Arbitrage strategy is a method to help investors seize short-term profit opportunities arising from price differences in different markets. It has long been favored by large funds for its low risk and stable profitability, allowing for an annualized return of 10% to 60%.
AICoin provides free tools for funding rate arbitrage and basis arbitrage. The following will introduce the principles of funding rate and basis arbitrage, helping you understand how to steadily gain profits.
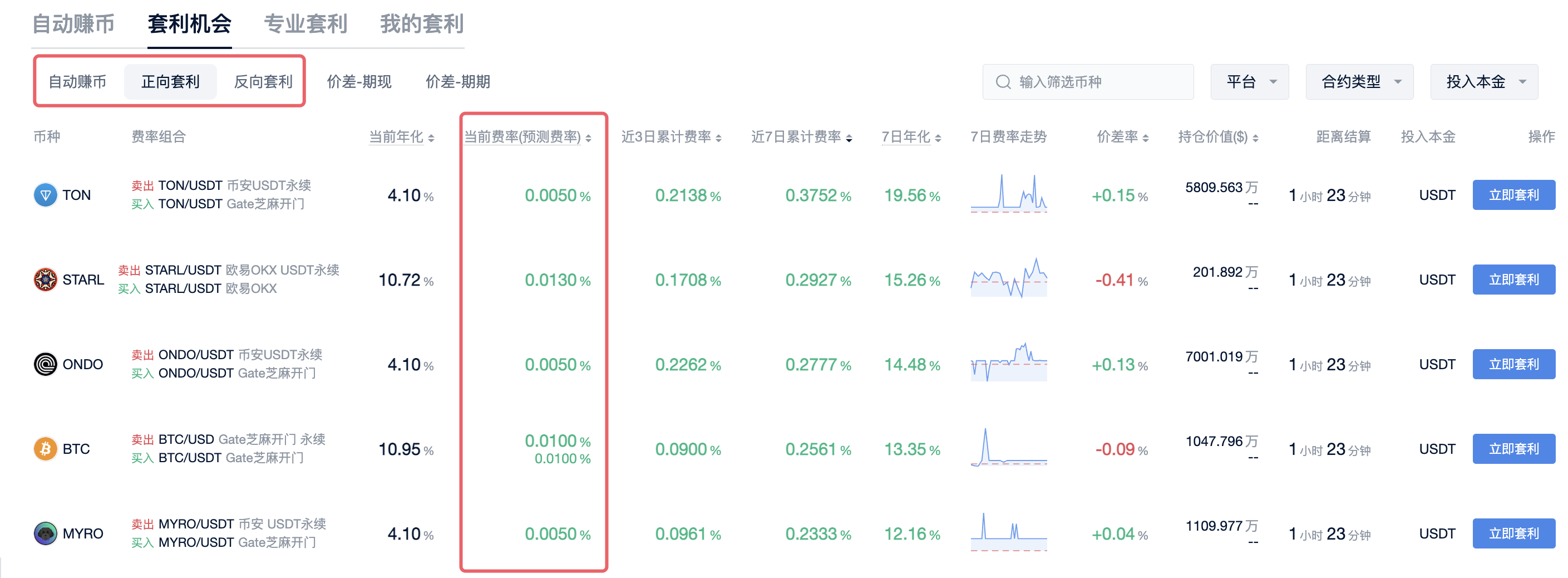
What is Funding Rate Arbitrage?
Funding Rate Arbitrage: The funding rate is the settlement mechanism in perpetual contracts. Since perpetual contracts do not have delivery, another mechanism is needed to stabilize the basis. This mechanism is the funding rate, which is settled every 8 hours. In short, the funding rate is the fee that long positions pay to short positions in order to balance the long and short sentiments.
Positive Arbitrage: When the funding rate is positive, investors can buy spot and short perpetual contracts to earn the funding fee.
Negative Arbitrage: When the funding rate is negative, investors can borrow coins to sell spot and long perpetual contracts to earn (funding fee - borrowing interest).

Taking BTC spot and perpetual contracts as an example:
Assuming the current BTC price is $5000, and the BTC funding rate is +0.1% and remains unchanged, Xiaoming can use arbitrage tools to buy 1 BTC in the spot market and short 1 BTC in the perpetual market. When the BTC price rises, the spot position makes a profit while the contract suffers a loss. The gains and losses on both sides offset each other, allowing for risk-free earning of the funding fee regardless of price fluctuations.
What is Basis Arbitrage?
