Original | Odaily Planet Daily (@OdailyChina)
Author | Nan Zhi (@Assassin_Malvo)

Yesterday, Trump won the U.S. election, leading Bitcoin to break its historical high, reaching a peak of 76,400 USDT, and the entire crypto market rose accordingly. The U.S. election is the most critical event following the Bitcoin spot ETF and Ethereum spot ETF, and after the election, the pace of the Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts has become one of the few core issues at the macro level.
At 3 AM this Friday, the Federal Reserve will announce its interest rate decision. How much will it cut this time? Will there be significant easing in the coming months? Odaily will summarize various viewpoints in this article.
November rate cut of 25 basis points is a certainty
Market has priced in a 25 basis point rate cut
First, on the data front, according to CME FedWatch, the Federal Reserve's 25 basis point rate cut in November is nearly fully priced in, with a current probability of 96.8%.
According to Jin10, considering that Federal Reserve Chairman Powell has previously stated that a reasonable rate cut speed should be 25 basis points, combined with the relatively stable economic data over the past two months, despite a significant weakening in October's non-farm payrolls, which was largely affected by one-time factors. Therefore, a 25 basis point rate cut by the Federal Reserve this week remains a high probability event, rather than a further cut of 50 basis points or no cut at all.
Impact of expansionary fiscal policy after Trump's victory
J.P. Morgan analyst David Kelly stated this Tuesday that the Federal Reserve will almost certainly cut rates by 25 basis points in its decision on Friday, even if the election takes place beforehand. However, Kelly further stated that if Trump wins the U.S. election this week, the Federal Reserve may pause its easing cycle as early as December, as Trump's expansionary fiscal policy plan will push up inflation and prevent interest rates from falling.
Kelly pointed out, "If Trump wins the election, he will adopt a more expansionary fiscal policy, which may trigger a trade war, increase the deficit, and raise interest rates."
December rate cut remains uncertain
Trump has successfully won the election, and as mentioned in the previous section, his policies will change the market economy and inflation situation. Analysts from the Edmond de Rothschild Group stated in a report that under Trump's leadership, U.S. inflation may rise rapidly. Specifically, the risks of trade tariffs and the threat of deporting undocumented immigrant workers may drive up the U.S. inflation rate. These factors could pose challenges to the Federal Reserve's efforts to curb inflation. They stated: "As the impact of Trump's plans on inflation becomes clearer, the Federal Reserve may partially abandon its expected 100 basis point rate cut plan in its latest report."
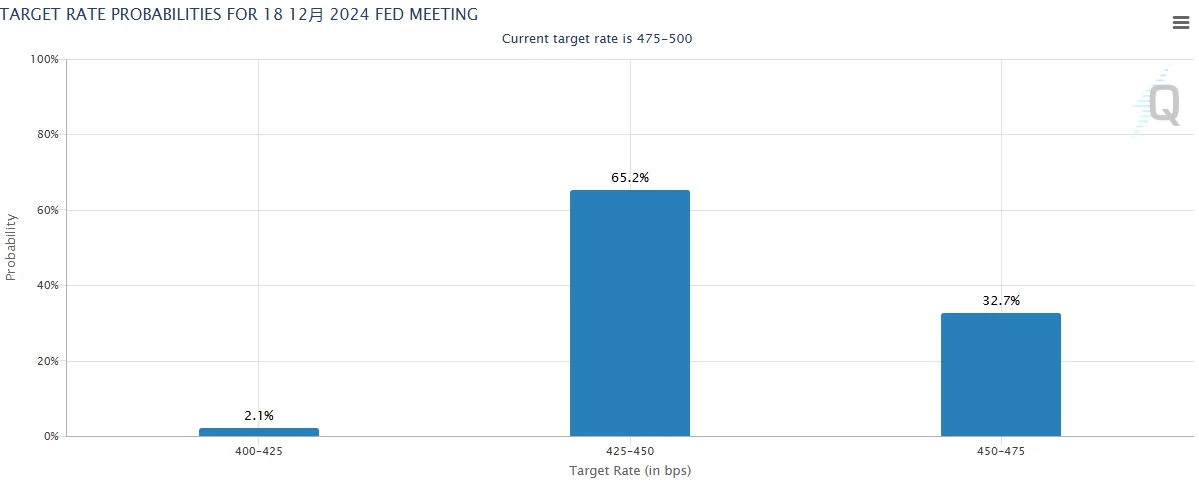
CME FedWatch data shows that the probability of maintaining a rate of 450-475 basis points in December is 32.7%, while the probability of further cutting to 425-450 basis points is 65.2%, with a 2.1% chance of cutting another 25 basis points.
Nordea Bank analysts stated that with Trump's victory in the U.S. election and the Republican Party likely controlling both the House and Senate, the market should expect that most of his campaign promises will be fulfilled.
The Federal Reserve may automatically cut rates by 25 basis points tonight and in December, as they believe the current interest rate is restrictive. If the current strong economic development continues, combined with the impact of Trump's victory, the Federal Reserve should soon become less certain about the necessity of these preemptive rate cuts.
The impact of Trump's policies on inflation will take some time to reflect in CPI data, but we should start seeing effects on more hiring and lower immigration early next year. We are uncertain when the Federal Reserve will ultimately decide to stop cutting rates, but it is most likely that the Federal Reserve will cut rates by another 25 basis points in March next year, although there is also a significant chance that they will not cut rates in 2025.
What is the mid-term outlook? Rate cuts may be nearing an end
Fund management company Navellier stated that the expected rate cut by the Federal Reserve this time may be the last one, as the Federal Reserve does not like to go against market interest rates. However, the specific situation still depends on the FOMC statement and Federal Reserve Chairman Powell's press conference on Friday.
Not only do many viewpoints suggest that the Federal Reserve's rate cuts are nearing their mid-term end, but market data also shows the same tendency. According to Jin10, interest rate futures traders continue to bet that the Federal Reserve will cut rates by 25 basis points this week and in December, but now expect the Federal Reserve may stop cutting rates after two 25 basis point cuts in the first half of 2025, bringing the federal funds rate target range down to 3.75%-4%.
The underlying logic of Trump's victory and the pace of rate cuts
Why will Trump's victory ultimately lead to a slowdown or even an end to rate cuts? CICC provided a specific explanation in a research report:
The report pointed out that the U.S. real GDP year-on-year growth rate for the third quarter of 2024 was 2.8%, slightly below the market expectation of 3.0%, and a slight decline from the 3.0% in the second quarter, but still a bright report card.
In terms of components, personal consumption expenditures were strong, corporate equipment investment expanded, and exports and government spending accelerated, indicating that U.S. economic growth remains healthy. Relatively weak were real estate investment and construction investment, showing that high interest rates are still having a suppressive effect. Additionally, inflation further declined in the third quarter, indicating that the U.S. economy is heading towards a soft landing. CICC believes that the Federal Reserve does not need to cut rates significantly at this time.
Under normal assumptions, CICC expects the Federal Reserve to continue cutting rates, but the pace of cuts will slow, and the terminal (neutral) rate may also be higher than the baseline scenario of 4%.
In extreme scenarios, the Federal Reserve's stance will turn "hawkish" and restart rate hikes in 2025, as decision-makers are unlikely to tolerate inflation rising back above 5%. Considering that curbing inflation generally requires the nominal policy rate to be above inflation (i.e., the real policy rate to be positive), this means the Federal Reserve may need to raise rates by 75 to 100 basis points in 2025.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




