computing power and hardware to the forefront of tech trends.
After the "Thousand Models War" of 2023, in 2024, as the market's understanding of AI large models deepens, global competition around large models is being divided into two paths: "capability enhancement" and "scene development."
In terms of enhancing large model capabilities, the market's biggest expectation is the rumored release of GPT-5 by OpenAI this year, eagerly anticipating its advancement to a truly multimodal stage.
In terms of developing large model applications, AI giants are pushing for faster integration of large models into industry scenarios to generate practical application value. For example, attempts in areas like AI Agents and AI search are continuously deepening the enhancement of existing user experiences by large models.
Both paths undoubtedly raise the demand for computing power. Capability enhancement of large models primarily focuses on training, requiring the invocation of vast high-performance computing power in a short time; large model application scenarios primarily focus on inference, which has relatively lower performance requirements but emphasizes stability and low latency.
As OpenAI estimated in 2018, since 2012, the demand for computing power to train large models has doubled every 3.5 months, with an annual increase of up to 10 times. As large models and applications are increasingly deployed in actual business scenarios, the demand for inference computing power is also rising.
The problem arises: globally, the demand for high-performance GPUs is rapidly increasing, while supply has not kept pace. For example, Nvidia's H100 chip experienced a severe supply shortage in 2023, with a supply gap exceeding 430,000 units. The upcoming B100 chip, which improves performance by 2.5 times with only a 25% increase in cost, is likely to face supply shortages again. This imbalance between supply and demand will lead to a rise in computing power costs, making it difficult for many small and medium-sized enterprises to bear the high computing expenses, thus limiting their potential for development in the AI field.
Large tech companies like OpenAI, Google, and Meta have stronger resource acquisition capabilities, with the funds and resources to build their own computing power infrastructure. But what about AI startups, especially those that have not yet secured funding?
Indeed, purchasing second-hand GPUs on platforms like eBay and Amazon is one feasible method. While it reduces costs, there may be performance issues and long-term maintenance costs. In this era of GPU scarcity, building infrastructure may never be the optimal solution for startups.
Even with on-demand rental GPU cloud providers, the high prices pose a significant challenge for them. For example, the cost of an Nvidia A100 is about $80 per day; if 50 units are needed to run for 25 days a month, the cost for computing power alone would reach $80 x 50 x 25 = $100,000/month.
This presents an opportunity for decentralized computing power networks based on DePIN architecture to step in and thrive. As seen with IO.NET, Aethir, and Hyperbolic, they shift the computing infrastructure costs of AI startups to the network itself. Moreover, they allow anyone globally to connect their unused GPUs, significantly reducing computing costs.
Aethir: A Global GPU Sharing Network for Inclusive Computing Power
Aethir completed a $9 million Pre-A financing round at a valuation of $150 million in September 2023 and achieved approximately $120 million in Checker Node sales between March and May of this year. Aethir generated $60 million in revenue from the sale of Checker Nodes in just 30 minutes, demonstrating market recognition and anticipation for the project.
The core of Aethir is to establish a decentralized GPU network that allows everyone to contribute their idle GPU resources and earn rewards. This is akin to turning everyone's computer into a small supercomputer, where everyone shares computing power. The benefit of this approach is that it can significantly increase GPU utilization, reduce resource waste, and allow businesses or individuals needing substantial computing power to acquire the necessary resources at a lower cost.
Aethir has created a decentralized DePIN network, functioning like a resource pool, incentivizing data centers, game studios, tech companies, and gamers worldwide to connect their idle GPUs. These GPU providers can freely connect or disconnect their GPUs from the network, thus achieving higher utilization than if they were idle. This enables Aethir to offer GPU resources ranging from consumer-grade to professional-grade and data center-grade, at prices over 80% lower than those of Web2 cloud providers.
Aethir's DePIN architecture ensures the quality and stability of these scattered computing powers. The three core components are:
Container: Aethir's computing unit, acting as a cloud server responsible for executing and rendering applications. Each task is encapsulated in a separate Container, running the client's tasks in a relatively isolated environment to avoid interference between tasks.
Indexer: Primarily used to instantaneously match and schedule available computing power resources based on task requirements. Additionally, a dynamic resource adjustment mechanism allocates resources to different tasks based on the overall network load to achieve optimal overall performance.
The Checker is responsible for real-time monitoring and evaluating the performance of Containers. It can monitor and assess the overall network status instantly and respond promptly to potential security issues. In the event of security incidents such as network attacks, it can issue warnings and initiate protective measures upon detecting abnormal behavior. Similarly, when network performance bottlenecks occur, the Checker can also issue timely alerts to ensure that issues are resolved promptly, thereby guaranteeing service quality and security.

The effective collaboration between the Container, Indexer, and Checker provides customers with a customizable computing power configuration, ensuring a secure, stable, and relatively low-cost cloud service experience. For fields such as AI and gaming, Aethir is a commendable commercial-grade solution.
In summary, Aethir has reshaped the allocation and utilization of GPU resources through the DePIN model, making computing power more accessible and economical. It has achieved notable success in the AI and gaming sectors and continues to expand its partnerships and business lines, with immense potential for future development.
IO.NET: A Distributed Supercomputing Network Breaking Through Computing Power Bottlenecks
IO.NET completed a $30 million Series A financing round in March this year, with investments from notable VCs such as Hack VC, Delphi Digital, and Foresight Ventures.
Similar to Aethir, IO.NET aims to create an enterprise-level decentralized computing network that aggregates idle computing resources (GPUs, CPUs) globally, providing AI startups with more affordable, accessible, and flexible computing power services.
