Introduction
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) has long been the core hub of the global cross-border payment system, ensuring the smooth operation of global financial transactions through standardized payment protocols and centralized regulation. Today, SWIFT is moving into the realm of digital asset trading through the deep integration of blockchain and Web3 technologies, exploring the transformation of the future global payment system. This experiment aims not only to optimize the efficiency of existing payment systems but also signifies a deep intersection between traditional financial institutions and blockchain technology, with potential impacts that extend far beyond payment innovation. This article will delve into SWIFT's digital asset trading experiment from multiple perspectives, including technology, market, compliance, risk management, and competitive landscape, analyzing the driving forces behind it, future prospects, and its profound impact on the global financial ecosystem.

1. Technological Innovation: From Traditional Cross-Border Payments to Blockchain Interoperability
1.1. Pain Points of Traditional Payments and Blockchain Disruption
Traditional cross-border payment processes face issues such as slow speed, high costs, and lack of transparency. SWIFT covers over 11,500 financial institutions, yet its payment processing time still takes several days, especially in small, high-frequency transactions, where costs are high and efficiency is low. In contrast, blockchain technology significantly shortens payment times and enhances transaction transparency through decentralized ledgers and smart contracts. For example, Ripple can complete cross-border payments in seconds, while traditional SWIFT payments take 1 to 3 days.
- Traditional Payments + Blockchain Technology
SWIFT integrates blockchain technology through experiments, utilizing distributed ledgers to optimize payment paths. By collaborating with Chainlink, SWIFT employs the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) to achieve seamless connections between different blockchains, breaking down information silos, enhancing payment efficiency, and building a more flexible global payment network.
- Historical Testing Situation
On August 31, 2023, SWIFT conducted blockchain payment transfer experiments in a testing environment, successfully demonstrating that its infrastructure can facilitate the tokenization of value across multiple public and private blockchains. This experiment addressed the interoperability challenges of managing tokenized assets across different blockchains.
SWIFT released a series of results from new experiments, indicating that its infrastructure can seamlessly facilitate the tokenization of value across multiple public and private blockchains. These findings have the potential to eliminate significant frictions that hinder the growth of the tokenized asset market, enabling them to scale globally as they mature.
Original: SWIFT unlocks potential of tokenisation with successful blockchain experiments
SWIFT's solution to this challenge is to collaborate with a dozen major financial institutions and Chainlink, coordinating real-world institutional resources to establish on-chain interoperability and operability channels through Chainlink.
SWIFT's partners include:
- TradiFi: Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Limited (ANZ), BNP Paribas, BNY Mellon, Citigroup, Clearstream, Euroclear, Lloyds Banking Group, SIX Digital Exchange (SDX), and The Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation.
- Web3: Chainlink is used as an enterprise abstraction layer, securely connecting the SWIFT network to the Ethereum Sepolia network, while Chainlink's Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) achieves full interoperability between the source and target blockchains.
The results indicate that SWIFT has successfully proven its ability to provide single-point access to multiple public chains using existing Web3 security infrastructure, thereby reducing operational challenges in the experiment and supporting the development of Real World Assets (RWA) needed by investment institutions.
1.2. Cross-Chain Interoperability: Breaking the Blockchain Island Effect
The interoperability of blockchains is one of the main bottlenecks currently hindering their large-scale application. Each public chain has its own independent architecture and consensus mechanism, making the transfer of assets between chains a significant challenge. SWIFT, in collaboration with Chainlink, explores how to achieve liquidity management across multiple blockchains using its cross-chain interoperability protocol.
SWIFT's experiment not only addresses the liquidity issues of assets between different public chains but also enhances the flexibility of its network, allowing financial institutions to explore multi-chain management of digital assets without sacrificing security and regulation. This lays the technological foundation for more complex financial application scenarios in the future, such as cross-border tokenized asset trading and real-time settlement.
Once this cross-chain interoperability matures, global financial institutions will be able to circulate assets more freely across different blockchain networks, promoting the large-scale application of digital currencies and tokenized assets in the global market. In the long run, this will further reduce operational costs for financial institutions and increase the global liquidity of assets.
