The Solv protocol has launched SAL (Staking Abstraction Layer), which aims to promote the large-scale application era of Bitcoin staking by enhancing the standardization and interoperability of the Bitcoin staking ecosystem.
Written by: Solv Protocol
BNB Chain, Ceffu, and Chainlink are the initial partners.
The uniqueness of the Bitcoin network and the complexity of Bitcoin staking present numerous challenges for Bitcoin staking. The Solv protocol has introduced SAL (Staking Abstraction Layer) to enhance the standardization and interoperability of the Bitcoin staking ecosystem, aiming to usher Bitcoin staking into an era of large-scale application.
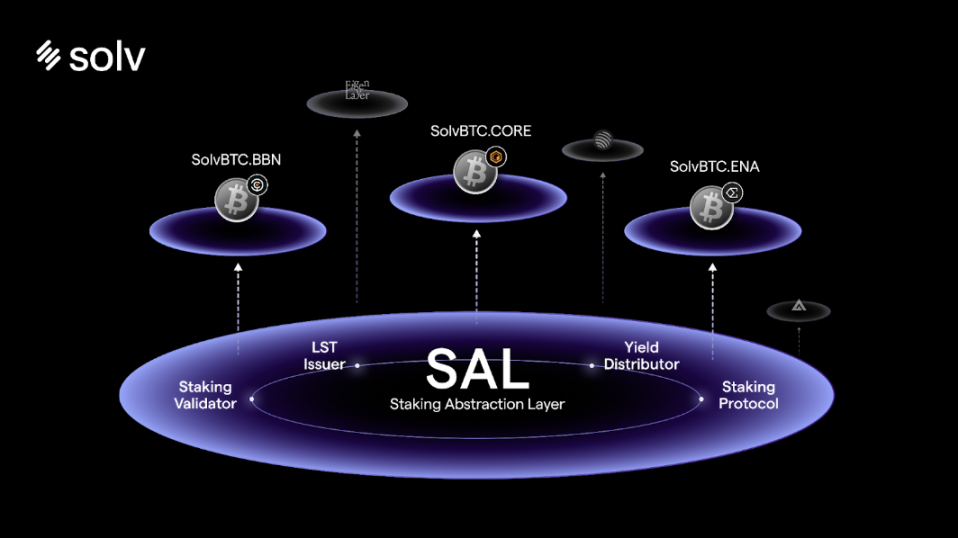
SAL consists of a series of smart contracts that leverage smart contract technology and Bitcoin mainnet technology to enable seamless collaboration among stakers, LST issuers, staking protocols, and other staking service providers, while simplifying user interactions with Bitcoin staking protocols and providing a convenient staking experience.
Solv began focusing on Bitcoin staking in April 2024, allowing users to stake their Bitcoin assets, including BTCB, FBTC, WBTC, etc. As of September 30, 2024, over 20,000 BTC (worth approximately $1.4 billion) have been staked in the Solv protocol, with more than 13,000 BTC coming from BNB Chain. Ceffu acts as a staking validator to ensure that all staked assets are genuinely and completely staked into protocols like Babylon and CoreDAO.
Why is SAL very important?
Today, the market capitalization of Bitcoin has exceeded $1.2 trillion, but due to a lack of valuable use cases, 99% of the liquidity remains idle. Bitcoin staking is the best solution to unlock large-scale Bitcoin liquidity; however, the current adoption rate of Bitcoin staking is very low, far behind Ethereum (28%). Imagine if Bitcoin could achieve a staking rate similar to Ethereum, which would mean releasing approximately $330 billion in value, significantly driving the explosion of BTCFi and becoming a massive pump for the entire industry.
However, Bitcoin staking has encountered bottlenecks in its actual development. First, in the past six months, we have witnessed a rapid emergence of various Bitcoin staking protocols in the market, such as Babylon, CoreDAO, and Botanix. These protocols support different public chains, underlying technology architectures, and asset security solutions, leading to high selection, decision-making, and operational costs for users.
Additionally, since the Bitcoin mainnet does not support smart contracts, Bitcoin staking involves cross-chain asset transfers between the Bitcoin mainnet and other chains, with staking activities often occurring on different chains. This requires users to engage in complex interactions across different networks, which not only raises the participation threshold for users but also increases the opacity and risk of the entire process.
