No Trading System Guarantees Profit
A trading system is essentially a set of operational protocols that can be understood as a complete human-computer interaction system. Through this system, humans instruct the computer to perform tasks; from a biological perspective, it is similar to a conditioned reflex, meaning "when signal A appears, action B will definitely follow."
A trading system is a comprehensive set of signal rules regarding entry, exit, stop-loss, and take-profit.
There are many misconceptions about trading systems. Some people believe that their inability to make a profit is due to a lack of their own trading system, and that once they have a trading system, they will be able to achieve profitability. Others think that the reason they fail to achieve excess returns is that their current trading system is not good enough, and thus they need to find a better system. Some are convinced that there exists a magical trading system that guarantees profit as long as one follows its operations.
Are these views true and credible?
First, it is important to clarify that there is no "perpetual motion machine" or "elixir of life" in the world, and naturally, there cannot be a universal trading system that consistently generates stable profits. If such a system existed, smart people would have already discovered and utilized it.
Second, even possessing an excellent trading system does not guarantee stable profitability. An excellent trading system first requires the user to have strong execution capabilities, able to follow its instructions 100%. Moreover, a good trading system may not be suitable for everyone. Each person needs to find a trading system that fits them, which cannot be measured by standardized "good" or "bad."
To find a trading system that suits oneself, one must first correctly understand and position the role of the trading system.
A trading system is akin to military guiding principles. Completely adhering to these guiding principles may not guarantee victory in every battle, but it at least ensures that one will not suffer a disastrous defeat and will leave opportunities for future actions. The trading system operates at a strategic level, while the combination of "operational thinking" and "operational strategy" belongs to the tactical level, with specific trading actions representing tactical expressions.
By correctly understanding the role and limitations of a trading system and finding a suitable system that aligns with one's characteristics, one can achieve better results in trading.
How to Evaluate an Operational System
When evaluating a trading system, I believe one should focus on a core key indicator: the "profit-loss ratio." The profit-loss ratio refers to the average profit amount divided by the average loss amount.
For example, if you invest 1 million yuan and trade according to a certain operational system 10 times, with 4 profitable trades yielding profits of 150,000, 250,000, 350,000, and 450,000 yuan respectively, and 6 losing trades with losses of 100,000, 150,000, 100,000, 50,000, 70,000, and 200,000 yuan. At this point, the average profit during profitable trades is 300,000 yuan, and the average loss during losing trades is 111,700 yuan, resulting in a profit-loss ratio of 30/11.17 ≈ 2.69. If you continue trading with this system, whether for 100 times or 1000 times, theoretically, you can achieve profitability with a profit-loss ratio of 2.69. A profit-loss ratio below 1 indicates a loss.
However, when objectively evaluating, we need to consider certain redundant factors. Personally, I believe the profit-loss ratio should not be lower than 2. Specifically:
A profit-loss ratio of 3 can be considered passing, equivalent to 70 points;
A profit-loss ratio of 4 can be considered good, equivalent to 80 points;
A profit-loss ratio of 5 can be considered excellent, equivalent to 90 points;
A trading system with a profit-loss ratio above 5 can be considered perfect.
It is important to note that trading systems with a profit-loss ratio above 5 are very rare. I recommend everyone calculate the profit-loss ratio of their long-term trading system (or buying and selling rules) to better assess its effectiveness.
What Elements Should Be Included in Designing an Operational System
Before establishing an operational system, we should first ask ourselves, what is the purpose of investing? Is it to get rich overnight? Is it for steady appreciation? Or is it for rapid growth? Additionally, what is the expected rate of return? Is it 100% in a year? 100% in a month? 30% in a year? 30% in a month? 200% in a year? Or 50% in a year? These questions will greatly influence how we design our operational system.
Furthermore, what is our risk tolerance and risk preference? Can we tolerate a significant drawdown of over 30%? Can we tolerate a small drawdown of under 20%? Can we only tolerate a slight drawdown of under 5%? Or can we not tolerate any drawdown at all? These questions regarding risk must also be considered. If these questions are not clarified, blindly establishing an operational system is not very meaningful, at least not the most suitable for oneself.
A complete operational system should include the following seven elements:
Cycle Judgment: Understand the overall market trend and determine the current market cycle (e.g., bull market, bear market, sideways market).
Operational Thinking: Clarify the basic philosophy and strategy of operations, whether to pursue short-term quick in-and-out or long-term holding.
Coin Selection: Choose potential coins based on certain standards and methods.
Timing: Determine the best timing for buying and selling.
