Challenges and Opportunities
Recently, we have observed two significant trends in the blockchain field:
First, with the vigorous development of the blockchain ecosystem and applications, the activities of individual accounts on the chain have become increasingly diverse and complex, leaving more comprehensive digital footprints for users on the chain. The rich on-chain interactions have also brought many new opportunities, such as building on-chain credit scores based on user asset portfolios and transaction histories. This trend of development has the potential to drive innovation in traditional financial practices such as non-overcollateralized lending protocols.
Second, as the industry matures, project parties are paying more attention to understanding user profiles and evaluating user quality when formulating targeted airdrop strategies or analyzing potential user groups. However, they face a huge challenge: EVM accounts are essentially transaction triggers, rather than "bank accounts" like traditional finance. This structural form limits the in-depth analysis of account-level data, making it difficult for project parties to gain meaningful insights into their user base.
These trends highlight the urgent need for advanced tools that can effectively analyze and interpret account-level data. To address this need, Hemera Protocol is developing a new generation of account-centric indexing protocols, aiming to provide developers with standardized account-level data retrieval and functional development services.
This innovation further extends to an account-centric indexing (ACI) network, ensuring decentralized data management. Leveraging this network, Hemera provides powerful solutions for processing and analyzing blockchain data, making it easy to build various user-oriented applications and suitable for multiple use cases.
What is Account-Level Data Extraction?
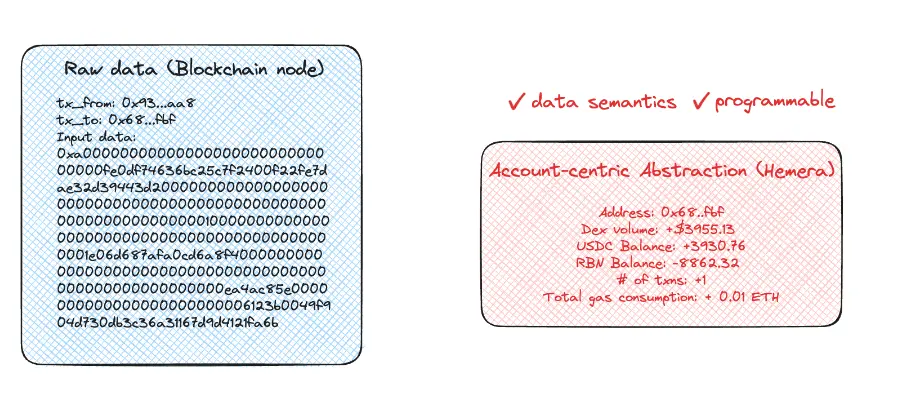
When a transaction occurs on the blockchain, its raw data does not intuitively appear as "transactions." If you retrieve this data directly from the blockchain node, it may look like the complex information array in the blue chart below—neither semantic nor easy to analyze. Essentially, it records who sent the transaction, where it was sent, and what was input.
The process of data extraction is to transform these difficult-to-understand data into meaningful semantics. For example, in a transaction, the main information we focus on is the types and quantities of tokens bought and sold, as well as the total value of the transaction. Therefore, a typical data extraction for a transaction may include key elements such as the transaction initiator, bought tokens, sold tokens, their respective quantities, and the transaction amount.
What is truly important is understanding how these transactions affect the overall state of your account. For example, a transaction will change your token balance, affect your trading volume, increase your total gas fees paid, and increase your on-chain interaction count.
Hemera encapsulates these account-level changes in a semantic and standardized format, called "features." The red chart below illustrates how this exchange transaction has affected your account status. Through the User Defined Function (UDF) module, developers can design and define these features according to specific needs. This data extraction method presents complex blockchain data in a more intuitive way, making development work convenient and facilitating meaningful analysis conclusions.
