API3 has a carefully designed, unique, and powerful token economic model.
Author: @0xmarkyzl
Advisor: @CryptoScott_ETH
LT;DR
API3 is an innovative first-party oracle project that focuses on enabling data providers to run their own oracles, ensuring first-party data is directly transmitted to blockchain applications without intermediaries, enhancing data integrity, and addressing critical trust issues. API3 ensures data quality standards by managing and monitoring data providers, replacing those who fail to meet the standards, reducing user reliance on trust while ensuring data integrity.
By deploying first-party oracles and decentralized APIs (dAPI) using Airnode technology, API3 facilitates a more direct, secure, and efficient connection between data providers and blockchain networks, mitigating potential issues of traditional third-party oracles, ensuring higher security, transparency, efficiency, and reducing data transmission costs and potential risks.
The combination of OEV Network and ZK-Rollup mechanisms brings greater competitiveness to API3 and significant progress to the dApp and oracle race. This approach captures MEV and channels value back into the protocol ecosystem, releasing new value flows for stakeholders, promoting a more balanced and financially sustainable ecosystem.
API3 has a carefully designed, unique, and powerful token economic model. Its tokens are empowered through burning mechanisms and one-year staking rewards to combat inflation, and encourage staking through dynamic APR. Importantly, its economic model integrates operational and risk factors of the protocol, introducing a self-regulating mechanism of negative feedback loops, enabling stakeholders and governors to quickly reach consensus on governance decisions for long-term project development, thereby enhancing protocol stability by suppressing excessive risks, ultimately forming a positive feedback loop for the protocol's development, benefiting multiple parties in the long term.
With its innovative first-party oracle approach, high focus on data reliability and security, complete decentralized governance model of DAO, and broader application scope in data provision, API3's future may not be limited to providing oracle feeding services as an intermediary component, but could become the infrastructure for on-chain ecosystems and diverse dApp development, providing the possibility of on-chain development for more ubiquitous API applications in our real life, continuously promoting ecosystem innovation while setting new standards for the oracle race.
Preface
In the evolving Web3.0 ecosystem, decentralized applications (dApps) are experiencing rapid growth, highlighting their increasing value and expanding the demand for real-world data integration, making the decentralized oracle race one of the most important components of the on-chain ecosystem.
However, a major challenge still exists: how to seamlessly and securely integrate off-chain data into the blockchain ecosystem. In this context, API3 emerges as a solution to this challenge, aiming to fundamentally change the data interface between off-chain and on-chain environments.
1. Project Introduction

API3 was launched in December 2020 as an innovative first-party oracle project, aiming to enable most APIs tailored for centralized applications to enter the decentralized world of Web3.0 without imposing significant burdens on API providers or dApp project developers.
Unlike traditional third-party oracle networks, API3 focuses on first-party data provision, with its infrastructure centered around decentralized APIs (dAPI), and through serverless oracle node technology Airnode, it allows API providers to directly connect their data to dApp projects, eliminating the reliance on traditional third-party intermediaries for data aggregation and transfer commonly found in traditional oracle networks. Essentially, dAPI is compatible with blockchain technology, enabling cross-chain integration and providing cross-platform oracle solutions.
API3's governance model is based on decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), empowering token holders with decision-making authority, ensuring a transparent and community-driven ecosystem. It is reasonable to expect that API3's innovative framework has the potential to meet the critical need for decentralized and trustworthy data sources in the blockchain field, potentially setting new standards for the oracle race and on-chain data integration, establishing a more interconnected and efficient decentralized future.
1.1 Team Background

Heikki Vanttinen, Co-founder of API3, has accumulated rich work experience in multiple fields, particularly in blockchain technology and smart contract development. As the founder and CEO of CLC Group, Heikki focused on achieving seamless integration of smart contracts with the real world, demonstrating outstanding capabilities in business development, decentralized application development, and research across multiple disciplines.
At the same time, his entrepreneurial and marketing experience showcases his leadership and business insight in cross-functional team management, business expansion, and new market development.

Burak Benligiray, Co-founder of API3 and head of the core technical team, holds a Ph.D. in Electrical and Electronics Engineering and has served as a research assistant at the university, delving into various technical fields. Burak possesses extensive experience and remarkable technical capabilities in technology innovation and research, demonstrating profound expertise in blockchain technology and smart contracts, dedicated to building a decentralized and minimally trusted system.
