Decentralized Science (DeSci) is revolutionizing the way funding, data sharing, paper publishing, and research collaboration are conducted in the scientific field through blockchain and decentralized mechanisms. Projects like VitaDAO, AthenaDAO, and GenomesDAO are representative initiatives driving the development of DeSci concepts.
Author: Hans Be
Translation: Plain Blockchain

What is Decentralized Science (DeSci)? Decentralized Science (DeSci) refers to the use of blockchain technology and its related features, such as Tokens, NFTs, and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), to promote openness, incentives, and community-driven collaboration in scientific research. Through DeSci, researchers can share data, publish papers, and obtain funding without traditional intermediaries, thereby enhancing the transparency and innovative development of science.
As many revolutions are driven by technology, and most topics discussed by CoinGecko often revolve around decentralized systems, the scientific field will also undergo similar transformations—transformations that will change the ways of research, publishing, financing, and collaboration, attempting to provide solutions to many issues in the scientific domain. In this article, we will explore this relatively new concept: Decentralized Science (DeSci), and delve into representative projects that have ambitious goals in this field.

1. What is Decentralized Science (DeSci)?
In an interview, Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin described Decentralized Science (DeSci) as a concept aimed at answering:
"What emerging open decentralized technologies can make science better?"
This statement encapsulates the core idea of decentralized science.
Before diving deeper, let's set aside various popular terms associated with blockchain and focus on the primary application scenario of decentralized blockchain technology: improving systemic issues in scientific research, fostering better collaboration, and enhancing funding efficiency.
1) DeSci: A Broad Concept
DeSci, or Decentralized Science, is a broad concept that encompasses many dynamic approaches and themes aimed at democratizing scientific research and discovery. It involves not only blockchain-based projects but also various forms of scientific advancement driven by emerging technologies like DAOs and Web3.
Problems in Traditional Science and the "Valley of Death"
In traditional science, the "Valley of Death" is a commonly used metaphor referring to the critical stage between basic scientific research and the successful development of beneficial innovations for patients. At this stage, many studies stagnate due to a lack of funding, resources, and effective collaboration methods.
To cross this "Valley of Death," we need a brand new, more effective approach. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized, transparent, and community-driven characteristics, is expected to play a significant role in this process. The following sections will analyze specific issues in traditional science and explore how decentralized science can alleviate these challenges through innovative solutions.
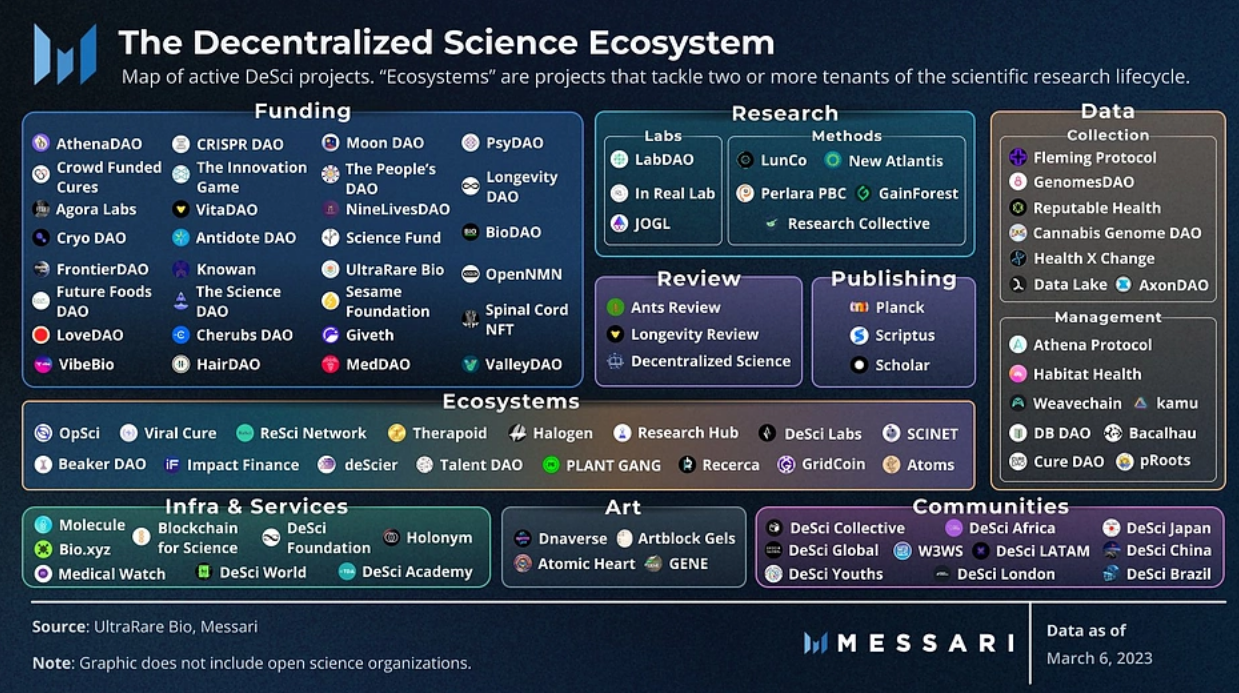
There are many areas in the scientific field that urgently need innovation, and beyond the solutions currently offered by many DeSci projects, there may be more branches in the future that require upgrades.
