On November 28 at 16:00, the AICoin editor conducted a graphic and text sharing session titled "From 0 to 1: How to Master Arbitrage?" in the [AICoin PC - Group Chat - Live Broadcast]. Below is a summary of the live broadcast content.
1. Arbitrage Principles
(1) Funding Fee Arbitrage
Funding fee arbitrage is a trading strategy that utilizes the funding fee mechanism in the perpetual contract market by simultaneously opening opposite positions of the same value in both spot and perpetual contracts for the same cryptocurrency.
When the funding fee is positive, longs pay shorts; when the funding fee is negative, shorts pay longs.
The goal of funding fee arbitrage is to earn stable funding fee income through trading between the spot market and the perpetual contract market.
AICoin's funding fee arbitrage is mainly divided into two categories:
- Forward Arbitrage: When the funding fee is positive, borrow coins to buy in the spot market and short the perpetual contract.
- Reverse Arbitrage: When the funding fee is negative, borrow coins to sell in the spot market and go long on the perpetual contract.
Reverse arbitrage carries higher risks, so it is recommended to engage in forward arbitrage.
Taking forward arbitrage as an example:
Assuming the current BTC price is 95,000 USDT, and the funding fee is 0.03%, using 4,000 USDT for funding fee arbitrage with 1x margin. The operation is as follows:
- Buy 2,000 USDT worth of BTC in the spot market while shorting 2,000 USDT worth of BTC in the perpetual contract market.
- Assuming the funding fee remains unchanged, every 8 hours, you will earn funding fee income of 2,000 USDT × 0.03% = 0.6 USDT.
- Daily earnings will be 0.6 USDT × 3 = 1.8 USDT, with an annualized return of 32.85%.
Note: Annualized return calculation: 1.8×365÷2000=32.85%
(2) Price Difference Arbitrage
Price difference arbitrage is a method of profiting from the price differences between the spot market and the futures market (including perpetual contracts and delivery contracts). It is mainly divided into two categories: spot-futures arbitrage and inter-futures arbitrage.
Spot-futures arbitrage refers to arbitraging the significant price difference between the spot market and the delivery contract futures market for the same trading cryptocurrency. Since the price of delivery contracts will revert to the spot price at expiration, this reversion opportunity can be seized.
Inter-futures arbitrage seeks to find price differences between contracts with different expiration dates for arbitrage.
Taking spot-futures arbitrage as an example:
- Spot price < Delivery contract price
Strategy: Buy in the spot market, short the contract (both have the same value), and profit when the price difference reverts (the price difference decreases).
- Spot price > Delivery contract price
Strategy: Sell in the spot market, go long on the contract (both have the same value), and profit when the price difference reverts (the price difference decreases).
Assuming the BTC spot price is 95,000 USDT, while the quarterly delivery price is 99,000 USDT, the price difference is 4,000 USDT.
Since the contract price is higher, the strategy is to buy in the spot market and short the contract.
If there is a unilateral downtrend, for example, if the spot price drops to 88,000 USDT and the quarterly delivery contract is at 90,000 USDT, the price difference shrinks to 2,000 USDT, close the position.
Spot loss: 95,000 USDT - 88,000 USDT = 7,000 USDT
Contract profit: 99,000 USDT - 90,000 USDT = 9,000 USDT
Final profit: 9,000 USDT - 7,000 USDT = 2,000 USDT (actual fees need to be deducted).
If the price rises, the same logic applies.
(2) Price Difference Arbitrage - Detailed Description Version
Price difference arbitrage is a method of profiting from the price differences between the spot market and the futures market (including perpetual contracts and delivery contracts). It is mainly divided into two categories: spot-futures arbitrage and inter-futures arbitrage. Investors can use professional arbitrage tools, such as AICoin, to trade the same cryptocurrency to obtain price difference income.
1. Spot-Futures Arbitrage
Spot-futures arbitrage refers to arbitraging the significant price difference between the spot market and the delivery contract futures market for the same trading cryptocurrency. Since the price of delivery contracts will revert to the spot price at expiration, this reversion opportunity can be seized.
The arbitrage process can be simply described as follows:
a. Identify the opportunity: Assume the BTC price in the spot market is 65,000 USDT, while the futures market price is 69,000 USDT, resulting in a 4,000 USDT difference.
b. Open position:
- Short 1 BTC in the futures market (sell at 69,000 USDT).
- Buy 1 BTC in the spot market (spending 65,000 USDT).
c. Close position for profit: When the price difference narrows, for example, if the futures market price drops to 60,000 USDT and the spot market price drops to 58,000 USDT:
- Futures profit: 69,000 USDT - 60,000 USDT = 9,000 USDT
- Spot loss: 58,000 USDT - 65,000 USDT = 7,000 USDT
- Final profit is 9,000 USDT - 7,000 USDT = 2,000 USDT (actual fees need to be deducted).
2. Inter-Futures Arbitrage
Inter-futures arbitrage seeks to find price differences between contracts with different expiration dates for arbitrage. Investors trade contracts with different expiration dates to profit from price difference changes.