Unlike Aethir, IO.NET utilizes the Ray framework (IO-SDK) to transform thousands of GPU clusters into a cohesive whole, serving machine learning (the Ray framework is also used by OpenAI to train GPT-3). When training large models on a single device, CPU/GPU memory limitations and sequential processing workflows present significant bottlenecks. By using the Ray framework for orchestration and batch processing, IO.NET achieves parallelization of computing tasks.
To this end, IO.NET adopts a multi-layer architecture:
User Interface Layer: Provides users with a visual front-end interface, including a public website, customer area, and GPU supplier area, aimed at delivering an intuitive and user-friendly experience.
Security Layer: Ensures the integrity and security of the system, integrating mechanisms such as network protection, user authentication, and activity logging.
API Layer: Serves as a communication hub for the website, suppliers, and internal management, facilitating data exchange and various operations.
Backend Layer: Forms the core of the system, responsible for managing clusters/GPUs, customer interactions, and automatic scaling operations.
Database Layer: Responsible for data storage and management, with the main storage handling structured data and caching used for temporary data processing.
Task Layer: Manages asynchronous communication and task execution, ensuring the efficiency of data processing and flow.
Infrastructure Layer: Forms the foundation of the system, including the GPU resource pool, orchestration tools, and execution/ML tasks, equipped with robust monitoring solutions.
From a technical perspective, IO.NET has introduced a layered architecture for its core technology IO-SDK to address the challenges faced by distributed computing power, along with reverse tunneling technology and mesh VPN architecture to solve security connection and data privacy issues. With Web3 gaining popularity and being touted as the next Filecoin, its prospects are quite promising.
In summary, IO.NET's core mission is to build the world's largest DePIN infrastructure, concentrating idle GPU resources from around the globe to support the AI and machine learning fields that require substantial computing power.
Hyperbolic: Building an "AI Rainforest" to Achieve a Prosperous and Cooperative Distributed AI Infrastructure Ecosystem
Today, Hyperbolic announced the completion of over $12 million in Series A financing, co-led by Variant and Polychain Capital, with total funding exceeding $20 million. Notable VC institutions such as Bankless Ventures, Chapter One, Lightspeed Faction, IOSG, Blockchain Builders Fund, Alumni Ventures, and Samsung Next participated. The fact that leading Silicon Valley VCs Polychain and LightSpeed Faction have made additional investments after the seed round underscores Hyperbolic's leading position in the Web3 AI sector.
Hyperbolic's core mission is to make AI accessible to everyone, affordable for developers, and usable for creators. Hyperbolic aims to build an "AI rainforest" where developers can find the necessary resources for innovation, collaboration, and growth within its ecosystem. Just like a natural rainforest, the ecosystem is interconnected, vibrant, and renewable, allowing creators to explore without limits.
According to co-founders Jasper and Yuchen, while AI models can be open-sourced, it is still insufficient without open computing resources. Currently, many large data centers control GPU resources, which deters many who wish to utilize AI. Hyperbolic aims to break this situation by integrating idle computing resources globally to establish a DePIN computing infrastructure, enabling everyone to easily access AI.
Thus, Hyperbolic introduces the concept of "open AI cloud," allowing everything from personal computers to data centers to connect to the computing power provided by Hyperbolic. On this basis, Hyperbolic has created a verifiable, privacy-assured AI layer that allows developers to build AI applications with reasoning capabilities, with the required computing power sourced directly from the AI cloud.

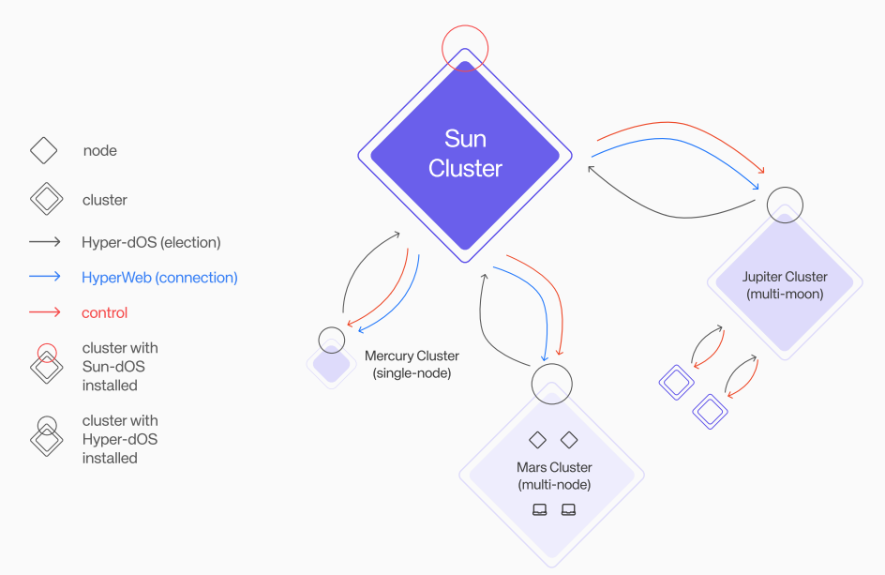
Similar to Aethir and IO.NET, Hyperbolic's AI cloud features its unique GPU cluster model, known as the "Solar System Cluster." As we know, the solar system contains various independent planets such as Mercury and Mars; Hyperbolic's solar system cluster manages clusters like the Mercury Cluster, Mars Cluster, and Jupiter Cluster. These GPU clusters are diverse in purpose and scale but operate independently, orchestrated by the solar system.
This model ensures that the GPU clusters meet two characteristics, being more flexible and maximizing efficiency compared to Aethir and IO.NET:
Balancing state adjustments, GPU clusters automatically scale up or down based on demand.