Buying and Selling Rules: Establish clear buying and selling strategies, including entry and exit conditions.
Capital Management: Allocate funds reasonably, avoiding excessive concentration or dispersion, ensuring the efficiency and safety of fund usage.
Risk Control: Develop risk management strategies, including stop-loss mechanisms and position control, to manage and reduce investment risks.
By comprehensively considering and integrating the above elements, one can establish a suitable operational system to more effectively achieve investment goals.
Now, let's take a closer look.
1. Cycle Judgment
Going with the trend is the first principle of investing. When the market is on the rise, the success rate of our various strategies, coin selections, and timing abilities will significantly increase. Even if the strategies and timing abilities are not perfect, in a rising market environment, it is still possible to profit from upward trends. Moreover, if one judges that the market is steadily rising, the psychological comfort of holding positions will be greater, even daring to buy at low points, thus reducing the cost of holding and maximizing profits. Conversely, if there is no clear judgment on the market trend, the psychological state of holding positions will be unstable, easily leading to overreactions due to minor fluctuations, resulting in distorted operations.
Additionally, cycle judgment provides important references for subsequent operations. In a bull market, all buying and selling operations should be heavily weighted and concentrated; in a bear market, all buying and selling operations should be lightly weighted and diversified.
2. Operational Thinking
Operational thinking can also be referred to as operational strategies under different market conditions, but this operational thinking can only be determined based on the judgment of the overall market, so its accuracy still depends on the ability to judge the market. Operational thinking is like planning a campaign: how long to fight, what the battlefield range is, these must be predetermined. One cannot modify the battle plan on the fly, arbitrarily increase troops, or change the direction of the battle.
3. Coin Selection
The importance of coin selection is even more pronounced in a bull market. To achieve excess returns, one must carefully select the coins held and, in a bull market, should avoid frequent coin switching as much as possible. Frequent coin switching may lead to missed upward opportunities, often resulting in sold coins rising significantly while held coins perform poorly. The key to profits in a bull market lies in the combination of heavy investment and holding time.
For large institutions and significant funds (managing over 100 million yuan), the importance of coin selection is even more significant. Global long-only equity funds rely on stock selection as their unique advantage, which is also an important marker distinguishing different funds. Timing operations usually assume that one can outperform the market. Operators managing several million yuan may still profit through timing, but once the fund size increases, the effectiveness of timing significantly decreases.
So, what characteristics should a coin with excess returns possess? We can look at it from the perspective of the market makers. If you were a market maker, or an institution, or what is referred to as a major player, with a large amount of capital to operate a coin, which coins would you choose?
First, a small circulating supply, but not too small; a very small supply may have poor liquidity, making it inconvenient for capital to enter and exit, thus unable to operate.
Second, it should have a trending major theme without historical legacy issues, such as having been previously manipulated by large market makers or having a poor market image.
Third, there should be solid on-chain data support or conditions for future performance improvement, so that when the coin price reaches a high point, "performance improvement + high distribution (such as airdrops, dividends, on-chain rewards, etc.) + theme" can facilitate selling without a significant price drop.
4. Timing and Buying/Selling Rules
Timing is the precise confirmation of entry and exit timing, mainly divided into medium-term waves and short-term speculation. Buying and selling rules are clear definitions of trading discipline. For example, when buying, technical indicators must meet the buying point requirements, and it should be a short-term buying point, with a need for rapid price increases after purchase. Timing is the primary means of controlling risk; even in a bull market, significant adjustments may occur, and the core role of timing is to avoid these adjustments and major bear markets. If market conditions are poor, it is advisable to stay in cash and observe.
In a trading system, buying and selling rules should have a certain degree of flexibility and subjectivity, accounting for about 20% to 30%. Completely fixed buying and selling rules can lead to programmatic trading, lacking adaptability. Buying rules vary based on different operational thinking and market conditions, and different market conditions will produce different buying points. However, there is a fundamental principle that cannot be violated: buying must be based on technical buying points.
Selling rules also change based on market conditions and operational thinking. Different expected returns will lead to different take-profit strategies. Selling does not necessarily have to wait for a technical selling point to appear, as that is often when one or two bearish candles have already appeared, leading to significant profit loss. Therefore, selling points require some pre-judgment; once the take-profit position or a possible high point is reached, one can consider selling.
Through such rule setting, traders can flexibly respond to different market conditions, maximizing profits while effectively controlling risks.
