2024 is destined to be the year of Bitcoin, with multiple favorable factors such as Bitcoin halving, Bitcoin ETF approval, and the eruption of the Bitcoin ecosystem narrative. Bitcoin has not only once again proven its unshakable position as the king of cryptocurrencies, but also led a financial revolution. The Layer2 ecosystem around Bitcoin will undoubtedly be one of the hottest tracks, becoming a key force driving the construction of the Bitcoin ecosystem and unlocking the potential of Bitcoin.
I. Overview of Bitcoin Layer2 Technology
The original design of the Bitcoin network architecture mainly focused on security and decentralization, rather than scalability, leading to significant limitations in processing capacity and transaction speed. With the expansion of user base and increasing transaction demand, these limitations have become a major bottleneck for Bitcoin's development. Each Bitcoin block is limited to about 1MB in size, with an average of one block generated every 10 minutes, resulting in limited processing capacity across the network, leading to transaction delays and rising fees. In the early days of Bitcoin's popularity, these issues were not so prominent, but as the number of cryptocurrency users increased, especially during market booms, these problems became significant obstacles to user experience.
To address the scalability issues of the Bitcoin network, Layer2 technology emerged. The core concept of Layer2 technology is to build a new layer on top of the existing Bitcoin base layer (Layer1) using various technical means such as state channels and sidechains to achieve higher transaction throughput and lower latency, while maintaining decentralization and security as much as possible. The introduction of these technologies has opened up new paths to address Bitcoin's scalability issues, not only increasing the processing capacity of the Bitcoin network, but also expanding Bitcoin's use cases, such as micro-payments, smart contracts, etc. With the development of technology and the deepening of applications, Layer2 technology has the potential to further explore new uses for Bitcoin, promoting the growth and innovation of the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Characteristics of Bitcoin Layer2 Technology
1. Improved Transaction Speed: Bitcoin Layer2 technology significantly improves transaction speed by processing transactions outside the Bitcoin main chain. Lightning Network, as a typical implementation, allows users to complete transactions almost instantly, greatly accelerating payment speed.
2. Reduced Transaction Costs: Bitcoin Layer2 technology significantly reduces transaction costs through batch processing of transactions and off-chain transaction processing mechanisms. In Layer2 networks, users can conduct multiple transactions, with settlement on the main chain only required at the beginning and end of transactions, reducing the transaction pressure on the main chain and the associated transaction fees. This is particularly important for applications that need to process a large number of small transactions.
3. Enhanced Scalability: By moving transaction processing from the main chain to the second layer, Layer2 technology significantly improves the network's scalability. This means the network can handle more transactions while reducing the cost of each transaction.
4. Security Guarantee: Although Layer2 technology strives to maintain the security of the Bitcoin main chain as much as possible, its security is still influenced by the specific technologies adopted. For example, state channels require users to be online regularly to monitor potential fraudulent behavior.
5. Maintaining Decentralization: While Layer2 solutions strive to maintain the decentralization of the network, certain technical implementations may introduce new trust layers or rely on specific nodes to operate, which to some extent affects the level of decentralization.
Differences Between Bitcoin Layer2 and Ethereum Layer2
Bitcoin and Ethereum Layer2 solutions provide ways to extend the original blockchain architecture to address scalability issues and increase transaction throughput. However, these two blockchain Layer2 solutions have significant differences in design, security inheritance, and interaction with validators. Here are several key differences between Bitcoin Layer2 and Ethereum Layer2:
1. Security Inheritance: Ethereum Layer2 solutions such as Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups directly inherit security from the Ethereum mainnet. By requiring validators to challenge fraudulent transactions (Optimistic Rollups) or using zero-knowledge proofs (zk-Rollups) to ensure transaction correctness, Ethereum Layer2 can leverage the security mechanisms of the Ethereum network to protect transactions. Bitcoin Layer2 solutions such as Stacks, Rootstock (RSK), or Liquid Network rely on their own security and consensus mechanisms, even though they anchor to the security and finality of Bitcoin. Bitcoin validators do not directly participate in the execution or validation of Layer2 transactions.