If a cluster experiences an interruption, the solar system cluster will automatically detect and repair it.
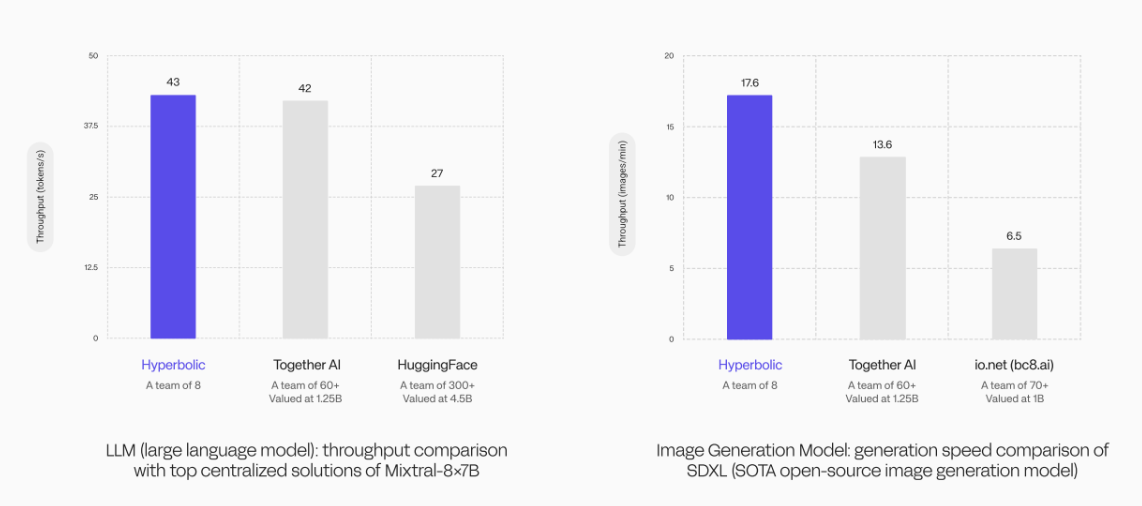
In performance comparison experiments of large language models (LLMs), Hyperbolic's GPU cluster achieved a throughput of 43 tokens/s, surpassing the 42 tokens/s achieved by the Together AI team of 60 members and significantly exceeding the 27 tokens/s of HuggingFace, which has over 300 team members.
In image generation model speed comparison experiments, Hyperbolic's GPU cluster also demonstrated formidable technical strength. Using the same SOTA open-source image generation model, Hyperbolic led with a generation speed of 17.6 images/min, surpassing Together AI's 13.6 images/min and far exceeding IO.NET's 6.5 images/min.
These data strongly demonstrate that Hyperbolic's GPU cluster model possesses high efficiency, and its outstanding performance allows it to stand out among larger competitors. Coupled with its cost advantages, this makes Hyperbolic highly suitable for complex AI applications requiring high computing power support, providing near real-time responses while ensuring higher accuracy and efficiency when processing complex tasks.
Additionally, from the perspective of crypto innovation, we believe Hyperbolic's most noteworthy achievement is the development of the verification mechanism PoSP (Proof of Sampling), which addresses one of the most challenging issues in the AI field — verifying whether outputs come from a specified model, thereby enabling the reasoning process to be economically and effectively decentralized.
