Author: Snow
Translator: Cedar
Reviewer: KOWEI, Edward, Elisa, Ashley, Joyce
Copyright: Gate.io
Preface
The traditional overall architecture of blockchain has many limitations, such as slow innovation speed, limited scalability, and a lack of development flexibility at the application layer. To address these limitations, modular blockchains have emerged, breaking down blockchain into different and interchangeable components.
In the past, modular blockchains were mostly summarized as layer 1 and layer 2, until the co-founder of Celestia first proposed this concept in his article "Fraud and Data Availability Proofs." Since then, discussions about modularity and layering have surged, and with the rise of the modular public chain Celestia, the concept of modularity has officially entered the public eye.
What is Celestia
Celestia is a modular network focused on Data Availability (DA) that can securely scale with the growth of users, allowing anyone to easily launch their own blockchain projects.
Celestia is referred to as a simplified blockchain because it separates the consensus layer from the application execution layer. The consensus layer requires Celestia to only be responsible for transaction ordering and ensuring data availability;
The execution layer provides an effective solution to data availability issues, allowing lightweight nodes to sample a small amount of random data from each block to verify data availability. The more lightweight nodes participating in data sampling, the larger the amount of data the network can securely handle, thus increasing block size without a corresponding increase in verification chain costs.
Technical Features of Celestia
Modular DA Network:
Celestia's design separates aspects such as execution, consensus, settlement, and data availability. This modular structure allows developers to specialize and optimize at each layer, improving the overall efficiency and scalability of the network.
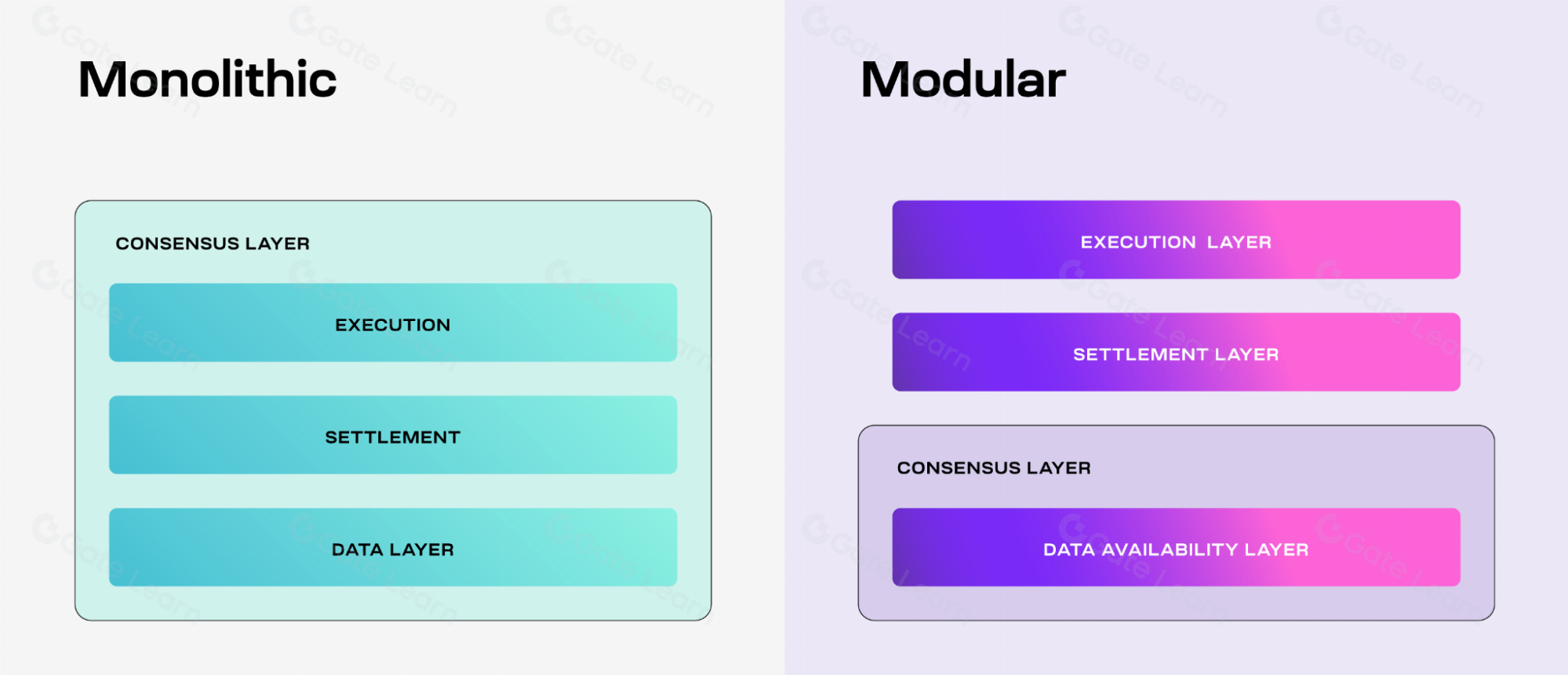
Source: https://docs.celestia.org/img/learn/monolithic-modular.png, 2024.3.09
Data Availability Sampling (DAS):
DAS is a method that allows lightweight nodes to verify data availability without needing to download the entire block. Lightweight nodes randomly sample data blocks, and if they successfully retrieve and verify this data, it indicates that the data for the entire block is available.