2. Interaction with Validators: The security of Ethereum Layer2 depends on the active participation of mainnet validators, who need access to necessary data or proofs to reconstruct the second-layer state and validate transactions. Validators in Bitcoin Layer2 primarily focus on verifying and confirming transactions on the Bitcoin main chain, without directly intervening in the validation of second-layer transactions. This means that the Bitcoin Layer2 network needs to rely on its internal security measures rather than direct intervention from Bitcoin validators.
3. Applications and Scalability: Ethereum Layer2 design mainly focuses on expanding the ability of smart contracts and the overall network's processing capacity. Through technologies such as Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups, it not only improves transaction speed and reduces costs, but also enables complex applications to run on Ethereum while maintaining the same level of security as the Ethereum mainnet. Bitcoin Layer2 is an extension of Bitcoin's limited use cases and relatively inefficient operational efficiency.
II. Types and Representative Projects of Bitcoin Layer2
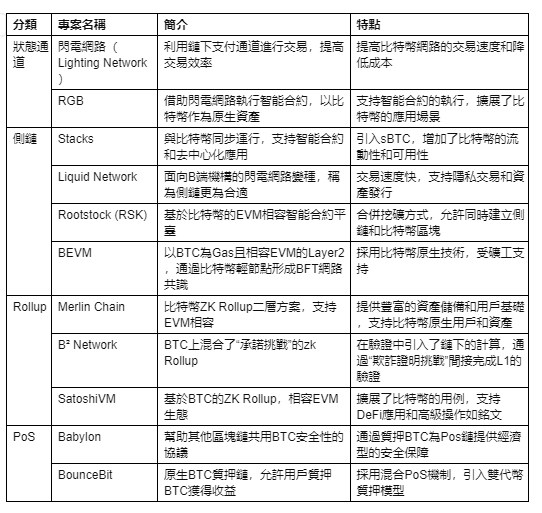
Bitcoin Layer2 solutions are mainly divided into state channels, sidechains, Rollup, and PoS extensions.
1. State Channels
State channels are based on payment channel technology, conducting transactions off-chain to achieve low cost, high speed, and high scalability transaction confirmations.
Validation Mechanism: Transactions in state channels are conducted off-chain and only submitted to the Bitcoin main chain when the channel is closed, reducing the burden on the main chain and maintaining security.
Representative Projects:
The Lightning Network creates a network of micro-payment channels to achieve instant, high-throughput transactions, suitable for small-value payments.
The RGB protocol aims to be a scalable and privacy-preserving Bitcoin and Lightning Network smart contract system, supporting asset issuance and transfer.
2. Sidechains
Sidechains are independent blockchains connected to the main chain (Bitcoin) through bi-directional cross-chain bridges, enabling secure transfer of assets between the main chain and sidechains. They allow payments using non-BTC tokens and can facilitate user asset issuance, DeFi solutions, commitment chain extensions, etc.
Validation Mechanism: Sidechains use their own consensus mechanisms, requiring assets to be locked when transferred from the main chain to the sidechain, and unlocked when returning from the sidechain to the main chain. Issues such as potential centralization due to a small number of validation nodes and not inheriting main chain security may arise.
Representative Projects:
Rootstock (RSK) maintains a high level of security and decentralization by merging mining mechanisms with the Bitcoin network. It is compatible with Ethereum smart contracts, allowing developers to deploy and execute complex smart contracts within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Stacks: Linked to the Bitcoin chain through the "proof of transfer" consensus mechanism, it achieves high decentralization and scalability, introducing smart contracts and decentralized applications.
3. Rollup
Rollup is a scalability solution that migrates most transaction data and computation off-chain, only recording transaction summaries on-chain.