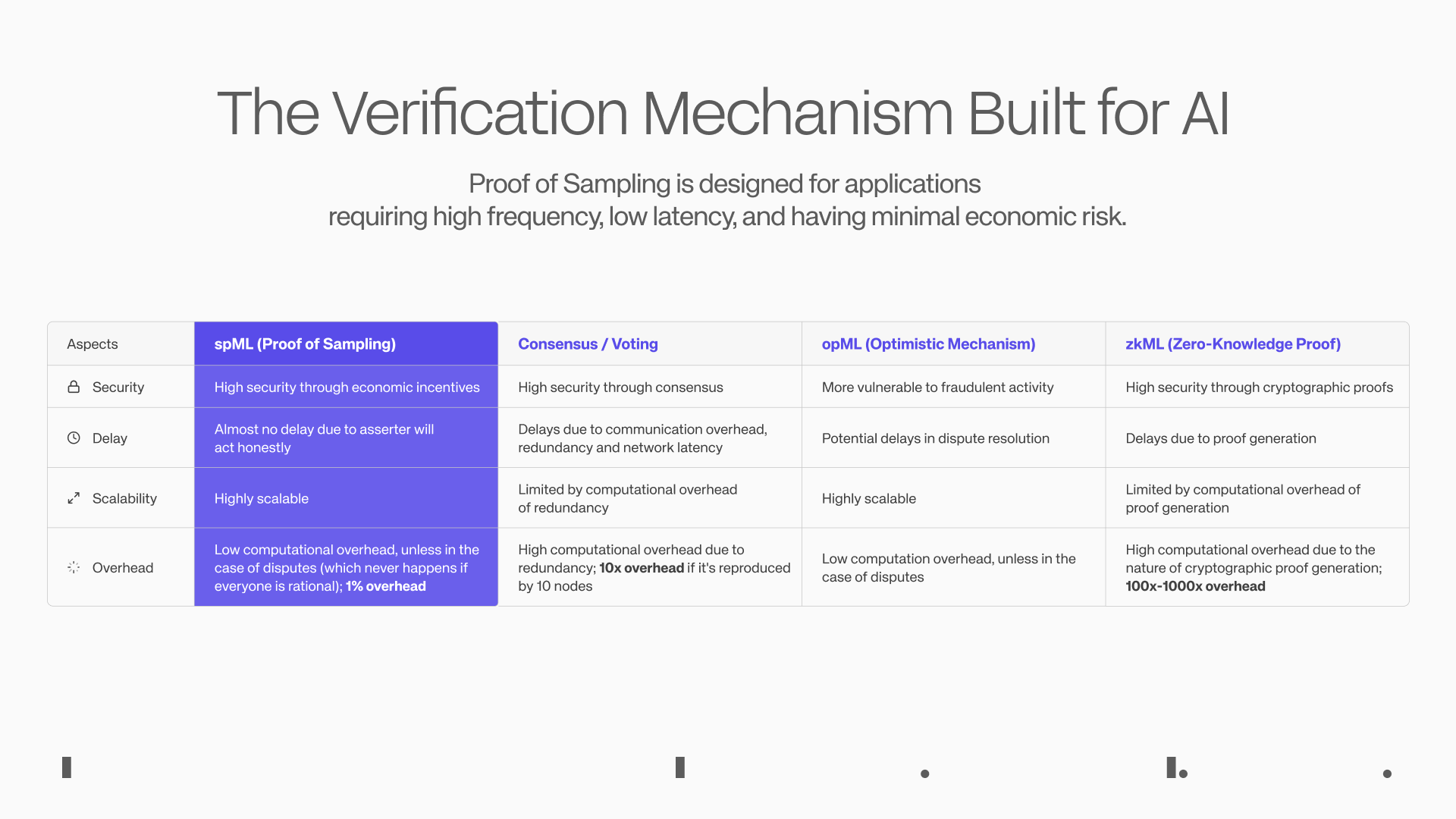
Based on the PoSP principle, the Hyperbolic team has developed the spML mechanism (Sampling Machine Learning) for AI applications, which randomly samples transactions in the network, rewarding honest participants and penalizing dishonest ones to achieve a lightweight verification effect, reducing the computational burden on the network, allowing almost any AI startup to decentralize their AI services in a verifiable manner.
The specific implementation process is as follows:
1) Nodes compute functions and submit results to the orchestrator in an encrypted manner.
2) The orchestrator then decides whether to trust this result; if trusted, the node receives rewards for the computation.
3) If the orchestrator does not trust the result, it will randomly select validators from the network to challenge the node and compute the same function. Similarly, the validators will submit their results to the orchestrator in an encrypted manner.
4) Finally, the orchestrator checks whether all results are consistent. If they are consistent, both the node and the validators will receive rewards; if not, an arbitration process will be initiated to trace back the computation process of each result. Honest participants will be rewarded for their accuracy, while dishonest ones will be penalized for deceiving the system.
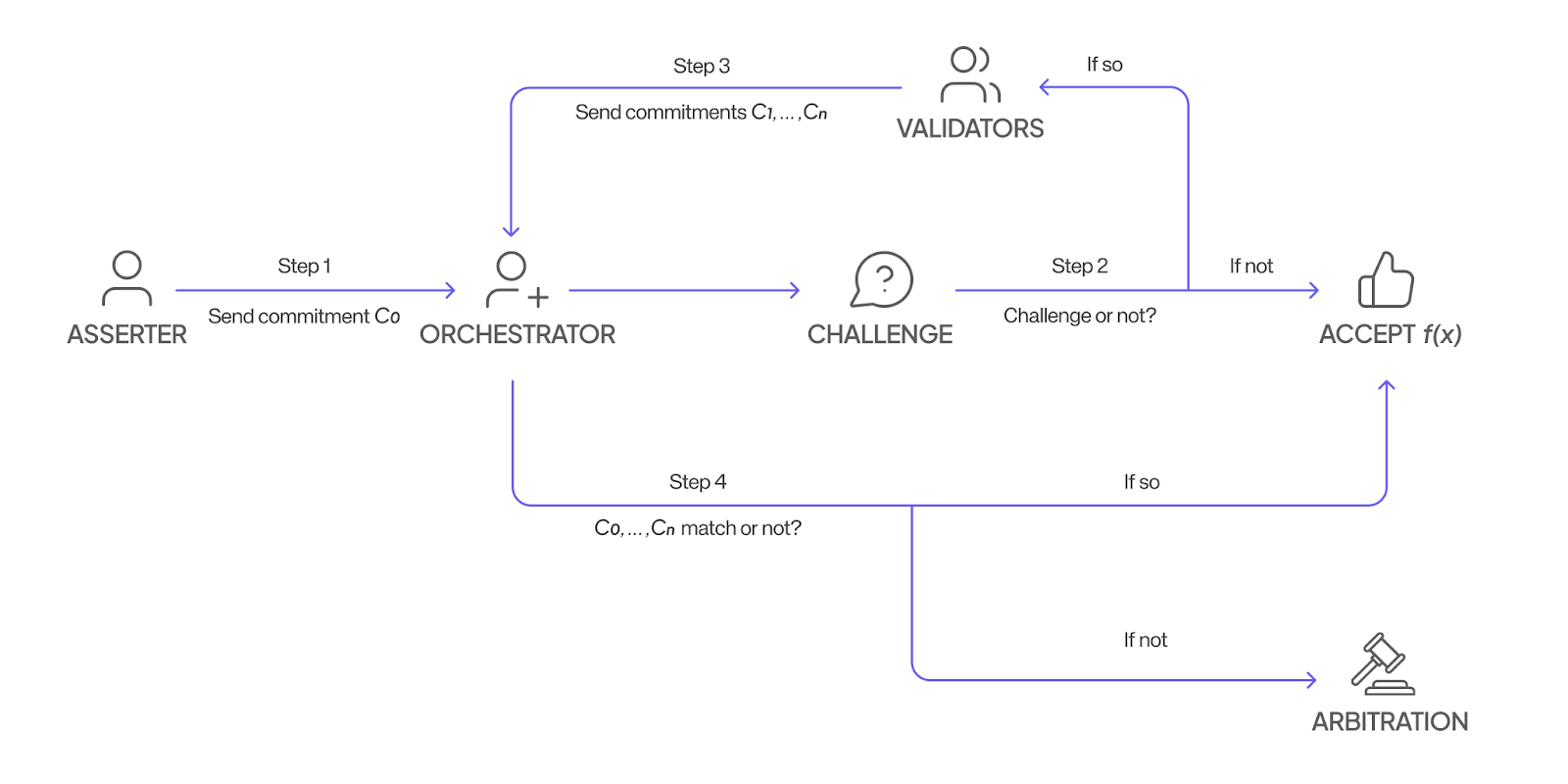
Nodes do not know whether their submitted results will be challenged, nor do they know which validator the orchestrator will choose to challenge, ensuring the fairness of the verification. The cost of cheating far exceeds the potential gains.
