_Author: shushu, _BlockBeats
Base is becoming a shining star in the EVM space, but according to Dune data analyst jpn memelord, while the trading volume on Uniswap on the Base platform seems prosperous, a large portion of the trades is driven by funds that are repeatedly "pulled out." This seems to confirm some community views that there are many "rug pulls" on Base. What do the real data show? BlockBeats has compiled and organized the research from jpn memelord for readers' reference.
The False Prosperity of Uniswap on Base
At the beginning of September, Uniswap tweeted that 98.9% of new trading pairs on Base were launched through the Uniswap protocol.
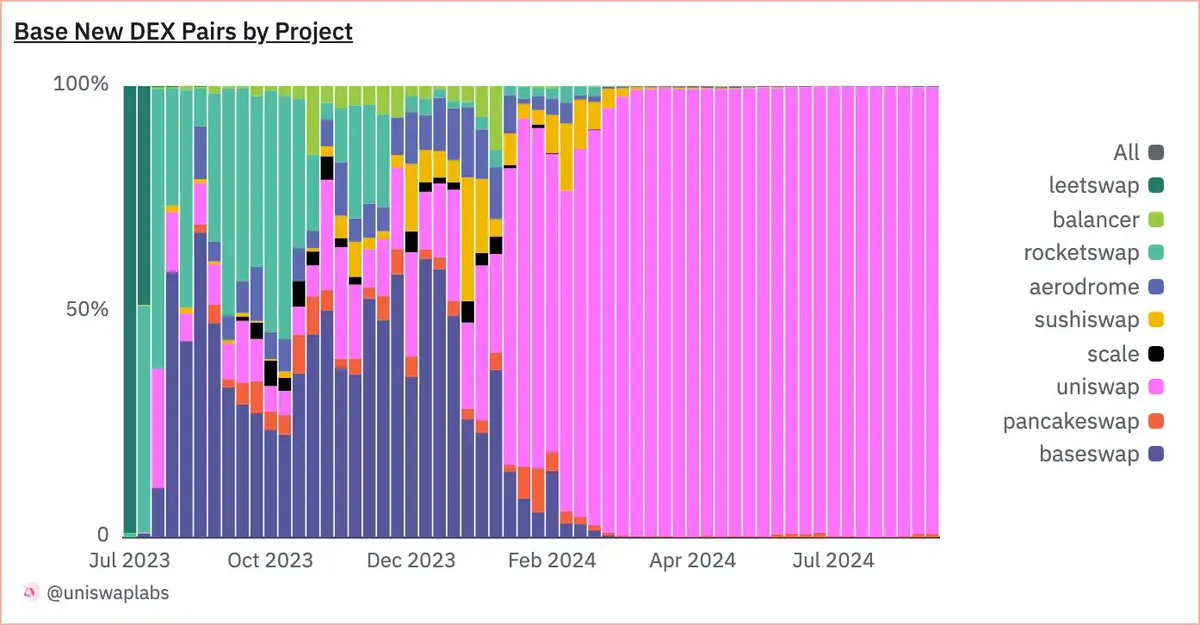
Data shows that over the past few months, the Base platform has launched more than 600,000 Uniswap v2 liquidity pools, accounting for 98.9% of all newly created trading pairs on the platform, which is undoubtedly quite remarkable. However, it is worth further exploring who actually created these trading pairs.
In fact, a significant portion of the liquidity pools was deployed by a few addresses, with the top three addresses being related, meaning that one person or entity created 3.7% of the liquidity pools on Base, and there are also other related addresses.
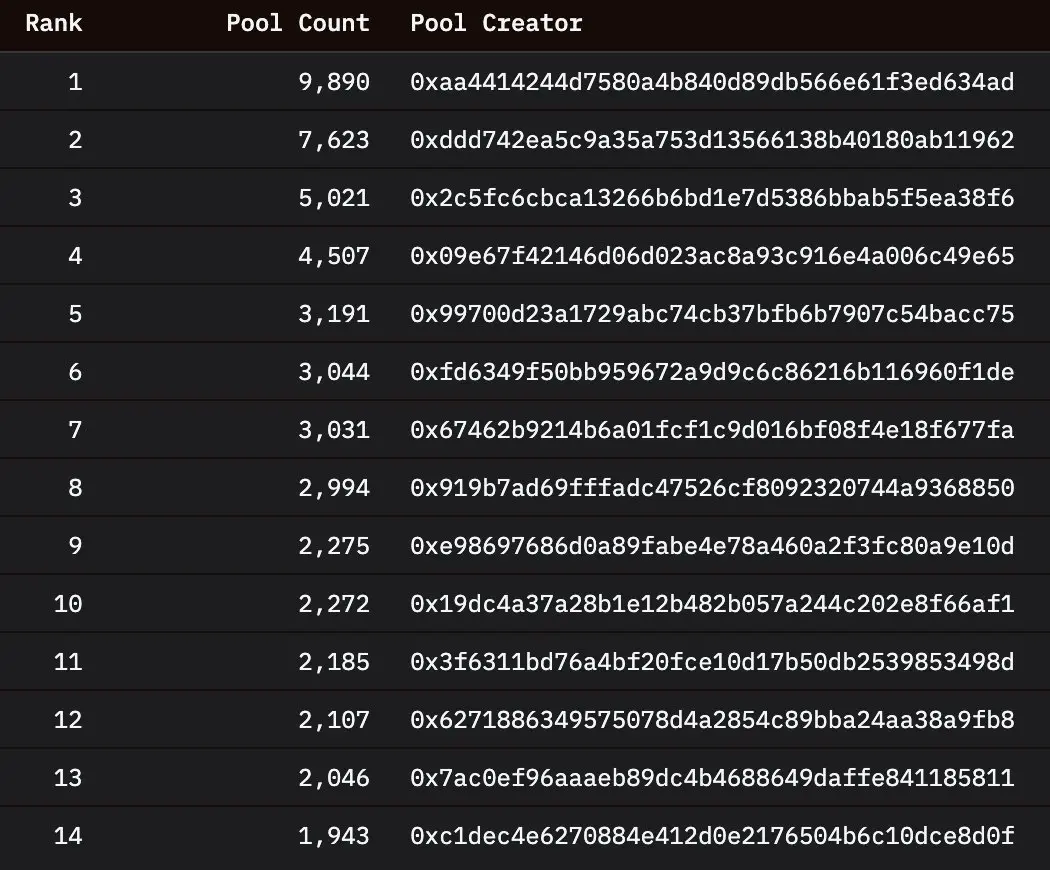
Source: Dune
Overall, addresses that created more than 500 liquidity pools contributed over 127,000 pools, and more than 20% of all pools deployed on Base were created by just 87 independent addresses (or even fewer independent entities).