2. Market Expansion: The Future of Tokenized Assets and Digital Currencies
2.1. The Rise of Tokenized Assets and Global Market Impact
Tokenized assets refer to the digitization of real-world assets (such as real estate, bonds, stocks, artworks, etc.) and their management and trading on the blockchain. According to market analysis, the global tokenized asset market size could reach $30 trillion by 2030. The liquidity, transparency, and efficiency brought by tokenization will have a profound impact on the global financial market.
One of the goals of SWIFT's experiment is to provide platform support for the cross-border flow of tokenized assets through its existing global network. By combining on-chain and off-chain elements, SWIFT can not only simplify the trading process of asset tokenization but also provide a standardized financial infrastructure to ensure that different asset types can circulate freely on a global scale. This architecture is not only designed to serve current digital assets but also prepares for more complex and diverse financial products in the future.
If SWIFT's experiment is successfully promoted, it will fundamentally change the way financial institutions manage and trade assets. More high-value assets will be tokenized, global investors' portfolios will become more flexible and diverse, and cross-border investment barriers will be broken, significantly promoting the deepening and expansion of global capital markets.
2.2. Integration of Digital Currencies and CBDCs
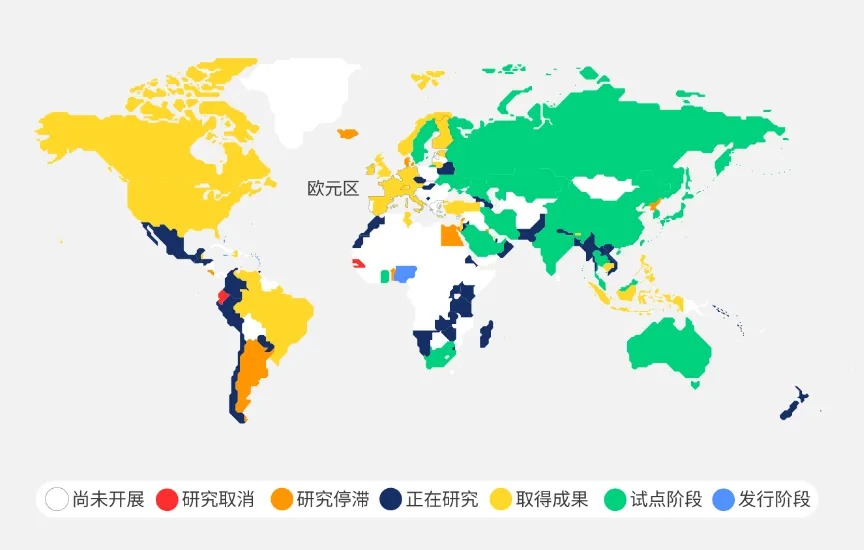
Many countries around the world are actively researching and developing Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). For example, China's digital yuan has entered the pilot stage, and Singapore, the European Union, and others are exploring its possibilities. CBDCs aim to redefine the global payment and monetary system by reducing intermediaries, lowering payment costs, and increasing transaction transparency.
Illustration of Global Central Bank Digital Currency Research Stages Source: World Economic Forum @10xWolfDAO
SWIFT demonstrates its technical capabilities for integrating digital currencies (including CBDCs) through its experiments. Its global payment network combined with blockchain interoperability technology provides a standardized global digital currency trading platform, enabling central banks to operate seamlessly. This provides technical support for the interconnectedness of global monetary policies and simplifies cross-border payment and settlement processes.
SWIFT's CBDC support will become a key link in the global digital currency ecosystem. In the future, central banks can achieve cross-border flow of CBDCs through SWIFT's global network, promoting the modernization and digitization of the global monetary system. For financial institutions, this will greatly simplify cross-border payment and settlement processes while providing a compliant and secure channel for digital currency trading.
3. Risk Management: Security of Digital Assets and Market Stability
3.1. Risk Control of Tokenized Assets
The rapid expansion of tokenized assets is accompanied by increased market volatility and operational risks, especially in the process of cross-chain flow and management of assets. SWIFT's experiment not only focuses on payment efficiency but also aims to explore how to enhance the security and transparency of digital assets through technological means.
By collaborating with Chainlink, SWIFT utilizes decentralized pricing mechanisms and the immutability of blockchain to ensure high transparency and security during the transfer of tokenized assets across different chains. At the same time, SWIFT's global network provides off-chain security support, allowing financial institutions to conduct digital asset transactions under controlled risk conditions.