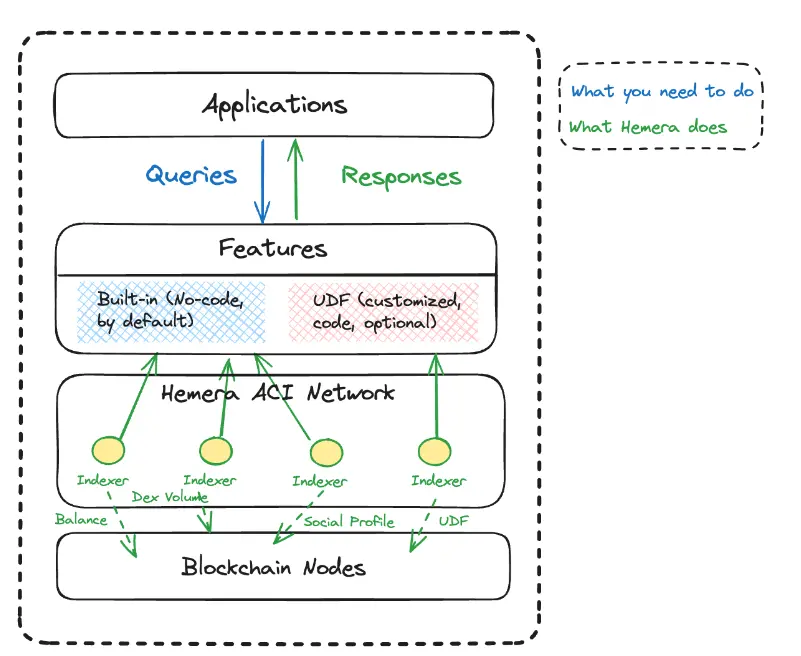
How Do Applications Utilize Hemera Protocol?
The process for applications to conduct in-depth account-level analysis using Hemera is straightforward. Applications only need to query the desired features from the ACI network. Hemera provides a range of built-in features, including commonly used metrics such as portfolio balance, trading volume, collateralized lending, and even social data. Developers can easily query any account of interest without writing additional code.
Hemera also provides the UDF module to meet developers' more personalized needs. With this module, developers can create custom features with minimal coding work. Thanks to the standardized format, these custom features can seamlessly integrate into existing features, facilitating more comprehensive and detailed analysis.
When requesting features, they are transmitted to Hemera's ACI network. Each indexer in the network is responsible for indexing one or more specific features by querying the raw blockchain data. The requester subsequently receives semantically meaningful account-level data provided by Hemera, avoiding the cumbersome task of directly handling complex raw data.
By leveraging Hemera's ACI network, applications can gain deep insights into account activities and user profiles. This not only helps make wiser decisions in the blockchain ecosystem but also provides a more personalized user experience, while simplifying the complexity of handling raw blockchain data.
How Are Features Updated?
Features in the Hemera ecosystem are dynamically updated based on on-chain transaction activities. Each indexer in the ACI network is responsible for indexing specific features. These indexers operate in real-time, continuously monitoring on-chain transactions relevant to the features they track.
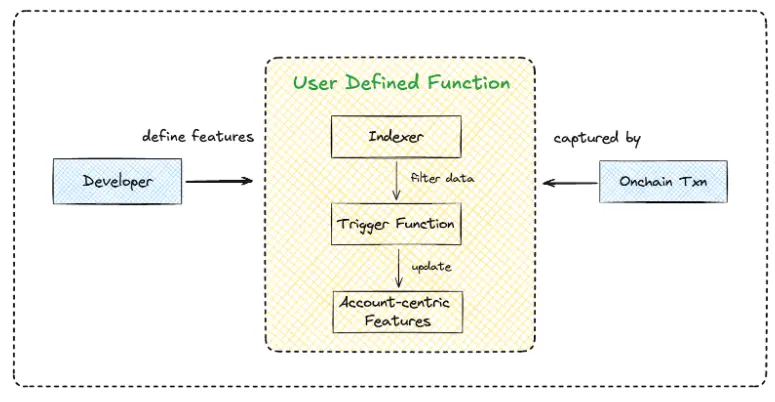
The simplified workflow begins with developers defining custom features and data classes in the UDF module. Subsequently, indexers capture relevant on-chain transactions, filter specified data, and pass it to the developers' trigger functions. These functions then process the data to update the account-centric features.
The real-time indexing and updating process ensures the timeliness and accuracy of feature data. By focusing on specific transactions that affect the allocation of features, indexers can efficiently process a large amount of blockchain data, transforming it into meaningful account-level information.
How to Create UDF?
To illustrate the process of building custom UDF, let's take the example of OpenSea-related features:
- Feature Definition: Developers first define specific features (such as NFT trading volume, NFT trading collections) and data classes. For example, the "OpenseaOrder" class may include variables such as "orderhash" (string), "offerer" (string), "recipient" (string), and "offer" (dictionary).
- Trigger and Feature Development: Next, developers create triggers, specifying which transactions or log events will change the state of the defined features. This step ensures that indexers effectively capture relevant on-chain transactions and filter the interested data. Then, developers can write custom logic to update feature values.
- Query Execution: Finally, developers run indexers and the new UDF, and process historical data. Subsequently, feature data is stored in the database, and developers can easily retrieve account-level data or query feature values from the database through standard REST API.