SAL Operating Mechanism
SAL attempts to address the above challenges by abstracting the technical differences and operational methods of different staking processes to build a standardized Bitcoin staking solution. Developers can quickly implement Bitcoin staking services using existing service providers within the SAL framework, which not only lowers the entry barrier for developers but also promotes rapid innovation in the Bitcoin staking ecosystem.
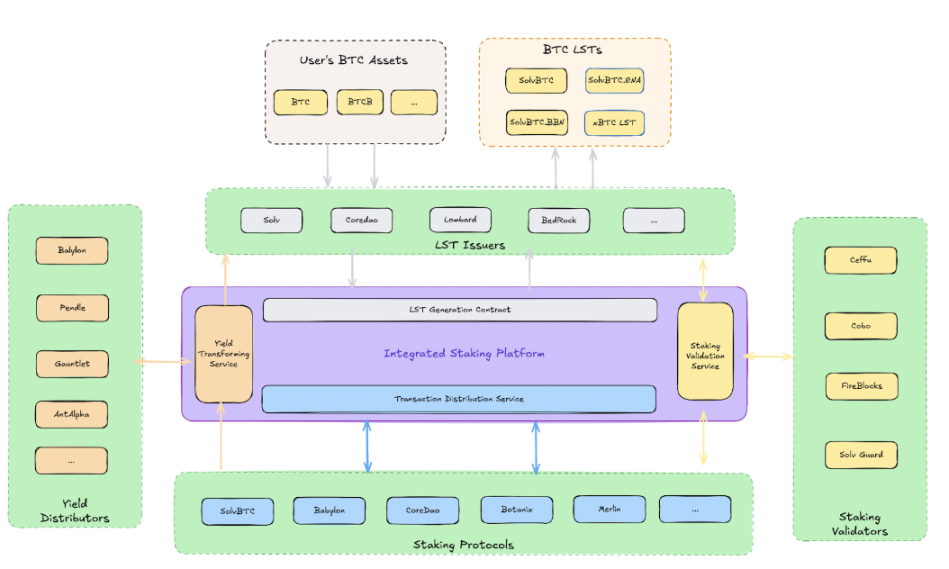
Essentially, the Bitcoin staking ecosystem consists of four core roles:
- LST Issuers: Refers to protocols that issue liquid staking tokens (LST) related to staked Bitcoin, bridging users and staking protocols. Typical examples include Solv, Lombard, and BedRock.
- Staking Protocols: Refers to protocols that accept Bitcoin assets and generate returns through operations, such as Babylon, CoreDao, and Botanix.
- Staking Validators: Refers to entities responsible for verifying the integrity of the staking and transaction processes, ensuring that LST issuers execute staking accurately and completely, preventing errors or fraudulent activities by LST issuers and staking protocols. Examples include Ceffu, Cobo, Fireblocks, and Solv Guard.
- Reward Distributors: Refers to entities that distribute staking rewards, responsible for efficiently and fairly distributing rewards. Typical examples include Pendle, Gauntlet, Antalpha, and most LST issuers also act as reward distributors.
SAL efficiently integrates these four roles using smart contract technology and Bitcoin mainnet technology.