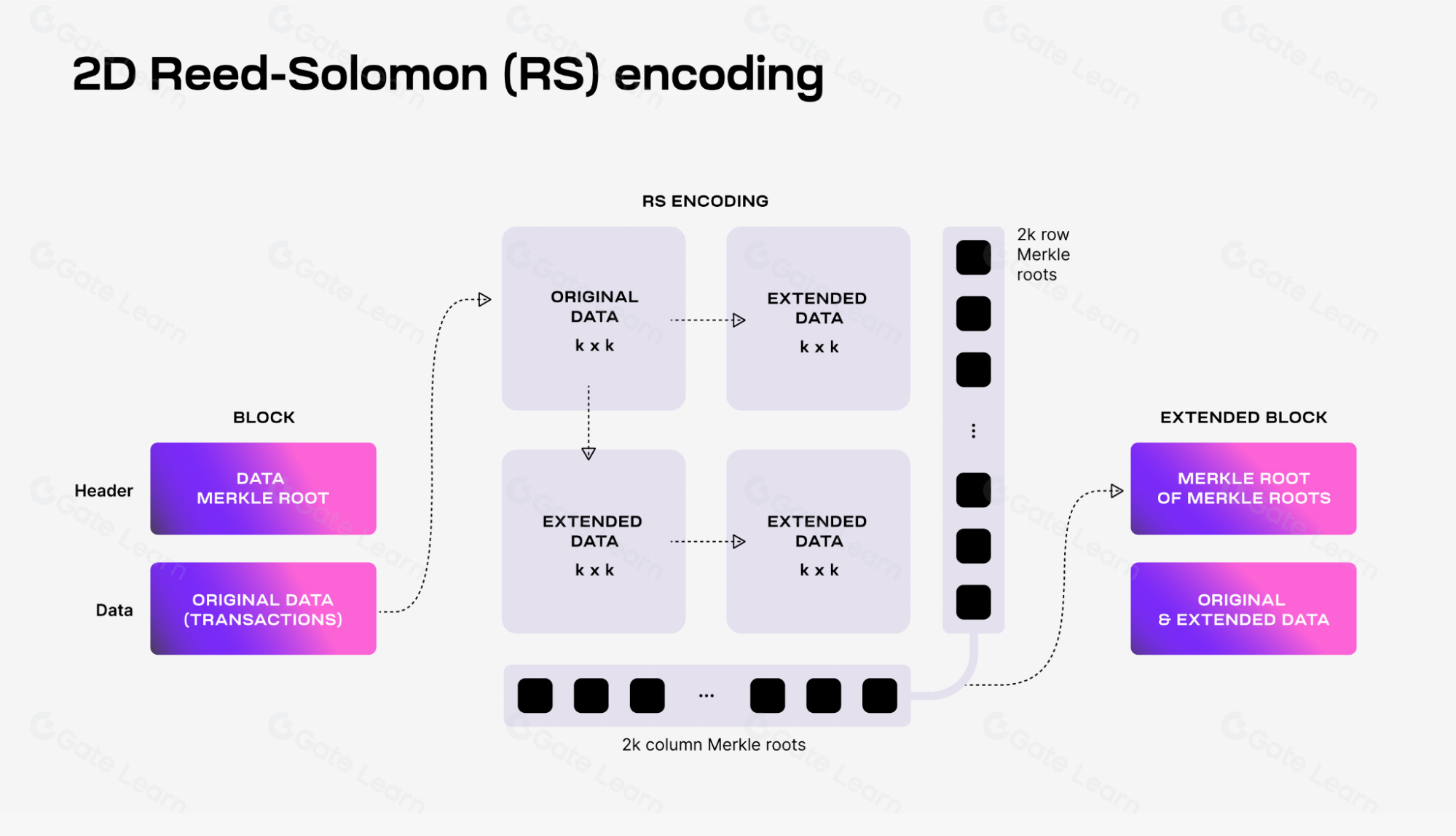
Source: https://docs.celestia.org/img/learn/reed-solomon-encoding.png, 2024.3.09
Scalability:
The DAS technology allows the data availability layer of Celestia to scale. Through DAS, resource-limited lightweight nodes can perform data availability verification since they only need to sample a small portion of block data. The more lightweight nodes participating in DAS, the larger the amount of data they can collectively download and store.
