On October 31 at 16:00, the AICoin editor conducted a graphic and text sharing session titled "Decoding the Economic Trio: Interest Rates, CPI, and Non-Farm!" in the 【AICoin PC - Group Chat - Live】. Below is a summary of the live content.
First Movement: Interest Rates
The market is currently speculating about a potential interest rate cut in the U.S. for November. The interest rate cut involves the Federal Reserve's interest rate, which actually adjusts the U.S. federal funds rate, the interest charged between banks for borrowing.
Taking interest rate hikes as an example, when the Federal Reserve raises rates, it increases the federal funds rate. After the increase, the interest (cost) for banks borrowing from each other will rise, prompting banks to increase their reserves to control costs.
【Note: Reserves refer to the cash and funds that banks hold and can use for expenditures at any time.】
To increase reserves, banks can only obtain the necessary funds from the public.
Therefore, banks will attract people to deposit money by raising deposit interest rates; at the same time, they will increase borrowing rates to suppress consumer and business loan demand, thereby controlling capital outflow.
Consequently, the ultimate result of an interest rate hike is that dollars flow into banks, reducing the amount of money circulating in the market, meaning consumers have less money, which suppresses consumer spending and achieves the goal of controlling inflation. At the same time, the dollar will appreciate, leading to a decrease in the money flowing into investment markets like the stock market. Given the close correlation with the U.S. stock market, this is a bearish signal for the cryptocurrency market.
For instance, after the Federal Reserve raised rates in 2022, Bitcoin's performance was as follows:
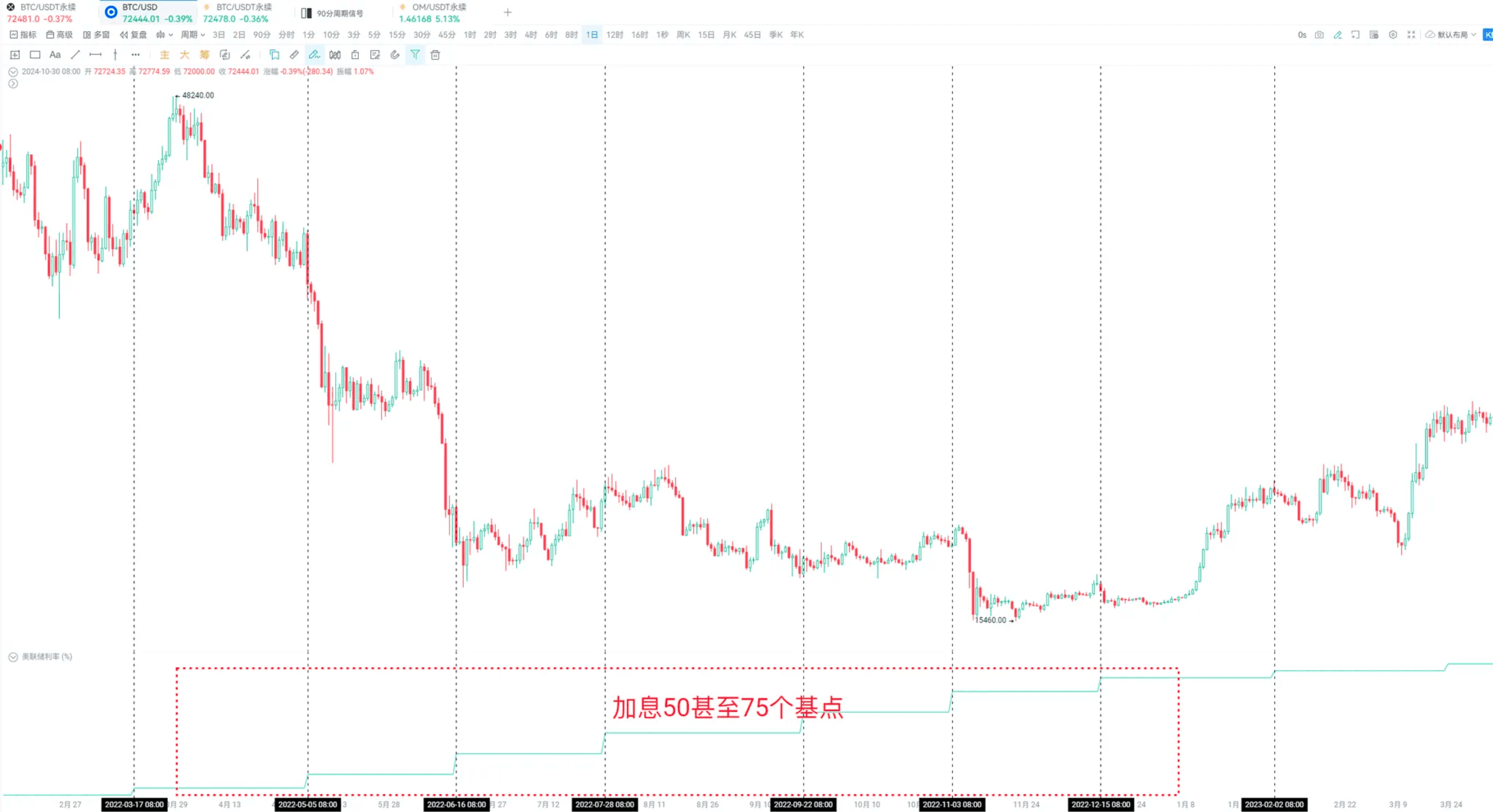
After significant rate hikes, Bitcoin generally declined.
