This article is from: AnChain.AI
Translation|Odaily Planet Daily (@OdailyChina)

In January 2023, the FBI accused the North Korean hacker group Lazarus Group of using the privacy protocol Railgun for money laundering, involving approximately 41,000 ETH (worth over $60 million at the time). These funds were stolen by the group during the Harmony Horizon Bridge attack in 2022. AnChain.AI is the main security company responding to this case. As of the writing of this article, the total value of the involved ETH has exceeded $120 million.
Since its establishment in 2022, Railgun has facilitated over $2 billion in cryptocurrency transactions, with WETH accounting for 76% of the total transaction volume. This transaction scale highlights Railgun's growing utility in on-chain privacy services.
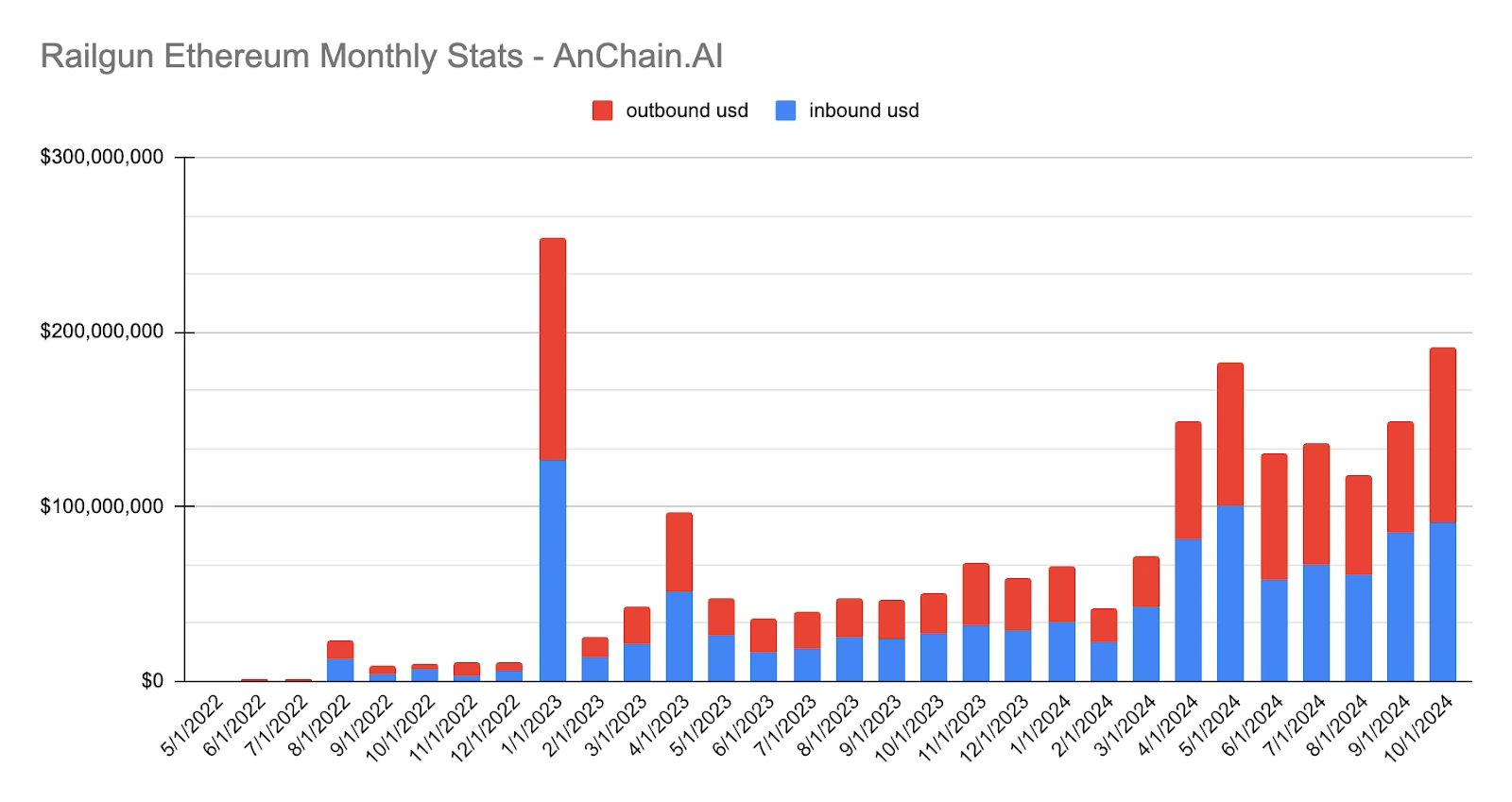
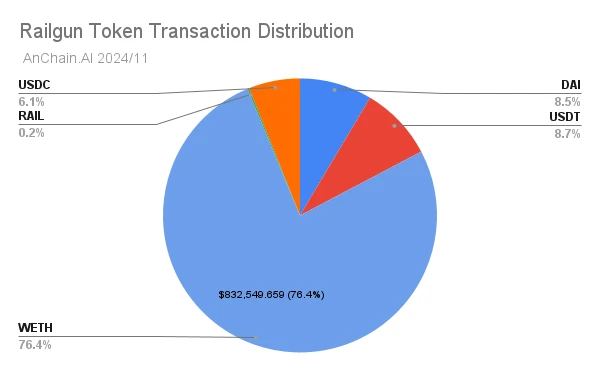
Railgun poses unique challenges for cryptocurrency-related investigations, particularly in tracking illegal activities. This article will delve into the foundational concepts of Railgun, its internal mechanisms, innovative privacy mechanisms, and how cutting-edge solutions trusted by global regulatory agencies can more effectively combat money laundering activities.
What is Railgun?
Railgun utilizes smart contracts and zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) technology, replacing traditional cryptocurrency mixing tools and becoming a new generation of privacy services. Unlike mixers that require pooling funds off-chain to obscure transactions, Railgun can directly integrate privacy features into on-chain transactions, helping users maintain anonymity in DeFi activities.