What is the actual situation of these liquidity pools?
In fact, most of them are ordinary altcoins that are "pulled out" within minutes, lacking any real value. As shown in the example below, these liquidity pools are not productive projects but outright scams.
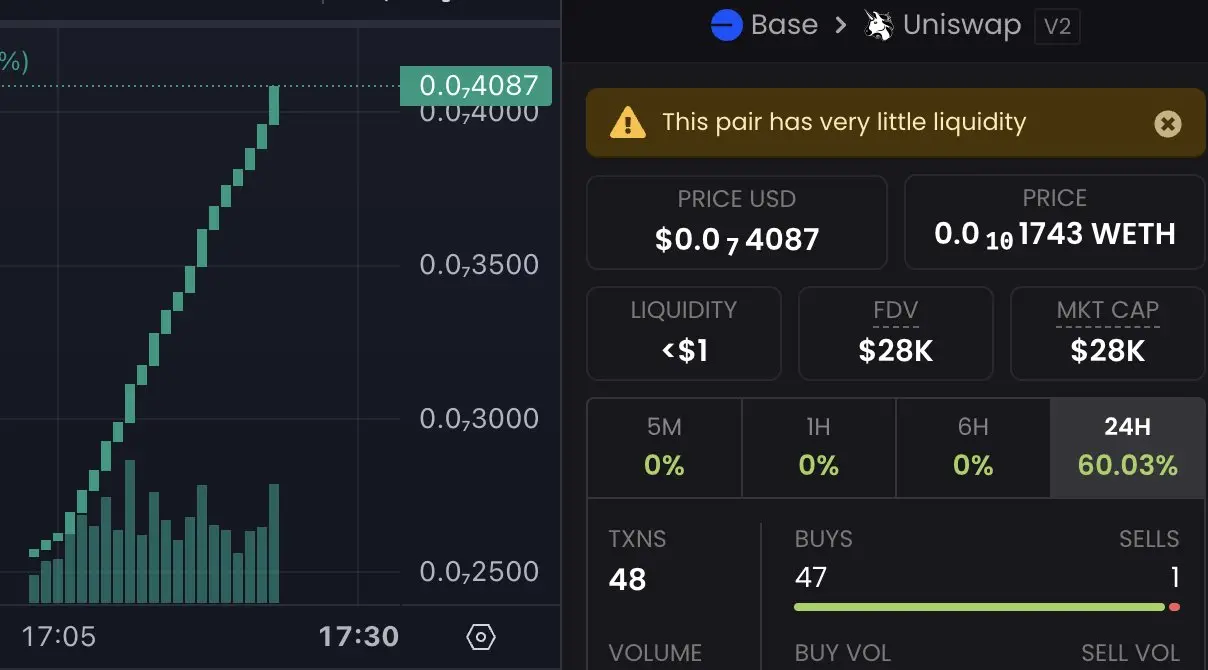
The strategy commonly used by operators creating a large number of liquidity pools is to first distribute ETH to multiple wallets, then issue new tokens, buy through these backup wallets, and finally quickly withdraw liquidity. This operation not only quickly profits but also artificially inflates trading volume metrics.
Each new "pull out" operation typically brings in thousands of dollars in trading volume. These operations are conducted around the clock by dozens of addresses, with each liquidity pool lasting only 20-30 minutes, allowing a single address to launch more than 50 such projects daily.
In this way, each address can generate $250,000 in trading volume daily with just a small amount of initial capital.
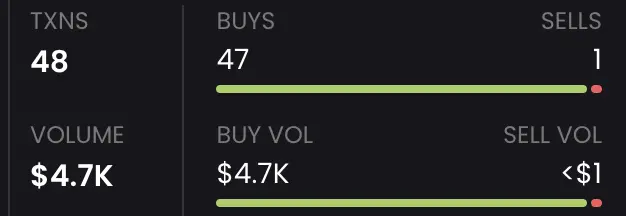
"This is like sticking a few $100 bills on a boomerang and throwing it out 50 times. You haven't really generated hundreds of thousands of dollars in trading volume; you're just entertaining yourself," jpn memelord believes.
The frequent occurrence of this phenomenon may have multiple reasons. On one hand, it is to deceive unsuspecting users into buying these tokens; on the other hand, it may be to profit from poorly calibrated front-running bots; additionally, it could be a strange form of farming for a potential (but unlikely) future Base airdrop.
The key question is how to effectively screen and filter these operations.
Initially, jpn memelord thought that setting a limit on the number of liquidity pools created by each address could serve as a filter, removing those junk addresses composed of a large number of liquidity pools. However, he found that over half of the liquidity pools were deployed by addresses that created fewer than 5 pools.
He speculated that many liquidity pools might be created by farming or "pull out" bots that frequently change addresses to evade detection, and they might even change addresses after deploying just one liquidity pool. Therefore, jpn memelord decided to continue his research, trying to find traces of human factors in the creation of liquidity pools.
He attempted to focus only on liquidity pools created by ENS users. This method proved more effective, with only 17,000 pools created by addresses with ENS, a number far lower than the total number of pools, and it may effectively exclude most pools created by bots.
Coincidentally, jpn memelord believes this filtering process may also reveal some influencers who repeatedly engage in "pull out" operations on Base tokens. However, this method still needs improvement, as the existing filtering may miss some real liquidity pools created by anonymous deployers while including scams or "pull out" projects from certain vanity influencers.
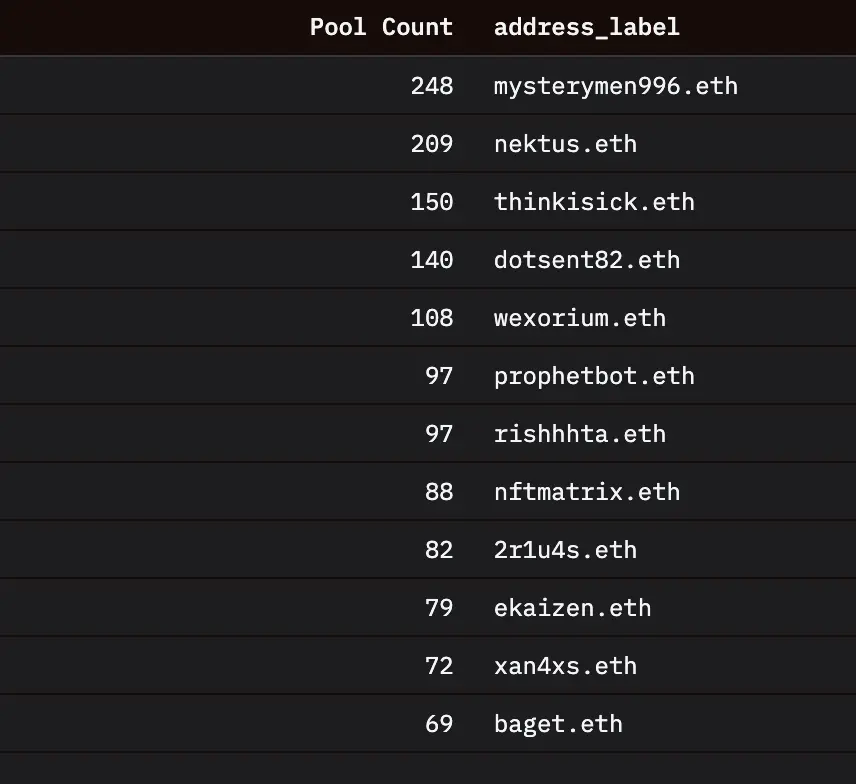
jpn memelord began to focus on liquidity pools with multiple liquidity addition events. "Pull out" projects typically only perform one liquidity injection and removal operation, while productive liquidity pools will have other liquidity providers and multiple liquidity injections.