For a more detailed guide on implementing UDF, please refer to our documentation: https://docs.thehemera.com

Essentially, each feature is a dynamic entity that is continuously updated based on on-chain activities. The role of UDF is to interpret raw transaction data, create appropriate triggers, and use these triggers to keep features continuously updated.
Unique Position of Hemera in the Data Analysis Field
To understand Hemera's unique position in the data field, it can be compared with existing data analysis tools and protocols. The main differences are shown below:
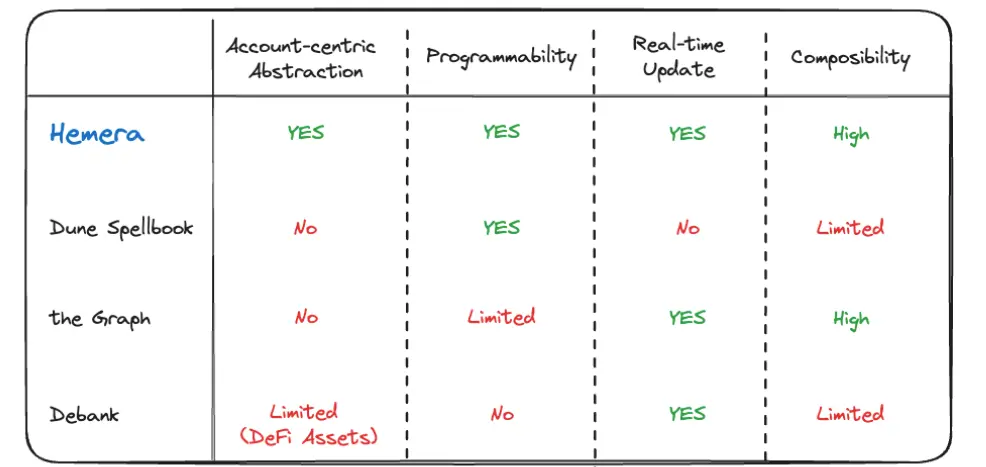
The core advantage of Hemera lies in its account-centric data extraction.
Dune's Spellbook also emphasizes data extraction, abstracting advanced data patterns from raw data, but it is not account-centric.
Although The Graph is a popular indexing protocol, it is centered around smart contract events. It is great for decoding data related to smart contracts but lacks the extraction of account-centric data.
Debank has the capability to extract account-level data, but it mainly focuses on DeFi assets, limiting its applicability in diverse on-chain activities (such as on-chain gaming records).
Hemera provides unparalleled flexibility in data processing.
With Hemera, users can easily access the required data with minimal coding operations.
The Graph allows users to build subgraphs for smart contract data retrieval but limits deeper data operations.
Debank provides fixed APIs to query asset information but lacks programmability.
Hemera's data updating method is proactive and real-time.
Hemera indexers continuously monitor the blockchain and update features in real-time through a "push" mechanism triggered by transactions.
In contrast, Dune updates data in a "pull" manner, requiring users to retrieve all data from the database to update their own data.
In the Web3 application field, Hemera excels in composability and integrability.
Hemera provides standardized formatted plotted data, simplifying database construction and maintenance.
Dune provides a comprehensive on-chain data query terminal within its platform, but the cost of building independent applications is high.
Debank's fixed API structure limits its ability to handle data related only to assets.
Looking ahead, as the industry develops and matures, we believe that user profiles will be crucial for user-oriented applications. In this evolving environment, Hemera's account-level, multi-dimensional data will play an indispensable role in precise and effective user targeting. Additionally, we foresee an increasing synergy between AI models and on-chain data, and Hemera's semantic extraction capabilities will help large language models understand and process data more efficiently.
Hemera's vision is clear and explicit: we are committed to building Hemera into a comprehensive data center for the entire Web3 industry. By significantly reducing access and utilization barriers, we will provide services to developers, researchers, marketing teams, end users, and AI systems. Hemera's ultimate goal is to become the preferred platform for all users who want to fully explore the value of blockchain data, making it easy for users in the blockchain ecosystem to access important resources and benefit.
Explore Hemera Products:
- Website: https://thehemera.com/
Develop Applications Based on Hemera ACI Network:
- Documentation: https://indexer-docs.thehemera.com/
- Github: GitHub - HemeraProtocol/hemera-indexer at pre-release/v0.3.0
Visit the SocialScan Agent Store:
- Website: https://socialscan.io/home
Follow on Twitter:
- Hemera: https://x.com/HemeraProtocol
- SocialScan: https://x.com/socialscan_io
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