Railgun operates on Ethereum and other EVM-compatible networks, leveraging zk-SNARKs to facilitate privacy-preserving on-chain transactions. zk-SNARKs allow users to prove the validity of transactions without revealing any sensitive information. This method eliminates the need for third-party layers or bridges that typically pose privacy risks or operational complexities, achieving seamless integration with DeFi applications.
How does Railgun achieve transaction privacy? According to Railgun, it involves just four simple steps:
Create: Set up your non-custodial RAILGUN wallet using a privacy 0 zk address;
Shield: Transfer any ERC-20 tokens or NFTs to the 0 zk address to achieve shielding;
Transact: Once shielded, tokens, balances, and transactions will be encrypted.
Use: Transfer assets between 0 zk addresses to use DeFi anonymously.
However, while these steps may seem straightforward, the challenges posed by Railgun become more pronounced when we examine its internal workings more closely.
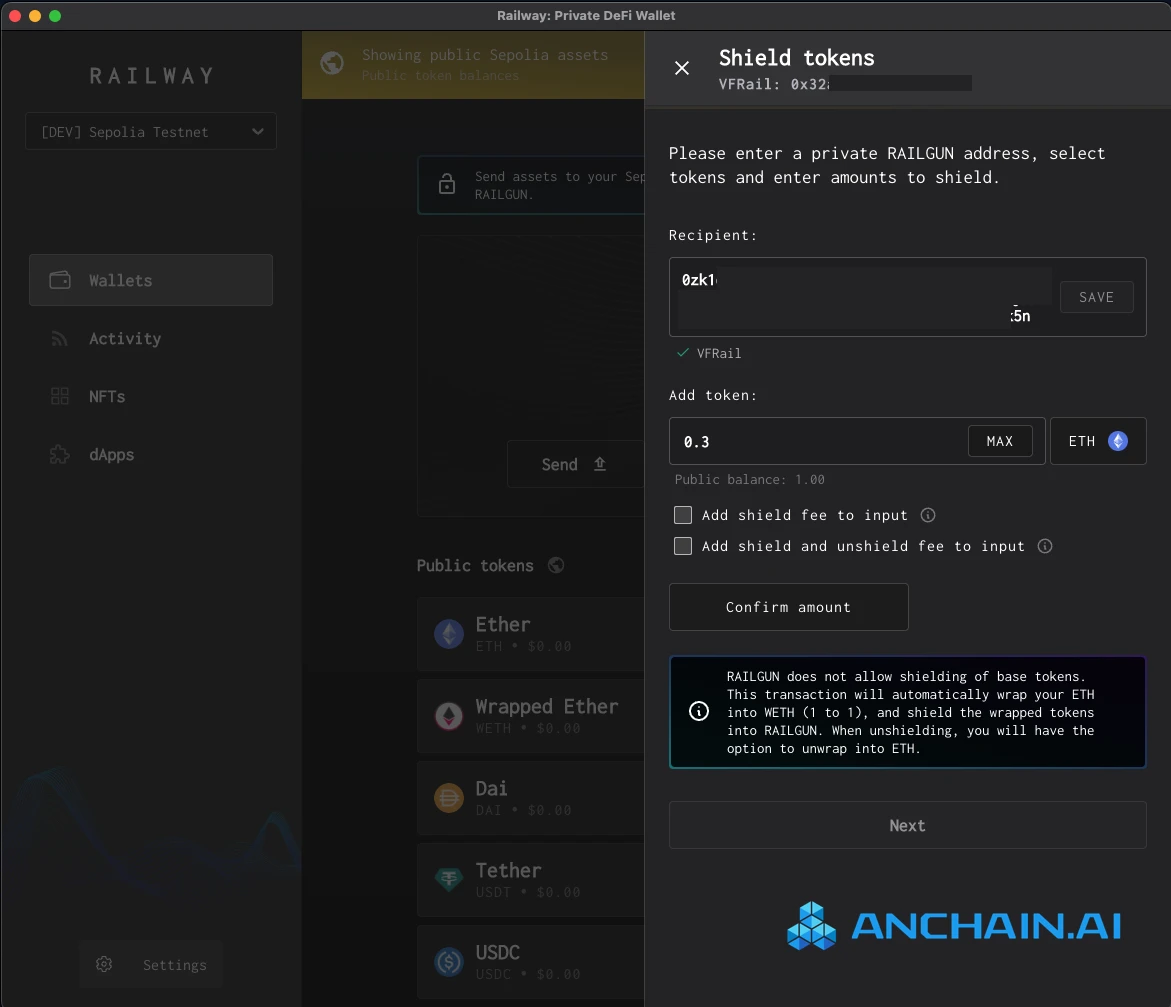
What are zk-SNARKs?
Railgun is essentially a smart contract DApp that uses zero-knowledge proofs, specifically zk-SNARK, to ensure transaction privacy.
Zero-knowledge proofs are a cryptographic technique that allows one party (the prover) to convince another party (the verifier) that they know a certain piece of information without revealing the actual information. zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge) are a specific form of zero-knowledge proof that emphasizes "non-interactive," meaning that no back-and-forth communication is required between the prover and verifier.
In Railgun's privacy system, zk-SNARKs allow smart contracts to act as verifiers. When a user wants to make a transaction, zk-SNARKs enable the user to prove that their actions (i.e., transferring tokens or interacting with DeFi protocols) comply with the rules without disclosing any sensitive details.
The technical process of Railgun involves several key components:
Trusted Setup: Using elliptic curves to generate cryptographic parameters needed for proof creation and verification, establishing a public parameter system. These parameters will be used to ensure that subsequent proofs can be verified.
Circuit: In the Railgun protocol, "witnesses" (private data, such as the user's token balance or transaction) are used in cryptographic "circuits." The circuit defines certain conditions that must be met (such as valid transaction amounts or sufficient balances). The prover can compute a solution (proof) based on the "witness" and the "circuit."
Proof Generation: Generating a concise, cryptographically valid proof that the user knows a "witness" that satisfies the "circuit" conditions without revealing the "witness" itself.
Verification: Submitting the proof to the network for verification using the public parameters from the trusted setup step. The verification process can be computed efficiently, allowing for real-time verification on-chain.
The magic of zk-SNARKs lies in their efficiency — they can generate small, easily verifiable proofs, which is particularly suitable for blockchains with strong demands for speed and privacy. This allows the Railgun system to utilize cryptographic "circuits" to handle different types of transactions, each defined by specific input (UTXO) and output amounts. These "circuits" can manage various transactions, from multi-sending to privacy NFT shielding. Railgun has 54 different "circuits" that can handle a variety of transaction combinations, and the system automatically routes transactions to optimize gas and save costs. This flexible design also enables Railgun to support various token standards, including ERC-20, ERC-721, and ERC-1155, allowing Railgun to efficiently handle various transaction types.