From this, we can infer that a rate cut by the Federal Reserve is a positive signal.
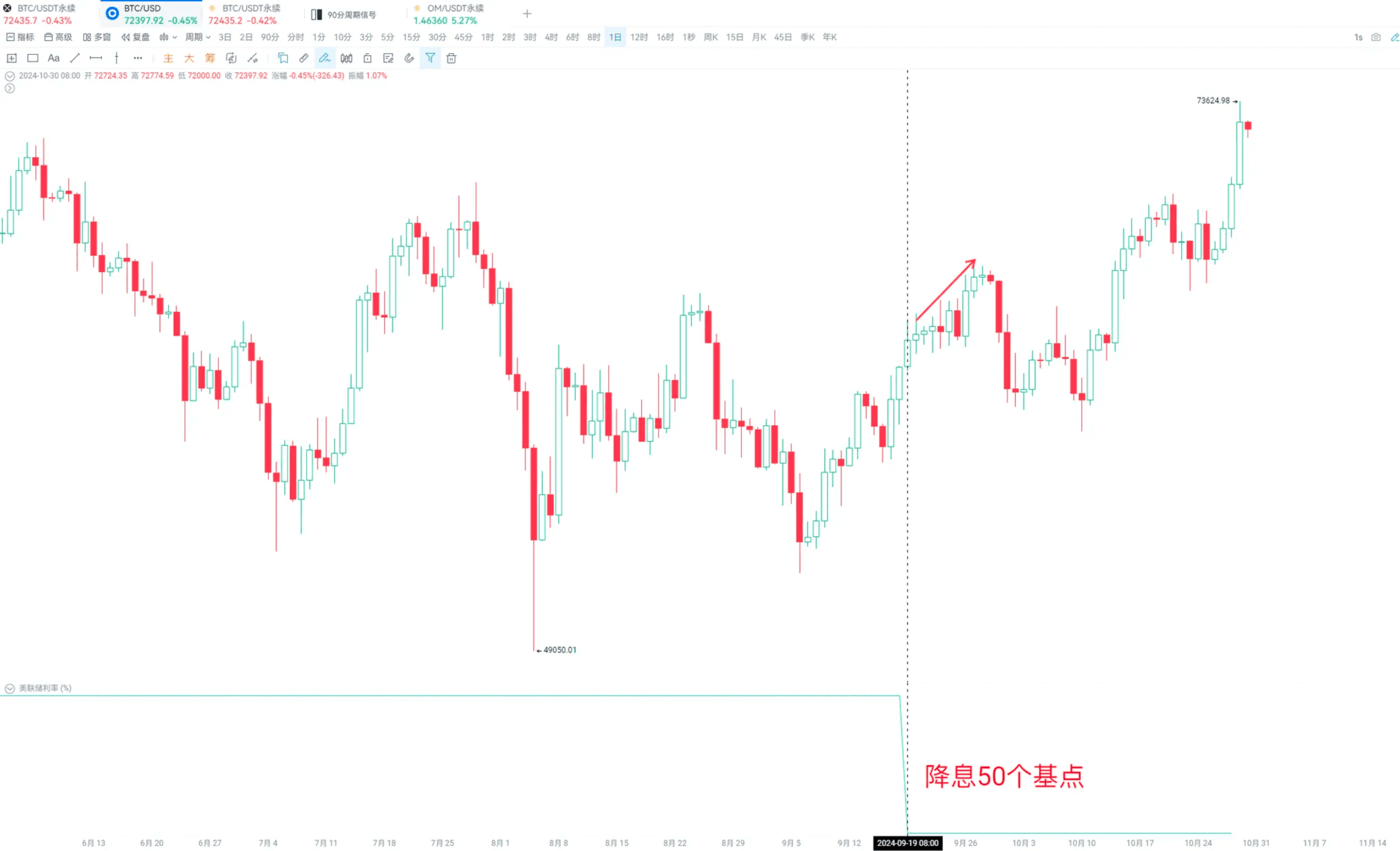
Thus, we can see that after the Federal Reserve cut rates by 50 basis points in September, Bitcoin rose.