The key focus areas of decentralized science currently include:
A. Data Sharing: Overcoming traditional, outdated data-sharing systems to enhance traceability, ownership, and sovereignty of data. This helps ensure the transparency and accuracy of research data and promotes broader collaboration.
B. Research and Publishing: Revolutionizing the research and publishing processes. The traditional publishing model has been a focal point of criticism in the scientific community, facing issues such as high costs, lengthy peer review times, and a lack of transparency. DeSci aims to improve these issues through decentralized platforms, enhancing the accessibility and fairness of academic outputs.
C. Funding: With the rise of borderless and immutable funding methods driven by cryptocurrencies, scientific research has welcomed a new crowdfunding model. This new funding approach can help more research projects obtain the necessary financial support, no longer relying on traditional government and institutional funding, significantly broadening the sources of research funding.

According to Messari's overview of DeSci projects
In the following sections, we will focus on some projects that consider themselves part of the Decentralized Science (DeSci) category, many of which identify as Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).
2) Research and Publishing
One of the biggest challenges facing traditional science, which anyone involved can deeply relate to, is that before research begins, and even when research results reach the publishing stage, a multitude of requirements must be met. Here are some challenges:
Peer Review Issues: Peer review is an indispensable part of scientific research, but it often brings limited value and significantly slows down the dissemination of new discoveries. Peer review can create a false impression of quality assurance, and in some cases, positive reviews are even required to ensure that research can be published.
Intellectual Property: Another complex factor is the protection of intellectual property (IP), such as patents, which can hinder the open sharing of information and slow down scientific progress. Many universities view patents as potential revenue sources and implement strict policies governing the use of any "proprietary" work.
Gatekeepers: In addition to various restrictions during the research process, the publishing field also faces similar gatekeeping. Even if scientists are willing to make their research results public, academic journals still control whether the research can be published. Journals, as the primary "gatekeepers" of research, often prioritize their commercial goals over promoting open science.
High Costs: Many academic journals have been criticized by the academic community for their high open-access publishing fees, accused of having unethical profit levels that even exceed those of some tech giants.
The income of these "gatekeepers" largely comes from the unpaid labor of the academic community—including the work of reviewing and writing research papers, which is often supported by public and charitable funding. Should we just let this continue? This could prevent some life-changing discoveries from being published.
3) Blockchain Solutions in Scientific Research and Publishing
This leads to a discussion of how blockchain technology can provide solutions for improving scientific research and publishing.
A. Open Science - Decentralized
It is necessary to decentralize the existing centralized structures and their problems. This is a (more) open science approach, where platforms redefine themselves as open collections focused on open sharing, and peer review should not introduce unnecessary delays.
This new system can recognize various forms of scientific contributions beyond journal publishing, as many breakthroughs in scientific history have come from individuals outside the scientific establishment. These opposing viewpoints have disrupted mainstream scientific thinking and provided us with new perspectives.
ResearchHub: A Crypto-Driven Scientific Discussion Platform
ResearchHub is a platform aimed at promoting a collaborative open science model, where researchers can share their favorite research articles, discover new papers, and engage with the scientific community.