Only about 7,800 v2 liquidity pools have undergone multiple liquidity additions, and when the filtering condition is raised to more than 2 liquidity additions, this number is halved again, leaving only about 3,500, which are the productive liquidity pools, not just "pull out" projects.
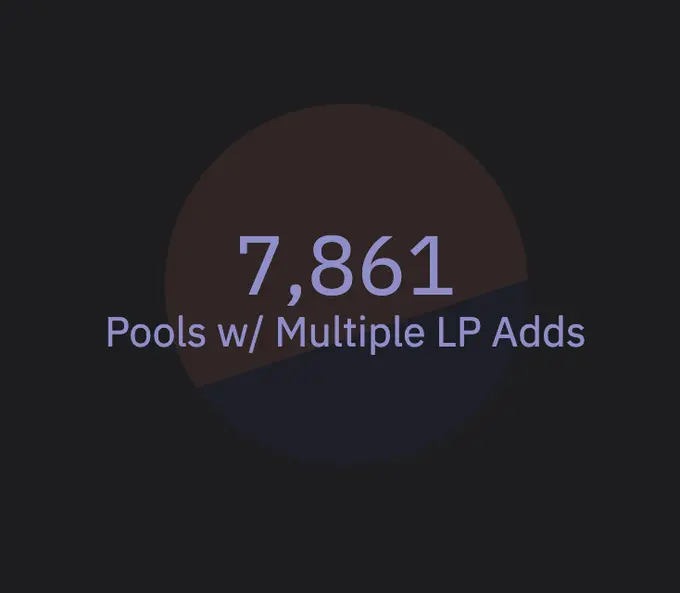
These valuable liquidity pools account for only 1.2%-0.5% of the initial total, meaning that after considering junk projects and scams, the actual data is inflated by about 99%, a figure that closely aligns with the number given by Uniswap at the beginning of the article.
jpn memelord believes that this behavior is not essentially Uniswap's fault, as it is a permissionless protocol where anyone can create liquidity pools for any asset, which is one of its design features. However, promoting metrics that are artificially inflated by worthless junk projects is something Uniswap has the ability to control.
Uniswap should filter its metrics; whether it’s 8,000 liquidity pools or 3,500, these truly valuable liquidity pools still represent impressive data. This filtering should also apply to trading volume, as a significant portion of the trading volume is actually generated by these "pull out" projects cycling between the same 5 ETH.
"The number of 'created liquidity pools' is an easily manipulated activity metric for a permissionless protocol with an operational cost of just a few cents. This type of metric should be carefully filtered and not simply promoted based on surface data. Those liquidity pools that go beyond the 'pull out' routine and truly have interaction are what deserve attention."
Rug Pulls Rampant, Uniswap's Real Trading Volume Lags Behind Aerodrome
jpn memelord further explored whether these easily executed "pull out" projects significantly contribute to trading volume.
At peak times, liquidity pools with only one liquidity addition event contributed about $300 million in trading volume per month, which is relatively small. As of now, this figure for September is only about $30 million, which actually verifies that about 99% of the liquidity pools created on Base by Uniswap are of low value.
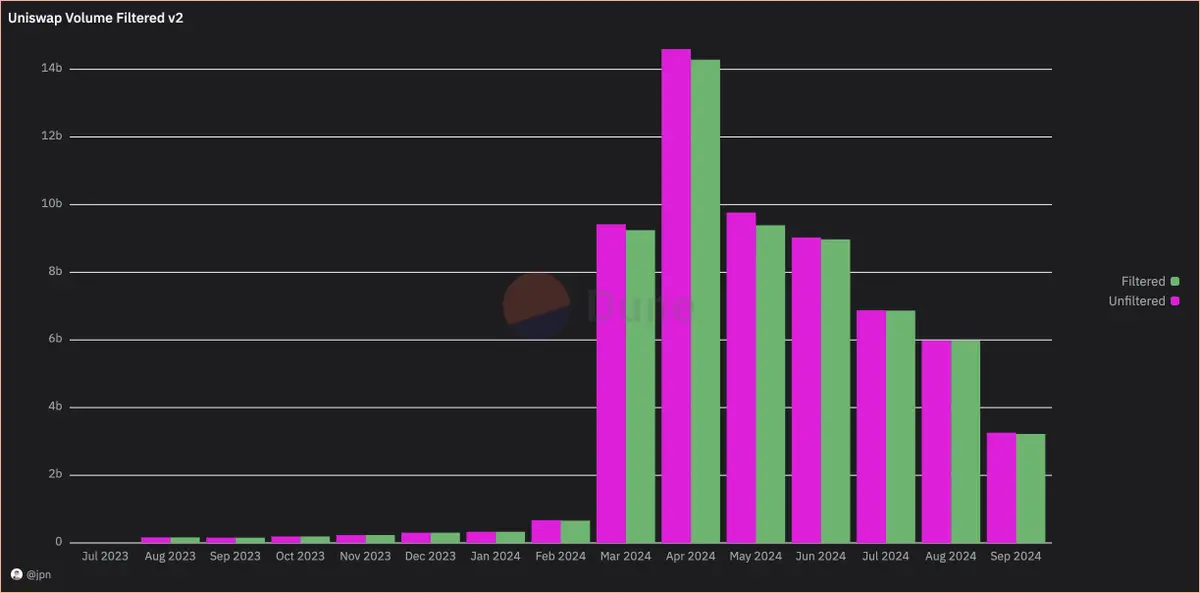
jpn memelord hopes to gain a clearer understanding of the true sources of this trading volume. In previous analyses, he mentioned that although these low-cost "pull out" projects do contribute to trading volume, he suspects that more complex operators frequently change addresses when launching new scams to evade detection.