Second Movement: CPI
Looking back at the Federal Reserve's rate hikes in 2022, they were primarily due to high inflation, which previously exceeded 7%, while the Federal Reserve's inflation target is 2%. Therefore, the Federal Reserve took measures to raise interest rates.
This brings us to our second indicator:
CPI (Consumer Price Index), also known as the U.S. Consumer Price Index, which reflects inflation data.
Inflation means money is losing value, simply put, "money is not worth much."
As mentioned earlier, the Federal Reserve raised rates to curb inflation, so we can deduce that:
● High inflation will prompt the Federal Reserve to raise rates to suppress price increases;
● Conversely, low inflation or deflation will encourage the Federal Reserve to cut rates to stimulate economic growth.
Third Movement: Non-Farm
After a series of adjustments, U.S. inflation is now getting closer to the target, so the Federal Reserve's focus has shifted to non-farm data.
Here, it is essential to understand the responsibilities of the Federal Reserve.
【The Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States, and its primary responsibilities include formulating and implementing monetary policy to promote full employment, maintain price stability, and achieve stable economic growth. Therefore, the Federal Reserve closely monitors CPI data to assess inflation levels and non-farm employment data to understand the state of the job market, allowing for appropriate monetary policy adjustments.】
This is why, among so many economic data points, we focus on non-farm and CPI!
Next, let’s discuss non-farm data.
The core data of the U.S. non-farm employment report includes the unemployment rate and non-farm payroll numbers:
● Unemployment Rate: This refers to the proportion of unemployed individuals in the total labor force and is an indicator of labor market health. Typically, an unemployment rate below 4% is considered ideal.
● Non-Farm Payroll Numbers: This refers to the number of new jobs added in industries outside of agriculture and serves as an indicator of labor market strength.
○ Generally, when we say "the labor market is strong," it means an increase in non-farm employment and a stable or declining unemployment rate; conversely, "the labor market is weak" indicates a decrease in new non-farm jobs or sluggish growth, along with an increasing unemployment rate. The former will prompt the Federal Reserve to raise rates, while the latter will lead to rate cuts.
○ A strong labor market means an increase in employment, which is related to wages. With jobs come wages, and with wages comes the ability to consume. Overheating consumption can lead to inflation, which in turn can lead to Federal Reserve rate hikes. Similarly, a weak labor market means reduced disposable income for consumers, leading to slower economic growth and concerns about recession. To stimulate economic activity, the Federal Reserve may cut rates, putting money back into consumers' pockets. Rate cuts essentially mean "injecting liquidity," where consumers' money is no longer sitting in banks but is instead invested in the stock market and other markets, which is a positive signal.
【All of this occurs under macroeconomic regulation.】
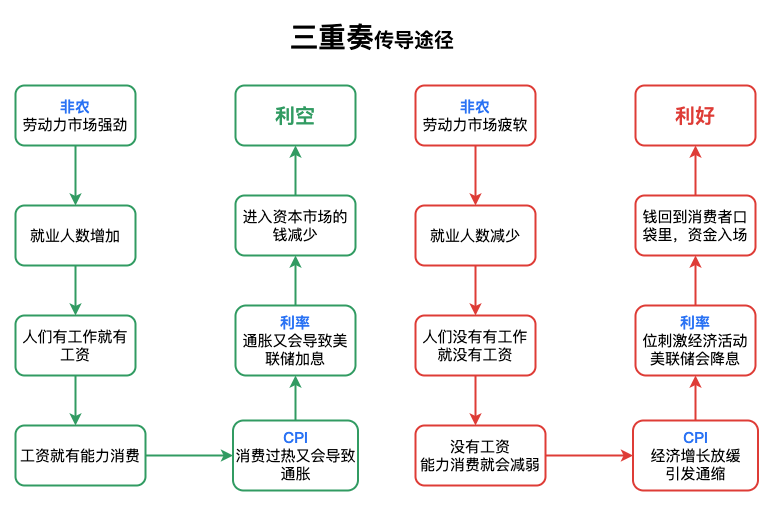
○ In terms of the labor market, the ideal situation is a declining unemployment rate alongside an increase in non-farm employment. The least ideal situation is a rising unemployment rate with a decrease in non-farm employment.