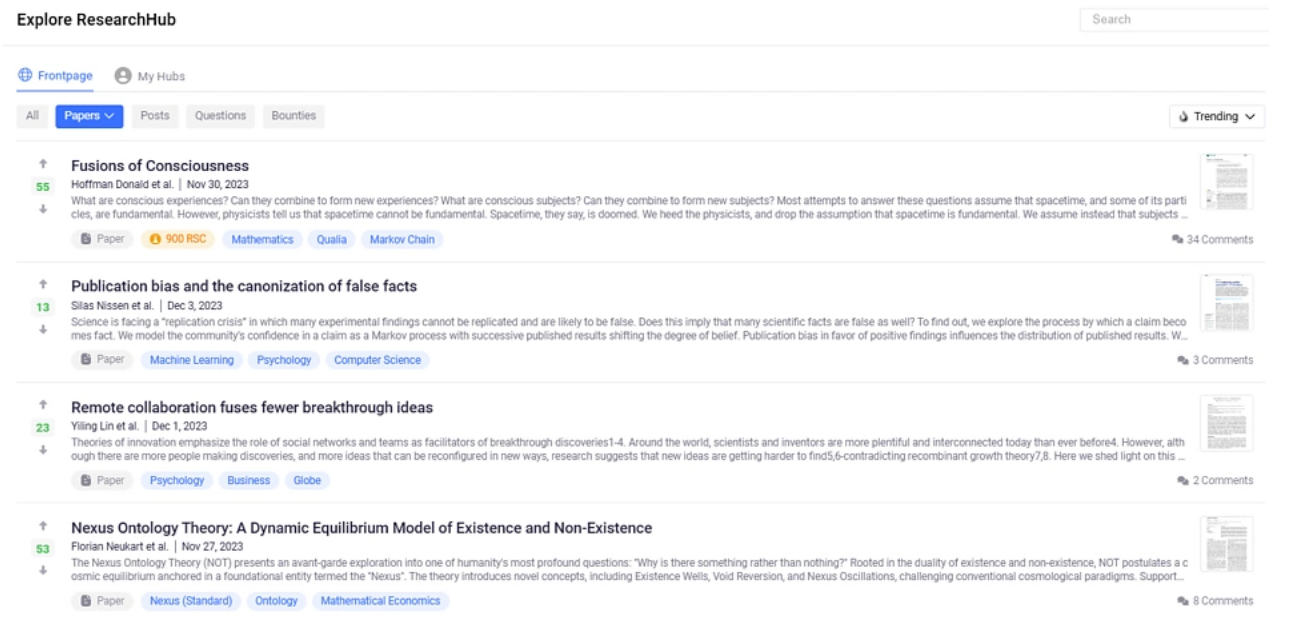
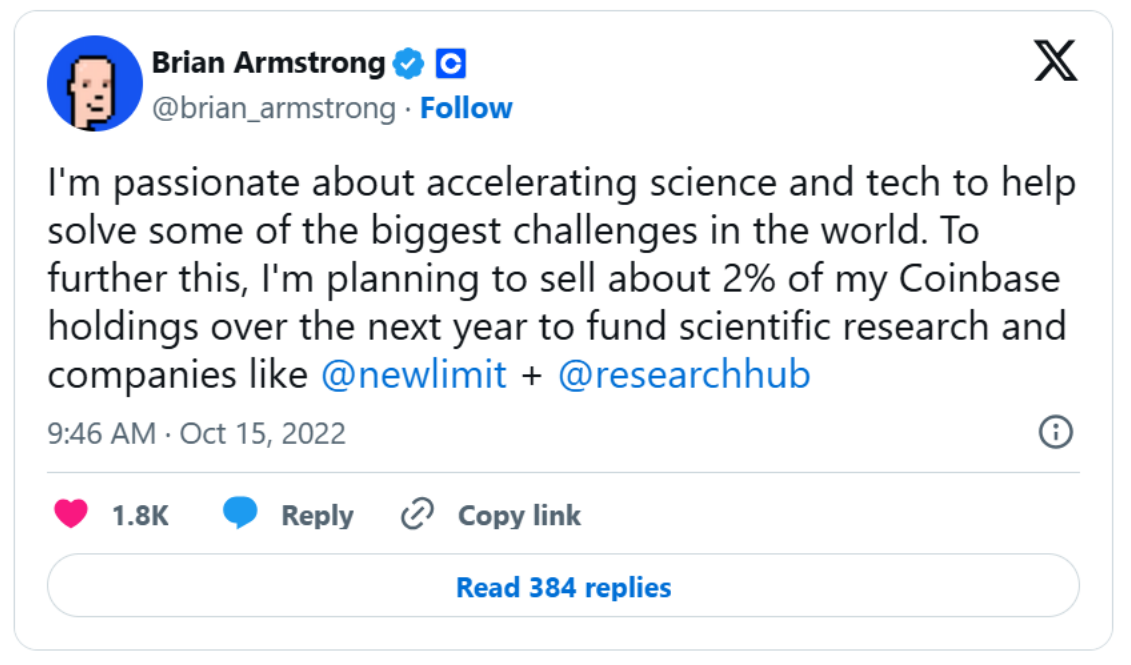
Their ultimate goal is to become the preferred platform for scientific discussions, rewarding contributors through incentive mechanisms to accelerate scientific breakthroughs. The project is supported by Coinbase founder Brian Armstrong, who is passionate about solving the world's biggest problems through technology. His enthusiasm even led him to sell 2% of his shares in Coinbase to fund ResearchHub—truly a philanthropist!