If spML is validated in the future, it could change the game for AI applications, making trustless reasoning verification a reality. Additionally, Hyperbolic possesses a unique capability in the industry to apply the BF16 algorithm in model inference (while peers are still using FP8), effectively improving inference accuracy, making Hyperbolic's decentralized inference service exceptionally cost-effective.
Moreover, Hyperbolic's innovation is reflected in its integration of AI cloud computing power supply with AI applications. The demand for decentralized computing power markets is relatively scarce; Hyperbolic attracts developers to build AI applications by constructing verifiable AI infrastructure, allowing computing power to be seamlessly integrated into AI applications without sacrificing performance and security. Once scaled to a certain extent, it can achieve self-sufficiency and reach a supply-demand balance.
Developers can build AI innovative applications around computing power, Web2, and Web3 on Hyperbolic, such as:
GPU Exchange, a GPU trading platform built on the GPU network (orchestration layer), which commodifies "GPU resources" for free trade, making computing power more cost-effective.
IAO, or tokenizing AI Agents, allowing contributors to earn tokens, with the income of AI Agents distributed to token holders.
AI-driven DAOs, which use artificial intelligence to assist in governance decisions and financial management.
GPU Restaking, allowing users to connect GPUs to Hyperbolic and then stake them to AI applications.
In summary, Hyperbolic has established an open AI ecosystem that allows everyone to easily use AI. Through technological innovation, Hyperbolic is making AI more widespread and accessible, ensuring that the future of AI is filled with interoperability and compatibility, encouraging collaborative innovation.
Data Returns to Users, Riding the AI Wave
Today, data is the new gold mine, with personal data being seized and commercialized by tech giants without compensation.
Data is the fuel for AI. Without high-quality data, even the most advanced algorithms cannot perform effectively. The quantity, quality, and diversity of data directly impact the performance of AI models.
As mentioned earlier, the industry is eagerly awaiting the release of GPT-5. However, its delay may be due to insufficient data volume. The GPT-3 model, at the paper publication stage, required 200 trillion tokens of data. GPT-5 is expected to reach 200 trillion tokens. In addition to existing text data, more multimodal data is needed, which must be cleaned before it can be used for training.
In today's publicly available internet data, high-quality data samples are scarce. A realistic situation is that large models perform exceptionally well in general question-answering across various fields but struggle with specialized domain questions, sometimes leading to the model "seriously talking nonsense."
To ensure the "freshness" of data, AI giants often reach agreements with large data source owners. For example, OpenAI signed a $60 million agreement with Reddit.
Recently, some social media platforms have begun requiring users to sign agreements, needing users to consent to allow their content to be used for training third-party AI models, yet users receive no compensation in return. This predatory behavior has sparked public debate over data usage rights.
Clearly, the decentralized and traceable nature of blockchain is inherently suitable for improving the predicament of data and resource acquisition, while also providing users with more control and transparency over their data. Users can earn rewards by participating in the training and optimization of AI models. This new way of creating data value will significantly enhance user engagement and promote overall ecosystem prosperity.
Web3 already has some companies focused on AI data, such as:
Data Acquisition: Ocean Protocol, Vana, PIN AI, Sahara, etc.
Data Processing: Public AI, Lightworks, etc.
Among them, Vana, PIN AI, and Sahara are particularly interesting as they have recently secured significant funding with impressive investor lineups. Both projects have transcended subfields by combining data acquisition with AI development, driving the implementation of AI applications.
Vana: Users Control Data, DAO and Contribution Mechanisms Reshape the AI Data Economy
Vana completed a $18 million funding round in December 2022 and secured an additional $5 million in strategic financing in September this year. Notable VCs such as Paradigm, Polychain, and Coinbase participated in the investment.
Vana's core philosophy is "data owned by users leads to AI owned by users." In this data-driven era, Vana aims to break the monopoly of large companies over data, allowing users to control their own data and benefit from it.
Vana is a decentralized data network focused on protecting private data, enabling users to use their data flexibly like financial assets. Vana seeks to reshape the data economy landscape, transforming users from passive data providers into active participants and co-beneficiaries in ecosystem building.
To achieve this vision, Vana allows users to gather and upload data through data DAOs, and then verifies the value of the data through a contribution proof mechanism while protecting privacy. This data can be used for AI training, and users are incentivized based on the quality of the uploaded data.