Unveiling the Veil of Railgun Smart Contracts
The Role of Smart Contracts in Cryptocurrency Tracking
The rise of smart contracts and Railgun fundamentally changes the way cryptocurrencies are tracked. The challenges are primarily twofold.
Technical Complexity: Railgun's privacy design and ZKP technology can obscure transaction details, making it difficult to link deposits and withdrawals without specialized tools.
Legal Ambiguity: The inherent privacy of the protocol raises accountability issues, especially when features originally intended to protect user privacy are exploited by bad actors.
For cryptocurrency investigators, understanding the mechanisms of smart contracts is no longer optional but an essential skill.
Main Contract Addresses of Railgun on the Ethereum Mainnet
Railgun operates through a series of dedicated smart contract networks. It has two main smart contracts on the Ethereum mainnet.
Railgun Relay Contract:
Address: 0xfa7093cdd9ee6932b4eb2c9e1cde7ce00b1fa4b9
Description: Facilitates transaction relays within the Railgun system, ensuring user interactions remain private and secure.
Railgun Smart Wallet Contract:
Address: 0xc0BEF2D373A1EfaDE8B952f33c1370E486f209Cc
Description: Manages the core functions of the Railgun privacy system, including asset shielding and unshielding, as well as how to handle privacy transactions.
It is important to note that while these addresses are specific to Ethereum, Railgun also operates on other networks such as BSC, Polygon, and Arbitrum, each with its unique contract addresses.
Analyzing Railgun's Relay Contract