The incentive mechanism operates through the ResearchCoin (RSC) Token, which is a community reward token and the currency of ResearchHub. Users can earn RSC by actively participating in platform activities, such as uploading papers, commenting, creating posts, etc.
Additionally, users can also earn RSC if other users deem their contributions valuable. Furthermore, they can create bounty tasks for community members, and completing specific tasks will also yield RSC rewards.
B. Tokenization of Intellectual Property – IP-NFTs
Non-fungible Tokens (NFTs) have the potential to fundamentally change the ownership and management of intellectual property, allowing creators and researchers to maintain control and monetization opportunities, rather than being controlled by the institutions that publish research.
They can represent unique digital assets such as research papers, patents, datasets, and code, and can be used to prove ownership, with all information verifiable on the blockchain. Transparency is key, and the peer review process can also be fully tracked, including reviewers and published comments.
4) Funding Issues in Traditional Science
The funding application process in traditional science is lengthy and complex, filled with administrative issues and regulations imposed by different institutions, which may require further updates and improvements.
A. A Large Number of Grant Applications
In the traditional academic world, applying for grants requires writing a large number of applications and listing many tasks in advance. This lengthy pre-publication work can hinder risk-taking and innovation. More importantly, to secure funding, researchers often need to cater to the interests of potential funders.
B. Asymmetry of Interests
The concentration of top contributors is high, while the private sector is the largest source of most funding. This conflict of interest is unavoidable and often skews research results in favor of the funders' interests.
C. Lack of Incentive Mechanisms
Additionally, we observe that scientists do not receive adequate rewards, and practices such as transparency, replicating others' work, and pursuing high-risk/innovative ideas do not receive sufficient compensation. This may lead to many valuable directions being unexplored, resulting in numerous missed opportunities.
5) Blockchain Solutions to Funding Issues in Science
Now, let's look at some blockchain-based solutions that address funding challenges in the scientific field.
A. Fundraising through Tokenization
As mentioned earlier, IP-NFTs can not only represent ownership of intellectual property but also raise funds for projects. Scientists can sell their IP-NFTs to investors, who can benefit from the income generated by the intellectual property. By tokenizing intellectual property, it can bring liquidity to early development stages, helping to overcome the "Valley of Death" barrier.
Molecule Protocol: Science and Intellectual Property NFTs
Molecule is a platform that bridges the gap between biomedical research projects and the funding they need. It primarily serves two types of users: researchers and investors.
Researchers with specific research goals, projects, or ideas can find various types of investors, from traditional pharmaceutical venture capital firms to patient advocacy groups and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
Molecule aims to provide IP-NFT legal frameworks, organizational templates, funding, talent, and other resources for biotechnology DAO builders. Specific disease DAOs funded by patients and researchers can shorten feedback cycles.
B. Intellectual Property Non-Fungible Tokens (IP-NFT)
The platform will use IP-NFTs, which are similar to standard NFTs as they manage ownership of specific assets and serve as keys to access underlying projects. For example, if a research project generates a dataset or obtains a patent, the IP-NFT can access this data stored in a decentralized data storage system. This also allows for the trading of intellectual property.
C. Venture Capital Funding
Fundraising through tokenization not only brings liquidity in advance and changes short-term risk allocation but also enables ongoing fundraising or earlier assessment of whether a project is worth pursuing.
This different risk allocation means that different types of investors and capital scales can participate. Anyone can fund and drive innovation at the earliest stages. This resembles a model of venture capital or startup funding.
For example, we saw Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin donate $1.5 billion in SHIB to Crypto Relief India in 2021. The fund currently has over $200 million, primarily in USDC. The rapid distribution of this funding relies on blockchain technology.