1.2 Funding Status
According to Crunchbase data, on November 12, 2020, API3 secured a $3 million seed round led by Placeholder. In this round of financing, a total of 13 institutions, including Pantera Capital, Accomplice, CoinFund, Digital Currency Group, Hashed, and Solidity Ventures, participated in the investment.
Additionally, in the token public sale conducted in December 2020, API3 raised a total of $23 million.
1.3 Important Developments
January 29, 2021: Announced a partnership with the Polkadot Layer 2 protocol Plasm Network to introduce Airnode-supported APIs and data feeding into the Polkadot ecosystem.
April 20, 2021: Announced a 10-year partnership with the Open Banking project to open up API usage, allowing developers to build applications and services around financial institutions and develop blockchain solutions.
June 3, 2021: Partnered with the crypto credit data company Credmark to launch a decentralized risk model platform for scoring decentralized finance projects.
March 25, 2022: Announced a partnership with the Ethereum Layer 2 scaling solution Metis to provide a Web 3 API directory for developers on Metis and provide data feeding for the Metis ecosystem.
May 4, 2022: Announced a collaboration with the Australian National University to launch a quantum random number generator (QRNG) usable for smart contracts, ensuring unpredictable randomness.
January 29, 2024: Announced the launch of the ZK-Rollup platform OEV Network, which enhances the income of DeFi protocols by capturing and utilizing extractable value from oracles, ensuring instant income for dApps and enhancing security, transparency, and accountability through on-chain auctions.
2. Project Implementation Mechanism
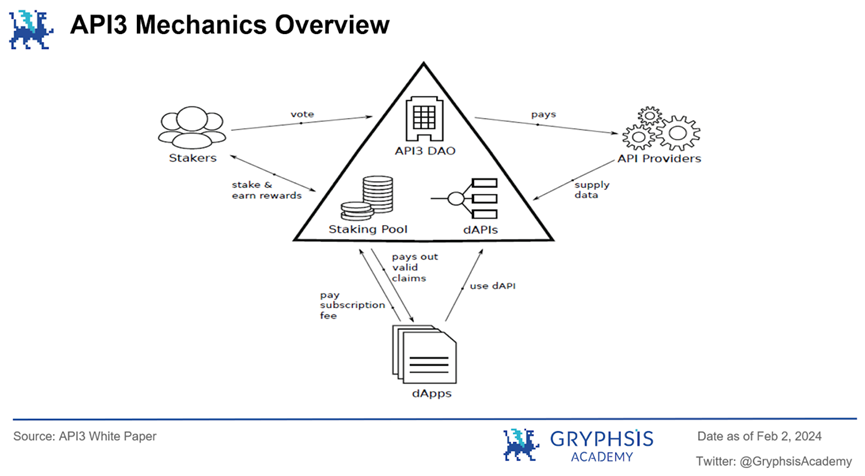
The overall mechanism of API3 is depicted in the diagram. API3 connects various parties through a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). API providers earn revenue by providing data, dApps pay subscription fees to access data services provided by dAPI, and if dApp users encounter issues with dAPI data, they can submit claims. Token stakers receive rewards and voting rights in the API3 DAO through staking mechanisms. The specific mechanisms will be detailed in the following sections.
2.1 From API to dAPI
In Web 2.0, APIs serve as crucial bridges for data exchange between various digital platforms, enabling seamless communication for software applications and supporting the functionality of modern digital services in our lives. For example, when we use a ticket booking website to reserve a flight, the website typically relies on APIs to retrieve real-time pricing and availability from various airlines' databases.
The concept of dAPI extends the application model of traditional APIs to the decentralized domain. Unlike traditional APIs that rely on centralized servers and third-party intermediaries, dAPI provides direct data feeds from data providers to users without any intermediaries.
API3's dAPI is built on Airnode-supported oracles, allowing API providers to directly connect their data sources to the blockchain network, enabling dApps to access real-world data in a secure, trustless manner.
API3 offers two types of data interface services: hosted dAPI and self-funded dAPI, catering to different potential use cases. API3 uses multi-signature wallets and governance protocols to manage changes to its dAPI configurations, balancing flexibility and security.