Theoretically, a decrease in inflation (CPI data) would lead the Federal Reserve to act positively; a declining unemployment rate with an increase in non-farm employment would increase consumers' disposable income (without causing inflation), which is also positive.
However, the actual market conditions are not always like this, especially this year, where preemptive expectations are quite common. Many positive events this year have turned out to be negative because people anticipated them too early.
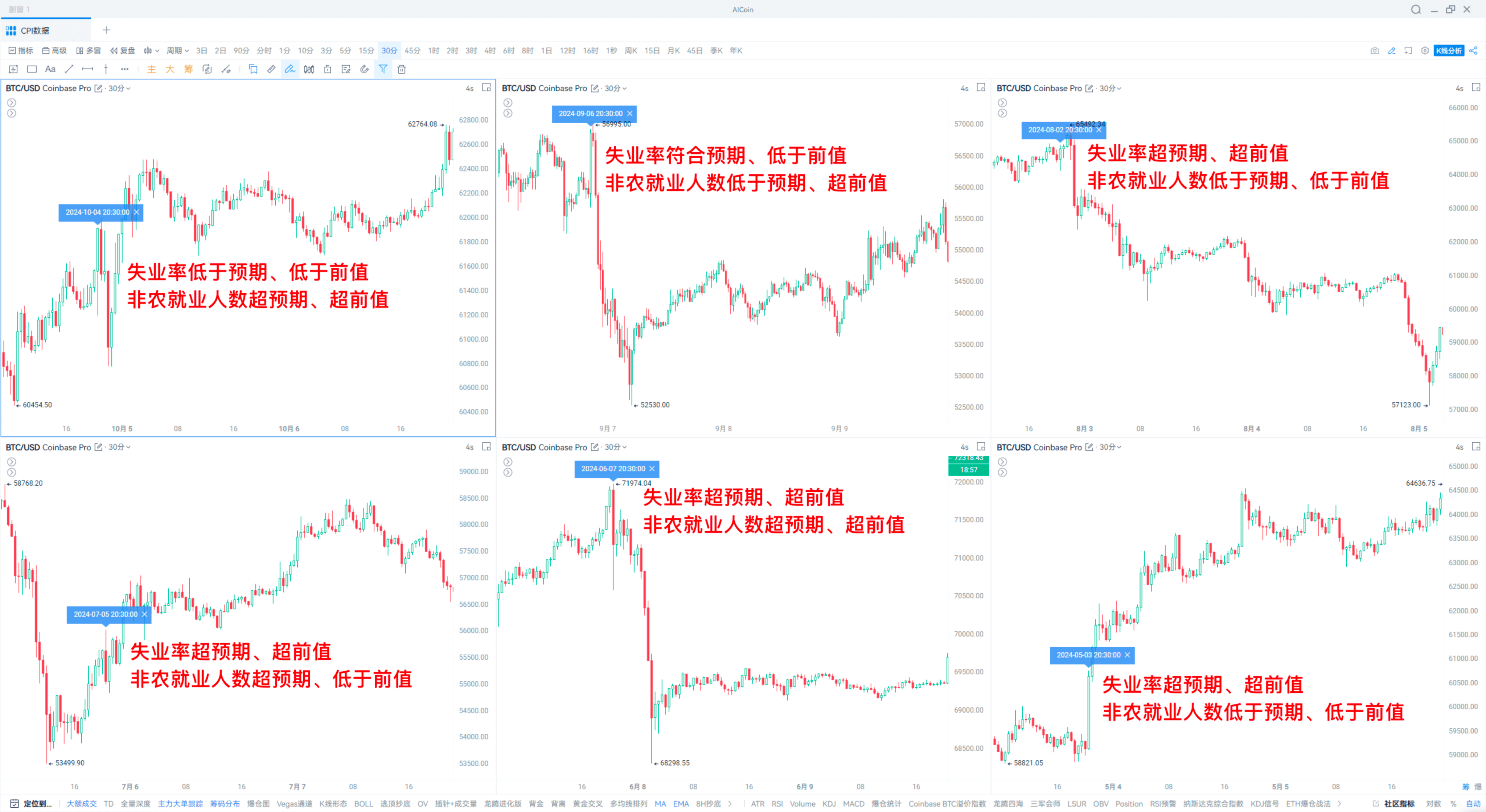
In the past six months, the trend after non-farm data releases has generally been downward, even when the unemployment rate decreases and employment numbers exceed previous values.
