Hyperinflation severely affects countries like Venezuela and Argentina. Although traditional solutions have proven ineffective, cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and stablecoins are becoming important tools for individuals to resist inflation.
Author: CoinGecko
Translation: Blockchain in Plain Language

Hyperinflation is an economic disaster characterized by skyrocketing prices of goods and services and the instantaneous devaluation of currency, becoming synonymous with the economic devastation in countries like Venezuela and Argentina.
While traditional methods, such as currency revaluation or price controls, are almost useless in addressing this issue, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and stablecoins pegged to more reliable fiat currencies (like the US dollar) are increasingly becoming attractive alternatives. The independence and decentralized nature of Bitcoin, along with the reliability of stablecoins, provide hope for people to withstand the most severe inflation. But can cryptocurrencies offer a truly sustainable solution for economies on the brink of collapse?
1. Causes and Consequences
Hyperinflation is an extreme form of inflation where prices soar uncontrollably, and the value of the national currency plummets rapidly. This situation triggers chaos and societal collapse. Although numerous factors can lead to hyperinflation, it typically stems from severe political turmoil, misguided economic policies, and unchecked money printing, ultimately resulting in a complete loss of confidence in the government and its institutions managing the country and economy. With few exceptions, governments that fail to maintain confidence in their currency often resort to such measures, accelerating their economic destruction.
In 2024, hyperinflation continues to wreak havoc in Venezuela. While it is far from the peak reached in 2018, it still clearly indicates unimaginable economic distress. The crisis in Venezuela stems from the country's continued reliance on oil exports and improper economic policies. This year, the inflation rate has dropped from 190% to 60%, but many analysts expect inflation to rise again to 150% by 2025. The government's efforts have failed to stabilize the economy and currency, with the increasingly severe devaluation of the bolívar leading to rising poverty levels. Zimbabwe, which suffered from hyperinflation in the 2000s, is now facing ongoing inflation, with the inflation rate nearing 600% in 2024. Record inflation has reignited concerns about another currency collapse as the central bank grapples with excessive monetary expansion.
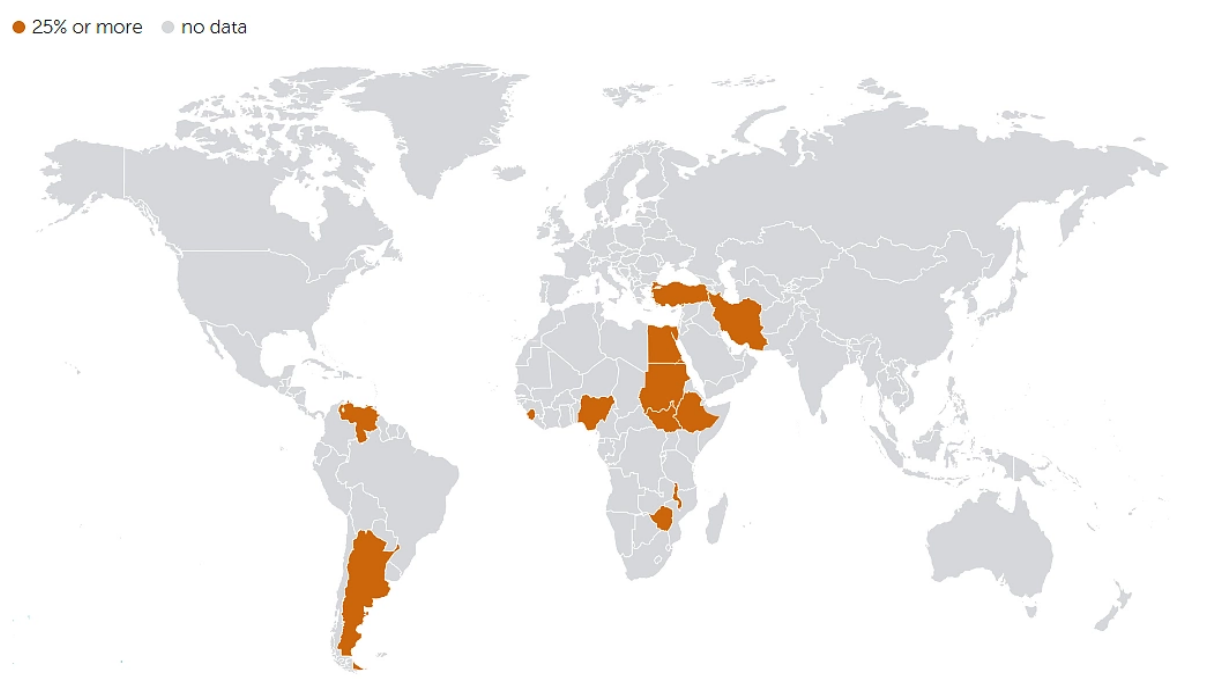
Inflation Rate vs. Average Consumer Prices (2024). Source: International Monetary Fund
2. Hyperinflation Typically Progresses Through Three Stages
1) First Wave: Accumulation of Inflation
This stage is characterized by increasing government debt and unrestricted spending, with annual inflation rates between 10% and 50%. If appropriate measures are taken, it is still possible to reverse the situation and restore the economy at this stage. Historically, this stage resembles early 2000s Argentina, when the country defaulted and ended the fixed exchange rate of the Argentine peso to the US dollar.
