If AIGC has ushered in the intelligent era of content generation, then AI Agent has the opportunity to truly productize the capabilities of AIGC.
AI Agent, like a more concrete all-around employee, is considered the primary form of artificial intelligence robots, capable of observing the surrounding environment, making decisions like humans, and taking actions automatically.
Bill Gates once said, "Controlling AI Agent is the real achievement. By then, you will no longer need to search for information on the Internet yourself." Similarly, authoritative experts in the field of AI also have high hopes for AI Agent. Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella once predicted that AI Agent will become the main way of human-machine interaction, able to understand user needs and provide services proactively. Professor Andrew Ng also predicted that in the future work environment, humans and AI Agent will collaborate in a more closely manner, forming an efficient work mode and improving efficiency.
AI Agent is not only a product of technology, but also the core of future life and work methods.
This inevitably reminds people that when Web3 and blockchain were widely discussed, people often used the word "disruptive" to describe the potential of this technology. Looking back over the past few years, Web3 has gradually developed from the initial ERC-20, zero-knowledge proof, to the integration with other fields such as DeFi, DePIN, GameFi, and so on.
If the two popular digital technologies, Web3 and AI, are combined, will it produce a synergistic effect? Can the increasingly large-scale Web3 AI projects bring new paradigm of use cases to the industry and create new real demands?
AI Agent: The Most Ideal Intelligent Assistant for Humans
Where does the imagination of AI Agent lie? There is a widely circulated high-score answer online, "A large language model can only code a game of Snake, while AI Agent can code an entire King of Glory." It sounds exaggerated, but it is not an exaggeration.
The concept of "Agent" is usually translated as "智体" in China. This concept was proposed by "the father of artificial intelligence" Minsky in his book "The Society of Mind" published in 1986. Minsky believed that certain individuals in society can reach a solution to a problem through negotiation, and these individuals are Agents. For many years, Agent has been the cornerstone of human-computer interaction. From Microsoft's Clippy to Google Docs' automatic suggestions, these early forms of Agent have shown the potential for personalized interaction, but their capabilities are still limited in handling more complex tasks. It wasn't until the emergence of large language models (LLM) that the true potential of Agent was unearthed.