Fraud Proofs for Erroneous Data Expansion:
To address the potential issue of data expansion errors by block producers, the fraud proof mechanism allows for the verification and rejection of blocks with invalid data, thereby enhancing the network's security.
Namespace Merkle Trees (NMTs):
NMTs allow block data to be divided into separate namespaces based on different applications. This means that applications only need to download and process data relevant to them, significantly reducing the demand for data processing.
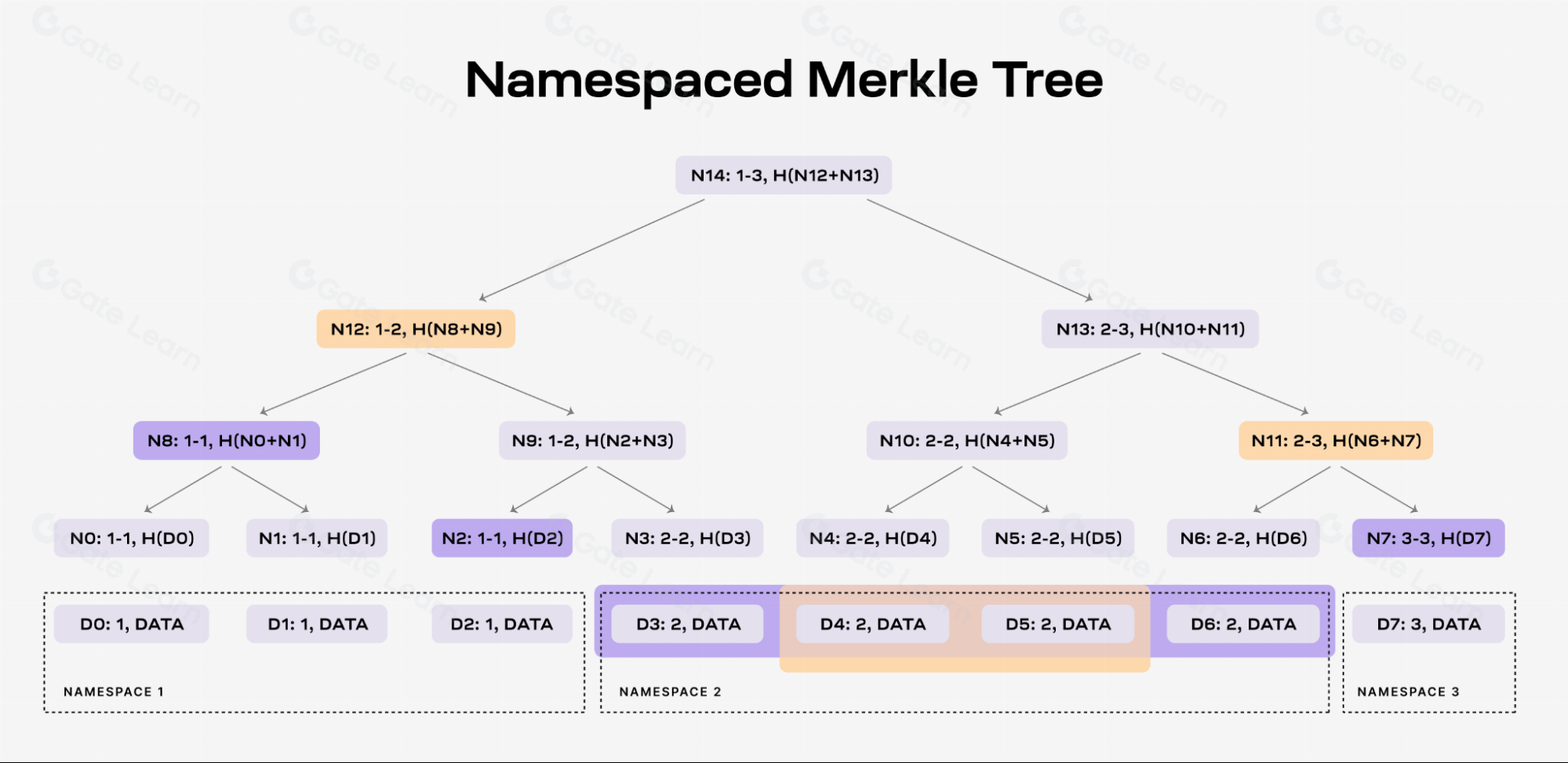
Source: https://docs.celestia.org/img/learn/nmt.png, 2024.3.09
Building a PoS Blockchain for Data Availability
Celestia employs a PoS blockchain called celestia-app to facilitate transactions and data availability. This layer is built on top of celestia-core, which is an improved version of the Tendermint consensus algorithm, specifically designed to meet the unique needs of the DA layer.