After analyzing Railgun's relay contract using AnChain.AI's SCREEN smart contract assessment platform, it was found that the contract is broadly classified as a "Pausable Upgradeable Proxy." This architecture allows for upgrades while maintaining operational control, providing flexibility and security.
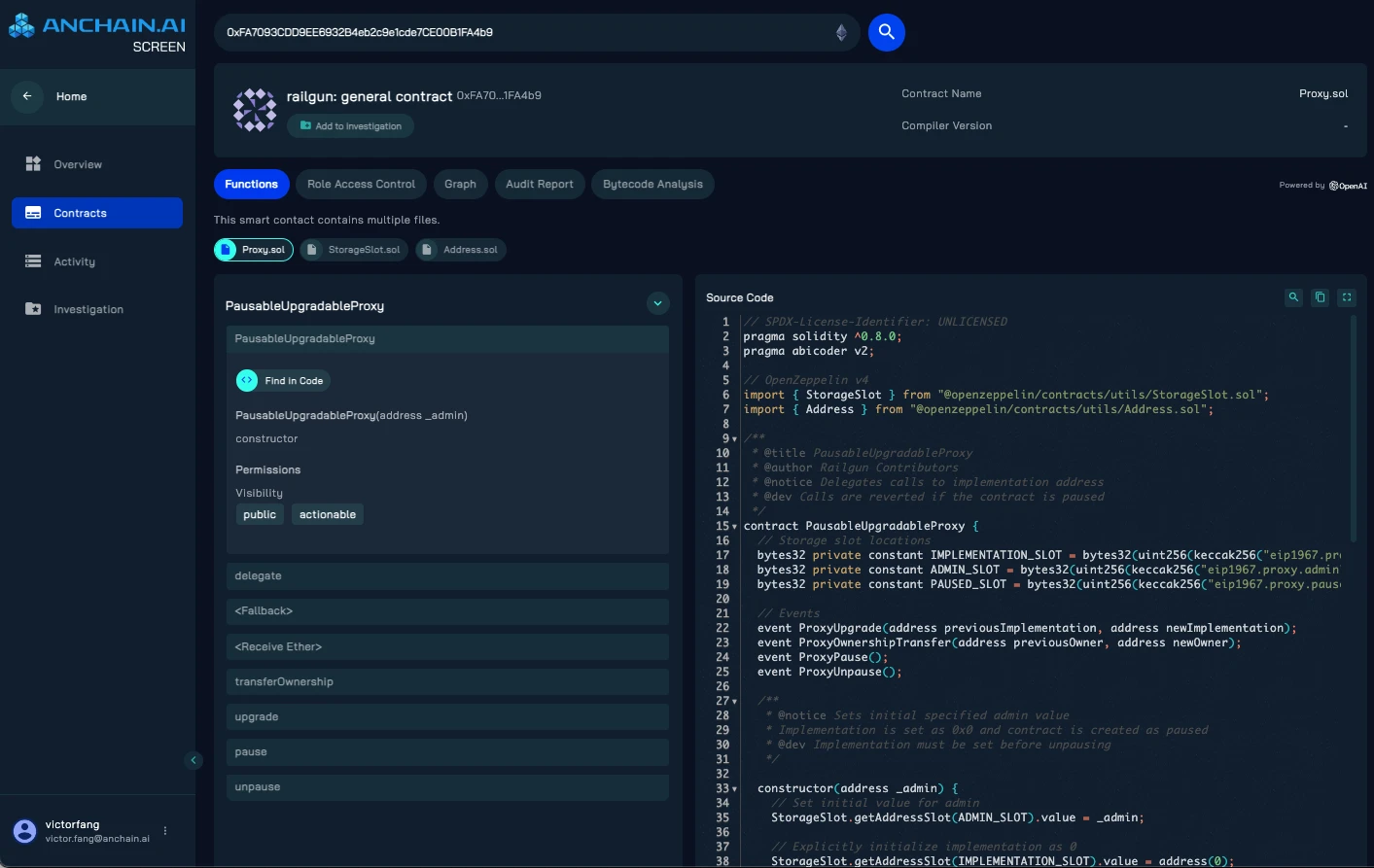
Through a case study involving complex money laundering activities, we can better understand the significance of this design in the real world.
Case Study: The Harmony Bridge Attack and the Utility of Railgun
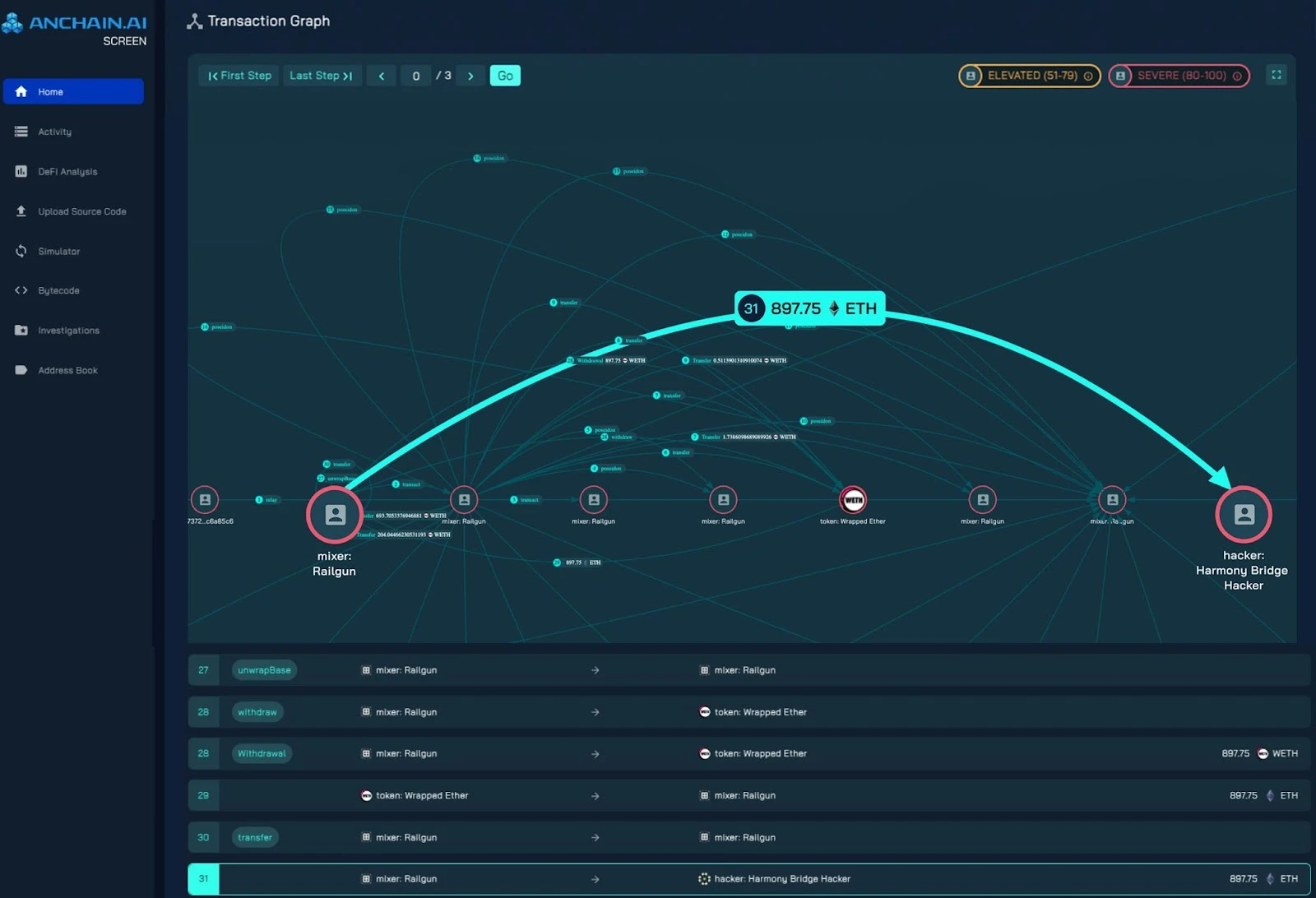
In January 2023, an address associated with the notorious Harmony Bridge hacker laundered 897 ETH (approximately $2.7 million) through Railgun. Although this transaction (as emphasized above) appears simple, it is supported by 31 different smart contract events, many of which evaded detection by traditional investigative tools. This complex transfer pattern highlights the intricacy of Railgun's privacy mechanisms and its ability to obscure the true flow of funds.
Revealing the Intricate Insider Trading
Traditional blockchain explorers cannot capture the details of Railgun's privacy transactions. To address this challenge, SCREEN's advanced transaction charting and simulation features help investigators break down Railgun's internal processes, revealing hidden flows and patterns of funds.
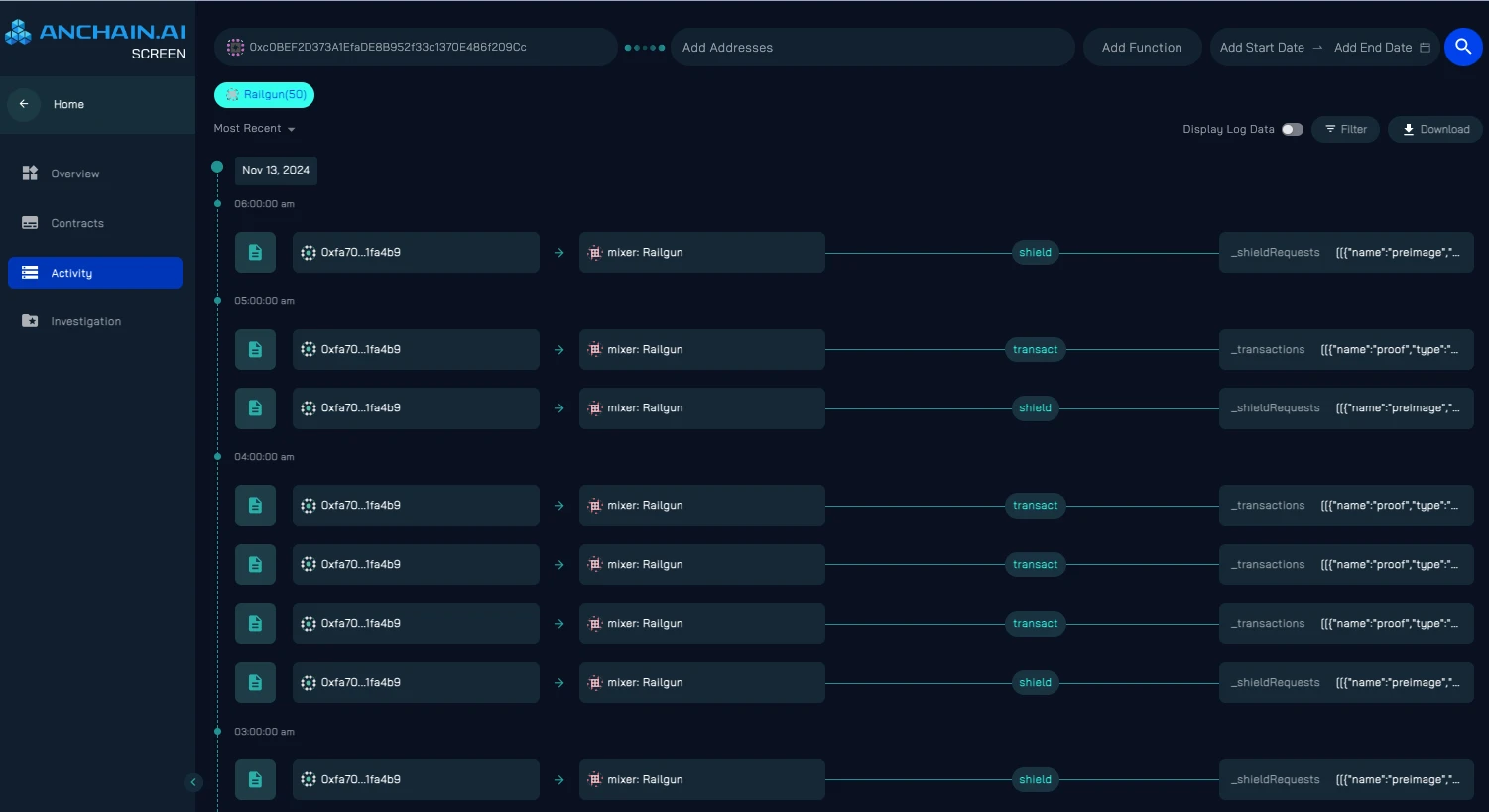
As shown in the image above, the internal transaction timeline in SCREEN can reveal complex patterns of fund movement, including back-and-forth transfers — a part of Railgun's privacy system.
New Challenges in Cryptocurrency Investigation
