Author | Huo Huo
Produced by | Plain Language Blockchain
On August 5th, the Bank of Japan's interest rate hike caused severe turbulence in the global financial markets. Both the Japanese and American stock markets collapsed, and the panic index for the cryptocurrency market, Bitcoin, surged by nearly 70%. Stock markets in multiple countries experienced several circuit breakers. Even the stock markets in Europe and emerging markets were similarly hit hard. Under tremendous market pressure, people began seeking remedies and called for the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates to rescue the market. The possibility of the Federal Reserve raising interest rates soon means that a "bigger" event than the Bank of Japan's interest rate hike is on the horizon. Can this event bring Bitcoin back to a bull market?
01. Why Does the Federal Reserve Have Such Great Influence?
1) What is the Federal Reserve?
Before understanding the concepts of the Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes and cuts and their impact, we first need to know what the Federal Reserve is.
The Federal Reserve, or the Federal Reserve System, is the central banking system of the United States, consisting of 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks. Its goal is to stabilize prices and maximize employment through monetary policy. Indicators such as the inflation rate and employment rate are crucial to economic health and are closely monitored by investors and market participants to assess economic prospects and investment risks.
As the central bank of the United States, the Federal Reserve has tremendous influence on the financial markets. So, how does the Federal Reserve exert its influence? It mainly adjusts interest rates through the following monetary policy tools to influence the economy, either by raising or lowering interest rates:
Raising interest rates means increasing the cost of interbank borrowing, thereby raising the loan interest rates for businesses and individuals. When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, the deposit interest rates for the US dollar increase, leading to capital inflows into the United States, reducing investments in other countries, deteriorating the economic environment, and increasing the unemployment rate. High interest rates also increase borrowing costs, leading to increased default risks for businesses and individuals, which may trigger corporate bankruptcies.
Conversely, lowering interest rates will reduce deposit interest rates and borrowing costs. When the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates, the deposit interest rates for the US dollar decrease, capital flows out of banks and into other countries, promoting global investment and economic recovery.
So, how many times has the Federal Reserve cut interest rates in the past? What impact did each cut have?
2) History of Interest Rate Cuts
Looking back at history, since the 1990s, the Federal Reserve has experienced six relatively significant interest rate cut cycles. From a pattern perspective, these include two preventive interest rate cuts, three relief interest rate cuts, and one mixed interest rate cut that combines both preventive and relief measures.
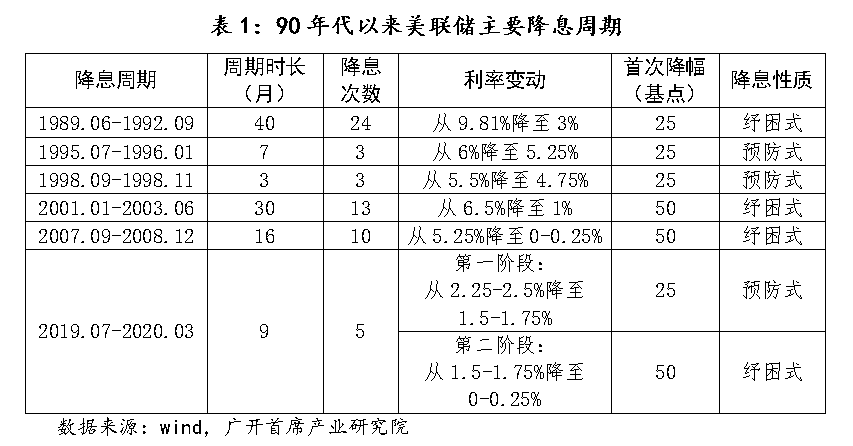
First, let's understand the differences between these types of interest rate cuts:
Preventive interest rate cuts refer to proactive policy adjustments to lower interest rates by monetary authorities when the economy shows signs of decline or faces potential external risks, in order to reduce the risk of recession and promote a "soft landing" for the economy. Characteristics include a relatively short interest rate cut cycle, a moderate initial interest rate cut, a limited number of interest rate cuts, and the federal funds rate not falling below 2%.
Relief interest rate cuts are continuous and substantial interest rate reduction measures taken by monetary authorities when the economy is threatened by severe recession or major shocks, aimed at helping the real economy and residents, avoiding severe recession, and promoting economic recovery. Characteristics include a longer interest rate cut cycle (possibly lasting 2-3 years), a steep initial interest rate cut (possibly consecutive substantial cuts), a strong initial interest rate cut (usually exceeding 50 basis points), and a large total interest rate cut (ultimately reducing the interest rate to below 2% or close to zero).