The arbitrage process is simplified as follows:
- When the price difference between different contracts widens, short the high-priced contract and go long on the low-priced contract.
- As the price difference narrows, close the position to realize profits when conditions are favorable.
Example:
Assuming the next quarter's contract price for BTC is 10,000 USDT, while the next week's contract price is 10,050 USDT, there is a 500 USDT difference. The opening operation is as follows:
a. Go long in the next quarter's contract market (buy at 10,000 USDT).
b. Go short in the next week's contract market (sell at 10,050 USDT).
c. Close the position when the price difference narrows; regardless of how it changes, profits will be realized through the price difference reversion.
The core of price difference arbitrage lies in the reasonable use of price differences between the spot and contract markets, as well as between contracts with different expiration dates, to achieve profits through buying low and selling high.
2. Methods to Obtain Real-Time Arbitrage Opportunities
The simplest method: Alerts + Seeking Opportunities!
1. Rates
Generally, in an upward trend, the funding fee is positive, and the higher the rate, the stronger the bullish sentiment, leading to greater funding fee income from arbitrage. However, the funding fee is not constant.
We need to monitor the rate situation; too low is not good, as it may turn negative at any time; too high is also not good, as it may indicate excessive FOMO, and the market may correct.
Therefore, we need to define a threshold.
When the rate reaches this threshold, we can pay attention to funding fee arbitrage opportunities.
However, constantly monitoring the market is obviously unreasonable.
At this point, our rate alert comes into play.
For example, for Binance BTC perpetual contracts, based on past performance, when the funding fee exceeds 0.03%, there are good arbitrage opportunities. We can set an alert for the Binance BTC/USDT perpetual pair when the funding fee reaches 0.03%.
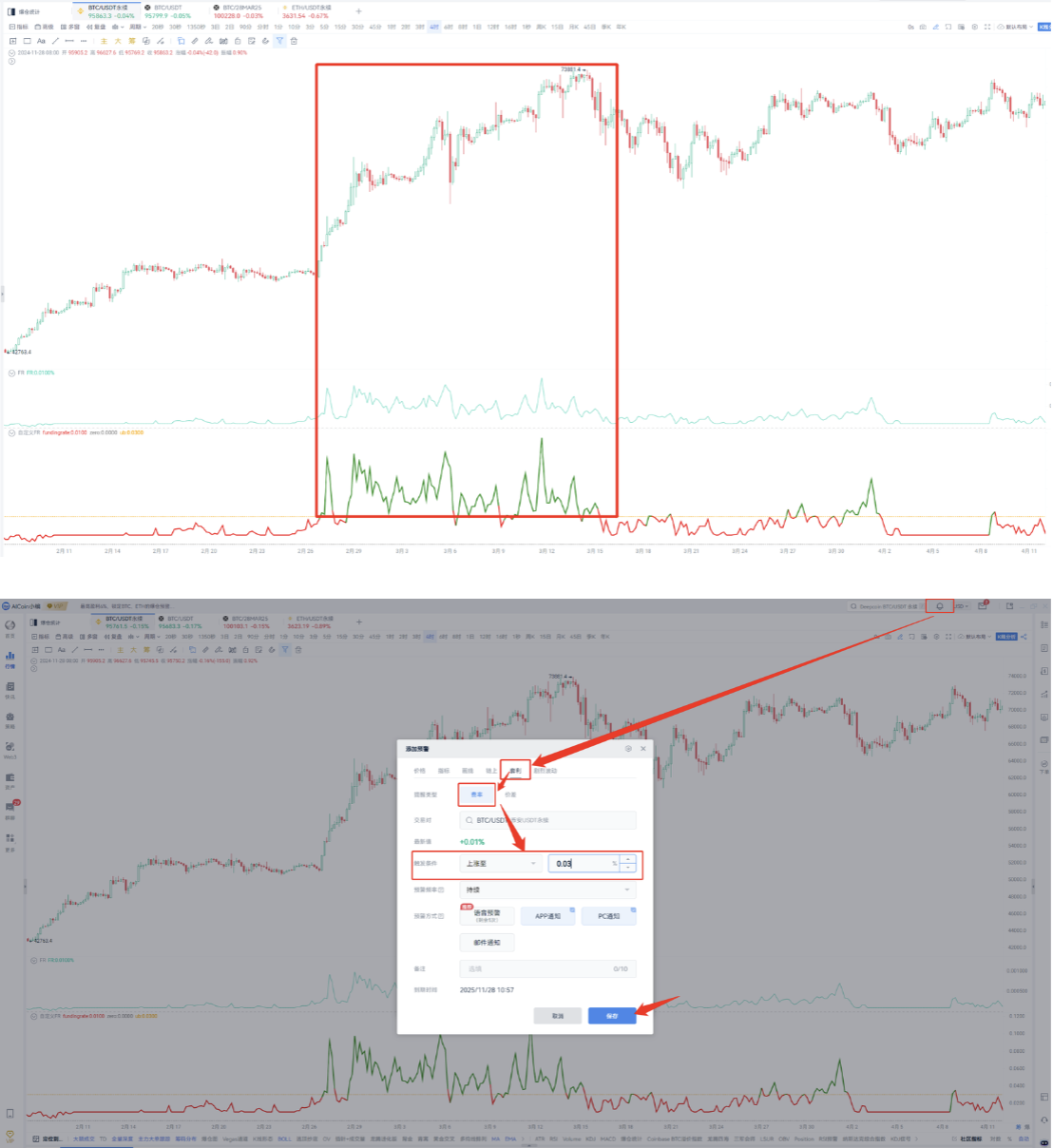
The same applies to other pairs; it is recommended to focus on projects with large market capitalization, good depth, and increasing open interest.