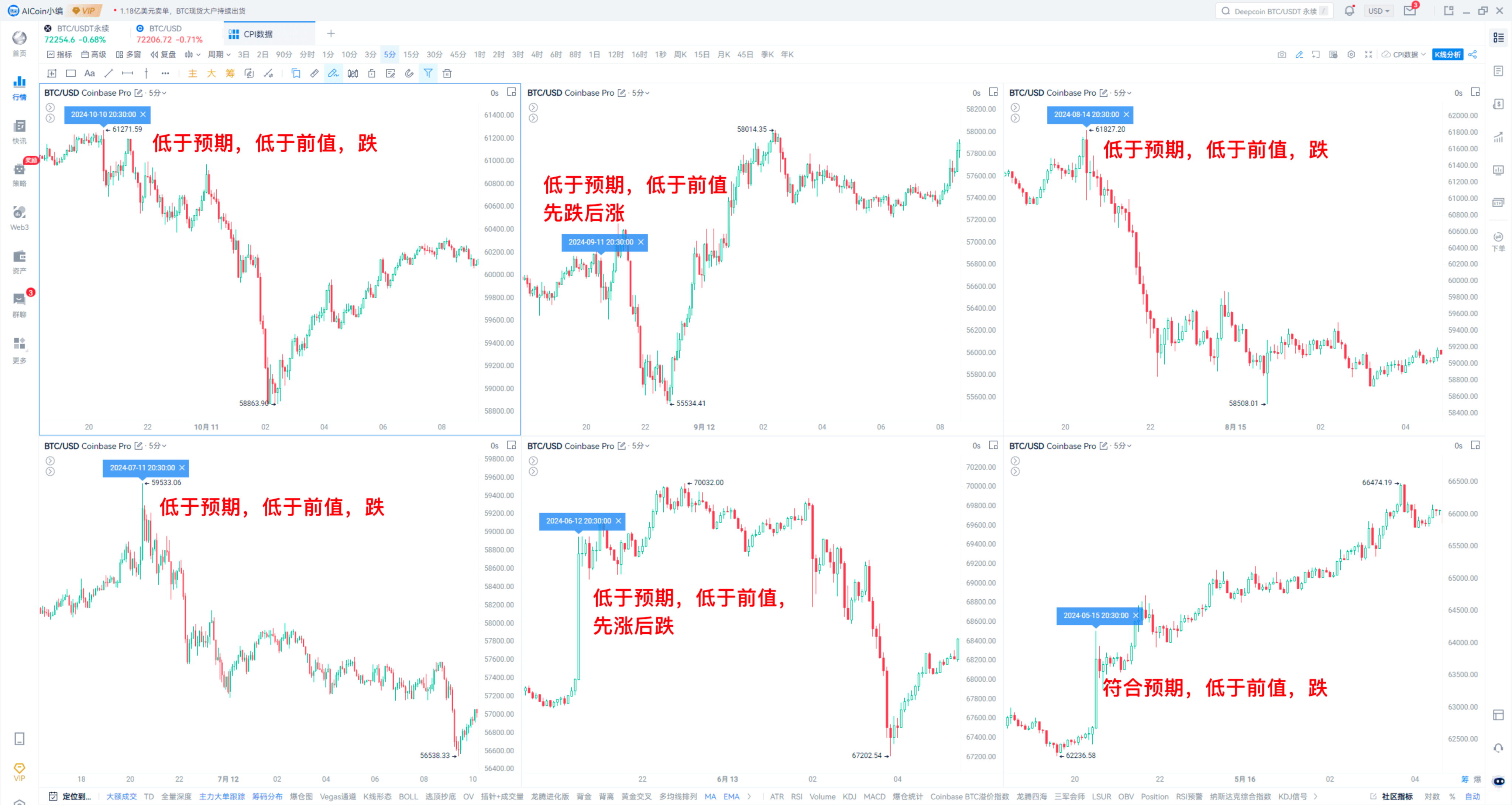
The inflation data follows a similar pattern, with many instances of prices rising before data releases and falling afterward, making it difficult to interpret. Therefore, at this time, it is essential to pay attention to short-term support and resistance levels, which can be observed through the peak of positions or moving averages, focusing on whether the closing price breaks through.