If SWIFT's experiment can effectively address the risk issues of tokenized assets, it will significantly enhance financial institutions' trust in tokenized assets. This will not only help promote widespread application in the global market but also provide references for global financial regulatory agencies, laying the groundwork for more refined digital asset management rules in the future.
3.2. Market Volatility and Financial Stability
The high volatility of the blockchain market and the lack of regulation are among the biggest concerns for traditional financial institutions. SWIFT's experiment aims not only to improve transaction efficiency but also to test how to reduce the impact of market volatility on financial stability through the robustness of its global payment network.
By building an interoperability framework between on-chain technology and off-chain financial infrastructure, SWIFT provides a buffering mechanism for market volatility, ensuring that transactions remain secure and stable even during instability. Once the experiment proves effective, more financial institutions will gain confidence in entering the digital asset market, significantly enhancing market liquidity and promoting the digital transformation of global capital markets.
4. Regulation and Compliance: Challenges of Cross-Border Digital Assets
4.1. Discrepancies and Unification of Global Regulatory Frameworks
Globally, there are significant differences in regulatory frameworks regarding digital assets. The United States has adopted strict regulatory measures for cryptocurrencies, while places like Singapore and Europe maintain a relatively open attitude towards blockchain and digital assets. As the core hub of global payments, SWIFT must find a balance in this changing regulatory environment.
SWIFT's experiment showcases its exploration of compliance in digital asset trading across different regulatory environments. By collaborating with multiple financial institutions worldwide, SWIFT can test the compliance of its technical solutions in various jurisdictions. This provides a feasible reference for future cross-border payments and transactions of digital assets and helps promote the gradual unification of global regulatory frameworks.
SWIFT's experiment will provide valuable experience for global regulatory agencies, promoting the standardized development of the digital asset market. Digital asset trading in the global financial market will be able to operate under a clearer regulatory framework, significantly reducing compliance risks and facilitating the widespread application of digital assets.
2. Compliance Needs of Central Banks and Financial Institutions
As more central banks and large financial institutions engage in the development and trading of digital assets and CBDCs, compliance will become a core factor determining their large-scale application. SWIFT demonstrates its capability to address compliance issues through this experiment, providing a template for global financial institutions in the realm of digital asset compliance operations.
As a long-trusted payment infrastructure provider for global financial institutions, SWIFT has accumulated rich experience in regulatory compliance. By combining blockchain technology with its global network, SWIFT offers an actionable framework for the compliance management of digital asset trading and CBDCs. In the future, this will help global financial institutions meet the stringent compliance requirements of various countries when participating in the digital asset market.
SWIFT's compliance experiment lays a solid foundation for the large-scale application of digital assets in the future. Central banks and financial institutions worldwide will be able to confidently engage in digital asset trading and cross-border payments through SWIFT's global network while ensuring compliance.
5. Competition and Strategy: Reshaping the Payment Market
1. Competition Between Fintech and Blockchain Payment Networks
Blockchain payment networks (such as Ripple and Stellar) and fintech companies (such as PayPal and Square) are rapidly emerging, challenging the dominant position of traditional payment networks. They are gradually eroding SWIFT's market share in cross-border payments through innovative payment solutions and low fees.
SWIFT's digital asset experiment is a proactive response to this competitive pressure. By introducing blockchain technology, SWIFT not only defends its core position in the global payment network but also explores innovative models for the future payment market. This experiment is not just a technical adjustment but the beginning of a strategic transformation.
The success of SWIFT's experiment will redefine the competitive landscape of the global payment market. In the future, the payment market will become more diversified, and the competition and cooperation between traditional financial institutions, blockchain companies, and fintech firms will accelerate the modernization of the global payment system.
2. Strategic Layout of Future Payment Architecture
SWIFT demonstrates its technological innovation capabilities through the experiment and makes strategic layouts for the future architecture of payment systems. As blockchain technology and the tokenization market expand, SWIFT will not only be a supplier of the global payment network but may also become an infrastructure provider for the global digital asset market.
SWIFT is building the future payment architecture through the experiment, which will increasingly rely on blockchain technology and decentralized networks. By deeply integrating with traditional financial institutions, SWIFT not only retains its existing customer base but also provides more flexible and innovative solutions for the trading and management of future digital assets.