2. Price Difference
Taking OKX's spot and quarterly delivery contracts as an example.
The first step is to determine the price difference threshold. Theoretically, the larger the price difference, the greater the profit opportunity for arbitrageurs.
So how do we determine the threshold?
The original method involves manually calculating the difference between the delivery contract and the spot pair, then comparing them one by one. After determining the threshold, set up alerts for arbitrage opportunities.
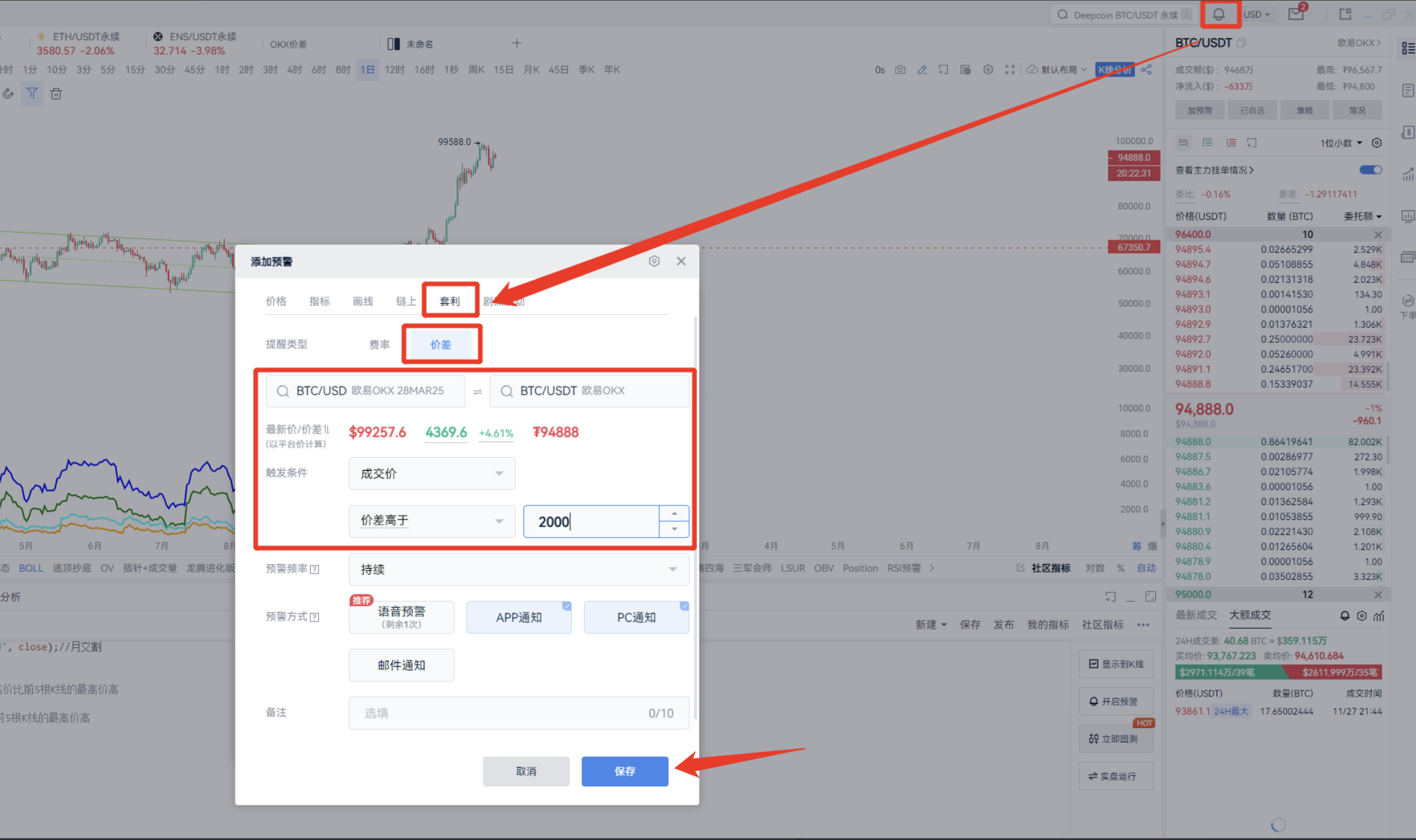
However, this is time-consuming and cumbersome.