Railgun's privacy design and the application of ZKP technology create significant obstacles for cryptocurrency investigations, but these are not insurmountable.
Successful investigations largely depend on contextual factors, such as external interactions with exchanges, patterns of deposit and withdrawal activities, and potential associations identified through behavioral or clustering analysis.
Exploratory Solutions for Investigating Railgun Transactions
Based on extensive investigative experience, AnChain.AI has developed the following exploratory solutions for probabilistic tracking and analysis of transactions conducted through Railgun. Different methods target various aspects of Railgun's functionality to infer potential links between deposit and withdrawal events.
Deposit and Withdrawal Monitoring Scheme:
Focus: Observe funds entering (shielding) and exiting (unshielding) Railgun;
Method: Track public addresses depositing funds into Railgun and monitor their withdrawal transactions to see where the funds reappear on public addresses;
Limitation: Cannot reveal transfers within Railgun but provides potential endpoints.
Time Monitoring Scheme:
Focus: Analyze the timing of deposits and withdrawals;
Method: Look for temporal relationships between large or isolated deposit and withdrawal events, which may indicate potential relationships;
Limitation: There is a degree of probability involved; monitoring isolated time events works best but may also produce false positives;
Off-Chain Association Scheme:
Focus: Associate on-chain Railgun activities with off-chain events;