In comparison, a mixed interest rate cut cycle is more complex. It may initially appear as a conventional preventive interest rate cut, but due to rapid changes in the situation, it may later transform into a relief interest rate cut.
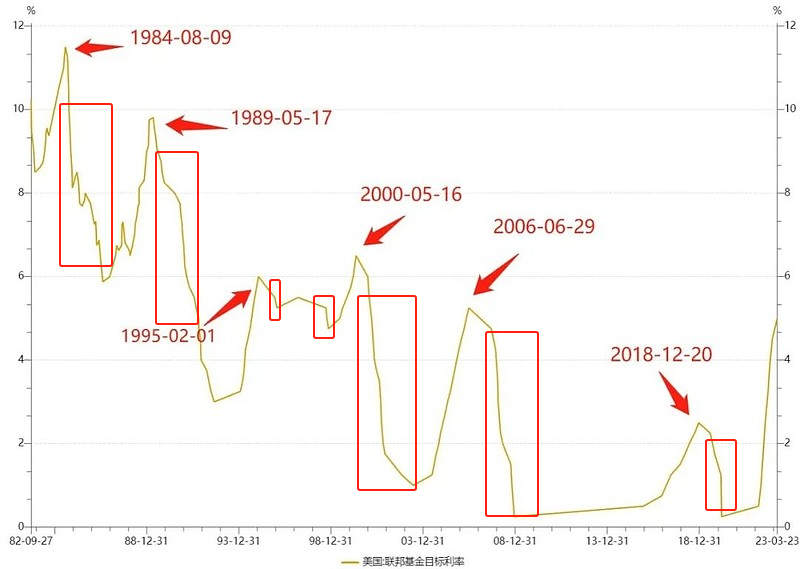
So, what impact did these significant interest rate cut cycles experienced by the Federal Reserve since the 1990s have on the markets and the economy?
- 1990-1992:
Interest rate cut situation: During this cycle, the Federal Reserve lowered the federal funds rate from 9.810% to 3.0%.
Market impact: This round of interest rate cuts helped support the recovery of the economy from the 1990 economic recession. The stock market began to rise during this period, and economic growth gradually recovered. Although there were still pressures from inflation and unemployment, the overall economic situation gradually improved.
- 1995-1996:
Interest rate cut situation: The Federal Reserve began cutting interest rates in 1995, lowering the federal funds rate from 6.0% to 5.25%.
Market impact: This round of interest rate cuts was mainly to address the slowdown in economic growth, support the rise of the stock market, and stabilize the economy. This period marked the continuation of economic expansion, with a strong performance in the stock market, especially benefiting technology stocks, which subsequently led to the tech stock boom of the 1990s.
- 1998 (September-November):
Interest rate cut situation: The federal funds rate was lowered from 5.50% to 4.75%.
Market impact: It alleviated market tension and supported economic growth. The interest rate cut had a positive impact on the stock market, especially with a strong rebound in technology stocks. The Nasdaq index saw a significant increase in 1998, laying the foundation for the subsequent boom in technology stocks.
- 2001-2003:
Interest rate cut situation: During this cycle, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates from 6.5% to 1.00%.
Market impact: These interest rate cuts were made after the 2001 economic recession. The interest rate cuts helped support economic recovery and drove the stock market up in 2002 and 2003. However, the excessive relaxation of this round of interest rate cuts also laid the groundwork for the subsequent real estate bubble and financial crisis.
- 2007-2008:
Interest rate cut situation: The Federal Reserve lowered interest rates from 5.25% to near zero (0-0.25%).
Market impact: This round of interest rate cuts was made to address the severe impact of the 2008 financial crisis. The low interest rate policy effectively alleviated pressure in the financial markets, supported the recovery of the economy and financial markets, and drove a strong rebound in the stock market after 2009.
- 2019-2020:
Interest rate cut situation: The Federal Reserve lowered interest rates from 2.50% to near zero (0-0.25%) in 2019 and 2020.
Market impact: The interest rate cuts initially aimed to address the economic slowdown and global uncertainty. After the outbreak of the pandemic, further interest rate cuts and large-scale monetary stimulus measures helped stabilize the financial markets and support economic recovery. The stock market experienced a rapid rebound in 2020. Although the pandemic caused severe economic impact, policy measures mitigated some of the negative effects. This round of interest rate cuts also indirectly contributed to the occurrence of the crypto "3/12" event.