So, how can these operators be distinguished?
jpn memelord turned to AerodromeFi and its whitelisting process, attempting to use it as a potential method to filter Uniswap's trading volume on Base. On Aerodrome, if a liquidity pool wants to receive incentives, its tokens must pass the whitelisting review by the Aerodrome team, which helps distinguish the trading volume of quality projects from other projects.
His analysis shows that a significant portion of Uniswap's trading volume on Base actually comes from assets that are not whitelisted. Since the explosion of projects on Base in March this year, this proportion has approached 50%.
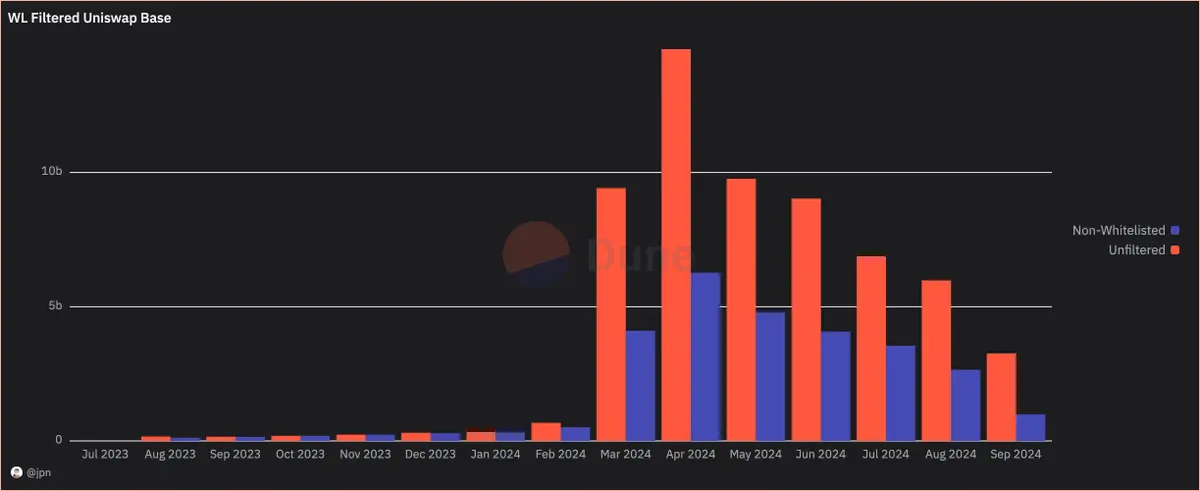
Does Uniswap have an advantage over certain assets? What is driving this trading volume?
jpn memelord extracted the trading volume data of individual liquidity pools for unlisted assets and found a large number of meme coins. Some meme coins he had never heard of had trading volumes of $10 million just in September.
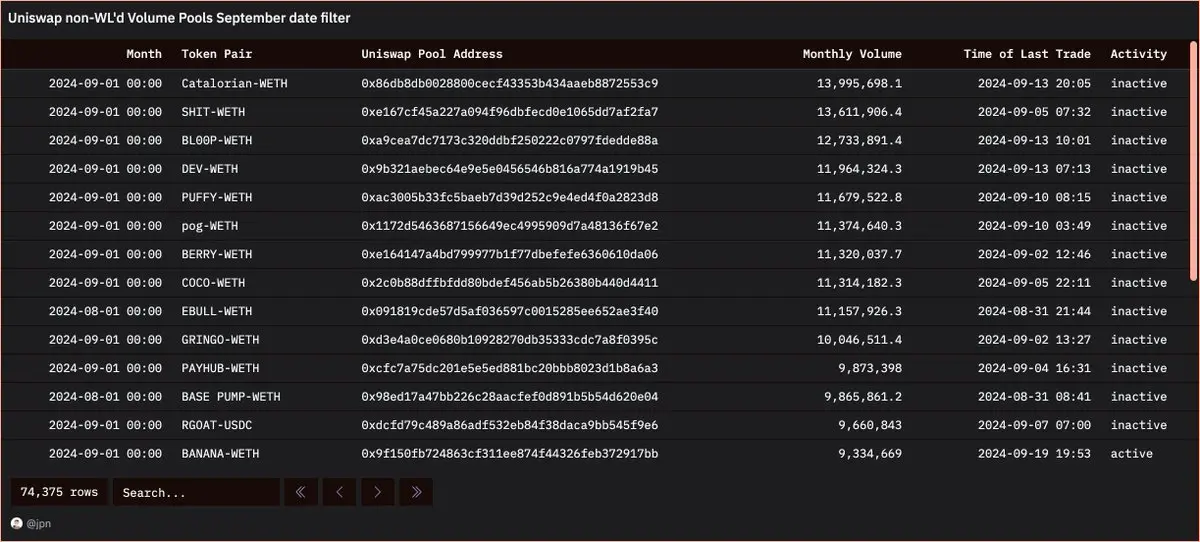
Upon reviewing these liquidity pools one by one, he found that most of the tokens were in a "pull out" situation. In fact, among the top 150 liquidity pools sorted by monthly trading volume, jpn memelord found only 4 that were not "pull out."
The performance of these liquidity pools was roughly the same: within hours of going live, trading volumes reached millions of dollars, only to be quickly "pulled out," with tokens sold to zero, and deployers profiting over 90 ETH.
This operation repeats over and over.
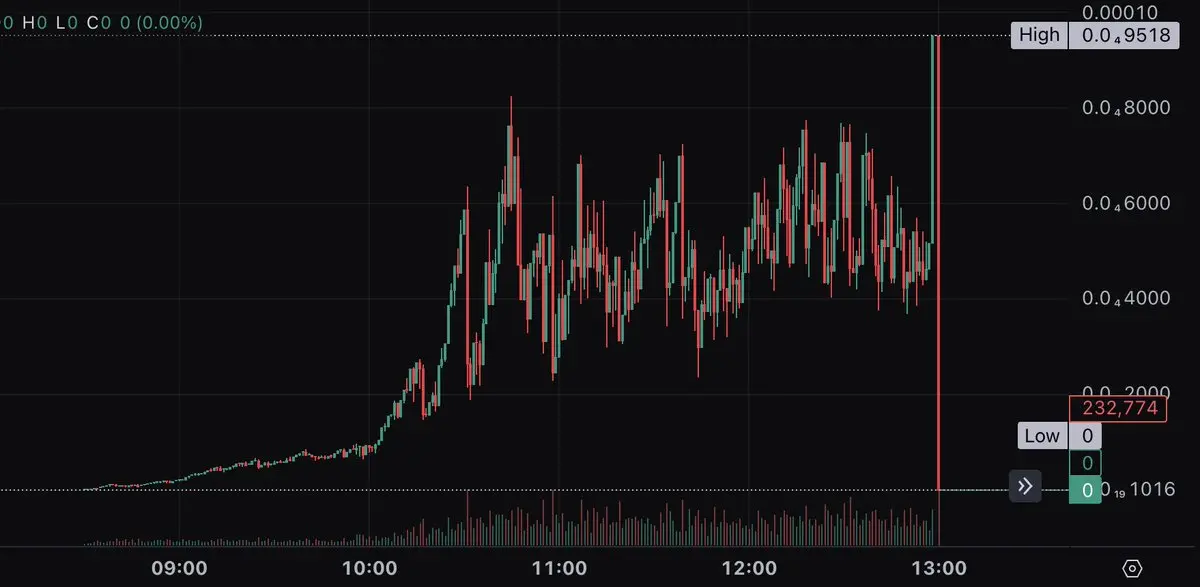
So, how can we identify these scams in trading volume data? A systematic approach is needed to recognize them.