In the hosted dAPI model, multiple first-party oracles aggregate data and provide more reliable and stable data sources through median functions, suitable for production environments with high requirements for data quality and stability. In this model, users need to pay fees to API3 to use the service, which covers operational and management costs.
The specific mechanism, as shown in the diagram, involves API providers sending data to a single aggregator, which processes and integrates data from different sources to ensure reliable and consistent information for dApps. dApps can access processed data by calling dAPI and provide services based on this data. API3 DAO supervises the entire process through governance mechanisms to ensure system transparency and security.
On the other hand, self-funded dAPI allows users to bear the costs and receive data from a single first-party oracle. This approach provides developers with more flexibility and autonomy, allowing them to experiment with and use data interfaces at lower costs, particularly suitable for early-stage projects or cost-sensitive applications. In this model, users need to fund the operation of self-funded dAPI, with the funds used to cover on-chain transaction fees to ensure timely data updates.
The innovation brought by API3 in the dAPI model may signify a paradigm shift in data consumption patterns in the future decentralized environment. This approach not only directly reduces the latency, costs, and potential failure points associated with third-party intermediaries but also enhances the security and reliability of data, representing an important step forward in seeking fully decentralized and efficient data solutions in Web3.0.
Furthermore, the concept of dAPI allows API3 to not be limited to oracle feeding services but to potentially provide decentralized implementation and support for ubiquitous API applications in our lives.
2.2 API3's Core Technology - Airnode
Airnode is the core key component of API3, allowing API providers to convert their APIs into dAPIs, creating a seamless flow of off-chain APIs to on-chain smart contracts, enabling real-world data to flow into the blockchain ecosystem.
Specifically, Airnode is a serverless oracle node, with a key emphasis on decentralization and security in its architecture. The node is both easy for API providers to deploy and maintain and highly scalable.
Unlike traditional oracles that typically require complex setups and intermediary services, Airnode's design allows API providers to directly become first-party oracles without the involvement of third parties, ensuring the integrity and security of data.
Another major advantage of Airnode is its simplified API integration process, requiring minimal blockchain knowledge and costs for API providers to set up and operate. This feature simplifies the process of API providers becoming first-party oracle nodes, promoting a more democratic use of blockchain technology and encouraging a wider range of data providers to participate in the decentralized data market.
Essentially, the design of Airnode is no longer just a solution for oracles but a foundational component for building a decentralized, secure, and user-centric data ecosystem. Through Airnode technology, API3 is expected to address common challenges faced by traditional oracle services, such as transparency, trust, and efficiency, paving the way for more robust and reliable dApp development.
2.3 OEV Network Capturing Value, Nourishing the Ecosystem
In the cryptocurrency field, Miner Extractable Value (MEV) has been an important concept. Due to the non-instantaneous completion of on-chain transactions, block producers (such as miners or validators) can manipulate blocks by altering transaction order, inserting, or replacing transactions to earn additional profit. Oracle Extractable Value (OEV) can be considered as a subset of MEV.
Recently, API3 announced the launch of the ZK-Rollup platform OEV Network. OEV Network is a ZK-Rollup network customized with Polygon CDK, designed to capture the Oracle Extractable Value (OEV) generated by all dApps using API3, aiming to alleviate the prevalent value leakage issue in current DeFi operations. The adoption of rollup makes the entire process transparent and verifiable, enhancing decentralization and trustlessness, and boosting user confidence in participation and usage.
To understand what OEV is, let's consider an example. Imagine participating in an auction where everyone's bids are visible, and the auctioneer can choose to consider the order of bids. This situation creates an opportunity for the auctioneer to strategically make certain bids to benefit themselves or others, thereby earning additional income.
When oracles update or push data to the blockchain, even minor differences in the timing or accuracy of the information can create opportunities for "providers" to capture potential value, such as frontrunning, arbitrage, or liquidation.
The OEV Network developed by API3 aims to systematize and democratize this process. Operating as a specialized order flow auction platform, the OEV Network captures the value generated by oracles during data updates and redistributes that value to DeFi protocols and their users. This process is executed through auctions, where the highest bidder wins the right to update the data source, and the fees paid are shared with dApps using API3 data sources.
