What Monad, MegaETH, Berachain, and Sei Bring to EVM
Written by: Jun, Bankless
Compiled by: Deng Tong, Jinse Finance
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) has quietly become a pillar of blockchain development. It is not just technology, but an ecosystem of developers, tools, and applications that have developed around the technology.
Today, many teams are rethinking Ethereum's design choices, enhancing the EVM to create blockchains capable of processing billions of users and thousands of transactions per second. They leverage the advantages of the EVM and push boundaries through new architectures and functionalities.
This article focuses on projects that accelerate the EVM's realization of large-scale scalability and pave the way for future cryptocurrency adoption. Today, we will delve into Monad, MegaETH, Berachain, and Sei.
Monad
First, let's talk about Monad.
Monad is an L1 blockchain that has raised $225 million, enhancing the EVM by introducing optimistic parallel execution, aiming for a throughput of 10,000 transactions per second.
Parallel execution allows independent transactions to run simultaneously, significantly speeding up processing. You can think of it as using multiple washing machines at the same time: there’s no need to wait for each machine to finish, everything can be done faster while still appearing orderly.
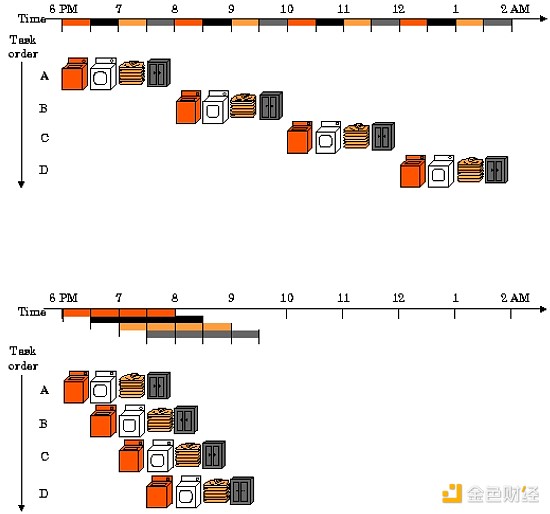
In addition to parallel execution, Monad also optimizes the performance of the entire stack:
- Enhances performance through its custom consensus mechanism MonadBFT, which achieves single-slot finality for faster transactions.
- Employs delayed execution to separate processing from consensus, improving efficiency and block time.
- Its parallelized custom database MonadDB allows for asynchronous state access, speeding up data processing.
Notably, Monad's architecture is optimized for consumer-grade hardware, making decentralization easier without the need for expensive validator setups.
MegaETH
Next is MegaETH.
MegaETH is an Ethereum L2 that elevates Ethereum's security to new performance levels. Its goal is bold: to establish the first real-time blockchain capable of processing 100,000 transactions per second while relying on Ethereum and EigenDA for security and data availability.
The key to MegaETH's throughput is specialization. Most blockchains require each node to perform the same tasks—validation, consensus, and transaction execution. MegaETH changes this through role division.
Nodes are divided into three types: sequencers, provers, and full nodes. Sequencers handle transaction ordering and execution. Full nodes only need to receive state updates to keep a local copy of the chain up to date. Provers work in the background, validating everything with cryptographic proofs.
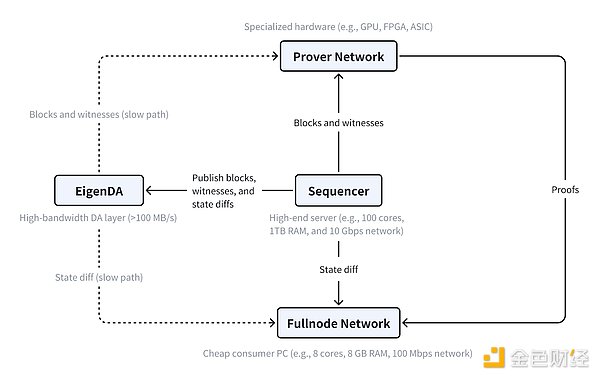
The main components of MegaETH and their interactions. Source: MegaETH Research
MegaETH also enhances the EVM through in-memory computation, where sequencers keep the entire EVM world state in memory. This increases state access speed by 1,000 times compared to traditional systems. Additionally, improvements in block building algorithms and other updates enable MegaETH to address issues such as latency and throughput.
