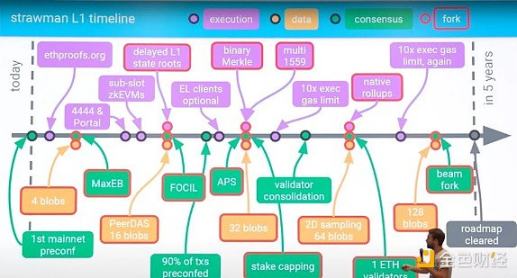
The Beam Chain fork will take 5 years, including continuous upgrades to Ethereum.
Written by: Jarrod Watts, Abstract Developer Relations Engineer
Translated by: Jinse Finance xiaozou
The Beam Chain is the most significant announcement at the Devcon summit, introducing 9 major upgrades to Ethereum. However, most people do not yet fully understand these upgrades, and this article will help you better understand these 9 upgrades.
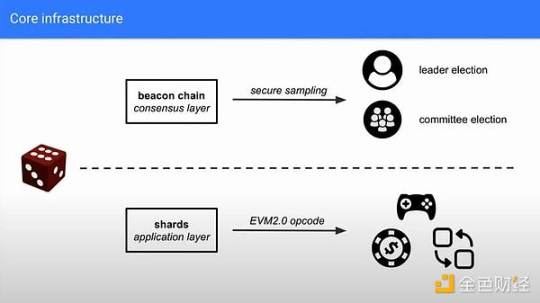
The Beam Chain is a redesign of the Ethereum consensus layer (CL) proposed by Justin Drake. Before diving into the specific upgrades, let's first take a brief look at what the Ethereum consensus layer actually is.
Every Ethereum node runs two components: an execution client and a consensus client.
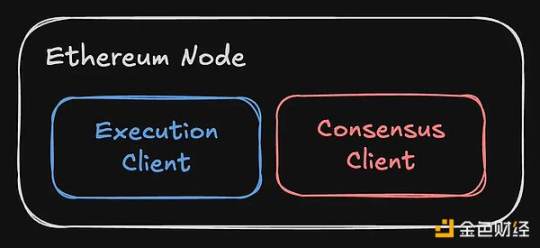
The consensus client is used by nodes to "agree" on what the next block in the blockchain is. You can stake 32 ETH to add a third component—a validator—who proposes new blocks through a proof-of-stake algorithm to earn rewards.
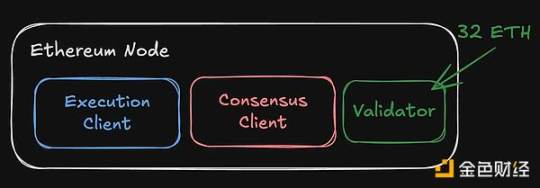
So why does the Ethereum consensus layer need to be redesigned?
Currently, the CL has several issues:
- It has been around for 5 years—facing technical debt and not utilizing the latest innovative technologies like ZK proof (zero-knowledge proof).
- This is an opportunity to execute upgrades and clean up Ethereum's technical debt.
These 9 upgrades can be divided into 3 categories:
- Block production
- Staking
- Cryptography
Next, I will summarize each upgrade.
Upgrade 1: Anti-Censorship
Current block production is very centralized. The two major block builders—Beaver Build and Titan Build—almost monopolize all Ethereum blocks:
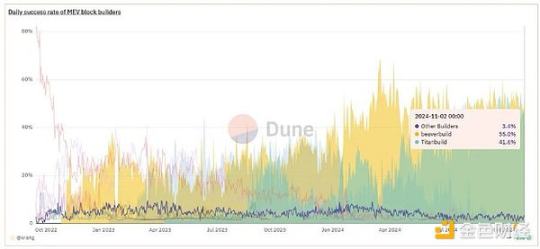
These builders create blocks in a way that maximizes their profits in the form of MEV; they can include, exclude, or reorder transactions in the blocks they produce.
Today, if your transaction is not favorable to these two block builders, they may choose to exclude your transaction from the block, censoring it.
The upgrade proposed in EIP-7805 increases Ethereum's anti-censorship by allowing validators to select transactions from the memory pool and enforce their inclusion through inclusion lists (ILs), meaning builders must follow the rules to have their blocks included by the network.
In the Beam Chain upgrade, the 16 validators for each slot will build a list of transactions that must be included by the block builders, meaning block builders will no longer have the ability to censor transactions.
Upgrade 2: Attester Proposer Separation
Attester Proposer Separation (APS) separates witnessing and proposing, similar to execution auctions.
While validators can build transaction blocks themselves, most validators use something called "MEV boost" to delegate block building to others (usually Beaver Builder or Titan Build), with the latter paying fees to the validators.
These two parties are referred to as:
- Witnesses (validators)
- Proposers (block builders)
Currently, the two are separated—validators accept blocks from proposers, but it is centralized through trusted intermediaries called relayers.
Relayers like Flashbots act as "middlemen," facilitating transactions between validators wanting to sell blocks and block builders wanting to create profitable blocks.
APS is an upgrade that adds or "embeds" this separation between validators and proposers in a decentralized manner; reducing the centralization risk of relayers like Flashbots.
One way to achieve this separation is through execution auctions; a system where anyone can purchase a ticket, giving them a chance to win the right to create future blocks.