Celestia's design aims to provide consensus and data availability without involving transaction execution. The role of lightweight nodes in this design is to review whether each block has reached consensus and to verify the availability of block data, rather than verifying transactions. This means that lightweight nodes do not need to rely on the consensus majority of honest nodes to verify the validity of the state, a feature typically only available to full nodes.
By adopting a carefully designed block encoding scheme, lightweight nodes can verify the rest of the block with high probability by sampling only a small amount of random block data. If any full node detects suspicious activity, it can notify lightweight clients through data availability fraud proofs.
Data Analysis on the Celestia Chain
Data Costs:
Numia Data released a report titled "The impact of Celestia’s modular DA layer on Ethereum L2s: a first look."
The report compares the costs incurred by different L2s in the second half of 2023 when publishing callData to Ethereum with the potential costs of using Celestia as a DA layer (assuming a TIA price of $12). The magnitude of the difference indicates that adopting a dedicated DA layer like Celestia can significantly save L2 Gas fees.
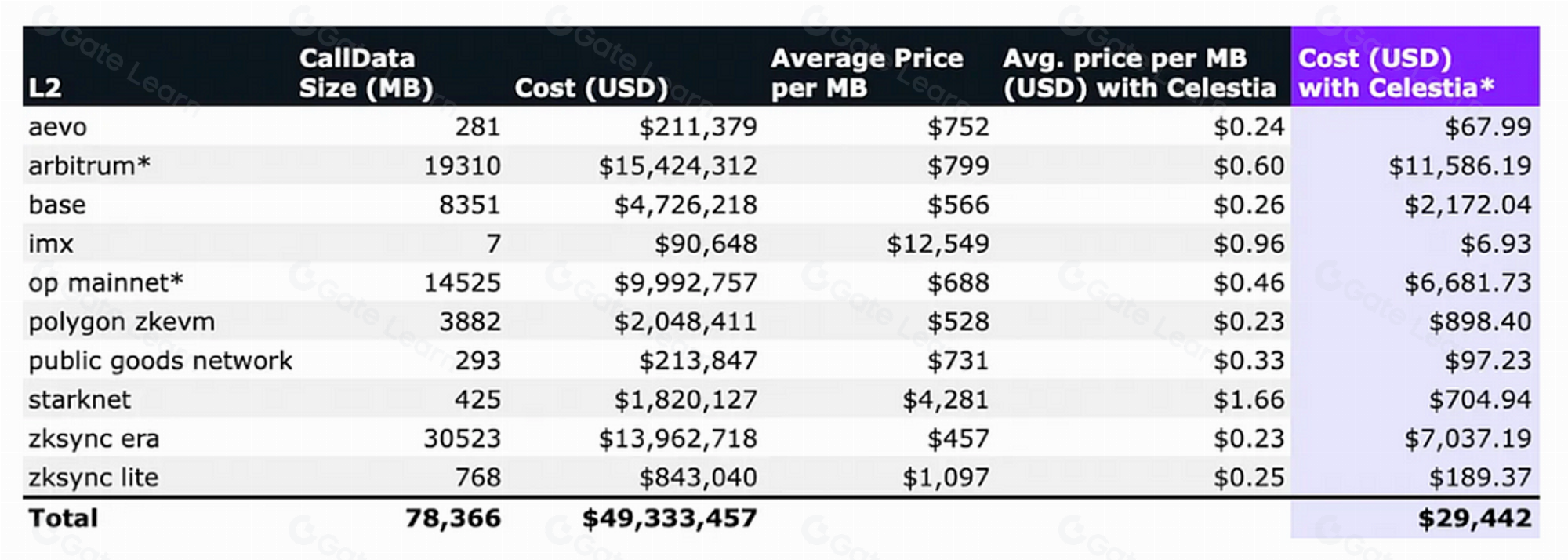
Data Source: @numia.data/the-impact-of-celestias-modular-da-layer-on-ethereum-l2s-a-first-look-8321bd41ff25">https://medium.com/@numia.data/the-impact-of-celestias-modular-da-layer-on-ethereum-l2s-a-first-look-8321bd41ff25
According to the following data, as of January 9, 2024, users have published data to a total of 56 namespaces. Typically, users publish 30 to 50MB of data to 3 to 6 namespaces daily.
Of all the data received by Celestia, 87% was published to 3 namespaces, which are:
- Astroglyph: Provides inscription services, allowing users to publish any data on Celestia.
- MantaNetwork: An OP Stack Rollup launched alongside Caldera.