Validation Mechanism: The underlying blockchain only needs to verify proofs submitted to the smart contract to validate activities in the Layer2 network, but the Bitcoin network itself cannot verify data availability (DA).
Representative Projects:
Merlin Chain: Aims to significantly improve speed and resource management (fees) by using zero-knowledge proof technology to batch process transactions in its execution layer and settle on the Bitcoin blockchain.
BitVM: Proposes a Turing-complete Bitcoin contract solution, allowing complex contracts to run on Bitcoin.
4. PoS Extensions
Enhances the use and management of digital assets, especially Bitcoin, on public blockchains through the Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism, improving its application and security in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Validation Mechanism: Allows Bitcoin holders to participate in PoS chain validation and earn rewards in a trustless, self-custody manner, enhancing the functionality and security of Bitcoin in the DeFi field.
Representative Projects:
Babylon: Aims to expand Bitcoin to protect the PoS economy, allowing Bitcoin holders to earn rewards from their idle Bitcoin without trusting third parties or bridging to another chain through the Bitcoin Proof of Stake protocol.
BounceBit: A BTC re-staking chain designed specifically for Bitcoin, providing a foundational layer for various re-staking products, with regulated custody guarantees from Mainnet Digital and Ceffu, using a BTC+BounceBit hybrid PoS mechanism for validation.
These technologies form the foundation of the Bitcoin Layer2 ecosystem, providing solutions to different issues within the Bitcoin network, collectively driving the Bitcoin network towards efficiency and scalability.
III. Current Development of Bitcoin Layer2
Since the rise of the Bitcoin ecosystem driven by the inscription in 2023, Bitcoin Layer2 projects have sprung up like mushrooms, giving birth to many new Bitcoin Layer2 projects, such as Merlin, Bison, Bouncebit, NuBit, and BitLayer, attracting a large amount of investment and financing activities. At the same time, some established projects have also turned to the Bitcoin Layer2 narrative. For example, Nervos Network has transitioned from a project focused on Layer1 solutions to a Bitcoin Layer2 project, announcing the integration of RGB++ and the launch of the