In May of this year, Professor Andrew Ng, an authoritative scholar in the field of AI, shared a speech about AI Agent at the Redwood AI event in the United States, in which he demonstrated a series of experiments conducted by his team:
Let AI write some code and run it, and compare the results obtained from different LLMs and workflows. The results are as follows:
GPT-3.5 model: Accuracy 48%
GPT-4 model: Accuracy 67%
GPT-3.5 + Agent: Performance higher than GPT-4 model
GPT-4 + Agent: Far higher than GPT-4 model, very outstanding
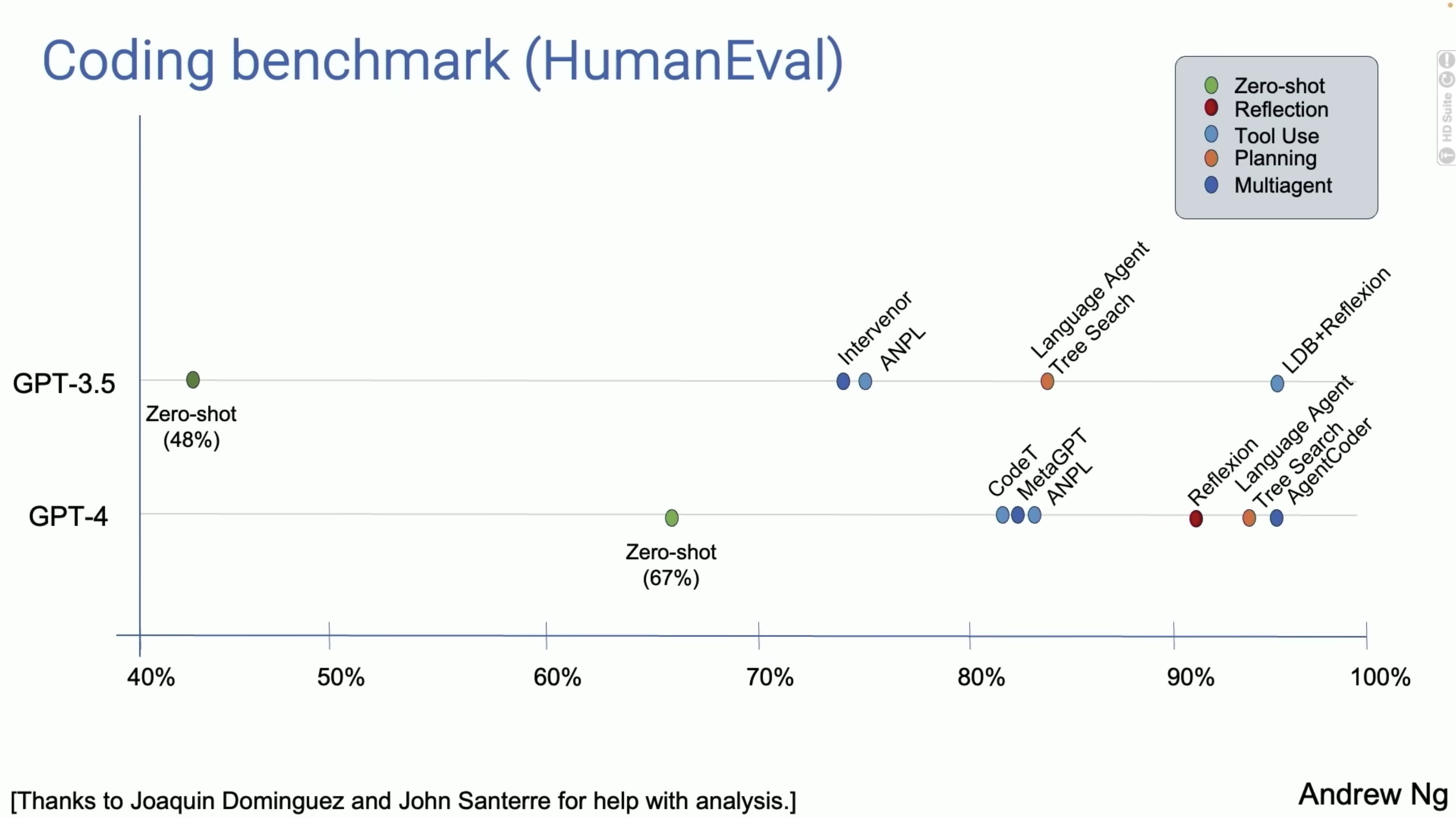
Indeed. Most people use LLMs like ChatGPT in a way that involves inputting a prompt, and the large model will immediately generate an answer without automatically recognizing and correcting errors or deleting and rewriting.
In contrast, the workflow of AI Agent is as follows:
First, let the LLM write an outline of an article, if necessary, conduct research and analysis on the Internet, output a draft, then read the draft and think about how to optimize it, iterate multiple times in this way, and finally output a logically rigorous, low-error-rate, high-quality article.
We can see that the difference between AI Agent and LLM is that the interaction between LLM and humans is based on prompts. AI Agent only needs to set a goal, and it can think and act independently based on the goal. It can break down the detailed steps of a given task, rely on feedback from the outside world and independent thinking, and create prompts for itself to achieve the goal.
Therefore, OpenAI defines AI Agent as: Driven by LLM as the brain, it has the ability to autonomously understand, perceive, plan, remember, and use tools, and can automate the execution of complex tasks.
When AI changes from being a tool used to being able to use tools, it becomes an AI Agent. This is also the reason why AI Agent can become the most ideal intelligent assistant for humans. For example, AI Agent can understand and remember a user's interests, preferences, daily habits based on the user's historical online interactions, identify the user's intentions, make suggestions proactively, and coordinate multiple applications to complete tasks.