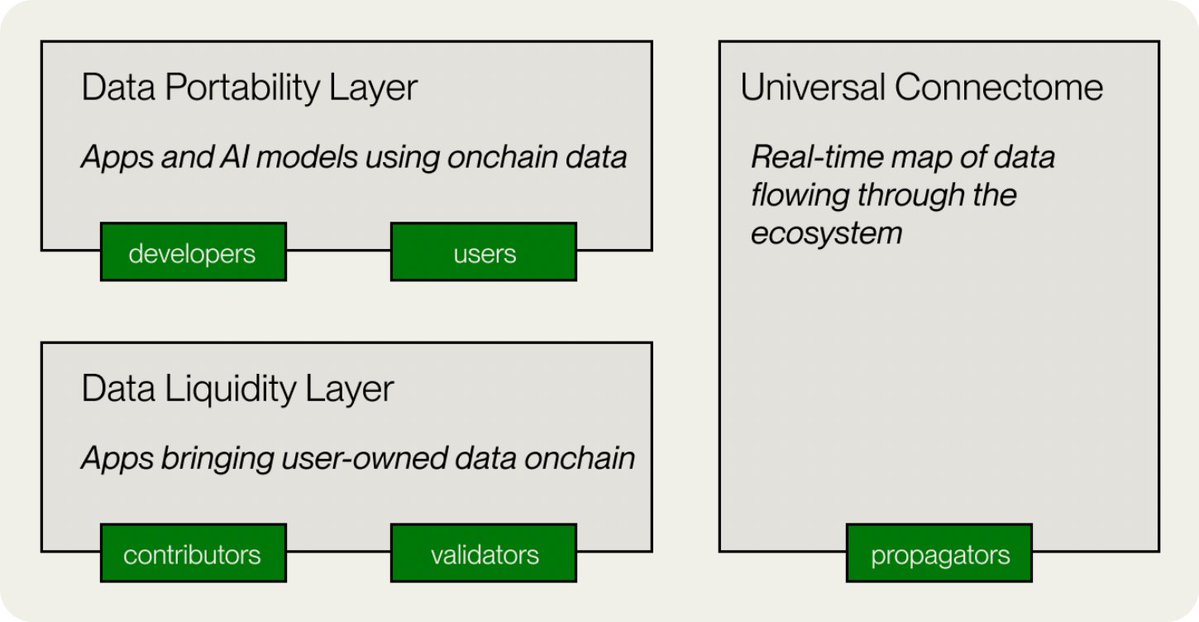
In terms of implementation, Vana's technical architecture includes five key components: data liquidity layer, data portability layer, universal connection group, non-custodial data storage, and decentralized application layer.
Data Liquidity Layer: This is the core of the Vana network, which incentivizes, aggregates, and verifies valuable data through data liquidity pools (DLPs). DLPs function like "liquidity pools" for data, with each DLP being a smart contract specifically designed to aggregate specific types of data assets, such as data from social media platforms like Reddit and Twitter.
Data Portability Layer: This component grants portability to user data, ensuring that users can easily transfer and use their data across different applications and AI models.
Data Ecosystem Map: This is a map that tracks the real-time flow of data throughout the ecosystem, ensuring transparency.
Non-Custodial Data Storage: Vana's innovation lies in its unique data management approach, allowing users to maintain complete control over their data. Users' original data is not stored on-chain but can be kept in locations of their choice, such as cloud servers or personal servers.
Decentralized Application Layer: Based on the data, Vana has built an open application ecosystem where developers can utilize the data accumulated in DLPs to create various innovative applications, including AI applications, while data contributors can receive dividend rewards from these applications.
Currently, Vana has built DLPs around social media platforms like ChatGPT, Reddit, LinkedIn, and Twitter, as well as focusing on AI and browsing data. As more DLPs join, and more innovative applications are built on the platform, Vana has the potential to become the next generation of decentralized AI and data economy infrastructure.
This brings to mind a recent news story where Meta is collecting data from Facebook and Instagram users in the UK to improve the diversity of LLMs, but has faced criticism for forcing users to "opt-out" rather than "opt-in." Perhaps, building separate DLPs for Facebook and Instagram on Vana would not only ensure data privacy but also incentivize more users to contribute data, making it a better choice.
PIN AI: Decentralized AI Assistant, Mobile AI Connecting Data and Daily Life
PIN AI completed a $10 million pre-seed funding round in September this year, with participation from notable VCs and angel investors such as a16z CSX, Hack VC, and Blockchain Builders Fund (Stanford Blockchain Accelerator).
PIN AI is an open AI network supported by a decentralized data storage network built on DePIN architecture, allowing users to connect their devices to the network, provide personal data/user preferences, and receive token incentives. This enables users to regain control and monetize their data, while developers can utilize this data to build useful AI Agents.
Its vision is to become a decentralized alternative to Apple Intelligence, dedicated to providing applications useful for users' daily lives, fulfilling user intentions such as online shopping, trip planning, and investment planning.
PIN AI consists of two types of AI: personal AI assistants and external AI services.
The personal AI assistant can access user data, gather user needs, and provide relevant data to external AI services when they require it. The underlying structure of PIN AI is composed of a decentralized data storage network built on DePIN, providing rich user data for external AI services' inference while ensuring that user personal privacy remains inaccessible.