2) Second Wave: Accelerating Inflation
As the economy collapses and government debt accumulates, the government excessively prints money in an attempt to solve the problem, entering a deadly vicious cycle. At this point, inflation rates may exceed 50% per year, marking the second stage of accelerating inflation. This stage was exemplified in Venezuela from 2014 to 2017, where inflation rates rapidly climbed from 56% to over 2600%. Similarly, Zimbabwe's inflation rate rose from 100% to over 11,000% between 2006 and 2007. Citizens begin to abandon their national currency, turning to foreign currencies or tangible assets to store value.
3) Third Wave: Full-Blown Hyperinflation
When inflation exceeds 50% per month, the economy enters the final stage of hyperinflation. In 2018, Venezuela reached this critical point, with prices doubling every 26 days that year. In 2024, Zimbabwe faces the risk of repeating this pattern as inflation soars to 600%, while effective monetary control by the government remains a challenge. The failure of policy measures accelerates the collapse, with citizens increasingly using foreign currencies, tangible assets, or more recently, cryptocurrencies to protect their savings and income.
4) Consequences of Hyperinflation
The social and economic consequences of hyperinflation are immense. In Venezuela, the prices of basic goods have skyrocketed, and many can no longer afford food, let alone anything else. By October 2024, the inflation-adjusted minimum wage remains below $10 per month, meaning the vast majority of the population struggles to survive on meager wages. In Argentina, inflation has severely eroded savings, pushing nearly 40% of the population into poverty. The rapid devaluation of the Argentine peso has significantly weakened purchasing power, while the government's monetary stabilization measures have generally been ineffective. In Zimbabwe, the price of basic foods like bread has surged to 15,000 ZWL, and the escalating inflationary pressures have led to social unrest, ultimately sparking protests against unaffordable living costs.
Traditional measures have failed: including interest rate hikes, price and capital controls, and currency revaluation. For instance, in Zimbabwe, there have been at least four currency revaluations since 2008, each time removing zeros from the currency, but failing to address the issue of fiscal instability.
Similarly, Argentina has undergone various currency resets, but confidence in the Argentine peso remains low.
Beyond the economic aspect, hyperinflation also undermines social structures, exacerbating inequality. Those able to hold foreign currencies or tangible assets are more resilient in this chaos, while the rest suffer greatly from the collapse of the national currency. During deeper hyperinflation, many seek alternative ways to preserve value, including cryptocurrencies that offer protection against inflation and allow transactions outside the traditional financial system.
2. The Promise of Cryptocurrencies
From speculative investments to essential survival tools, cryptocurrencies are playing an increasingly important role in countries like Argentina and Venezuela as they experience hyperinflation. Bitcoin and stablecoins are becoming new necessities, providing a safer haven as traditional systems fail to meet this demand.
1) Bitcoin
In 2024, with an inflation rate of 276% in Argentina, Bitcoin began to gain popularity as a hedge against the rapidly devaluing Argentine peso. Unlike centralized fiat currencies, Bitcoin's supply is capped at 21 million, with a stable issuance schedule, making it unaffected by sudden increases in supply. These characteristics make it extremely attractive in a country where storing wealth in local currency faces the risk of total devaluation. Currently, Argentina has one of the most active Bitcoin markets in the world. For example, between 2023 and 2024, the country's total cryptocurrency trading volume exceeded $91.1 billion, placing it ahead of Brazil.