Method: Compare Railgun transactions with external factors, such as exchange activities or known blockchain social interactions.
Limitation: Relies on the availability and quality of off-chain data.
Transaction Pattern Analysis Scheme:
Focus: Identify related addresses through transaction patterns;
Method: Use clustering algorithms to find behavioral similarities among interacting addresses in Railgun, thereby identifying a particular entity or group.
Limitation: Privacy transactions may reduce analysis accuracy; transaction patterns are often complex and ambiguous.
Governance Interaction Scheme:
Focus: Examine interactions with Railgun governance or public wallets;
Method: Analyze known governance or public addresses that may be linked to Railgun and observe their transaction behaviors;
Limitation: Applicable only when Railgun uses known governance addresses.
Conclusion
The challenges posed by Railgun highlight a common issue faced in cryptocurrency investigations today — how can investigators begin to track illicit funds when widely used privacy protocols obstruct their most commonly used tools?
In today's digital asset ecosystem, understanding smart contracts is not just a recommendation but a necessity. Protocols like Railgun challenge traditional methods of blockchain tracking, underscoring the need for ongoing innovation in forensic technologies and investigative strategies.
AnChain.AI is committed to addressing this issue through technology and continues to provide leading global regulatory agencies with the tools to penetrate smart contracts, redefining the way cryptocurrency investigations are conducted.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