Just as in Gates' vision, in the future, we will no longer need to switch to different applications for different tasks. We only need to tell the computer and phone what we want to do in ordinary language, and based on the data the user is willing to share, AI Agent will provide personalized responses.
Single-Person Unicorn Companies Are Becoming Reality
AI Agent can also help companies create a new intelligent operation mode with "human-machine collaboration" at its core. More and more business activities will be completed by AI, while humans will only need to focus on the decision-making of the enterprise's vision, strategy, and critical paths.
Just as Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, mentioned in an interview, with the development of AI, we are about to enter the era of "single-person unicorns," where companies founded by a single person will reach a valuation of $1 billion.
It sounds like a fantasy, but with the assistance of AI Agent, this view is becoming a reality.
For example, let's make a hypothesis. If we were to start a technology startup now, using the traditional method, it is obvious that I would need to hire software engineers, product managers, designers, marketers, salespeople, and finance personnel, each with their own responsibilities but all coordinated by me.
But what if we use AI Agent? I might not even need to hire employees.
- Devin — Automated Programming
Instead of software engineers, I might use the popular AI software engineer Devin, which can help me complete all front-end and back-end work.
Devin, developed by Cognition Labs, is known as "the world's first AI software engineer." It can independently complete the entire software development process, analyze problems independently, make decisions, write code, and fix errors, all autonomously. This greatly reduces the workload of developers. Devin raised $196 million in funding within a short six months and its valuation quickly soared to tens of billions of dollars. Investors include well-known venture capital companies such as Founders Fund and Khosla Ventures.
Although Devin has not yet released a public version, we can glimpse its potential from another recently popular product in Web2, Cursor. It can almost complete all the work for you, turning a simple idea into functional code in a few minutes. You only need to give orders, and it will "make it happen." There are reports that an eight-year-old child, with no programming experience, actually used Cursor to complete coding work and build a website.
- Hebbia — Document Processing
Instead of product managers or finance personnel, I might choose Hebbia, which can help me complete all document organization and analysis.
Unlike Glean, which focuses on enterprise document search, Hebbia Matrix is an enterprise-level AI Agent platform that uses multiple AI models to help users efficiently extract, structure, analyze data and documents, thereby driving productivity improvement in enterprises. Impressively, Matrix can process millions of documents at once.
In July of this year, Hebbia completed a $130 million Series B round, led by a16z, with participation from notable investors such as Google Ventures and Peter Thiel.
- Jasper AI — Content Generation
Instead of social media operations and designers, I might choose Jasper AI to help me with content generation.
Jasper AI is an AI Agent writing assistant designed to simplify content generation processes for creators, marketers, and businesses, improving productivity and efficiency. Jasper AI can generate various types of content, including blog articles, social media posts, ad copy, and product descriptions, in the style requested by the user. It can also generate images based on user descriptions to provide visual support for the text content.
Jasper AI has raised $125 million in funding and reached a valuation of $1.5 billion in 2022. According to statistics, Jasper AI has helped users generate over 500 million words, making it one of the most widely used AI writing tools.
- MultiOn — Web Automation
Instead of an assistant, I might choose MultiOn to help me manage daily tasks, schedule reminders, and even plan business trips, automatically booking hotels and arranging rideshare services.
MultiOn is an automated web task AI agent that can help autonomously execute tasks in any digital environment, such as assisting users with online shopping, appointments, and personal tasks to improve personal efficiency or simplify daily tasks to enhance work efficiency.
- Perplexity — Search, Research
Instead of a researcher, I might choose Perplexity, which is used daily by NVIDIA's CEO.
Perplexity is an AI search engine that can understand user queries, break down questions, search and integrate content, and generate reports to provide clear answers to users.
Perplexity is suitable for various user groups, such as students and researchers who can simplify the information retrieval process for writing and improve efficiency, and marketers who can obtain reliable data to support marketing strategies.