Recommended Method:
- Use combined K-lines to automatically calculate and synthesize new K-lines, directly for OKX BTC/28MAR25-OKX BTC/USDT, and then obtain new combined K-lines.
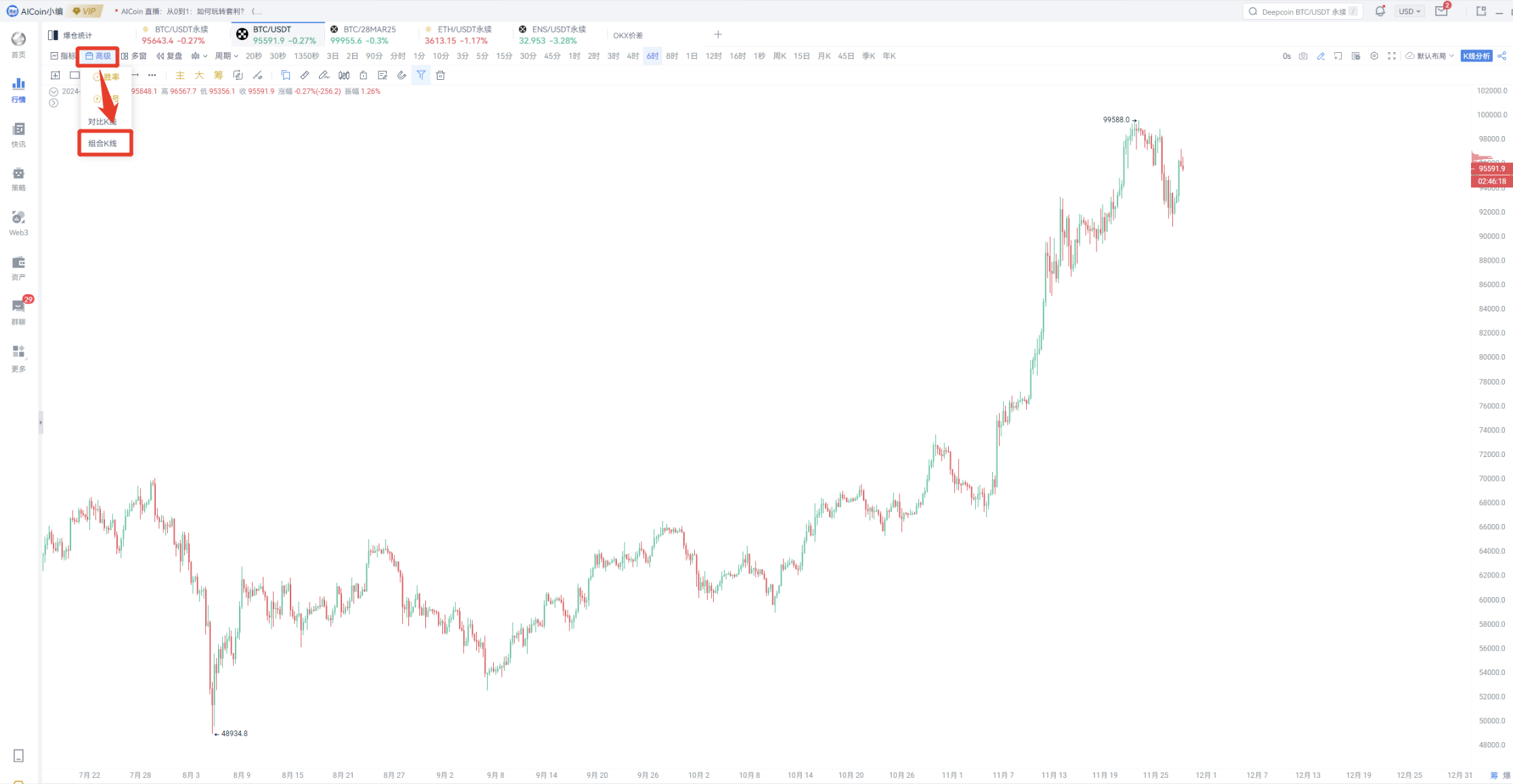
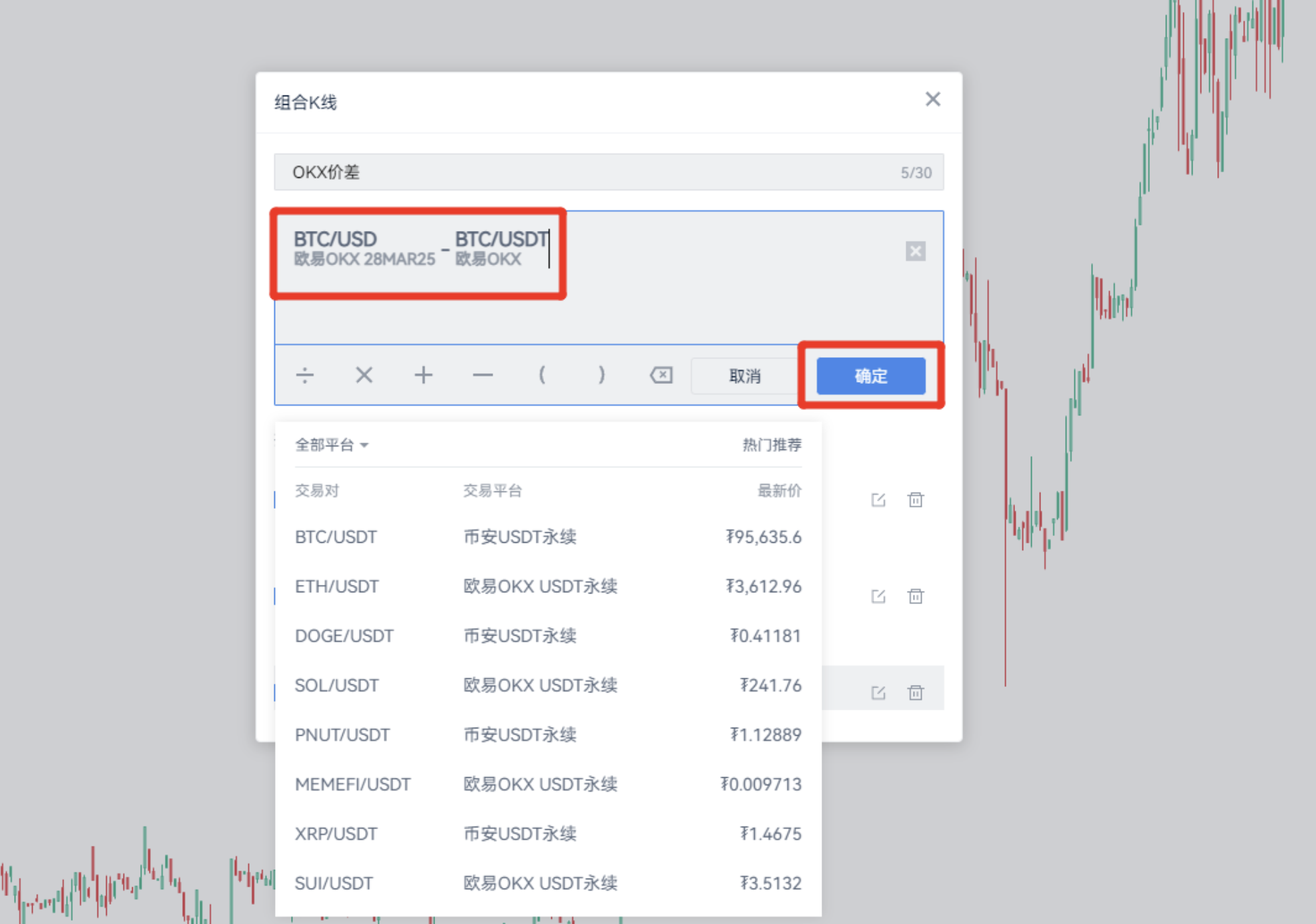