5. Capital Management
Capital management is a set of disciplinary management regulations. For example, "In one accounting year, transfer out and protect profits once a 10% profit is made"; "After opening a position for the first time, open a new position only after making a profit," etc. Another important point to consider is the "leverage issue." Of course, many big players in the crypto space achieve financial freedom through leverage, so whether to use leverage and how much leverage to use varies from person to person. However, it is important to note that there is a saying in the investment industry: "Profits and losses come from the same source," meaning that the places that make you money are often the same places that can cause you to lose money. Many have become wealthy, but many have also faced liquidation. For beginners, it is advisable to use leverage cautiously, as leverage can amplify the emotional fluctuations caused by market volatility, leading to undesirable trading results.
6. Risk Control
Risk control consists of certain ironclad rules; everyone has different experiences and regulations. The terms of risk control serve as the final safeguard during operations, ensuring that one does not make mistakes due to "greed" or "wishful thinking." Additionally, firmly remembering risk control terms can help maintain a calm mindset, avoiding unnecessary losses caused by emotional fluctuations.
Example of a Trading System
A trading system provides clear entry and exit signals, making trading behavior more standardized. Trades are only executed when the system issues a signal; at other times, one must patiently wait. For positions already held, regardless of profit or loss, one should stick to holding; for those in cash, they must wait for the system signal to appear before taking action.
The reason trading systems are referred to as standardized operating systems is primarily to avoid arbitrary trading by investors. Human nature has its weaknesses, and mindset is a crucial factor in trading. While subjective trading can be conducted, even the simplest systems can provide a certain level of standardization. For example, a moving average strategy: buy when the price is above the line, sell when it is below. Even rules like buying stocks on smoggy days in Beijing and selling them on sunny days constitute a system. Similarly, there are even simpler so-called "systems," such as buying stocks on odd days and selling them on even days. Although these systems may not necessarily be profitable, they at least provide a complete set of rules to help traders avoid emotional trading.
The most complex operating systems require top mathematicians, who, with the help of computers, establish several complex mathematical models based on vast amounts of data for automated trading. For ordinary traders, an operating system is not necessarily better if it is simpler or more complex; rather, it is better if it is more efficient. Simplicity, complexity, and quality are not inherently related.
For example, in simple moving averages, the most famous is the Granville Eight Method.
Granville's Four Major Buy Rules:
(1) When the average line transitions from a downward trend to a flat or upward trend, and the stock price breaks through the average line from below, it is a buy signal.
(2) If the stock price falls below the rising average line but soon turns upward and operates above the average line, one can add to their position.
(3) If the stock price drops but does not break the average line and then resumes an upward trend, while the average line continues to rise, it is still a buy signal.
(4) If the stock price breaks below the average line and moves far away from it, a strong rebound is likely to occur, which is also a buy signal. However, remember that after the rebound, the price will continue to decline, so one should not hold on too long. This is because the overall trend has weakened, and prolonged battles will inevitably lead to being trapped.
Granville's Four Major Sell Rules:
(5) When the average line transitions from an upward trend to a flat or downward trend, and the stock price breaks below the average line from above, it is a sell signal.
(6) If the stock price rebounds and breaks above the average line but soon falls back below it while the average line is still declining, this is also a sell signal.
(7) If the stock price falls below the average line and then bounces back toward it but fails to break through and retreats, it remains a sell signal.
(8) If the stock price rises sharply and moves far away from the rising average line, investment risks surge, and a pullback may occur at any time, which is another sell signal.
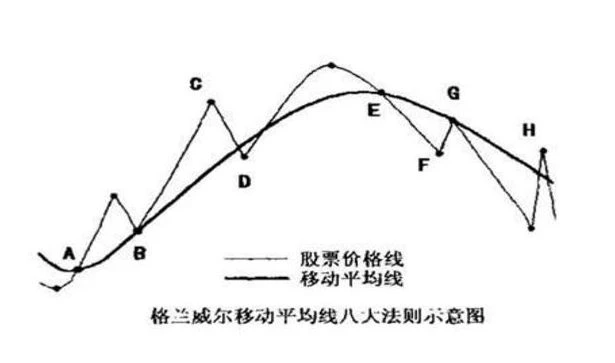
In summary, the Granville Eight Method uses moving averages to analyze price trends and generally follows these rules:
When the average line is rising, it is a buying opportunity; when it is falling, it is a selling opportunity. When the average line turns from falling to rising, and the stock price breaks through the average line from below, it is the best buying time. When the average line turns from rising to falling, and the stock price breaks below the average line from above, it is an important selling time.
The Granville Eight Method is a very simple trading system that everyone knows, but it seems somewhat too general and requires specific adjustments in different markets.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