Berachain
Of course, we have to talk about Berachain.
Berachain is a high-performance L1 blockchain that mirrors the EVM runtime environment of the Ethereum mainnet. This results in a system that supports all the familiar tools and operations known to developers, but with additional advantages.
At the core of these advantages is BeaconKit, a modular, EVM-centric consensus client framework on which Berachain is built. The main benefit of BeaconKit is its ability to integrate the functionality of the CometBFT consensus algorithm with the EVM execution environment. This effectively modularizes the stack, separating the consensus layer from the execution layer to enhance the overall Berachain experience.
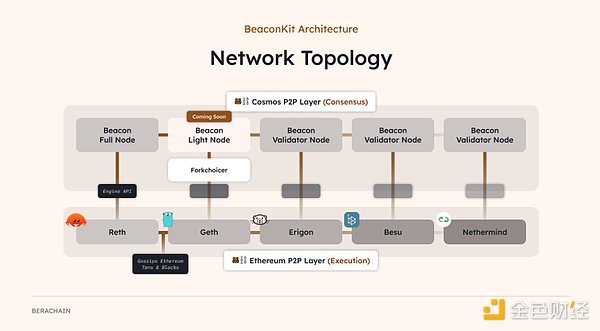
Source: BeaconKit - A modular framework for building EVM consensus clients
BeaconKit can also pair with any EVM execution client, allowing for automatic application of every upgrade to the EVM (e.g., Dencun) to Berachain. This means Berachain not only retains the same state as the EVM but also accelerates its speed, expands it, and increases composability without losing compatibility. For example, with BeaconKit, Berachain can achieve single-slot finality, meaning blocks are finalized immediately rather than waiting 12-15 minutes or more as on Ethereum.
Sei
Finally, let's take a closer look at Sei.
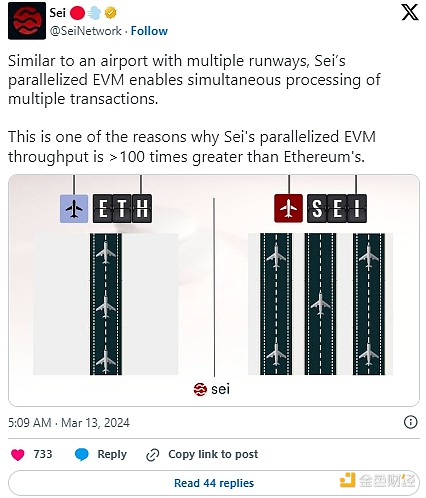
Sei combines the EVM environment with parallel execution, achieving faster and cheaper transactions while leveraging existing tools and developer communities. Its parallel execution allows multiple transactions to occur simultaneously, significantly increasing throughput, supplemented by SeiDB for rapid state updates.
What’s novel about Sei is its "Twin Turbo" consensus mechanism, which accelerates block times to just 400 milliseconds. It achieves this through two key technologies that eliminate common inefficiencies in consensus protocols:
- Smart block propagation—accelerating block creation, reducing validator wait times, and ultimately decreasing latency.
- Optimistic block processing—validators begin processing transactions immediately upon receiving block proposals, speeding up finality.
Additionally, Sei integrates features such as interoperability between EVM and CosmWasm, opening doors for the Cosmos ecosystem.
However, Sei does sacrifice some decentralization between nodes, as these features introduce quadratic communication complexity. This means that as more validators join, the number of messages increases significantly, making network scaling more challenging.
Conclusion
These ambitious projects aim to build on Ethereum's achievements, scaling throughput to thousands of transactions per second. Most are still in the early stages; three out of the four have yet to launch on the mainnet. Only time will tell their success in scaling, driving adoption, and achieving efficient application development.
What does this mean for Ethereum?
One silver lining is that some of these high-performance chains are L2 chains, aligning with Ethereum's aggregation-centered scaling roadmap. Another positive aspect is that they are all EMV compatible, building on existing tools while enhancing them in unique ways, thus promoting EVM adoption.
This is also a critical moment for the Ethereum community, as many are questioning why there isn’t more focus on scaling Ethereum itself as L1. Vitalik seems to be in "war mode," continuously publishing blog posts about Ethereum's potential future. The point is that Ethereum has multiple pathways to scale the throughput of Ethereum L1, and importantly, all pathways are under discussion and exploration.

免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