When the price difference starts to widen, consider the price difference arbitrage opportunity.
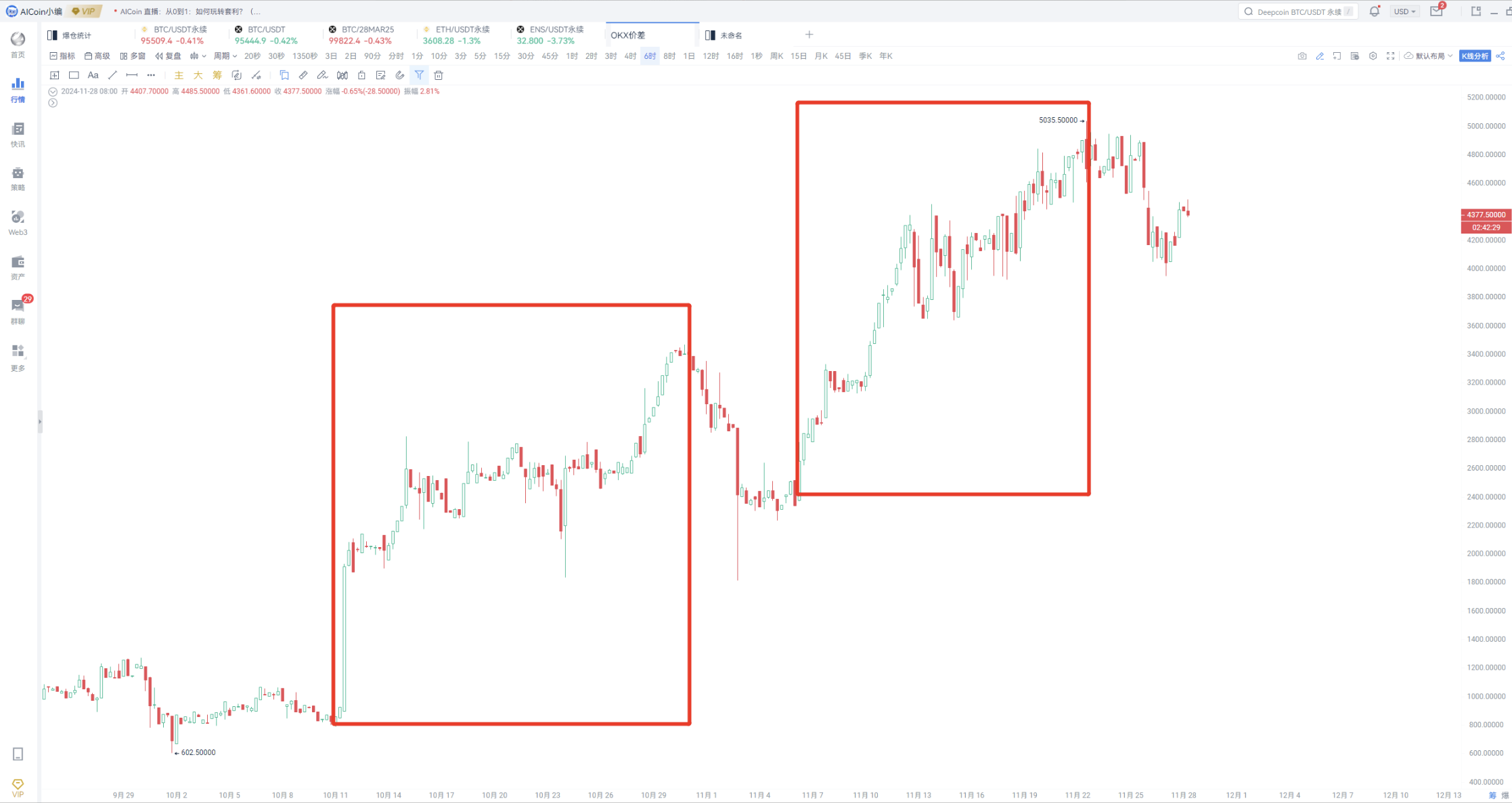
Combined K-lines can also be used to compare premium situations, such as Binance spot and Coinbase spot, Binance spot and Upbit spot (kimchi premium).