- 808080808080808: This is an unknown namespace, but it appears to resemble a Rollup.
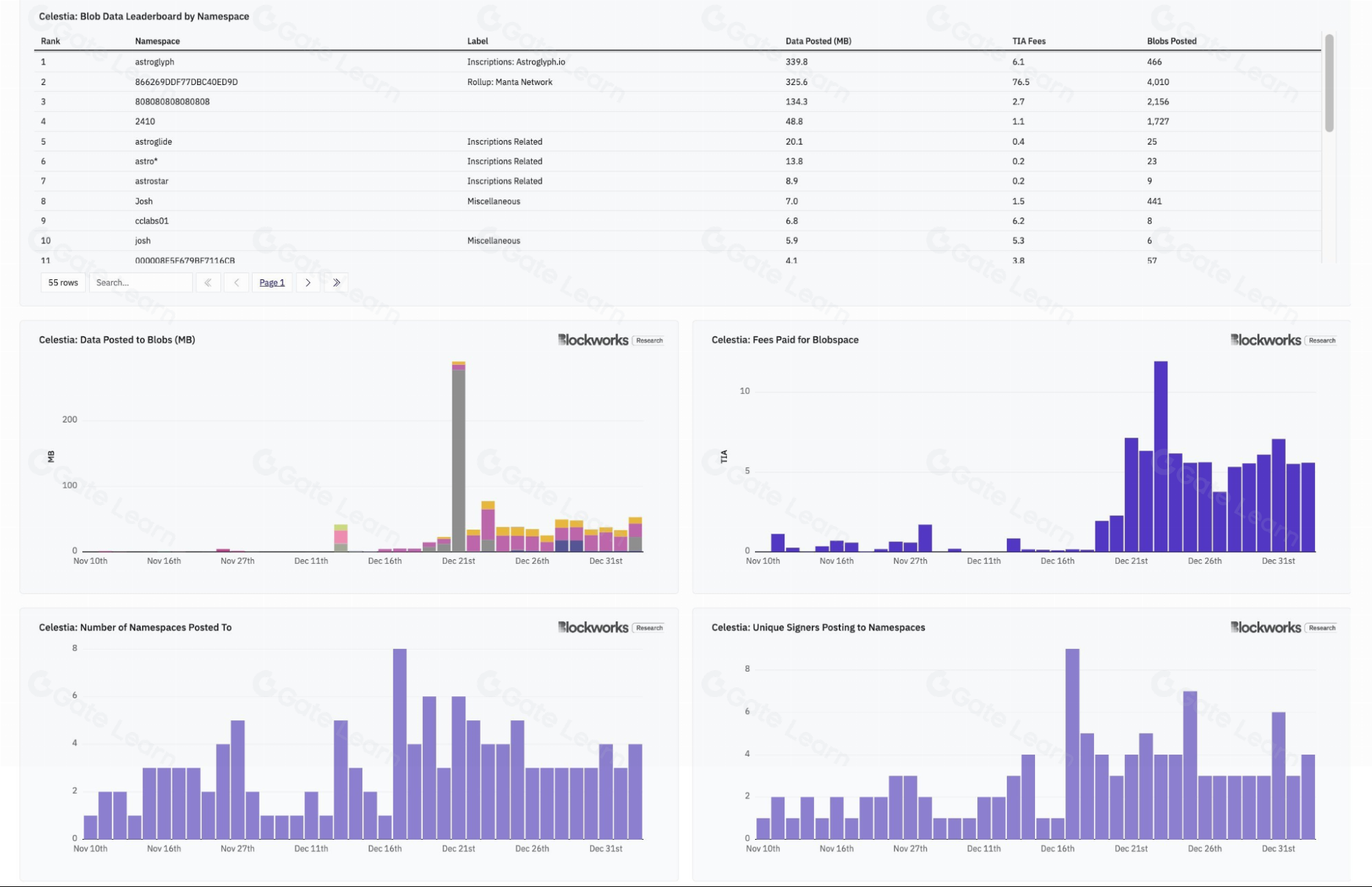
Source: https://twitter.com/smyyguy/status/1744419436449222864, 2024.3.09
Operational Data
Celestia currently has a staking rate of 52.8%, with a staking APR of 14.44%.