The above content is purely hypothetical, as the current capabilities and levels of these AI Agents are not yet sufficient to replace elite talents in various industries. As Logenic AI co-founder Li Bojie said, the current capabilities of LLM are only at an entry-level, far from expert-level, and at this stage, AI Agents are more like fast but not very reliable workers.
However, these AI Agents are leveraging their respective strengths to help existing users improve efficiency and convenience in diverse scenarios.
The benefits of the AI Agent wave are not limited to tech companies. Various industries can benefit from AI Agents. In the education sector, AI Agents can provide personalized learning resources and tutoring based on students' learning progress, interests, and abilities. In the financial sector, AI Agents can help users manage personal finances, provide investment advice, and even predict stock trends. In the medical field, AI Agents can assist doctors in disease diagnosis and treatment plan formulation. In the e-commerce sector, AI Agents can also serve as intelligent customer service, automatically answering user inquiries, handling order issues, and return requests, thereby improving customer service efficiency.
Multi-Agent: The Next Step for AI Agent
In the previous section on the concept of single-person unicorn companies, a single AI Agent faces limitations when handling complex tasks and may not meet actual needs. When using multiple AI Agents, due to the heterogeneous LLM-based AI Agents, collective decision-making is difficult, and their capabilities are limited, requiring humans to act as schedulers between these independent AI Agents, coordinating them to work in different application scenarios. This has led to the rise of the "Multi-Agent" framework.
Complex problems often require the integration of diverse knowledge and skills, and the capabilities of a single AI Agent are limited and may not be able to handle them. By organically combining AI Agents with different capabilities, the Multi-Agent system allows AI Agents to leverage their respective strengths and complement each other, thereby more effectively solving complex problems.
This is very similar to our actual workflow or organizational structure: a leader assigns tasks, individuals with different abilities are responsible for different tasks, and the results of each process are passed on to the next process, ultimately achieving the final task outcome.
In the implementation process, lower-level AI Agents execute their respective tasks, while higher-level AI Agents allocate tasks and supervise their completion.
Multi-Agent can also simulate our human decision-making process, just as we consult with others when we encounter problems, multiple AI Agents can simulate collective decision-making behavior to provide better information support. For example, AutoGen developed by Microsoft meets this requirement:
It can create AI Agents with different roles. These AI Agents have basic conversational abilities and can generate responses based on received messages.