- Custom Indicators
The greatest advantage of this method is that it can simultaneously plot price differences for multiple pairs.
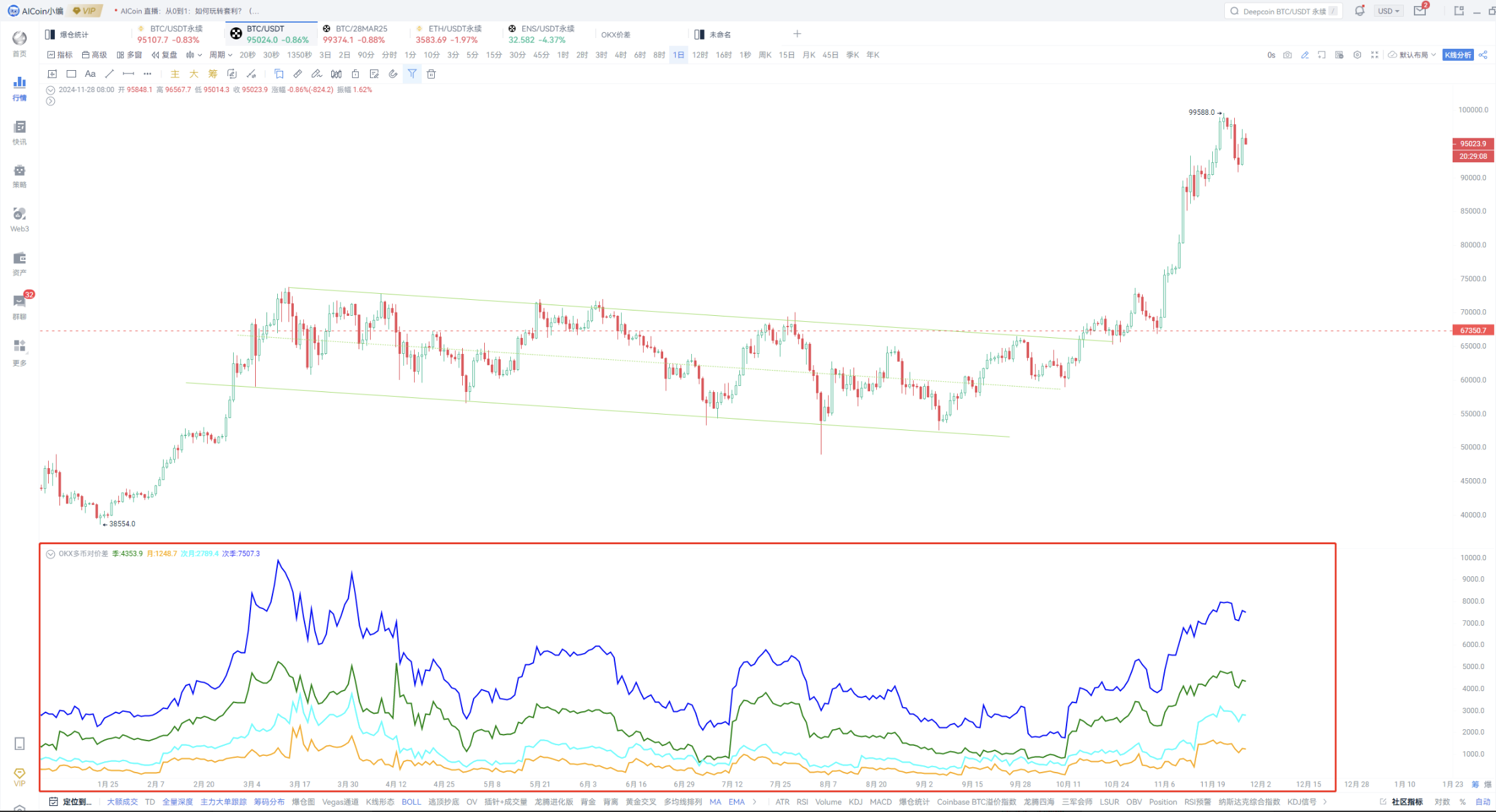
After plotting, you can also compare past trends and set a threshold alert.