However, while SWIFT brings positive feedback, its limitations cannot be ignored. As the central hub of global financial infrastructure, SWIFT must strictly adhere to international financial regulatory requirements, making complete decentralization nearly impossible for SWIFT.
6. SWIFT's Geopolitical Role and Centralized Control
1. Will it be used as an enhanced political monopoly tool?
SWIFT's digital asset trading experiment is closely related to geopolitical contexts, especially its role in global sanctions. As the central hub of the global payment system, SWIFT has been used in recent years as an important tool by the U.S. and Western countries to implement foreign economic sanctions. Countries like Russia and Iran have faced blockades from the SWIFT system due to geopolitical conflicts, prompting these nations to seek alternatives to cope with sanctions. Russia's TON chain (The Open Network) is one such example, rapidly developing and gradually acquiring payment and financial service capabilities.
In this context, SWIFT's digital asset experiment can be seen as a response from the traditional financial system to the trend of decentralization. The experiment showcases how SWIFT is preparing for a potentially diverse financial ecosystem by integrating digital currencies with fiat currency systems.
From a geopolitical perspective, the rapid development of decentralized finance may weaken the effectiveness of Western countries in implementing sanctions abroad using SWIFT. Therefore, SWIFT's collaboration with Web3 technologies may not only aim to enhance transaction efficiency and technological innovation but also respond to changes in geopolitical dynamics and the global financial power balance.
2. Does it reflect a political inclination to relax restrictions on crypto assets?
SWIFT's experiment does not necessarily imply that the mainstream financial system will relax its regulation of crypto assets. On the contrary, it may resemble traditional financial institutions exploring how to leverage the efficiency and security advantages brought by blockchain technology within a compliance framework. By incorporating digital asset trading into its global payment network, SWIFT is effectively paving the way for the legitimization and compliance of crypto assets rather than allowing them to develop freely. Thus, this approach is more akin to an attempt at standardized management of crypto assets rather than a political signal of a comprehensive relaxation of restrictions.
In the current geopolitical context, SWIFT may be more focused on ensuring the security and traceability of financial transactions globally. Therefore, SWIFT's experiment reflects its cautious acceptance and integration of crypto assets rather than a relaxation of regulation or a close relationship with them. This suggests that SWIFT's digital asset experiment is more likely an exploration of the future direction of digital finance, particularly how to fully leverage the advantages of decentralized technology within a compliance and regulatory framework.
3. The Future Global Payment Landscape: Integration of Mainstream Financial Systems and Blockchain
SWIFT's experiment does not completely eliminate its role as an intermediary. It does not adopt a fully decentralized consensus mechanism like Bitcoin or Ethereum but enhances the flexibility and operability of centralized networks through blockchain technology. Although SWIFT may allow digital assets to be traded within its network, it still maintains centralized control over network participants and transaction processes.
SWIFT's experiment reflects the gradual recognition by traditional financial institutions of the potential of blockchain technology and crypto assets in the future global finance landscape, but it has not relaxed its control over them. Instead, SWIFT is ensuring that crypto assets are integrated into the existing system within a compliance framework through the introduction of regulatory frameworks and technological innovations.
SWIFT's digital asset experiment resembles an exploration of a hybrid model—introducing the technological advantages of blockchain while retaining the core control and regulatory framework of the traditional financial system. The primary goal of this hybrid model is to maintain the efficiency and transparency of the financial system while ensuring regulatory compliance and centralized control are not weakened.
This gradual integration may indicate that the future global payment landscape will be a hybrid model, encompassing both traditional fiat currency systems and digital assets and decentralized finance, but the latter will still require strict regulation and control.
The ultimate outcome of this integration model will depend on the level of cooperation between global financial institutions, regulatory agencies, and technology providers. SWIFT's experiment has already provided an important guide for this trend, but it is more inclined to control the development of crypto assets rather than relax their restrictions.

7. Impact on the Existing Crypto Market
SWIFT's digital asset trading experiment is exploring how to deeply integrate blockchain technology with the global financial network, a move expected to have a significant impact on various sectors and specific projects within the crypto market:
1. Cross-Border Payment Sector ⬇️
Cross-border payments are one of the important sectors in the crypto market. Many crypto projects provide fast, low-cost cross-border payment services through blockchain technology, and SWIFT, as a pillar of the global payment network, will inevitably bring a huge impact upon entering this field.