However, despite Bitcoin's appeal, its inherent volatility means it is more suitable for long-term value storage rather than daily transactional assets for many. Some Argentinians use Bitcoin to escape inflation, while others opt for more stable stablecoins for everyday transactions.
2) Technical Analysis of Bitcoin
BTCUSD, Weekly Chart
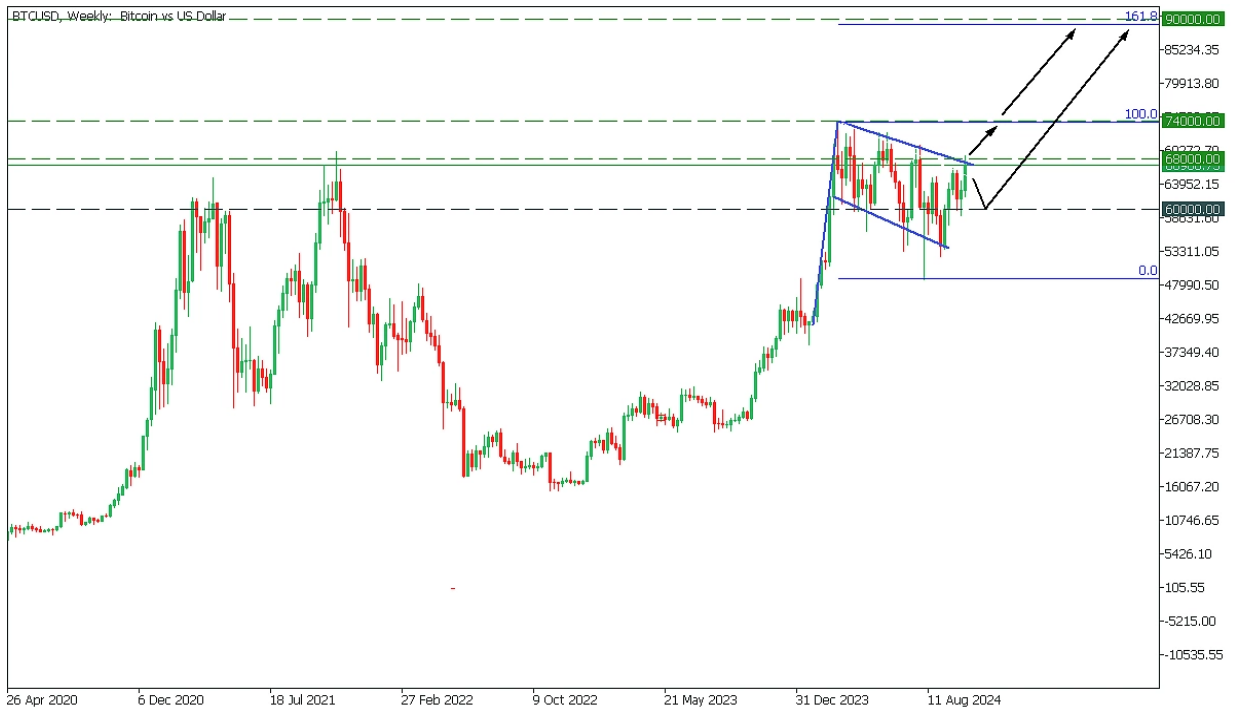
4) Weekly Chart Analysis
On the weekly timeframe, BTCUSD has formed a bullish flag pattern. The price has reached the upper boundary of the flag, but a slight pullback may occur before the bull market begins.
If the price breaks above the upper trendline, it will begin to rise to $74,000, then to $90,000, reaching the 161.8% Fibonacci level; while a rebound from the trendline may cause Bitcoin to drop to $60,000 before starting to rise again.
5) Stablecoins
Stablecoins like Tether USDT and USDC have become crucial for financial security in countries like Argentina and Venezuela. These currencies are pegged to the US dollar, making them a safe haven for economies experiencing hyperinflation. In Argentina, 61.8% of cryptocurrency transactions are stablecoins, far exceeding the global average. This trend reflects a preference for reliable value storage and efficient mediums of exchange in the context of severe currency devaluation.