For example, if seeking opportunities reveals that when the price difference between the quarterly contract and the spot reaches 2,200, there is significant arbitrage potential, we can define alert conditions and set up alerts.
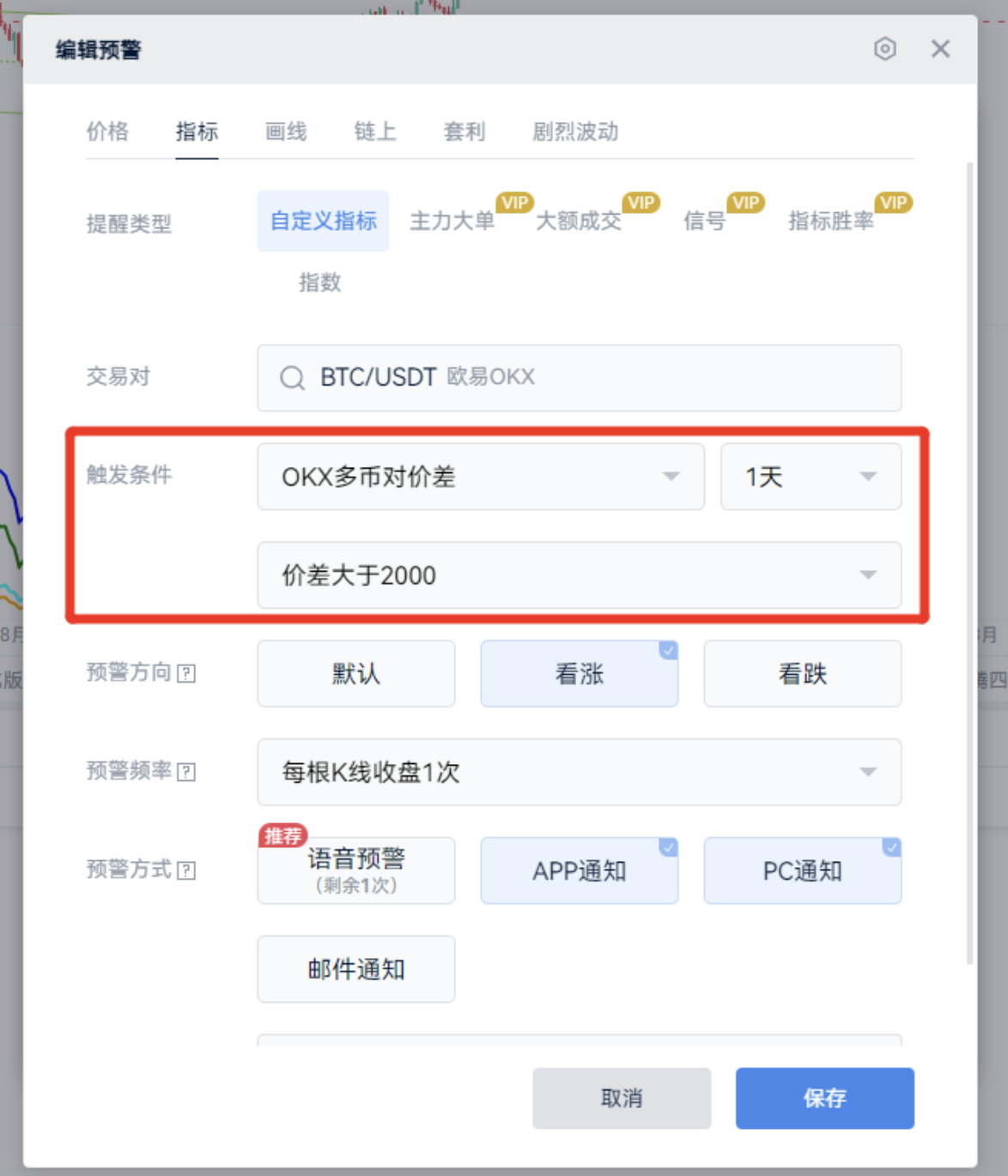
Extension:
Based on the patterns of funding fees and price differences, leverage custom indicators for real-time trading.