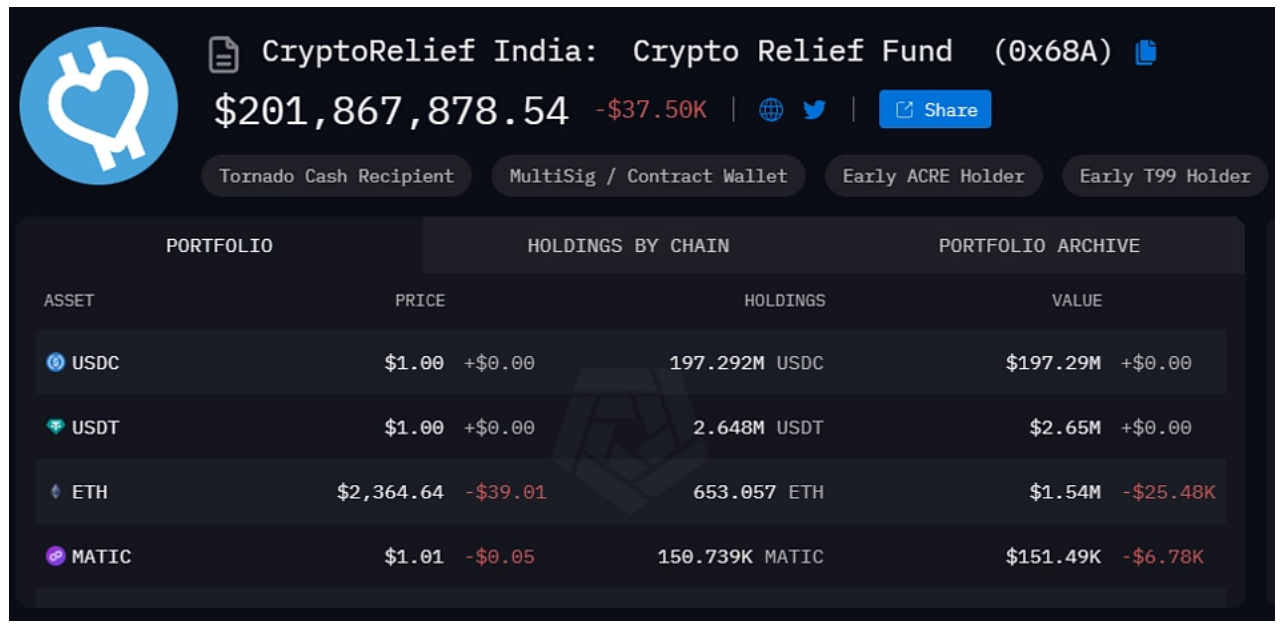
Source: 0x68A99f89E475a078645f4BAC491360aFe255Dff1
2. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
The aforementioned problems and challenges are often systemic issues. Bureaucratic inertia prolongs processes, and the imbalance of incentives in project control means that if we want different outcomes, we must change these control mechanisms.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are a broad array of projects and innovative solutions with unique capabilities to allocate funding and control processes.
This new type of decentralized organization provides a platform for like-minded individuals and can be led by experts when evaluating funding proposals. Governance proposals from the scientific community will be decided through on-chain voting.
When discussing the decentralized scientific ecosystem, it is essential to mention many DAOs that are taking on the new DeSci narrative, where interoperability between DAOs is the rule rather than the exception.
1) VitaDAO
VitaDAO is the first collective funding early-stage longevity research, aiming to extend healthy lifespans and health spans by raising funds for early research projects and incubating startups for commercialization. It has raised $4.1 million, supported by Pfizer and former Coinbase CTO Balaji Srinivasan.

One of the most important trends is the decentralization and democratization of emerging therapies in the biotechnology field. VitaDAO aims to decentralize these assets, making them widely accessible to people around the world.
Over the past few decades, the biopharmaceutical system has largely been monopolized by pharmaceutical companies through patents. If led by VitaDAO, this status quo will change as they challenge the monopoly of the traditional biopharmaceutical system by decentralizing the acquisition of intellectual property and democratizing its ownership.
2) Athena DAO: A Research Center Focused on Women's Health
Funding for women's health research is insufficient. In fact, menopause and its related symptoms do not appear in the global burden of disease databases, which track the leading causes of death and disability. This indicates a lack of adequate research and appropriate solutions for women's health issues, which could have serious consequences.
Athena DAO's mission is to change the landscape of women's health research. A global decentralized community is needed to drive critical shifts in understanding and treating women's unique health needs and diseases.