For instance, when the Argentine peso devalued to below $0.004 in July 2023, the trading volume of stablecoins surged. By the end of 2023, stablecoin trading volume had jumped to over $10 million per month, as citizens sought to protect their wealth in response to government economic reforms, including a 50% devaluation of the peso.
In Venezuela, where the economic collapse has persisted for over a decade, cryptocurrencies, especially stablecoins, have become important alternatives to the unstable bolívar. Despite government crackdowns and the failure of the national cryptocurrency experiment Petro, public acceptance of cryptocurrencies remains high. This year, cryptocurrencies accounted for 9% of the $5.4 billion in remittances in Venezuela, highlighting their crucial role in maintaining financial lifelines.
6) DeFi and Remittances
Cryptocurrencies are also taking over the realm of basic financial services and cross-border remittances. In countries like Venezuela and Argentina, where traditional financial systems have failed, many rely on DeFi platforms for basic services like loans and savings. Cryptocurrencies also avoid the costly and slow pitfalls of traditional remittance systems. For example, Venezuelans abroad can send money home faster and at a lower cost using Bitcoin or stablecoins, providing families with better survival opportunities in impossible economic environments.
3. Practical Applications
In the fight against hyperinflation, cryptocurrencies have become indispensable tools in several countries, offering alternatives to fiat currency.
1) Brazil
Brazil's interest in cryptocurrencies is closely linked to economic volatility and the depreciation of the Brazilian real against the US dollar. By 2024, stablecoins like USDT and USDC accounted for 70% of local trading platform traffic, reflecting the growing demand for dollar-pegged assets to combat inflation. Unlike Venezuela or Argentina, where adoption is primarily driven by individual transactions, Brazil's adoption is mainly driven by businesses for cross-border payments, with stablecoins becoming an important tool for companies facing domestic currency instability.
The rapid digital transformation has attracted major players like Circle to collaborate with local Brazilian companies, enabling Brazilians to make low-cost, instant payments. As more companies begin to use stablecoins for international trade, the demand for traditional banking services faces the risk of being replaced by these more efficient decentralized alternatives. In addition to B2B uses, Brazilian consumers are also starting to use stablecoins as a tool to guard against inflation. From 2023 to 2024, stablecoin trading volume grew by 207%, a trend expected to continue as inflation remains high in Brazil.
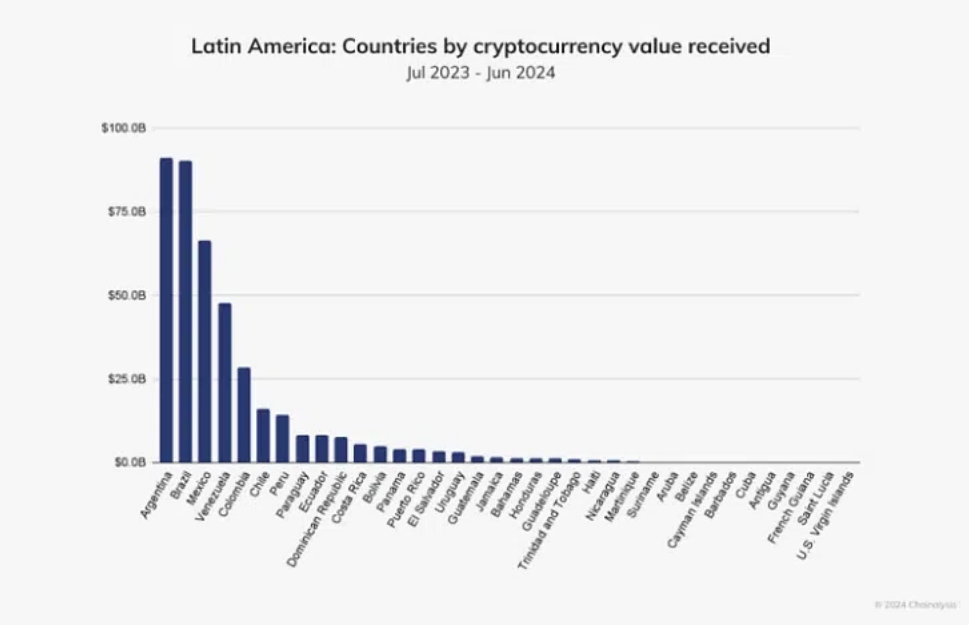
2) Argentina
Among these countries, Argentina, which is experiencing hyperinflation, may be the most striking example of cryptocurrencies as tools to combat inflation. As the currency continues to devalue, Argentine citizens are increasingly using stablecoins, particularly USDT and USDC, to protect their wealth. In 2024, 60% of cryptocurrency transactions in Argentina involved stablecoins, a figure far above the global average.