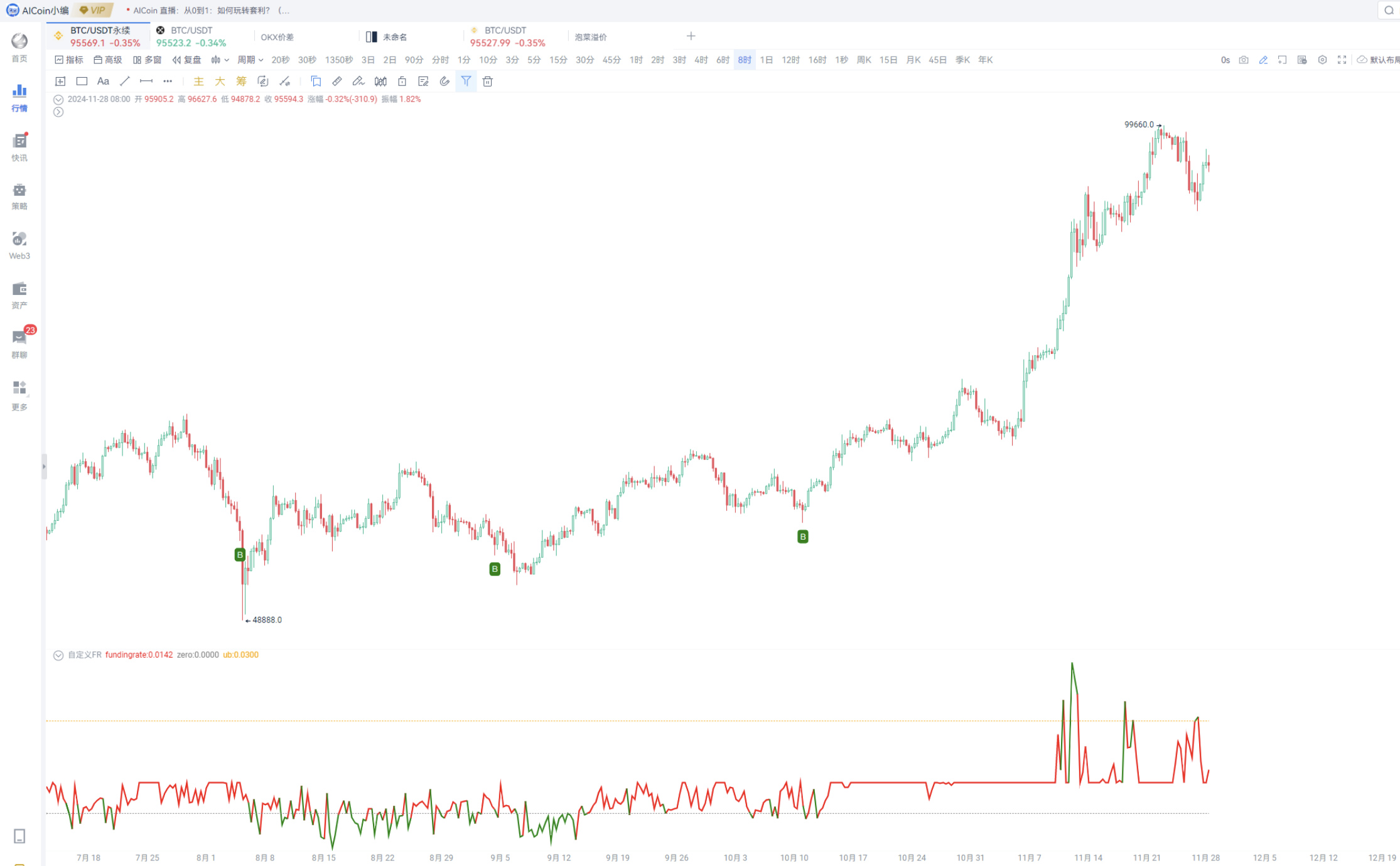
3. Related Tutorials
Detailed operation guides are as follows:
Operation Tutorial: https://www.aicoin.com/en/article/430710
Beginner Tutorial: https://www.aicoin.com/en/article/396797
Arbitrage Terminology Explanation: https://www.aicoin.com/en/article/396815

That concludes all the content from the live broadcast!
Thank you all for your attention, and stay tuned to our live broadcast room.
In a bull market, let's explore the market together and find trading opportunities! Use AICoin to earn a free life.
Recommended Reading
For more valuable live broadcast content, please follow AICoin's "AICoin - Leading Data Market, Intelligent Tool Platform" section, and feel free to download AICoin - Leading Data Market, Intelligent Tool Platform.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