It can be said that each interest rate cut cycle has had different impacts on the markets and the economy, and the formulation of interest rate cut policies is also influenced by the economic environment, market conditions, and global economic situation at the time.
3) Why Does the Federal Reserve Have Such Great Influence?
The Federal Reserve has a huge impact on the global financial markets, so its policies directly affect global liquidity and capital flows. Its specific influence is reflected in the following points:
Global reserve currency: The US dollar is a major global reserve currency, and most international trade and financial transactions are denominated in US dollars. Therefore, changes in the Federal Reserve's monetary policy directly affect global financial markets and the economy.
Interest rate determination: The Federal Reserve's interest rate policy directly affects the level of global financial market interest rates. Raising or lowering interest rates by the Federal Reserve will guide other central banks to adjust their policies. This interest rate transmission mechanism means that the Federal Reserve's policy decisions have far-reaching effects on global capital flows and financial market trends.
Market expectations: The Federal Reserve's remarks and actions often trigger global market fluctuations. Investors closely monitor the direction of the Federal Reserve's policies, and market expectations for the Federal Reserve's future policies directly affect asset prices and market sentiment.
Global economic interconnection: Due to the high degree of interconnection in the global economy, the economic conditions of the United States, as the world's largest economy, also have a significant impact on the economies of other countries. The Federal Reserve's regulation of the US economy through monetary policy also affects the global economic trend.
Volatility of risk asset prices: The Federal Reserve's policy measures have an important impact on the prices of risk assets (such as stocks, bonds, and commodities). Market interpretations and expectations of the Federal Reserve's policies directly affect the volatility of global risk asset markets.
Overall, due to the importance of the US economy and the global status of the US dollar, the Federal Reserve's policy measures have a profound and direct impact on global financial markets, making its decisions highly anticipated by global markets.
So, for the upcoming Federal Reserve interest rate cut cycle, what will be the magnitude, speed, and frequency? How long will the entire interest rate cut cycle last? How will it affect the global financial markets?
02. How to View the Current Round of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts
1) Expectations for the Current Round of Interest Rate Cuts
As we enter the third quarter of 2024, signs in the US domestic market indicate a possible need to adjust monetary policy. Data on unemployment rates, employment numbers, and wage growth show a decrease in market activity, a slowdown in the tech sector indicating a deceleration in economic growth, and the substantial amount of unpaid debt interest in the US. All these signs indicate that the Federal Reserve may need to cut interest rates to stimulate consumption, revitalize the economy, and engage in currency over-issuance. Before Black Monday, it was widely predicted in the market that the Federal Reserve might start cutting interest rates as early as September this year.
According to market expectations, Goldman Sachs previously predicted that the Federal Reserve would cut interest rates by 25 basis points in September, November, and December, and pointed out that if the August employment report was weak, there might be a 50 basis point cut in September. Citibank also predicted that there might be 50 basis point cuts in September and November. Economists at JPMorgan adjusted their forecast, suggesting that the Federal Reserve might cut interest rates by 50 basis points in September and November, and mentioned the possibility of an emergency rate cut between meetings.
After Black Monday, some radical analysts believe that the Federal Reserve might take action before the September meeting, with a 60% probability of a 25 basis point cut, which is extremely rare and generally used to address severe risks. The last emergency rate cut occurred at the beginning of the pandemic.
However, there is still a great deal of uncertainty about the global economic trends, including the US economy. Whether this round of interest rate cuts will be preventive or relief-oriented is still a matter of debate among major institutions. The difference in the impact of the two on the market is also significant and requires further observation.
2) Potential Impact of the Current Round of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts
Expectations of the Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts have already begun to affect global financial markets and capital flows. In response to downward economic pressure, bets on interest rate cuts by the Bank of England and the European Central Bank are also heating up. Previously, some investors believed that there was a more than 50% chance of an interest rate cut by the Bank of England in September. For the European Central Bank, traders expect two interest rate cuts by October, and the expectation of a significant interest rate cut in September is not far off.
Next, let's take a look at some of the potential impacts of this round of interest rate cuts:
A. Impact on Global Markets
The expected interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve is expected to have a significant impact on global financial markets.
First, the reduction in US dollar interest rates may lead to funds flowing into markets and assets with higher yields, increasing global capital flows.