Upgrade 3: Faster Slots
On the Beam Chain, slots will change from 12 seconds to 4 seconds.
Slots refer to the time period during which a validator can propose a new block and get agreement from other validators.
Faster slots mean quicker transaction finality and higher transaction throughput.
Upgrade 4: Smarter Issuance (e.g., Staking Cap)
The issuance curve refers to how new ETH is created and distributed over time.
Currently:
- ETH is distributed as rewards to validators every epoch (approximately 6 minutes).
- ETH is burned as part of each transaction.
Depending on network activity, ETH fluctuates between inflation and deflation. For example, in a certain hour, you might see ETH in inflation because the issued ETH rewards exceed the ETH burned in transactions:
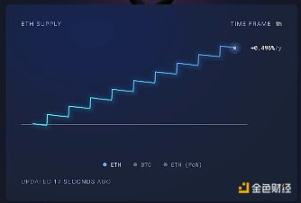
There has been much debate in the community about whether and how issuance should change, but Justin Drake mentioned a staking cap in the Beam Chain demonstration. The staking cap sets a maximum amount of ETH that can be staked, providing validators with more predictable rewards, and possibly aiming to make ETH deflationary.
Upgrade 5: Smaller Validators
Currently, you need to purchase 32 ETH to become an individual validator on Ethereum. At today's prices, that is about $100,000.
The Beam Chain proposes to reduce this to 1 ETH, which will help address some centralization issues with liquid staking providers like LIDO or Coinbase, which currently control nearly 40% of staked ETH:
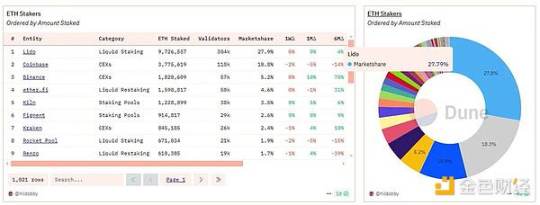
Users who want to run a validator to earn rewards but do not have 32 ETH will benefit from this upgrade, as they will be able to run a validation node with just 1 ETH.
The next upgrade (Pectra) will allow stakers to stake more than 32 ETH, up to 2048 ETH. This means that on the Beam Chain, users will be able to stake between 1-2048 ETH.
Justin mentioned the Orbit staking method, which describes a system where larger validators are selected more frequently and receive smaller rewards, while smaller validators are selected less often but receive larger rewards.
Upgrade 6: Faster Finality (e.g., 3 Slot FFG)
Currently, finalizing transactions on Ethereum takes about 15 minutes (64 slots).
Single-Slot-Finality has been proposed as a way to reduce this time to 1 slot, but a newer proposal—3-Slot-Finality—may actually be faster as it runs in parallel with voting rounds.
This means a transaction will be finalized in 36 seconds instead of 15 minutes. This is particularly important for services that rely on L1 finality (such as DeFi applications or cross-chain/interoperability protocols).
Upgrade 7: Chain Snarkification
Beam Chain aims to "snarkify" the consensus layer (using ZK-SNARKs, a type of secure ZK proof). Justin Drake refers to this as the "ZK Era."
Specifically, the Beam Chain proposes to use ZK-SNARKs to:
- Compile deployments of the beam chain in different languages into zkVM bytecode.
- Aggregate signatures generated by witnesses into ZK proofs.
The ELI5 here is that ZK technology has made significant progress over the past 5 years, and Ethereum hopes to natively deploy it in both the consensus and execution layers.
Upgrade 8: Quantum Security
Today, quantum computers can potentially break parts of Ethereum, such as cracking your private key or forging signatures in transactions using methods like Shor's algorithm.
Quantum computers are likely to be available within the next decade; therefore, the Beam Chain proposal aims to provide Ethereum security for a post-quantum world by using methods like hash signatures with post-quantum security.
Upgrade 9: Strong Randomness
Finally, the Beam Chain upgrade proposes a new primitive for building a source of randomness using something called VDF (Verifiable Delay Function).
In 2018, Justin Drake discussed this, saying it could be used for:
Consensus layer—e.g., randomly selecting validators.
Application layer—e.g., publicly providing an opcode that can offer verifiable randomness.
This is not possible today without third-party services like Chainlink or Pyth VRF.
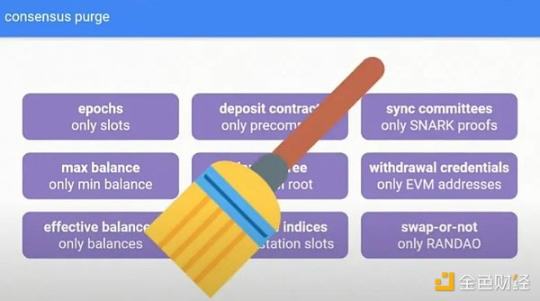
In addition to these 9 upgrades, the Beam Chain upgrade will also clean up most of its existing technical debt and unnecessary components, which will become redundant after the upgrade.
For example, faster slot finality may mean that epochs are no longer needed.
However, some believe that the timeline for the Beam Chain is too long. Nevertheless, Justin later clarified that Ethereum will continuously receive updates over these 5 years.
The Beam Chain fork will take 5 years, including continuous upgrades to Ethereum.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