When macroeconomic data is released, it is advisable to monitor Bitcoin, the U.S. dollar index, and Nasdaq futures together. You can use multiple windows or add the indices to sub-chart indicators for easy comparison, as Bitcoin has an inverse relationship with one and a direct relationship with the other.
For example:
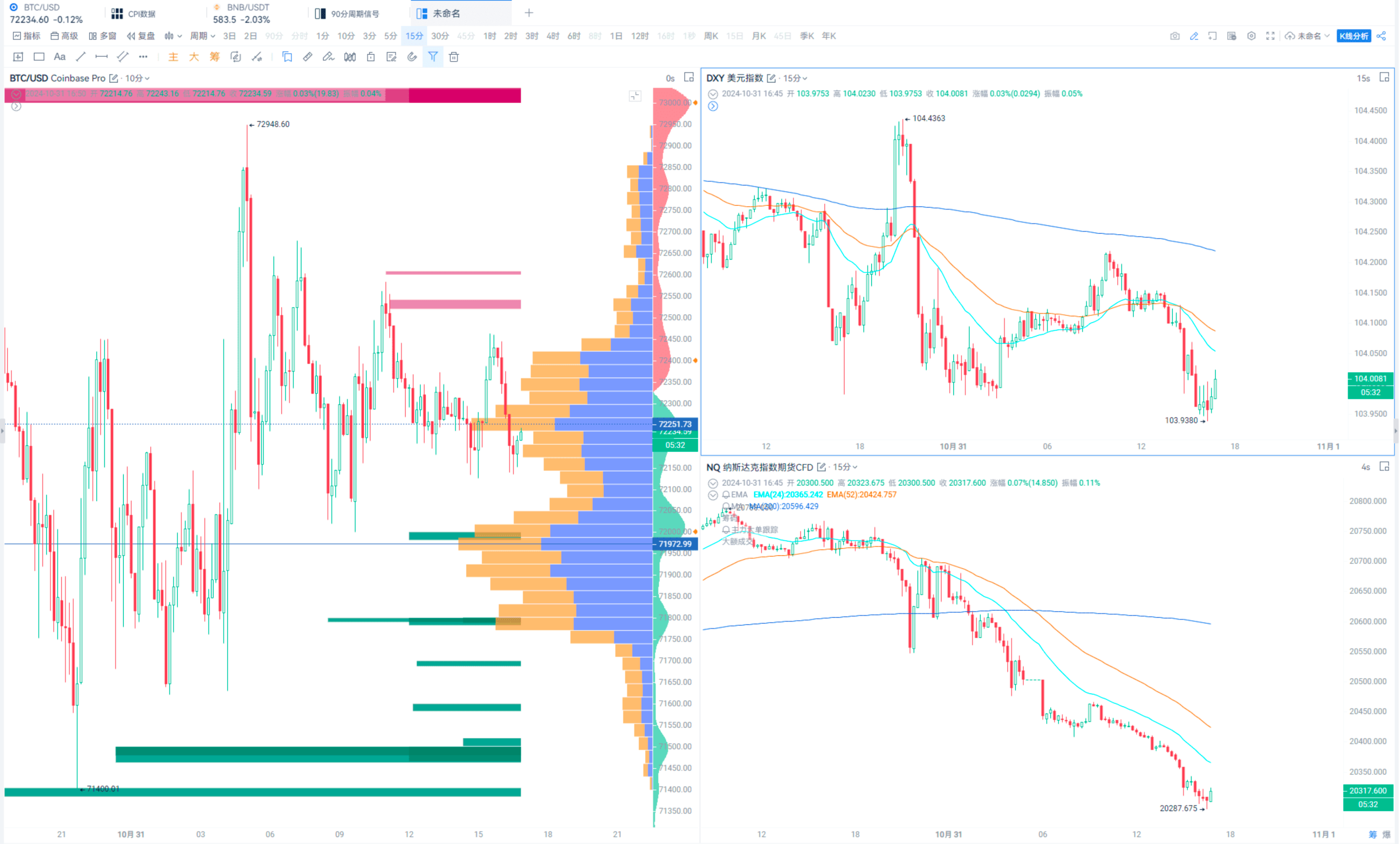
This concludes the content of this sharing session.
Thank you for watching. We hope every AICoin user can find suitable indicator strategies and enjoy abundant financial resources!
Recommended Reading
For more valuable live content, please follow the AICoin section “AICoin - Leading Data Market and Intelligent Tool Platform”. We welcome you to download “AICoin - Leading Data Market and Intelligent Tool Platform”.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。