Interest rate cuts may also lead to a depreciation of the US dollar, potentially causing exchange rate fluctuations and driving up prices of commodities priced in US dollars, such as crude oil and gold. In addition, a depreciation of the US dollar may enhance US export competitiveness, but it may also exacerbate international trade tensions.
At the same time, interest rate cuts may lower the borrowing costs for global stock markets, boost corporate profit expectations, and drive stock market gains.
The reduction in international capital costs will encourage more investment, but its impact on heavily indebted countries and companies is limited.
Because although the reduction in international capital costs will encourage investment, heavily indebted countries and companies may find it difficult to use these low-cost funds for new investments due to debt pressure and strict borrowing conditions.
Finally, interest rate cuts may bring global inflationary pressures, especially when currency depreciation and commodity price increases affect economic stability and central bank policies.
B. Will Interest Rate Cuts Directly Benefit the Cryptocurrency Market?
Although many people believe that interest rate cuts increase market liquidity, reduce borrowing costs, and may drive up cryptocurrency prices, in an environment of interest rate cuts, economic uncertainty increases, and investors may turn to safe-haven assets such as Bitcoin. However, there are also reservations that caution against potential economic recession risks.
But many institutions generally believe that in a complex and changing market environment, significant market fluctuations may occur during interest rate cuts. During the 2008 financial crisis, even though the Federal Reserve took initial interest rate cut measures, the market still sharply declined after a brief peak. Although the Federal Reserve quickly and significantly lowered interest rates, it failed to effectively contain the crisis. The root of this crisis can be traced back to the successive bursting of the dot-com bubble and the real estate bubble, which had a profound impact on the economic recession.
As for whether the current interest rate cut policy will repeat the same mistakes and trigger events such as an artificial intelligence bubble or a US debt crisis, which could then drag down the cryptocurrency market, remains to be seen.
However, in the short term, interest rate cuts by global central banks, represented by the Federal Reserve, are a shot in the arm for both the global financial markets and the cryptocurrency market. Undoubtedly, the expectation of interest rate cuts will directly promote increased market liquidity, trigger market optimism, and may lead to a short-term uptrend in the cryptocurrency market, providing investors with opportunities for quick profits.
In the long term, the trend of the cryptocurrency market will be influenced by more complex and changing factors, and price fluctuations are driven by a combination of factors:
First, market trends mainly depend on the strength of economic recovery. If interest rate cuts can promote economic growth, the cryptocurrency market may benefit; conversely, if economic recovery is weak and market confidence wanes, the cryptocurrency market is also likely to be affected. During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Bitcoin experienced a collapse along with the stock market and commodities. Markus Thielen of 10x Research recently pointed out that the US economy is weaker than expected by the Federal Reserve, and if the stock market follows the decline in the ISM manufacturing index, the price of Bitcoin may continue to fall. In addition, during an economic downturn, investors may sell Bitcoin.
Second, inflation factors need to be considered. Central bank interest rate cuts are intended to stimulate the economy and promote consumption, but they may also lead to inflation risks such as price increases. Rising inflation may in turn lead to central bank interest rate hikes, bringing new pressure to the cryptocurrency market.
Third, changes in the US presidential election and global regulations also have far-reaching effects. Who will be the new president of the United States? It is still unknown what policies the new president will adopt regarding cryptocurrencies.
In conclusion, the opening of the interest rate cut era by global central banks has undoubtedly brought new opportunities and challenges to the cryptocurrency market. Interest rate cuts are likely to provide liquidity support for cryptocurrency assets in the short term, including factors such as increased liquidity and heightened demand for safe-haven assets. However, they also face the lessons of historical financial crises and other complex factors, making it difficult to guarantee that they will definitely benefit the development of cryptocurrencies.
03. Conclusion
Overall, Black Monday was a result of concerns about a US economic recession leading to a market crash, combined with industry giants' pessimistic expectations for the US economy and global geopolitical turmoil. In the short term, these factors will continue to keep the market in a period of policy fluctuations.
Based on the cyclical patterns of past financial crises, crises and opportunities go hand in hand. Economic downturns, market fluctuations, and potential investment losses may bring anxiety and panic, but they also provide an opportunity for investors and businesses to regroup and seek innovative opportunities. At the same time, crises force companies to improve their business models and efficiency, leading to more robust development in the future.
However, how this round will ultimately play out, how long the negative impacts of the crisis will last, and whether the market will really turn around after the Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts, are still open questions. What are your thoughts on these matters? Feel free to discuss in the comments section.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