When a token is thoroughly "pulled out," trading will cease. Therefore, a filter can be set to check how long it has been since the last trade of the token, which can help identify these scams.
The method jpn memelord adopted is to apply a filter to exclude tokens that have had trades in the last N days, allowing for a distinction between "active" tokens and "inactive" tokens. Combined with the previously used whitelisting filter, Uniswap's trading volume can be categorized into four types:
- Whitelisted active tokens: including quality tokens, stablecoins, and established meme coins.
- Whitelisted inactive tokens: referring to tokens that have significantly declined in recent months.
- Non-whitelisted active tokens: containing new tokens, which include both scam projects and legitimate projects.
- Non-whitelisted inactive tokens: typically severe "pull out" projects or assets that are gradually forgotten by the market.
So, what does Uniswap's trading volume look like?
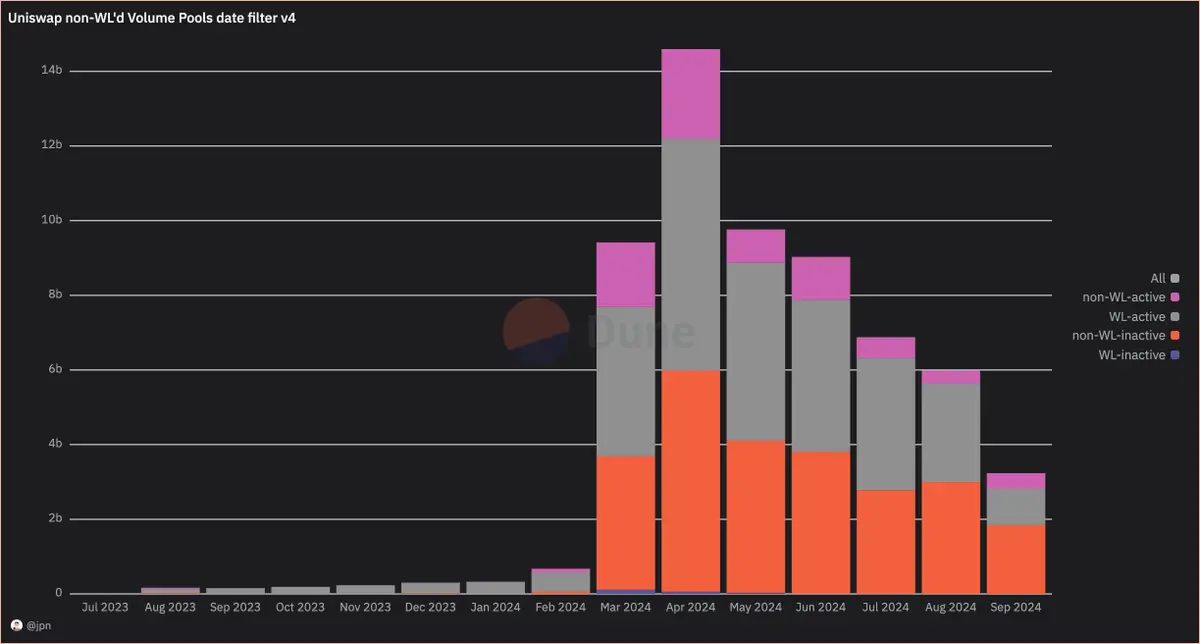
First, the trading volume of these "pull out" tokens reached $1.85 billion in September, with no trades occurring in the last two days (about 10% of the month), meaning these tokens accounted for 57% of Uniswap's total trading volume on Base this month.
The situation is even more severe. Some of these "active" tokens were just "pulled out" in the last 48 hours and are categorized in the pink section of the chart (non-whitelisted active). If the trading volume from "pull out" remains nearly unchanged, it can be anticipated that another 6% of the monthly trading volume is also from scam projects.
This portion accounts for 12% of the total trading volume this month, while last month it was about 6%. Therefore, it is likely that by the end of this month, after the activity filter identifies the recent "pull out" projects, this 6% will join the 57%. In other words, approximately 63% of Uniswap's trading volume on Base comes from "pull out" projects.
This month's whitelisted assets (quality token pairs, stablecoins, mature meme coins) only account for 30% of Uniswap's trading volume. The remaining approximately 7% of monthly trading volume is the "advantage" that Uniswap possesses.
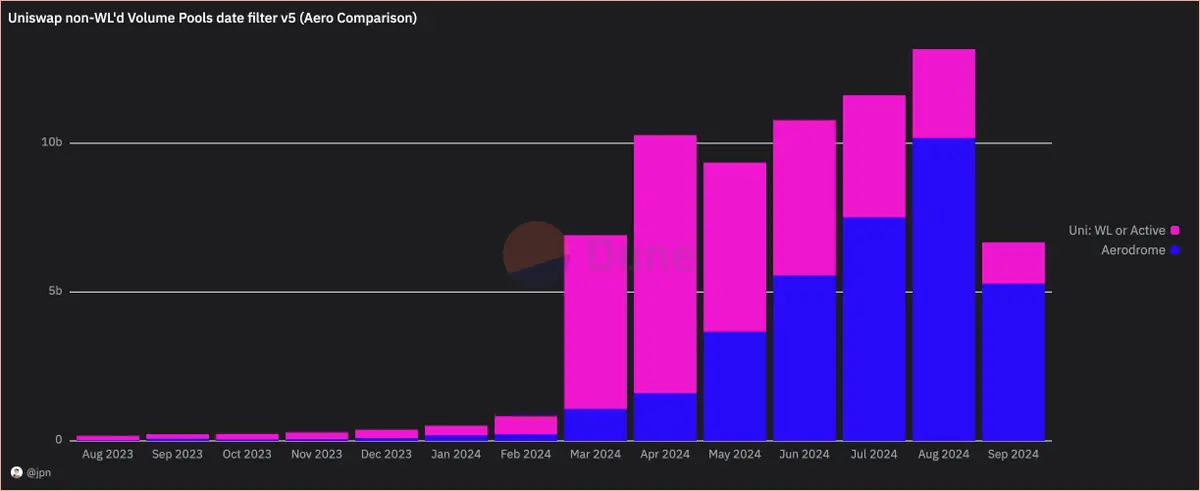
jpn memelord provided two sets of charts, one showing the raw Uniswap trading volume (typically used to compare these trading volume data), and the other removing the "pull out" trades from Uniswap's data. The dominance of Aerodrome's trading volume is much stronger than people imagine.