1.1 Ripple (XRP)
Ripple provides real-time cross-border payment solutions through its XRP Ledger and has attracted numerous financial institutions and banks for collaboration. Ripple's core competitive advantage lies in its efficient cross-border payment capabilities and network coverage. However, SWIFT's digital asset experiment, by leveraging blockchain technology to achieve cross-chain and real-time payment functions, may directly weaken Ripple's market advantage.
Risk of customer loss: As SWIFT integrates blockchain technology into its network, existing Ripple bank clients may be attracted to SWIFT's global payment network, opting for the more familiar and compliant SWIFT system (especially as the SEC continues to apply pressure on Ripple, while SWIFT has a significant compliance advantage).
1.2 Stellar (XLM)
Similar to Ripple, Stellar focuses on the cross-border payment sector, particularly in small to medium-sized cross-border payments and financial inclusion. Stellar offers fast, low-cost payment channels, attracting some financial institutions and businesses in developing countries.
- Threat to Market Share: SWIFT's entry may reduce Stellar's appeal in the cross-border payment market, especially as financial institutions may prefer SWIFT's blockchain technology for broader global coverage and compliance support.
2. Stablecoins and Fiat Payment Sector ⬇️
SWIFT's global payment network is gradually integrating blockchain technology, particularly in the integration of tokenized assets and fiat payments, which will directly impact the stablecoin and fiat payment sector.
2.1 USDC and USDT
USDC and USDT are the two most widely used stablecoins globally, primarily for cross-border payments, DeFi, and exchange trading. Their success is largely due to providing a bridge between fiat currencies and crypto assets.
- Compliance Competition: SWIFT has the advantage of a global compliance system. Once its digital asset trading network offers similar functionalities to stablecoins while better aligning with global regulatory standards, USDC and USDT may lose their appeal to financial institutions, especially in large cross-border payments (USDT has been striving for compliance, while USDC's biggest advantage is compliance and institutional backing, but compared to SWIFT, it will clearly be at a disadvantage).
- Decline in Stablecoin Market Demand: If SWIFT's tokenized fiat payment network can seamlessly achieve cross-border payments and transactions, financial institutions and large enterprises may reduce their reliance on USDC and USDT, especially when strict regulatory compliance is required.
2.2 Facebook (Meta)'s Diem
Although Facebook's Diem (formerly Libra) project has been shelved, its concept aimed to create a global payment network through stablecoins. SWIFT's digital asset experiment may attract financial institutions and corporate clients that originally planned to use Diem, choosing SWIFT as a safer and more compliant solution.
- Loss of Competitive Opportunities in the Market: SWIFT's global influence and compliance network will significantly weaken the competitiveness of similar stablecoin projects like Diem. Financial institutions are more likely to choose SWIFT for converting and paying with fiat and digital assets.
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Sector ⬇️
The DeFi sector has developed rapidly in recent years, with applications like decentralized lending, liquidity mining, and decentralized exchanges (DEX) attracting a large number of users and funds. However, SWIFT's digital asset trading experiment, by providing a compliant blockchain payment and asset management network, will impact the DeFi sector.
3.1 Aave and Compound (Lending Platforms)
Aave and Compound are leading decentralized lending platforms where users can obtain lending services by collateralizing crypto assets. The appeal of the decentralized lending market lies in its intermediary-free and decentralized nature.
- Risk of Institutional Client Loss: The compliance and connection to global financial institutions provided by SWIFT may attract institutional investors who are currently hesitant to enter the DeFi market. These institutions may prefer to conduct lending operations within SWIFT's blockchain payment network to ensure compliance with global regulatory requirements.
3.2 Uniswap and SushiSwap (Decentralized Exchanges)
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) like Uniswap and SushiSwap rely on liquidity providers to offer users intermediary-free trading services. The core competitiveness of DEX lies in its openness and decentralized trading mechanism.
- Liquidity Competition: SWIFT's network may divert liquidity from decentralized trading platforms by integrating financial institutions and mainstream investors. Institutional investors may prefer to use a compliant, regulated platform for asset trading rather than a decentralized exchange.
- Increased Technical and Compliance Pressure: As SWIFT's network attracts more compliant trading flows, DEX may face greater compliance and technical pressures. Decentralized platforms will have to find a balance between compliance and innovation to attract and retain users.