CKB Layer2 Lightning Network. After the announcement, the token price rose by over 300%. MAP Protocol has transformed from a full-chain interoperability protocol to a Bitcoin Layer2 project, undergoing multiple rounds of financing and achieving a significant increase in token price. The momentum of Bitcoin Layer2 has also driven the prosperity of their respective ecosystems, giving rise to decentralized applications such as Alex, Sovryn, Bounce, and Multibit.
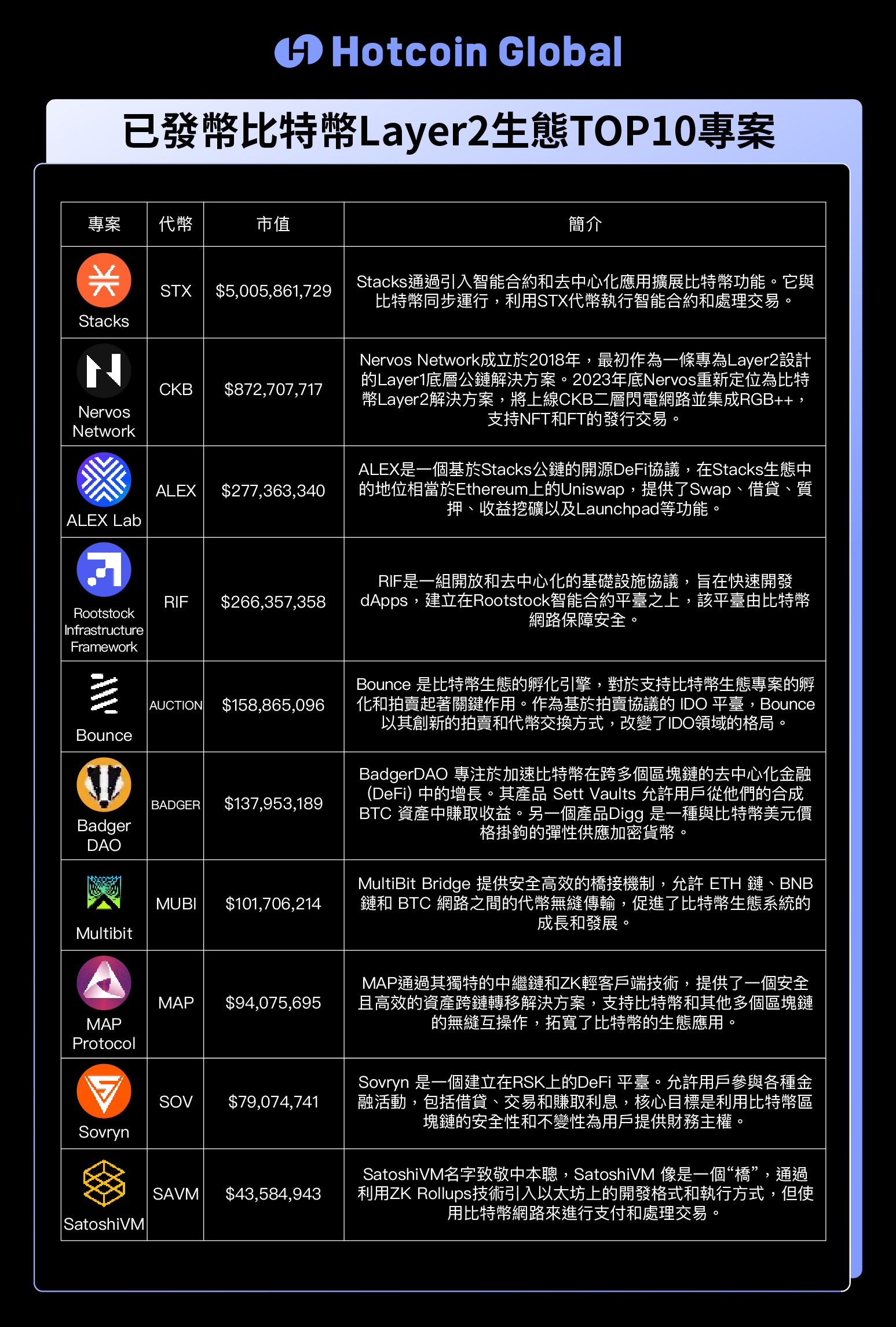
According to Defilama data, as of March 29th, BounceBit's Total Value Locked (TVL) reached $440 million, Lightning Network TVL reached $320 million, Stacks TVL reached $170 million, and Merlin Chain TVL reached $97 million. According to the latest data from Dune, the amount of BTC staked in Stacks is 2,717 coins, while the amount staked in Merlin Chain is 25,472 coins, with a value of up to $1.7 billion.
Top 10 Bitcoin Layer2 Ecosystem Projects
IV. Analysis of Challenges and Risks of Bitcoin Layer2
The rapid development of Bitcoin Layer2 technology presents unprecedented opportunities for the scalability and transaction efficiency of the Bitcoin network. However, this emerging field also faces numerous challenges and risks:
1. Technical Complexity and User Acceptance: Layer2 solutions increase the technical complexity of the entire system by adding a new processing layer on top of the Bitcoin base layer. Understanding and trusting these new systems may be a challenge for ordinary users. Users need to understand how to open and manage payment channels on Layer2 networks, as well as how to perform cross-chain asset transfers, and the complexity of these operations may hinder the acceptance and use by ordinary users.
2. Security and Bridge Protocol Risks: Security is another important challenge for Bitcoin Layer2 networks. In particular, bridge technologies that Layer2 networks such as sidechains rely on have serious security vulnerabilities. Bridge protocols achieve cross-chain asset transfers by locking and minting equivalent assets between the original chain and the target chain, but this design has been proven to have security and user experience issues. Although advanced bridge protocols are exploring more secure cross-chain connection methods, as of now, Bitcoin Layer2 projects still rely on such arrangements, so potential security issues still exist.