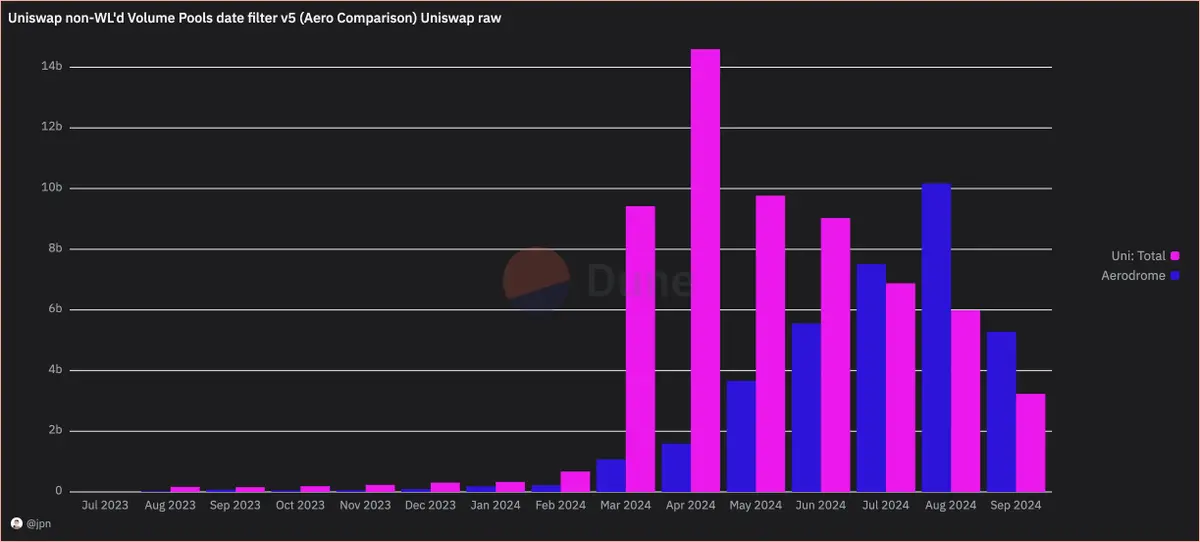
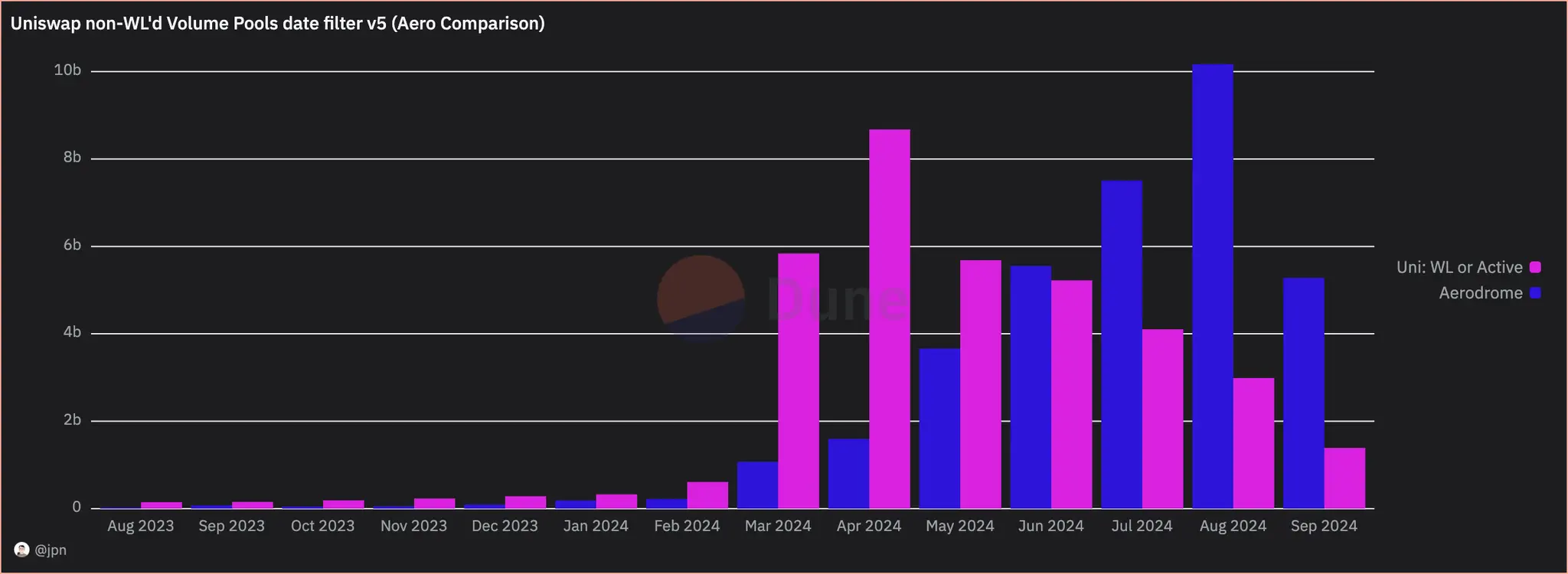
Interestingly, even after filtering out scam trades, the overall trading volume on Base continues to rise steadily, and Aerodrome's market share is gradually expanding. By observing the increase in trading volume percentages, it can also be seen that Aerodrome experienced significant growth following the launch of Slipstream (CL) at the end of April.
Delving into Rug Details, A Few Lines of Code "Empty-Handed"
As market enthusiasm rises, jpn memelord continues to monitor the ongoing "pull out" operations on Base. This time, he discovered that these numerous abnormal operations might originate from a single individual or group.
Their operation begins with deploying a token, curiously using a non-standard 9 decimal places and adding most of the liquidity to the Uniswap v2 pool. They then enable trading, relinquish ownership of the contract, and destroy the liquidity tokens, making this series of actions appear to be a compliant setup.