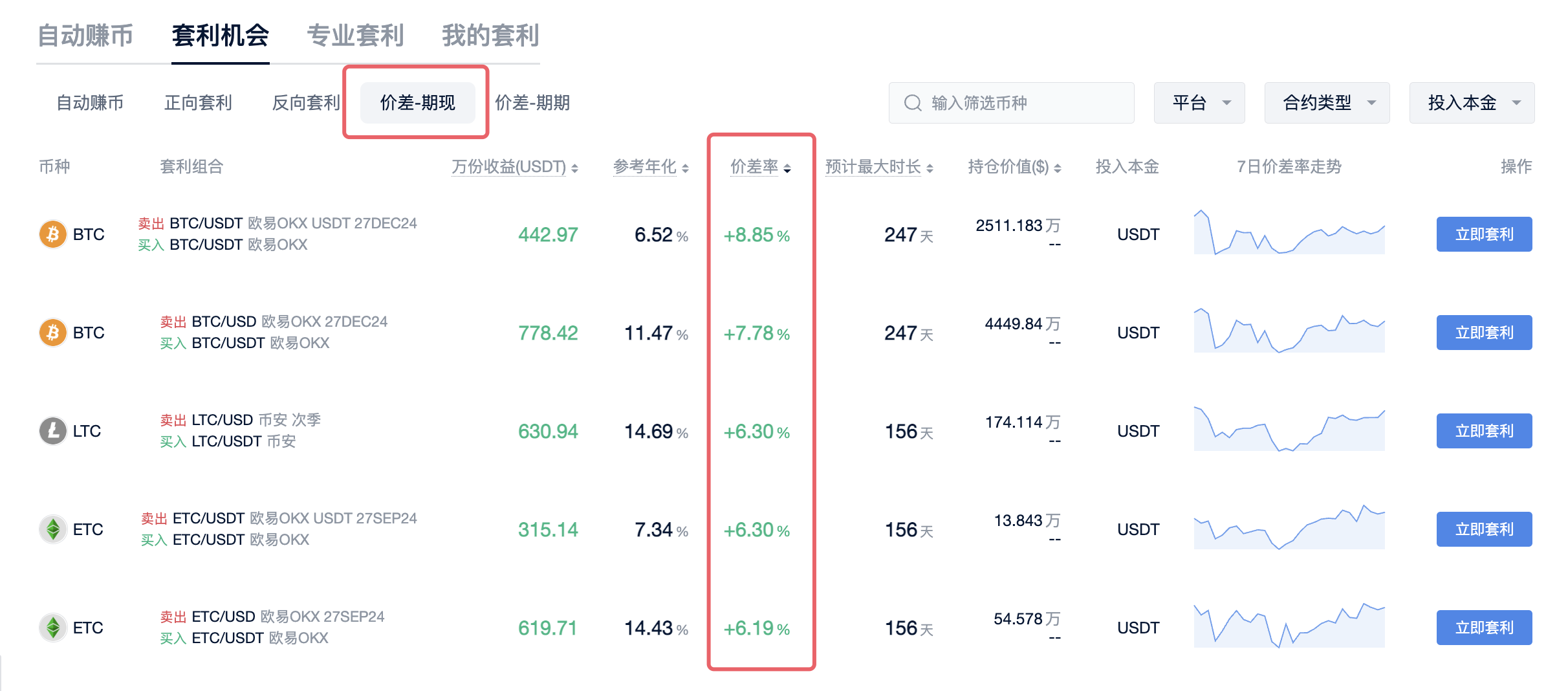
Basis Arbitrage: Basis arbitrage refers to arbitrage opportunities using price differences between the spot market and the futures market (including perpetual contracts and delivery contracts). It can be divided into two types: spot-futures arbitrage and futures-futures arbitrage. Investors can use AICoin's arbitrage tools to buy and sell the same trading currency in different markets to capture the price difference profit.
1.1 Spot-Futures Arbitrage
Spot-futures arbitrage refers to arbitrage between delivery futures contracts and spot markets. It generally refers to the significant price difference between the same trading currency in the futures market and the spot market. When the futures contract expires, the price will definitely return to the spot price, creating an arbitrage opportunity. By buying the lower-priced side and selling the higher-priced side, when the price difference narrows, closing the position can yield the price difference profit.
For example, if the BTC price in the delivery futures market is 69000U and the spot market BTC price is 65000U, creating a difference of 4000U, one can short 1 BTC in the futures market (similar to selling 1 BTC at 69000 price) and buy 1 BTC in the spot market for 65000U. When the price difference narrows, such as the BTC price in the futures market being 60000U and the spot price being 58000U, the futures profit is 9000U (69000 - 60000), and the spot loss is 7000U (58000 - 65000), resulting in a net profit of 2000U (actual profit needs to deduct fees).
1.2 Futures-Futures Arbitrage
Futures-futures arbitrage is a strategy to arbitrage between different types of contracts in the futures market, involving finding and utilizing price differences between different types of contracts. By buying and selling contracts of the same currency with different delivery dates, one can profit from the change in their price difference. Similar to spot-futures arbitrage, the core is to short the high-priced side and long the low-priced side when the price difference is large, and close the position when the price difference starts to narrow.
Combinations include: perpetual contract to perpetual contract, delivery contract to delivery contract, perpetual contract to delivery contract
Under the influence of various market factors, contract prices will change, and the fluctuation range of different-term contracts (i.e., the rise and fall range of the price difference) will also change. For example, the price of BTC next quarter contract has dropped by 0.20%, and the price of BTC next week contract has dropped by 0.26%. The premise of inter-period arbitrage strategy is that the "price difference" always fluctuates within a certain range, and traders can determine the probability distribution range of the price difference through historical data calculations.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