Argentinians use stablecoins not only for large purchases or savings but even for buying everyday groceries and paying utility bills. The inflation issue has also driven the adoption of Bitcoin in the country, but many believe that Bitcoin's volatility makes it unsuitable for daily use compared to stablecoins pegged to the US dollar. The rise of digital dollar alternatives reflects a significant change in how Argentine citizens manage their finances in an economy plagued by hyperinflation. Additionally, as consumers increasingly engage in digital currency transactions outside the informal banking system to evade taxes and circumvent currency controls, peer-to-peer markets have emerged in Argentina.
3) Venezuela
In Venezuela, hyperinflation has led to the rapid devaluation of the bolívar, and cryptocurrencies have become an important part of the economy. Although the government-backed cryptocurrency Petro went bankrupt in 2024, citizens have widely adopted Bitcoin and stablecoins. This year, the use of cryptocurrencies for remittances surged: 9% of the $5.4 billion in annual remittances to Venezuela is now transferred via cryptocurrencies. Remittances from overseas expatriates are a lifeline for millions of families. Compared to traditional remittance services, cryptocurrency transactions offer a faster, cheaper, and safer way to transfer funds, which can be costly and may take days to complete.
Bitcoin's status as a store of value in Venezuela is also strengthening, especially for savers looking to combat inflation that reached 400% in 2023. However, by October 2024, this figure had decreased significantly. The failure of Petro and the further reliance on decentralized alternatives exemplify the natural adoption of independent digital currencies due to distrust in government-controlled assets. Despite government crackdowns creating a chaotic cryptocurrency environment in Venezuela, crypto mining remains highly volatile.
4) Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe's economic challenges are well-known, with an inflation rate exceeding 300% in 2024. For years, Zimbabweans have used foreign currencies, particularly the US dollar, but access to these currencies has become extremely limited. This has made cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and USDT popular choices for protecting savings and conducting business.
Unlike Argentina or Venezuela, Zimbabwe does not have a strong peer-to-peer market. However, Zimbabweans are gradually realizing the potential benefits of decentralized assets in coping with harsh economic policies and sanctions. Although still lagging behind in some of the aforementioned countries, cryptocurrency remittances are becoming increasingly popular in Zimbabwe, with families utilizing blockchain as a better way for cross-border transfers.
5) Nigeria
Nigeria has grown to become one of the largest cryptocurrency markets in Africa. Despite the Nigerian government's attempt to launch a CBDC called eNaira, citizens prefer to use cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. In 2024, Nigeria ranked second globally in cryptocurrency adoption. Citizens in the Philippines and Nigeria also utilize cryptocurrencies to combat the devaluation of their respective currencies—the peso and the naira—as well as the high transaction costs associated with traditional banks.
The Nigerian government's response has been quite complex. On one hand, it attempts to regulate cryptocurrency trading platforms, while on the other hand, it promotes the use of eNaira. However, the decentralized nature of Bitcoin makes it difficult for the government to control, and Nigerians continue to use it as a means of storing value and making cross-border payments. Nigeria's peer-to-peer market is rapidly developing, with cryptocurrency trading volume exceeding $200 million per month in 2024.
4. Conclusion
The rise of cryptocurrencies in economies experiencing hyperinflation highlights a key shift in how individuals respond to financial crises. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and stablecoins provide timely and practical solutions for protecting wealth and facilitating transactions, especially when traditional currencies fail. However, while they offer valuable tools for individuals, they cannot replace the fundamental economic reforms needed to address the root causes of hyperinflation. Sustainable recovery relies on governments implementing sound fiscal and monetary policies and restoring trust in the national financial system. Cryptocurrencies can support this transformation but must become part of a broader strategy for achieving long-term economic stability.
Article link: https://www.hellobtc.com/kp/du/11/5511.html
Source: https://www.coingecko.com/learn/how-do-cryptocurrencies-combat-hyperinflation?utmcampaign=learn&utmsource=x&utm_medium=social
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