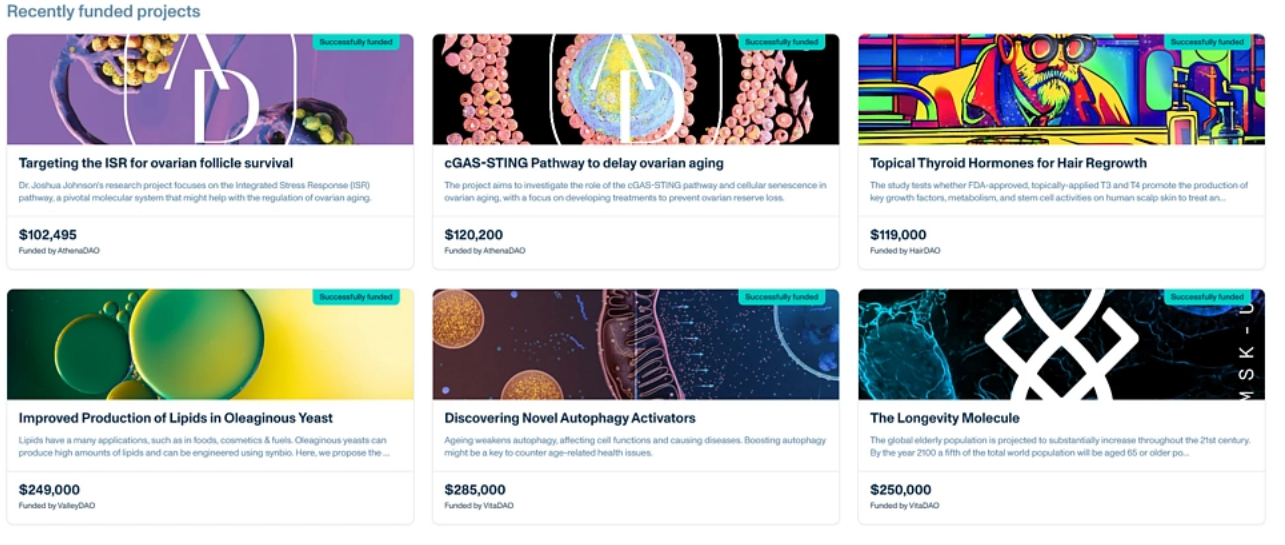
Athena DAO is evaluating treatments, computational models, and research projects related to ovarian aging, menopause, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and uterine fibroids.

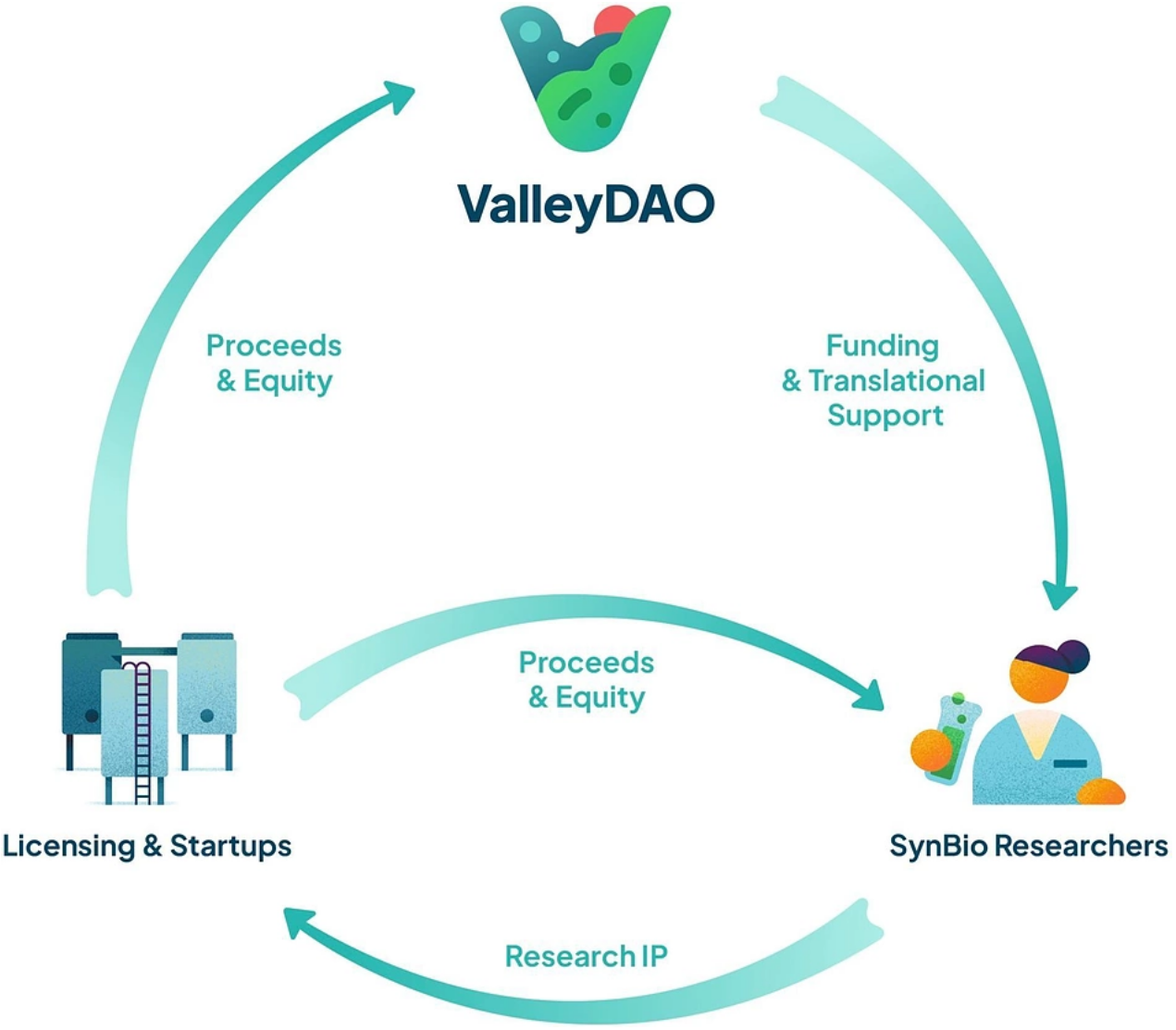
3) Valley DAO: Synthetic Biology Solutions for Climate Change
ValleyDAO is a community of scientists, entrepreneurs, and enthusiasts aimed at making synthetic biology more accessible, a field with tremendous potential in addressing global sustainability challenges.
By engineering new biological systems and modifying existing ones, synthetic biology can be used to tackle challenges related to climate change, disease, food, and energy production. For example, developing new sustainable energy sources, creating bacteria that can clean up pollution, and growing more nutritious crops.
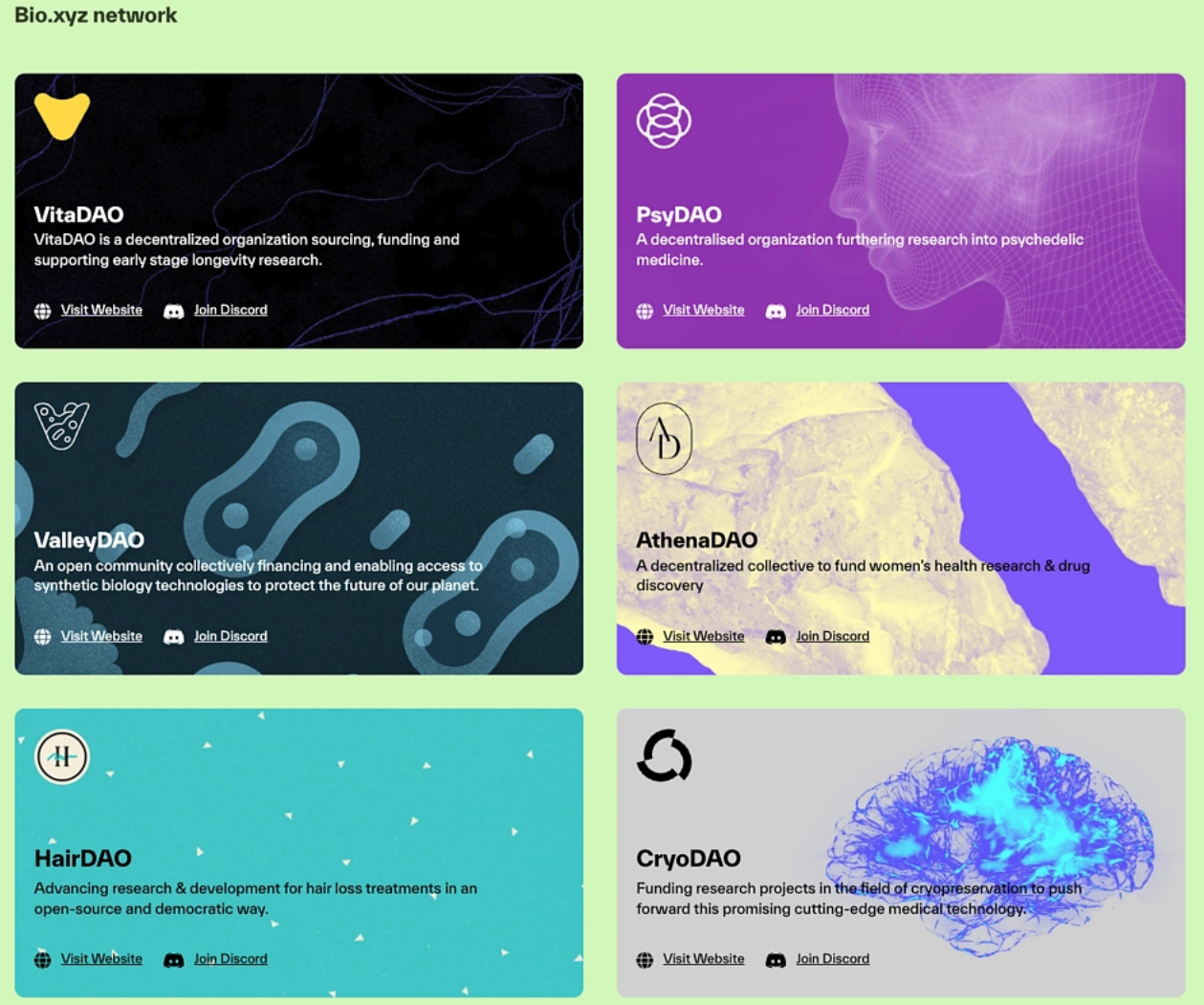
4) Bio.xyz: DeSci DAO Accelerator
Bio.xyz is an accelerator supporting several of the previously mentioned DAO projects, such as VitaDAO, ValleyDAO, and AthenaDAO. This means that through Bio.xyz's Launchpad platform, these DAOs can obtain generated tokens through token auctions.
Individuals wishing to apply for BioDAO launch must submit an application, which will undergo thorough review. Once successful applicants are selected, they will receive the first funding from BioDAO based on the completion of necessary milestones. Non-DAO participants can also engage in real-time auctions, ensuring they have sufficient balance in their wallets to bid, monitor auction progress, and claim token allocations.
5) Genomes DAO