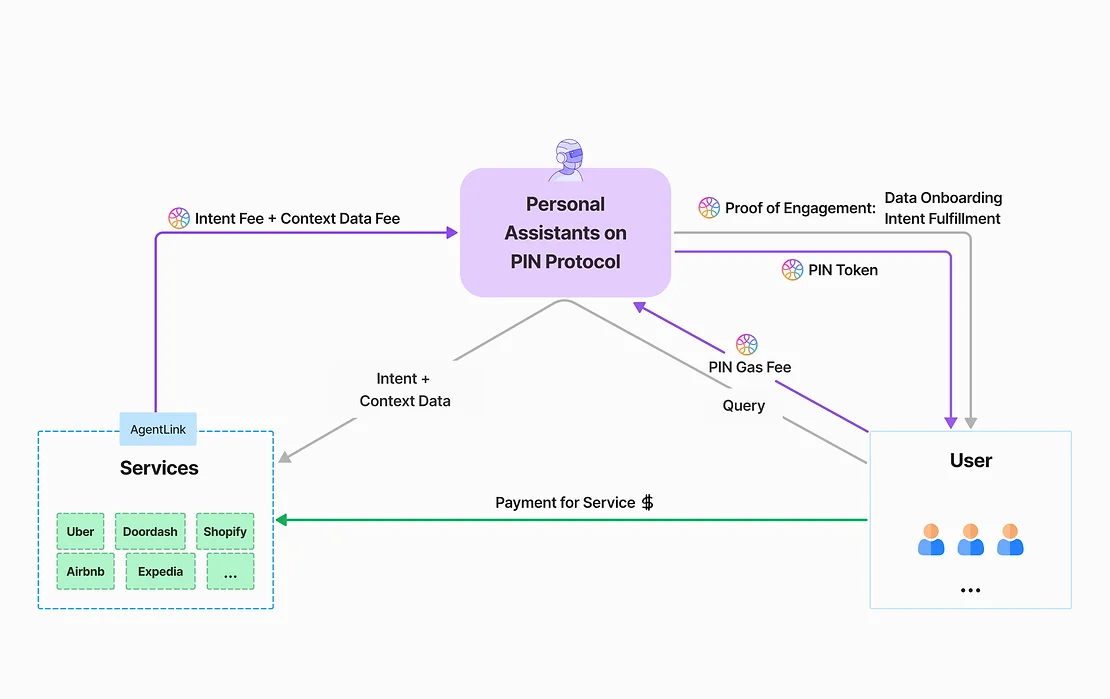
With PIN AI, users will no longer need to open thousands of mobile apps to complete different tasks. When users express intentions to their personal AI assistant, such as "I want to buy a new piece of clothing," "What kind of takeout should I order?" or "Find the best investment opportunity in this article," the AI not only understands the user's preferences but can also effectively execute all these tasks—finding the most relevant applications and service providers to fulfill the user's intentions through a bidding process.
Most importantly, PIN AI recognizes the necessity of introducing a decentralized service that can provide more value in the current situation where users are accustomed to directly interacting with centralized service providers for services. The personal AI assistant can legitimately obtain high-value data generated during user interactions with Web2 applications on behalf of the user, storing and calling this data in a decentralized manner, allowing the same data to create greater value and benefiting both data owners and users.
Although the mainnet of PIN AI has not officially launched yet, the team has shown a prototype of the product to users through Telegram, facilitating the perception of its vision.
Hi PIN Bot consists of three sections: Play, Data Connectors, and AI Agent.
Play is an AI virtual companion supported by large models such as PIN AI-1.5b, Gemma, and Llama. This serves as PIN AI's personal AI assistant.
In Data Connectors, users can connect their Google, Facebook, X, and Telegram accounts to earn points to upgrade their virtual companion. In the future, support will also be extended to allow users to connect accounts from Amazon, eBay, Uber, etc. This represents PIN AI's DePIN data network.
Users can use their own data; after connecting their data, they can make requests to the virtual companion (Coming soon), which will provide the user's data to AI Agents that meet the task requirements for processing.
The official team has developed some AI Agent prototypes, which are still in the testing phase, and these correspond to PIN AI's external AI services. For example, X Insight can analyze the operational status of a Twitter account when the account is inputted. Once Data Connectors support accounts from e-commerce and takeout platforms, AI Agents like Shopping and Order Food will also be able to function autonomously to handle user orders.
In summary, through the combination of DePIN and AI, PIN AI has established an open AI network that allows developers to create truly useful AI applications, making users' lives more convenient and intelligent. As more developers join, PIN AI will bring forth more innovative applications, allowing AI to truly integrate into daily life.
Sahara: Multi-layer Architecture Leading AI Data Rights, Privacy, and Fair Trade
Sahara completed a $43 million Series A financing round in August this year, with investments from well-known VCs such as Binance Labs, Pantera Capital, and Polychain.
Sahara AI is a multi-layered AI blockchain application platform focused on establishing a more fair and transparent AI development model in the AI era, capable of attributing data value and sharing profits with users, addressing pain points such as privacy, security, data acquisition, and transparency in traditional AI systems.
In simple terms, Sahara AI aims to build a decentralized AI network that allows users to control their own data and earn rewards based on the quality of the data they contribute. This way, users are no longer passive data providers but become active participants and co-beneficiaries in ecosystem building.
Users can upload data to their decentralized data marketplace and then prove ownership of this data through a special mechanism ("rights confirmation"). This data can be used to train AI, and users will receive rewards based on the quality of the data.
Sahara AI consists of four layers: application, transaction, data, and execution, providing a strong foundation for the development of the AI ecosystem.
- Application Layer: Provides tools such as secure vaults, decentralized AI data marketplaces, no-code toolkits, and Sahara ID. These tools ensure data privacy and promote fair compensation for users while further simplifying the process of creating and deploying AI applications.
In simple terms, the vault uses advanced encryption technology to ensure the security of AI data; the decentralized AI data marketplace can be used for data collection, labeling, and transformation, promoting innovation and fair trade; the no-code toolkit makes AI application development easier; Sahara ID manages user reputation to ensure trust.
Transaction Layer: The Sahara blockchain ensures network efficiency and stability through a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, allowing consensus to be reached even in the presence of malicious nodes. Additionally, Sahara's native precompiled functions are designed specifically to optimize AI processing, enabling efficient computation directly in the blockchain environment, enhancing system performance.