It creates a group chat environment where multiple AI Agents participate, and in this GroupChat, an administrator role AI Agent manages the chat records of other AI Agents, speaker order, and terminates speech, etc.
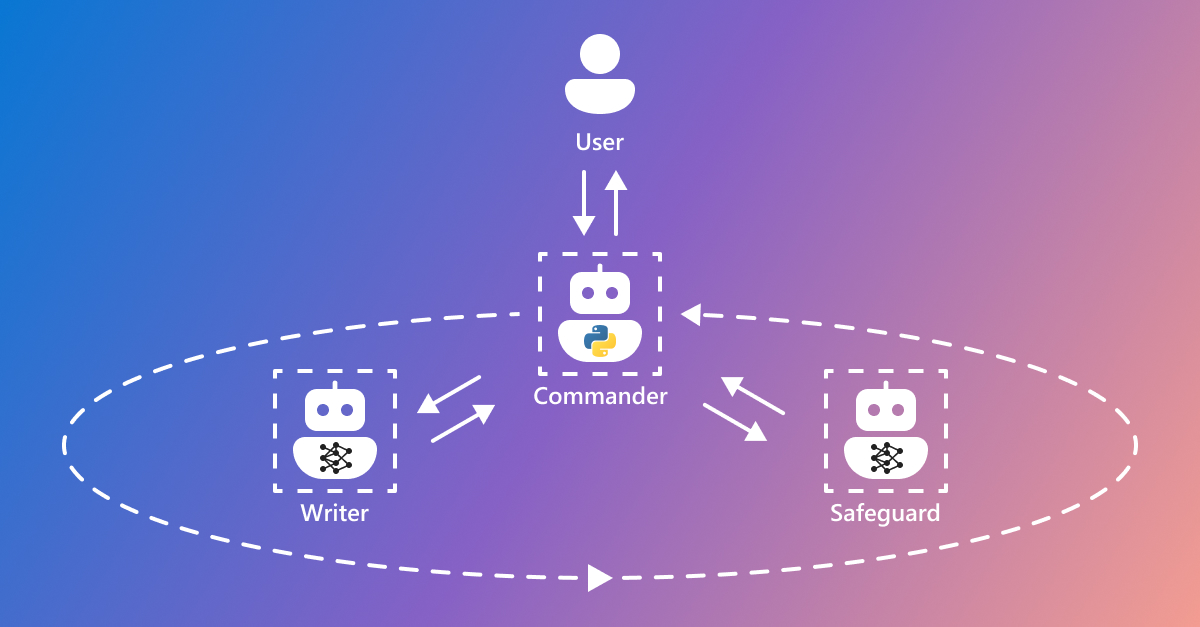
If applied to the concept of single-person unicorn companies, we can create several AI Agents with different roles using the Multi-Agent architecture, such as project managers, programmers, or supervisors. We tell them our goals and let them figure out how to achieve them, and we just listen to their reports. If we have any opinions or if they are not doing things right, we ask them to make changes until we are satisfied.
Compared to a single AI Agent, Multi-Agent can achieve:
Scalability: Handling larger-scale problems by increasing the number of AI Agents, with each AI Agent handling a portion of the tasks, allowing the system to expand as demand grows.
Parallelism: Natural support for parallel processing, with multiple AI Agents able to work simultaneously on different parts of the problem, thereby accelerating problem-solving.
Decision Improvement: Enhancing decision-making by aggregating insights from multiple AI Agents, as each AI Agent has its own perspective and expertise.
As AI technology continues to advance, it is conceivable that the Multi-Agent framework will play a greater role in various industries and drive the development of various new AI-driven solutions.
The Rise of AI Agent, Blowing Towards Web3
Stepping out of the laboratory, the road ahead for AI Agent and Multi-Agent is long and challenging.
Leaving aside Multi-Agent, even the most advanced single AI Agent currently faces clear physical limits in terms of the computational resources and capabilities it requires, and it cannot achieve unlimited scalability. When faced with extremely complex and computationally intensive tasks, AI Agent will undoubtedly encounter computational bottlenecks, resulting in significantly reduced performance.
Furthermore, AI Agent and Multi-Agent systems are essentially a centralized architecture pattern, which determines the high risk of single-point failure. More importantly, the monopolistic business model based on closed-source large models by companies such as OpenAI, Microsoft, and Google seriously threatens the survival environment of independent, single AI Agent startups, making it difficult for AI Agents to smoothly utilize vast amounts of enterprise private data to make them smarter and more efficient. There is an urgent need for a democratic collaboration environment among AI Agents, enabling truly valuable AI Agents to serve a broader range of demand groups and create greater value for society.
Lastly, although AI Agent is closer to the industry compared to LLM, its development is based on LLM, and the current characteristics of the large model track are high technical barriers, high capital investment, and an immature business model, making it difficult for AI Agents to obtain funding for continuous updates and iterations.
The paradigm of Multi-Agent is an excellent perspective for Web3 to empower AI, and many Web3 development teams are investing in research and development to provide solutions in these areas.