GenomesDAO is based on the belief that everyone should own their own genome. Their goal is to establish the world's largest user-owned genomic database and share it with the public, organizations, and researchers. It is committed to meeting the growing expectations of research institutions, organizations, and clients regarding the security of genomic data and the quality of research workflows.
Data is securely stored in users' personal DNA vaults, which they can control through the Genomes mobile application. Researchers from pharmaceutical/biotechnology companies and academia can easily query the database to help understand the causes of diseases and develop new drugs, all while respecting individual privacy and ownership.
How to sequence DNA on Genomes? Get your DNA sequenced through Genomes.io:
Click "Get DNA Sequenced" and log in.
Choose a sequencing provider and order a kit.
Use the code in the kit to activate it online.
Download the Genomes.io application.
Scan the QR code on the kit activation page.
Follow the instructions to complete the process.

The integration of DAOs in scientific research not only democratizes decision-making but also paves the way for more collaborative and open scientific research, marking a revolutionary step forward.
6) INNBC: Innovative Biological Research Coin

INNBC has published peer-reviewed papers on the application of blockchain technology in scientific research. The study involves the decentralization of biomedical data storage and sharing, and how features such as immutability, timestamps, and identity can ensure the permanent availability of data, provide proof of existence, and protect authors' rights.
3. What is the Future of Decentralized Science (DeSci)?