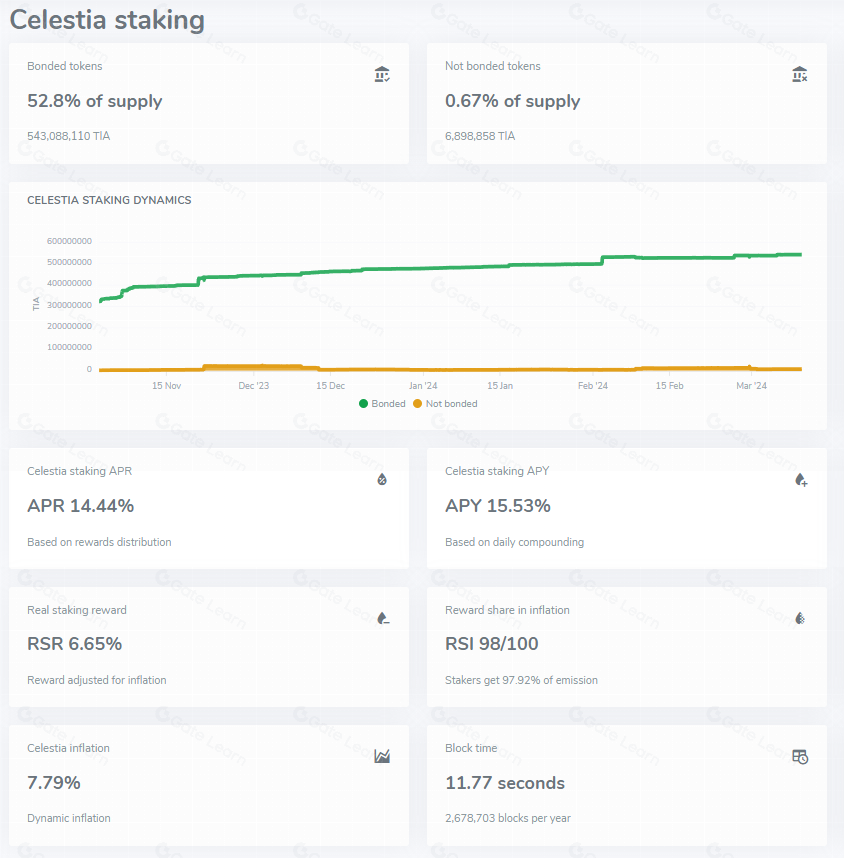
Source: https://staking-explorer.com/staking/celestia, 2024.3.09
The mainnet is still operating stably, with a total of 905,000 blocks produced and a total staked token amount of approximately 543.27M TIA, with 100 initial validator nodes, of which the top 10 nodes account for 49.94% of the network share, indicating a high degree of centralization in the mainnet.
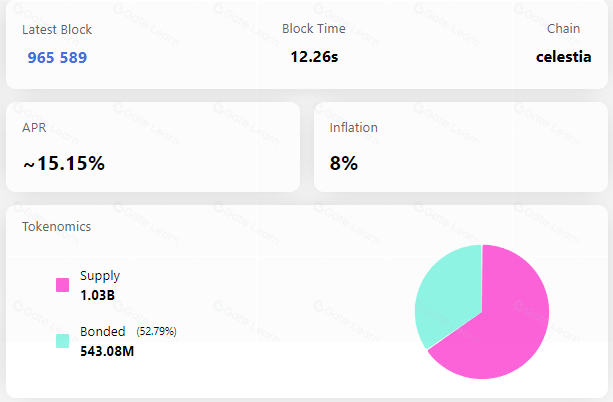
Source: https://celestia.explorers.guru/, 2024.3.09
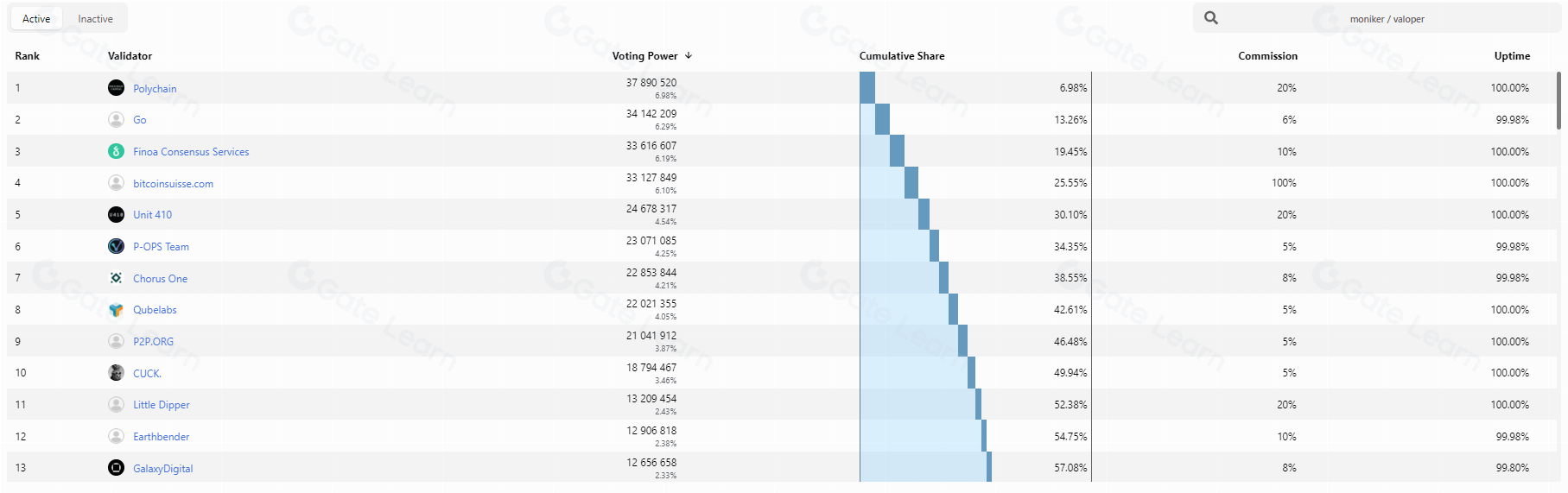
Source: https://celestia.explorers.guru/validators, 2024.3.9
TIA Token Economics
Supply and Distribution
The total initial supply of TIA is 1 billion tokens, with the specific distribution as follows:
- 20% of the total is allocated for public distribution, of which 7.4% is for the genesis airdrop and incentive testnet distribution, and another 12.6% is for future incentive distribution. This portion of tokens is fully unlocked at release.