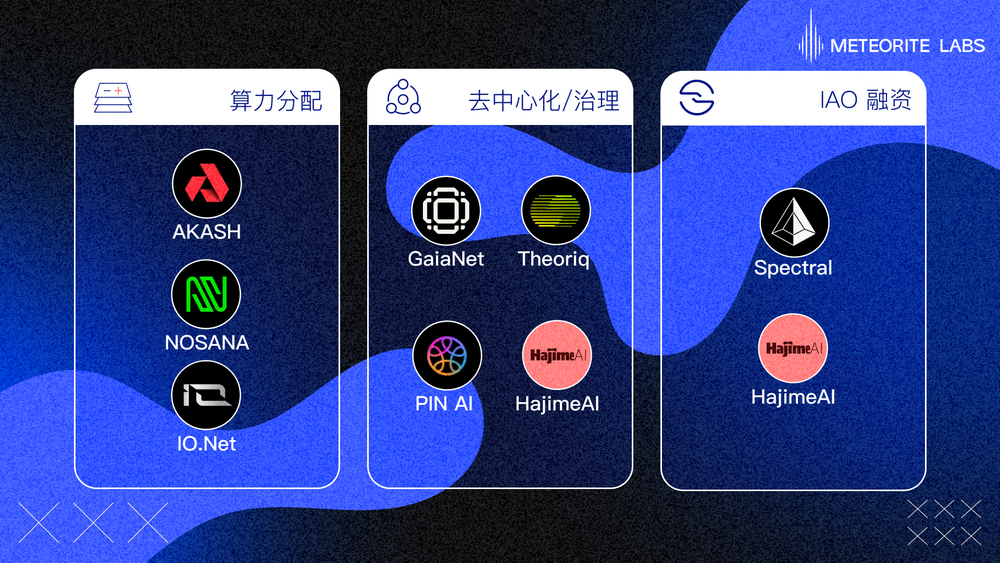
AI Agent and Multi-Agent systems typically require a large amount of computing resources to make complex decisions and perform tasks. Web3, through blockchain and decentralized technology, can build a decentralized computing power market, allowing computing resources to be distributed and utilized more fairly and efficiently on a global scale. Web3 projects such as Akash, Nosana, Aethir, and IO.net can provide computational capabilities for AI Agent decision-making and reasoning.
Traditional AI systems are often centrally managed, leading to single-point failures and data privacy issues for AI Agents. The decentralized nature of Web3 can make Multi-Agent systems more decentralized and autonomous, with each AI Agent able to run independently on different nodes, autonomously fulfilling user demands, enhancing robustness and security. Establishing incentive and penalty mechanisms for stakers and delegators through mechanisms such as PoS and DPoS can promote the democratization of single AI Agent or Multi-Agent systems.
In this regard, GaiaNet, Theoriq, PIN AI, and HajimeAI are making very cutting-edge attempts.
Theoriq is a project serving "AI for Web3" and aims to establish the calling and economic system of AI Agents through the Agentic Protocol, popularizing the development of Web3 and many functional scenarios, providing verifiable model reasoning capabilities for Web3 dApps.
GaiaNet is a node-based AI Agent creation and deployment environment, with the goal of protecting the intellectual property and data privacy of experts and users, countering the centralized OpenAI GPT Store.
HajimeAI focuses on establishing AI Agent workflows in practical needs and intelligent and automated intent, echoing PIN AI's mention of "personalization of AI intelligence".
Additionally, Modulus Labs and ORA Protocol have made progress in the algorithm direction of zkML and opML for AI Agents.
Finally, the development and iteration of AI Agent and Multi-Agent systems often require substantial financial support, and Web3 can help potential AI Agent projects obtain valuable early support through its pre-liquidity characteristics.
Spectral and HajimeAI have proposed product concepts to support the issuance of AI Agent assets on the chain: issuing tokens through IAO (Initial Agent Offering), AI Agents can directly obtain funding from investors while becoming a member of DAO governance, providing investors with the opportunity to participate in project development and share future profits. HajimeAI's Benchmark DAO hopes to organically combine decentralized AI Agent scoring and AI Agent asset issuance through crowdfunding and token incentives, creating a closed loop for AI Agent financing and cold start based on Web3, which is a novel attempt.
The Pandora's box of AI has been opened, and everyone in it is both excited and confused. Under the heat wave, is it an opportunity or a reef, no one knows. Today, every industry is no longer in the era of PPT financing, and no matter how cutting-edge the technology is, it can only realize its value through implementation. The future of AI Agent is destined to be a long marathon, and Web3 is ensuring that it will not quietly exit the competition.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