3. Liquidity Concerns and Centralization Risks: For example, the Lightning Network requires users to lock funds in payment channels, which may lead to liquidity issues, where funds cannot be used for other purposes. In addition, certain Layer2 solutions may inadvertently introduce centralization risks. For example, larger payment channels in the Lightning Network may centralize transactions through a few dominant nodes, potentially undermining the decentralization spirit of Bitcoin.
4. Integration and Interoperability Issues: Seamless integration of Layer2 solutions with existing Bitcoin infrastructure and interoperability between different Layer2 solutions are crucial. Lack of interoperability may lead to ecosystem fragmentation, reducing the overall effectiveness of these solutions. In addition, different technologies and standards in Layer2 networks may lead to compatibility issues, increasing the complexity and cost of user usage.
V. Prospects for the Development of Bitcoin Layer2
Bitcoin Layer2 has shown tremendous potential in addressing the scalability of the Bitcoin network and improving transaction efficiency, and its development prospects are promising. Currently, several Layer2 projects have made significant progress, with technologies such as the Lightning Network and sidechains evolving, providing more diverse application scenarios and solutions for the Bitcoin network.
1. Stronger Technological Foundation: With continuous innovation in cryptographic technology and consensus algorithms, it is expected that Layer2 solutions will become more complete, secure, and user-friendly. In particular, the application of advanced technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs may provide new paths to enhance the performance and privacy of these networks. Upgrades such as Taproot/Schnorr signatures will enhance Bitcoin's performance in privacy and efficiency, further strengthening the infrastructure of Bitcoin Layer2 technology.
2. Popularization of Layer2 Solutions: The Lightning Network, by establishing a network of payment channels, enabling instant transactions and extremely low fees, has become an important driver for Bitcoin micro-payments. This indicates that it may become an important infrastructure for daily Bitcoin payments and small-value transactions in the future. Sidechain technology, through its asset locking and unlocking mechanism with the main chain, supports asset and data transfers between different blockchains, bringing broader application scenarios for Bitcoin.
3. Diversified Applications and Functions: With the maturity of technology and the completeness of the ecosystem, Layer2 is expected to bring higher transaction throughput and broader application scenarios for the Bitcoin network, including but not limited to fast payments, smart contracts, and decentralized finance. The development of projects such as RGB and Stacks will enable more native assets to be issued on the Bitcoin network and expand Bitcoin's smart contract capabilities, making it a multi-functional blockchain platform.
4. Participation of Developers and Enterprises: With more developers and enterprises deeply involved in the research and application of Bitcoin Layer2, it is expected to accelerate the innovation of Layer2 technology, bringing new application models and business opportunities. In the future, Layer2 technology may become a key bridge connecting Bitcoin with a wide range of application scenarios, driving the overall development of the cryptocurrency industry.
5. Global Payments and Financial Inclusion: With the introduction of Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs), Bitcoin has entered the stage of institutional adoption. Its cross-border nature and decentralized characteristics make it a potential global payment tool, especially in regions with underdeveloped financial infrastructure, where Bitcoin may become an important tool for improving financial inclusion.
In conclusion, the exploration and practice of Layer2 technology is not only a solution to the scalability issues of Bitcoin but also an important innovation in the development of cryptocurrency technology. Through Layer2 technology, Bitcoin is expected to break free from its limitations as just a store of value and expand into areas such as value transfer and smart contract platforms. With the maturity of technology and community support, Bitcoin Layer2 solutions are expected to unlock more application scenarios in the future, paving the way for widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies.
Hotcoin Global, as a 7-year-old established exchange, pays close attention to the development of Bitcoin Layer2 and has listed related tokens such as STX, BADGER, MUBI, AUCTION, and will continue to focus on and list more high-quality assets in the Bitcoin Layer2 track. Stay tuned.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