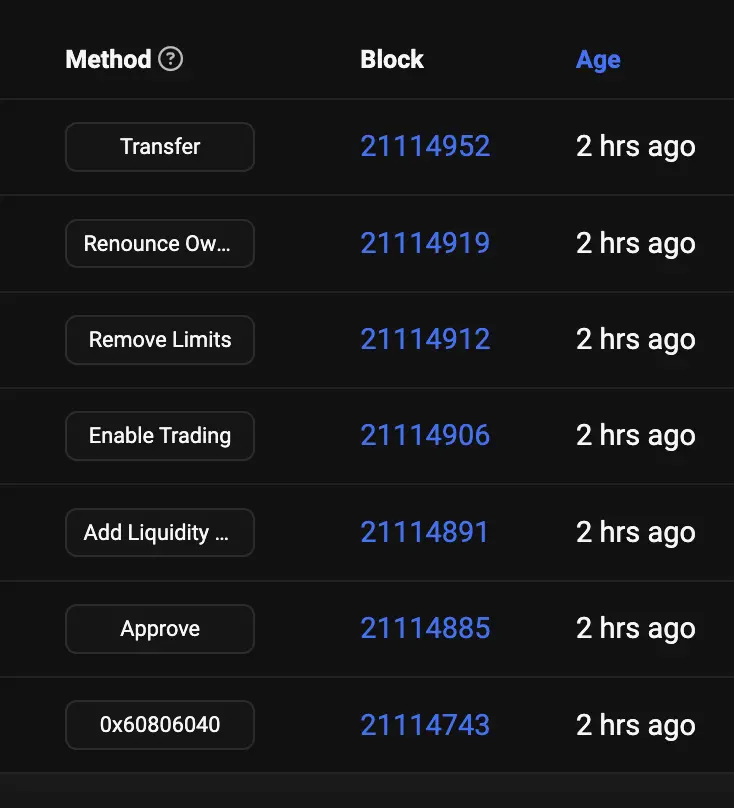
The wallet holding the most tokens on Basescan is the liquidity provider, and everything seems safe, attracting many people to flock in.
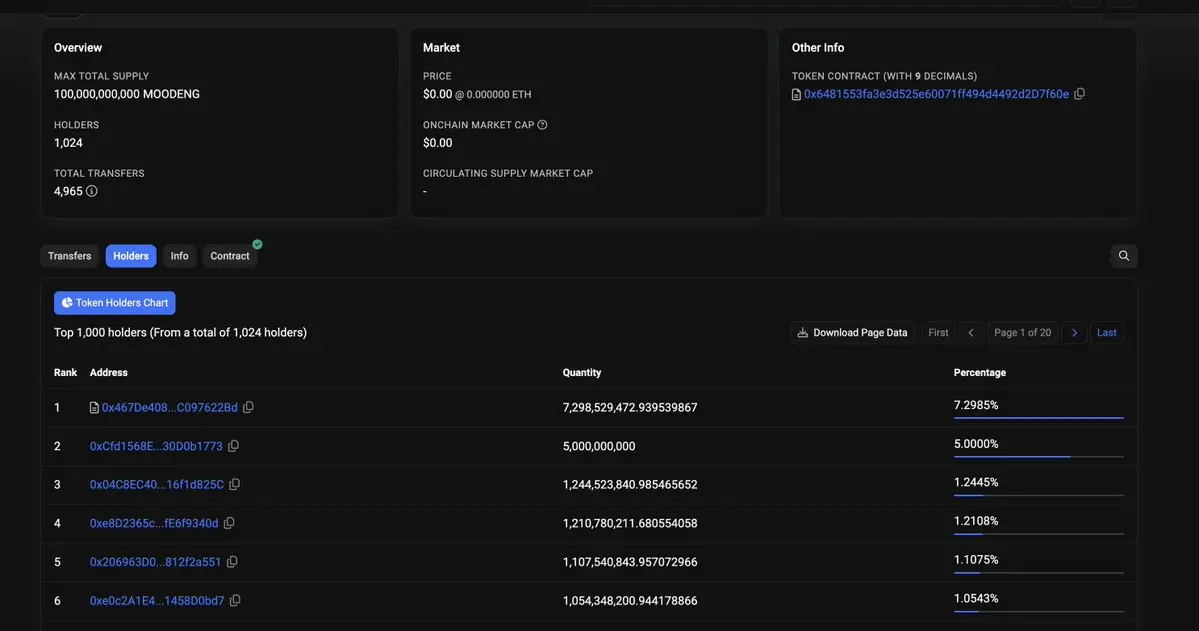
The "security check" also seems to have passed validation (LP has been destroyed, contract ownership has been relinquished, no honeypots, etc.). Nevertheless, @Token_Sniffer has already flagged this scammer.
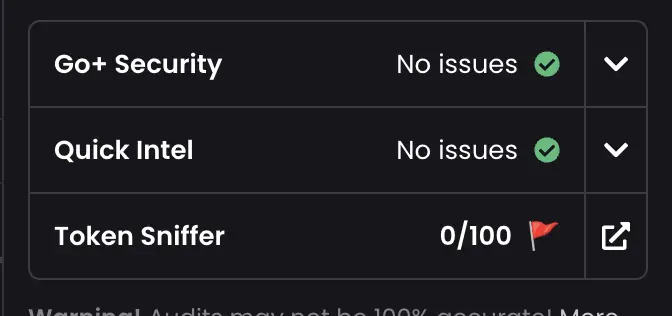
Subsequently, they manipulate trading volume through bots to lure unsuspecting users into the trap.
ETH is semi-randomly distributed to dozens of wallets controlled by the deployer, which simulate natural market demand through buy and sell operations, pushing up the chart trends.
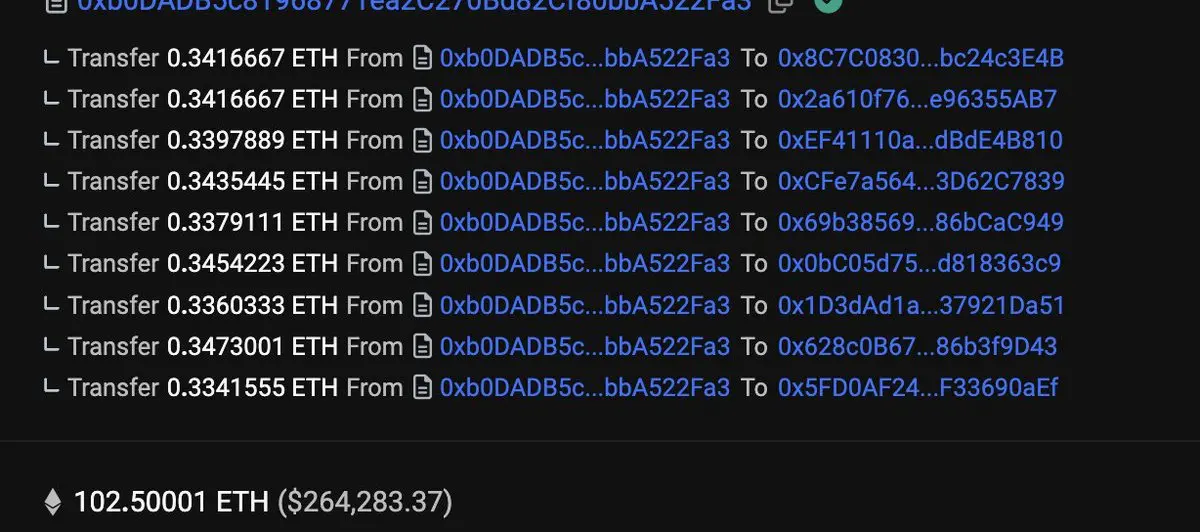
Everything appears normal until the deployer receives a token transfer far exceeding the "circulating supply" displayed, and all ETH in the pool is withdrawn to the deployer's account, leaving this seemingly safe meme coin abandoned.