- 26.8% of the tokens are allocated to the Celestia Foundation and core developers for research, development, and ecosystem programs. Of this, 25% is unlocked at release, and the remaining 75% is gradually unlocked from Year 1 to Year 4.
- 19.7% of the tokens are allocated to early supporters in Series A and B. Of this, 33% is unlocked in the first year, and the remaining 67% is gradually unlocked from Year 1 to Year 2.
- 15.9% of the tokens are allocated to early investors in the seed round. Of this, 33% is unlocked in the first year, and the remaining 67% is gradually unlocked from Year 1 to Year 2.
- 17.6% of the tokens are allocated to initial core contributors. Of this, 33% is unlocked in the first year, and the remaining 67% is gradually unlocked from Year 1 to Year 3.
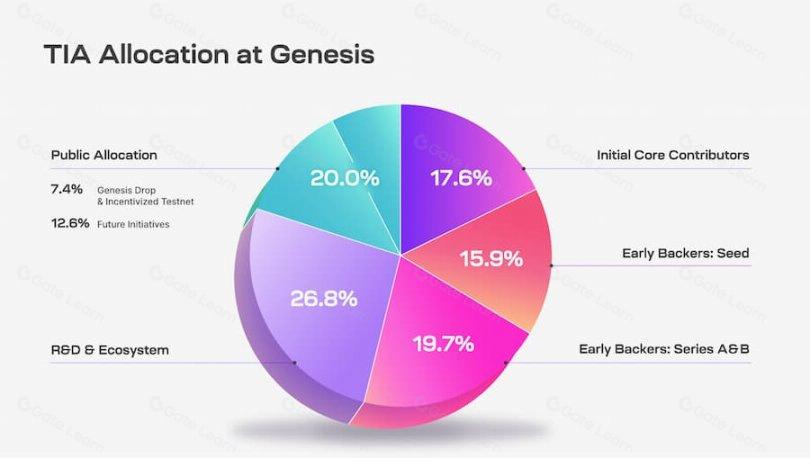
Source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply, 2024.3.09
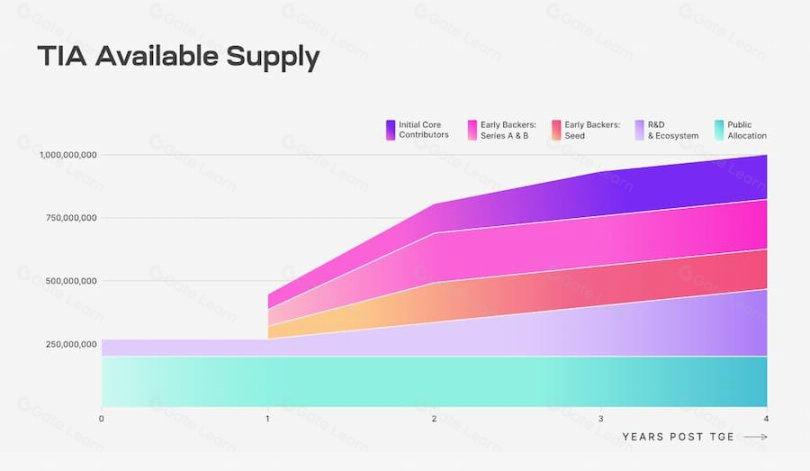
https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply, 2024.3.09
In terms of token release and supply changes, Celestia's TIA token has a total supply of 1 billion tokens, which will be constrained according to different unlocking schedules. All locked or unlocked tokens can be used for staking, and staking rewards will be unlocked immediately upon receipt.