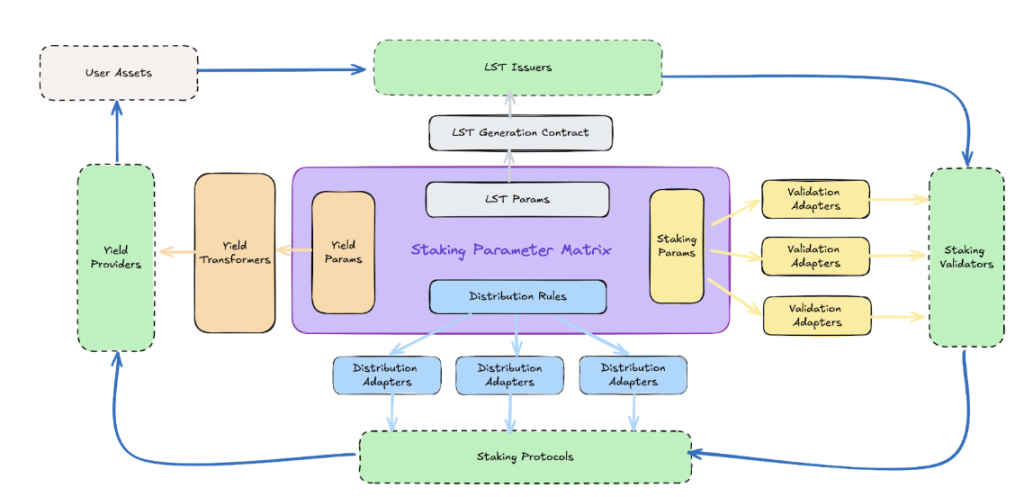
Specifically, SAL consists of five core modules, including a core data model and a series of services:
Staking Parameter Matrix (SPM)
The core data model of the Staking Abstraction Layer is called the Staking Parameter Matrix, which abstracts the parameters used in multiple staking processes, including Bitcoin script configurations, staking transaction parameters, LST contract parameters, and reward distribution rules. These parameters are shared not only among the various modules of SAL but also among the roles participating in the staking process.
LST Generation Module
This module will ensure the issuance and redemption of BTC LST. The LST generation module will be responsible for interactions between the Bitcoin mainnet and EVM chains, including a set of smart contracts on the EVM chain and services for creating and monitoring transactions on the Bitcoin mainnet.
Transaction Construction Module
The transaction generation module is responsible for creating staking transactions, estimating optimal transaction fees, and broadcasting transactions to the Bitcoin mainnet. All parameters of the constructed transactions are defined in the SPM for validators to verify.
Validation Nodes
Validation nodes are a set of algorithms based on the Bitcoin mainnet that check the correctness and integrity of each staking transaction according to the staking transaction parameters defined in the SPM. They can also participate in verifying the issuance quantity of LST, ensuring that the quantity of LST issued equals the quantity of underlying BTC assets, preventing errors or fraudulent activities by LST issuers and staking protocols.
Reward Distribution Module
The reward distribution module is responsible for calculating the value of rewards and mapping it to the price of LST or providing solutions for airdropping reward assets to users. The functions of the reward distribution module include LST price oracles, reward exchange services, reward storage and redemption services, and point redemption, among others.
SAL: A Win-Win One-Stop Solution
As the BTCFi narrative continues to evolve, Bitcoin staking, as a key business to release Bitcoin liquidity, is destined to become a crucial part of the future Bitcoin ecosystem. The market urgently needs a secure, scalable solution, and SAL is a universal solution that effectively meets the needs of all parties involved.

For stakers, it provides a convenient Bitcoin staking experience while reducing the risk of asset loss due to operational errors and protocol opacity; for staking protocols, joining SAL can significantly lower development costs and quickly obtain liquidity to achieve ecological cold starts; for LST issuers, collaborating with various service providers within the SAL framework can enhance protocol trust, simplify development processes, and obtain efficient reward distribution solutions, improving product user experience; for custodians, this represents a new business model that can effectively increase business revenue.
Current Status of SAL Development
As of now, several protocols and service providers have joined the SAL protocol ecosystem created by Solv. Babylon, CoreDAO, Stacks, Eigenlayer, and GMX are among the first batch of staking protocols adopting SAL, while Pendle is the first reward distribution protocol to join. Chainlink utilizes its CCIP technology to achieve cross-chain and underlying asset transparency proof for LST assets generated based on SAL. More protocols are expected to join in the coming months.

Conclusion
As Bitcoin staking continues to develop, its impact on the blockchain ecosystem will grow increasingly significant. The demand from stakers seeking to maximize yield potential and developers seeking protocol innovation will continuously unlock new on-chain opportunities. SAL, by enhancing the standardization and interoperability of the Bitcoin staking ecosystem, brings tangible benefits to developers, users, and the entire Bitcoin community, and is expected to trigger a series of chain reactions for Bitcoin's sustained growth, reshaping Bitcoin staking and paving the way for true large-scale adoption.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