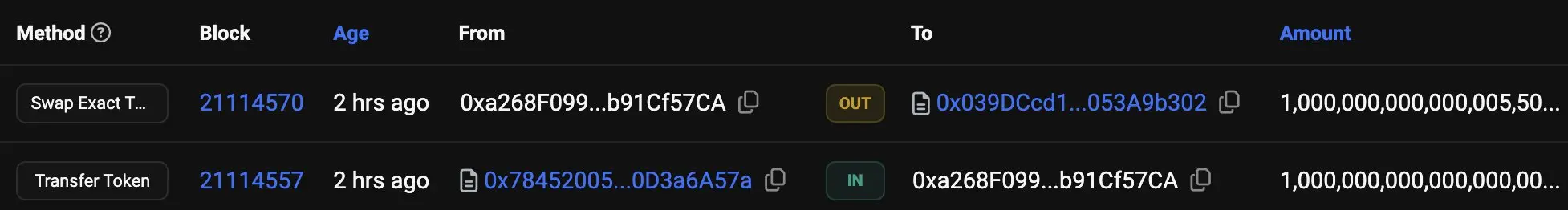
Where did these tokens come from?
The contract contains a constructor that deliberately uses integer underflow to allocate the maximum uint256 amount of balance to a "hidden" wallet controlled by the deployer. Therefore, these tokens do not appear in the "max supply" or the holders list on Basescan.
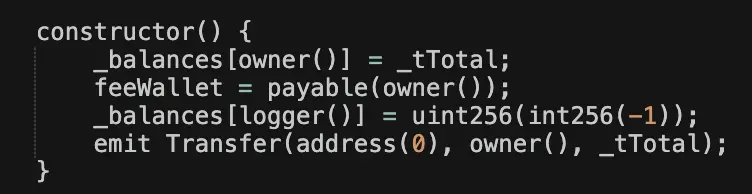
It is these few lines of code that create such a chart trend.
These ETH are recycled for the next operation, and the entire "performance" will restart with a new token code, usually choosing a name that is currently popular on Ethereum or Solana.
Has Base Become a "Death Zone"?
jpn memelord continues to follow up on the analysis of Uniswap's trading volume on Base and discovered an active continuous "pull out" operator. In short, this individual or group now accounts for 65%-80% of Uniswap's trading volume on Base daily.
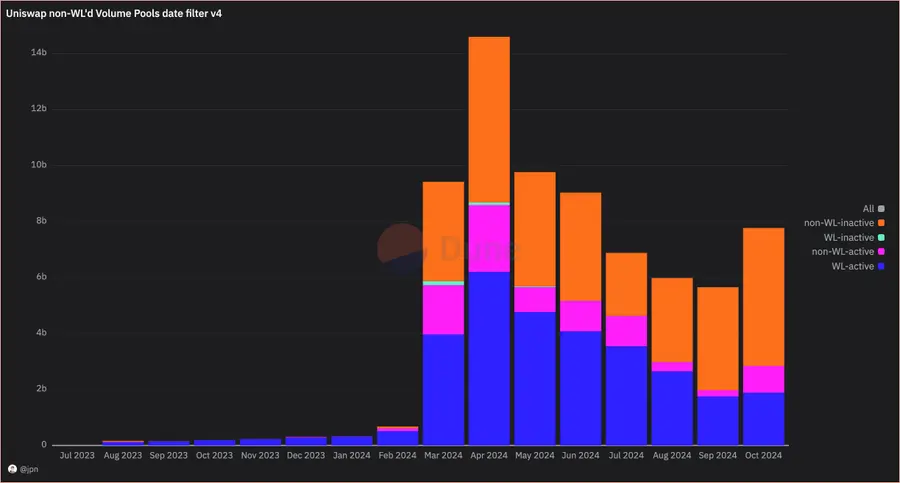
The orange section represents the trading volume of liquidity pools that have had no trades in the past two days (i.e., "pull out" tokens/pools). In October alone, this trading volume approached $5 billion, reaching the highest level since April.
Worse yet, the proportion of this trading volume relative to the total has increased in recent weeks, peaking at 82% of total trading volume on October 12. The remaining trading volume mostly comes from token liquidity pools on the Aerodrome whitelist (including WETH, cbBTC, and DEGEN, etc.).
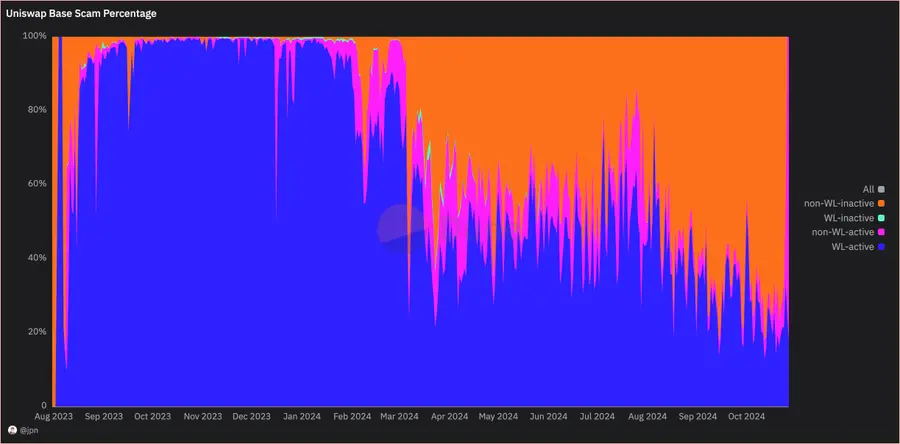
This means that Base has become a minefield, and anyone trying to find new tokens there has a high probability of encountering these "pull out" projects.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