The future of decentralized science is unfolding rapidly, with extensive debates surrounding its effectiveness and necessity. Some believe it will promote inclusivity and freedom in scientific research, while others worry it may face strong opposition from traditional academic circles and large pharmaceutical companies, which often become "too big to fail" with the help of regulators.
The future of decentralized science holds immense potential, and if implemented correctly and cautiously, it could give rise to a new economic and social system that redefines the priorities of progress and profit.
4. Conclusion
The combination of blockchain technology and science offers a compelling path to address systemic challenges such as the "Valley of Death," inefficient peer review, intellectual property disputes, and funding barriers.
Perhaps DAOs have the potential to transform the monopolies of the pharmaceutical industry into collaborative communities, optimizing capital and labor for the benefit of patients. Although this field is still in its early stages, it represents an exciting new frontier for decentralized science.
However, we should not overlook that decentralized science will be based on universal mechanisms of blockchain technology, but this does not mean it must be limited to blockchain, as the answers will depend on how these technologies and methods facilitate the scientific method and in what areas they play a role.
Note: The information in this article is for educational reference only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. Always conduct your own research before investing in any protocol or token.
Article link: https://www.hellobtc.com/kp/du/11/5537.html
Source: https://www.coingecko.com/learn/what-is-desci-decentralized-science
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