4. Tokenized Asset Sector ⬇️
SWIFT's digital asset trading experiment primarily focuses on the cross-border flow and management of tokenized assets, particularly the tokenization of traditional assets (such as real estate and bonds) for circulation within the global financial system. Existing tokenized asset platforms will be directly affected by SWIFT's market entry.
4.1 Polymath and Securitize
Platforms like Polymath and Securitize focus on the trading of tokenized securities and other assets. These platforms are dedicated to providing blockchain solutions to help financial institutions digitize traditional assets and manage and trade them on the blockchain.
- Compliance Competition: SWIFT's global payment network offers a more mature and compliant framework, and financial institutions may choose SWIFT over decentralized platforms for asset tokenization and trading to ensure compliance with international regulatory standards.
- Market Share Competition: With SWIFT's global coverage capabilities, its tokenized asset solutions may attract more large institutional clients, directly threatening the market share of existing decentralized tokenization platforms.
4.2 RealT and Propy (Real Estate Tokenization Platforms)
Platforms like RealT and Propy focus on real estate tokenization, simplifying the real estate transaction process through blockchain technology, especially playing a significant role in cross-border investments.
- Risk of Loss in Cross-Border Investments: SWIFT's compliant cross-border investment channels provided through its global payment network and blockchain technology may attract more high-net-worth individuals and institutions, reducing the demand for decentralized platforms. This will lead to market losses for platforms like RealT and Propy, particularly in the high-end real estate investment sector.
- Liquidity Competition for Tokenized Assets: SWIFT's entry may increase the market liquidity of high-value tokenized assets, creating significant competitive pressure for existing decentralized real estate platforms.
5. Cross-Chain Interoperability Sector ⬆️
SWIFT has achieved cross-chain interoperability between multiple blockchains through its collaboration with Chainlink. This functionality may have a relatively positive impact on existing cross-chain platforms compared to the direct impact and suppression on the aforementioned sectors.
5.1 Chainlink
While Chainlink is an important partner in SWIFT's cross-chain interoperability technology, as SWIFT's experiment matures, Chainlink, as a market leader in decentralized price feeds and cross-chain solutions, may face new challenges.
- Shift in Technical Direction: As SWIFT gradually integrates cross-chain interoperability features, Chainlink may need to further enhance its technical capabilities or seek more application scenarios in decentralized fields to maintain its market leadership.
- Market Synergy Effects: At the same time, SWIFT's experiment may also promote the application and expansion of Chainlink technology in the global financial market, further enhancing Chainlink's market value.
6. Digital Currency Sector ⬆️
SWIFT's digital asset experiment will inevitably impact the digital currency sector, especially in the competition between central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and stablecoins.
6.1 CBDC Projects
Central banks around the world are actively developing and piloting central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), including China's digital yuan and Europe's digital euro. If SWIFT's blockchain payment network can seamlessly integrate CBDCs, it will bring more liquidity and innovation to the global payment system.
- Accelerated Globalization of CBDCs: By integrating central bank digital currencies, SWIFT may promote the globalization of CBDCs, allowing them to enter mainstream payment systems more quickly and weakening the position of decentralized stablecoins in the existing crypto market.
Conclusion
SWIFT's digital asset trading experiment is not only a technical exploration but also a core pillar of its future payment strategy. Through the introduction of blockchain technology, SWIFT has made comprehensive innovations and layouts in payment efficiency, tokenized asset management, market risk control, compliance, and global competition. The success of this experiment is expected to significantly enhance the efficiency of the global payment system and promote the widespread application of digital currencies and tokenized asset markets.
In the future, SWIFT will continue to play a key role in financial innovation and technological advancement, and the results of its experiment will have a profound impact on the global payment network and financial markets, driving the global financial ecosystem towards a more efficient, secure, and digital direction. However, its inherent centralized nature will not bring a complete celebration and embrace to the crypto market, and may even have a significant impact and shock on the current crypto landscape due to its prominent market share and payment attributes.
Special Thanks
Creating content is not easy. If you need to reprint or quote, please contact the author for authorization or indicate the source in advance. Thank you again for the support of the readers;
Written by: Cage / Mat / Darl / WolfDAO
Proofread by: Punko Chief Editor: Vessel
Special Thanks: Thanks to the above partners for their outstanding contributions to this issue.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。