The annual inflation rate is shown in the figure below:
The TIA inflation rate starts at 8% per year and decreases by 10% each year until it reaches a long-term issuance rate of 1.5%.
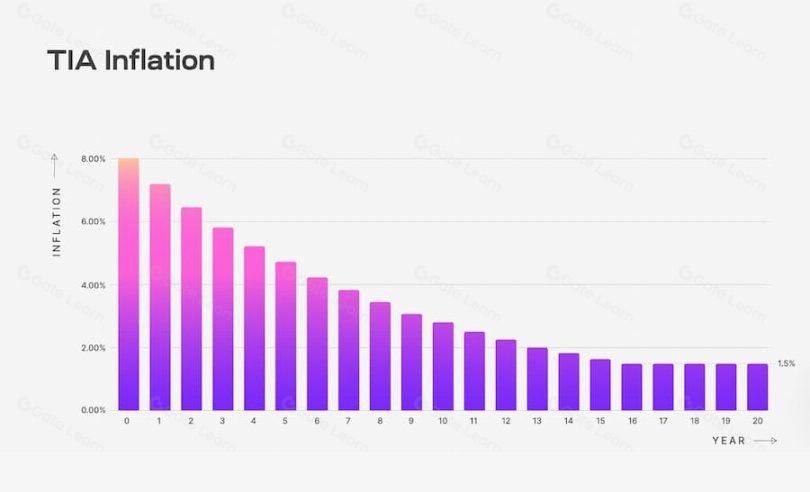
https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply, 2024.3.09
Token Utility
Paying for data storage fees: Developers can submit PayForBlobs transactions on Celestia to pay fees using TIA to obtain the availability of their data on the network.
- New Rollup solutions: Developers can use TIA as a gas token to launch new blockchains, similar to the use of ETH in Ethereum-based Rollups. This helps them focus on the development of the application or execution layer without the need to issue new tokens.
- Proof of Stake mechanism: Celestia is built on the Cosmos SDK and employs a proof of stake mechanism to ensure the security of consensus. Users can delegate TIA to validators and receive a portion of the staking rewards.
- Decentralized governance: TIA holders can participate in the governance of the network, voting to determine network parameters and manage the community fund pool, which will receive 2% of the block rewards.
Team Introduction
The Celestia team has an impressive background, consisting of outstanding scholars, researchers, and engineers in the field of blockchain scalability, all of whom have rich work or entrepreneurial experience in the blockchain scalability domain.
Celestia Labs CEO Mustafa Al-Bassam holds a PhD in blockchain scalability from University College London. He previously co-founded the sharded smart contract platform Chainspace, which was later acquired by Facebook.
CTO Ismail is the Chief Technology Officer of Celestia Labs and has worked as a software engineer at Tendermint (the parent company of Cosmos), Interchain Foundation, Google, and other companies, possessing extensive experience in blockchain technology. CRO John has a PhD in computer engineering from the University of Toronto and has served as a researcher and engineer at ConsenSys, later co-founding the Optimistic Rollup solution Fuel Labs. COO Nick holds a master's degree from Stanford University and was previously a co-founder of the public chain Harmony.
Investment Institutions
In March 2021, Celestia completed a $1.5 million seed round of financing, led by Binance Labs, with other investors including Interchain Foundation, Maven 11, KR1, Signature Ventures, Divergence Ventures, Dokia Capital, P2P Capital, Tokonomy, Cryptium Labs, Michael Ng, Simon Johnson, Michael Youssefmir, and Ramsey Khoury.
On October 20, 2022, Celestia Labs announced the completion of $55 million in Series A and B financing, led by Bain Capital Crypto and Polychain Capital, with participants including Placeholder, Galaxy, Delphi Digital, Blockchain Capital, NFX, Protocol Labs, Figment, Maven 11, Spartan Group, FTX Ventures, Jump Crypto, W3.Hitchhiker, and a number of angel investors. An informed source revealed to Coindesk that this fundraising made Celestia a unicorn valued at $1 billion, with four times oversubscription.
Summary
Modular blockchains are seen as one of the main trends in the future development of blockchain architecture, and Celestia plays an important role in this. The success of Celestia benefits from the successful practices of Rollups and the technological advancements of Ethereum.
Looking ahead, it is important to focus not only on the development progress of the Celestia project itself but also on the Ethereum Cancun upgrade and the development of upstream and downstream sectors. With the popularization of blockchain technology and modular public chains, Celestia will demonstrate greater potential and value.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