Data Layer: Manages on-chain and off-chain data. On-chain data processing includes untraceable operations and attribute records, ensuring credibility and transparency; off-chain data handles large datasets and uses Merkle Tree and zero-knowledge proof technologies to ensure data integrity and security, preventing data duplication and tampering.
Execution Layer: Abstracts the operations of vaults, AI models, and AI applications, supporting various AI training, inference, and service paradigms.
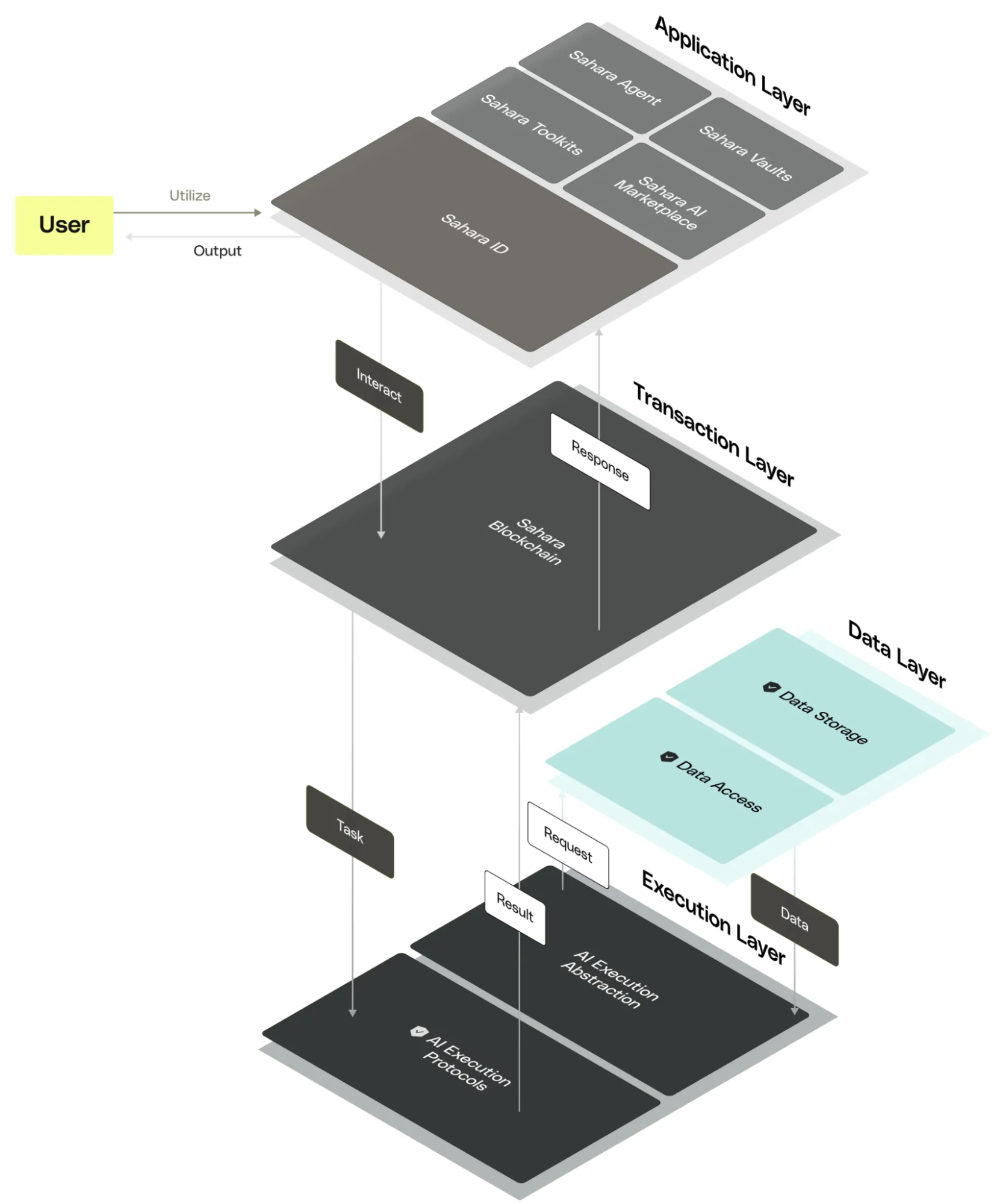
The entire four-layer architecture not only ensures the security and scalability of the system but also embodies Sahara AI's grand vision of promoting a collaborative economy and AI development, aiming to fundamentally change the application model of AI technology and provide users with more innovative and fair solutions.
Conclusion
With the continuous advancement of AI technology and the rise of the crypto market, we are standing on the threshold of a new era.
As large AI models and applications continue to emerge, the demand for computing power is growing exponentially. However, the scarcity of computing power and rising costs pose significant challenges for many small and medium-sized enterprises. Fortunately, decentralized solutions, particularly Hyperbolic, Aethir, and IO.NET, provide new avenues for AI startups to acquire computing power, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
At the same time, we also see the importance of data in the development of AI. Data is not only the fuel for AI but also the key to driving the implementation of AI applications. Projects like PIN AI and Sahara encourage user participation in data collection and sharing through incentive networks, providing strong data support for AI development.
Computing power and data are not just for the training phase; for AI applications, every stage from data ingestion to production inference requires different tools to achieve massive data processing, and this is a continuously repeating process.
In this intertwined world of AI and Crypto, we have reason to believe that the future will witness more innovative AI projects coming to fruition, which will not only change our work and lifestyle but also drive society as a whole towards a more intelligent and decentralized direction. With continuous technological advancements and market maturation, we look forward to the arrival of a more open, fair, and efficient AI era.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