By capturing OEV, API3 introduces a novel revenue source for dApps, strengthening the economic models of API providers and dApp projects. The winning bidder is required to pay an additional 10% fee on top of their bid, with half of it serving as API3's revenue source and the other half being allocated to the oracle provider. This method of distributing captured OEV to API providers also incentivizes them to directly participate in the construction of the Web3.0 ecosystem, fostering a fairer and more transparent data ecosystem. Additionally, the mechanism of auctioning off the data feeding rights creates a decentralized and secure environment, promoting a fairer data ownership model and mitigating risks associated with centralized data feeding.
It's worth mentioning that Polygon co-founder Sandeep Nailwal praised API3's innovative solution for oracle value extraction, calling it a significant breakthrough for the DeFi ecosystem.
Overall, API3's OEV Network represents a significant advancement in the dApp and oracle domains, addressing critical inefficiency issues and unlocking new value flows for participants, potentially bringing about a more balanced and financially sustainable ecosystem for data providers and users in the future.
3. Protocol Revenue Sources
According to the whitepaper, API3's protocol revenue sources mainly include subscription fees paid by dApps, Oracle Extractable Value (OEV), and Service Coverage fees. The uses of protocol revenue include but are not limited to supporting ongoing project development, enhancing network security, operational costs, staking rewards, and rewarding potential stakeholders within the ecosystem. API3 governs the project through DAO to determine the allocation of its resources, ensuring the sustainability and stable growth of the project.
4. Token Economic Model
4.1 Basic Information
According to Etherscan data, the current maximum total supply of $API3 tokens is approximately 128 million, with a circulating supply of around 103 million. The uncirculated portion consists of reward tokens minted for token stakers, which will be unlocked one year after the reward date.
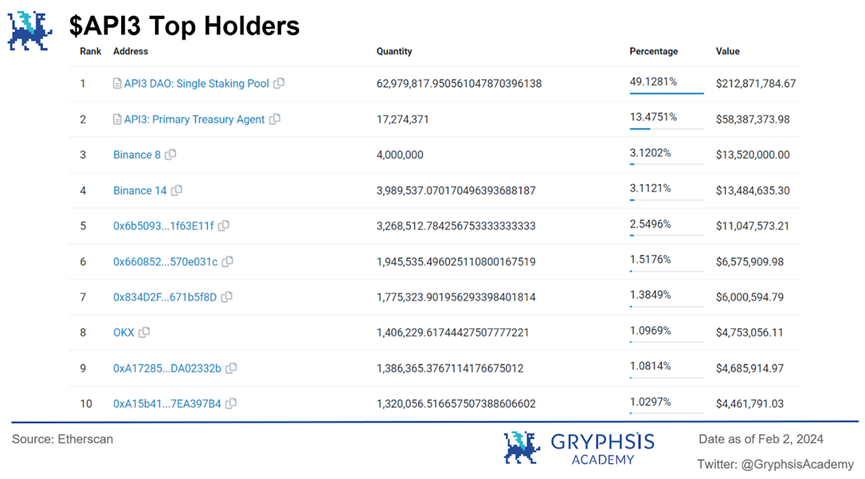
As shown in the diagram, the largest holder of $API3 tokens is the $API3 staking pool, and the second-largest holder is its treasury, together accounting for 62.6% of the total circulating supply of tokens. Additionally, exchange addresses such as Binance and OKX are also major holders of $API3. Therefore, the actual circulating supply of $API3 tokens in the market is not large, to some extent avoiding the occurrence of severe selling pressure.
Overall, API3 comprehensively adopts staking, collateralization, and governance in its token economic model. Its purpose is to incentivize participation, protect the network, and drive the growth of the project by ensuring that token holders can influence the trajectory of the project, effectively manage resources, and participate in the expansion of the ecosystem. By combining three utilities to build a sound token system, API3 achieves true decentralization of governance and operational activities.
4.2 Staking Mechanism
The staking mechanism is the most important core component of API3's token economic model, aiming to align the incentives of stakeholders with the long-term success of the project. By staking $API3 tokens, holders can receive newly minted tokens (rewarded weekly) as staking rewards and gain governance voting rights in the API3 DAO. The staked tokens also serve as collateral, and in the event of dAPI failure, these tokens will be used as compensation for users.
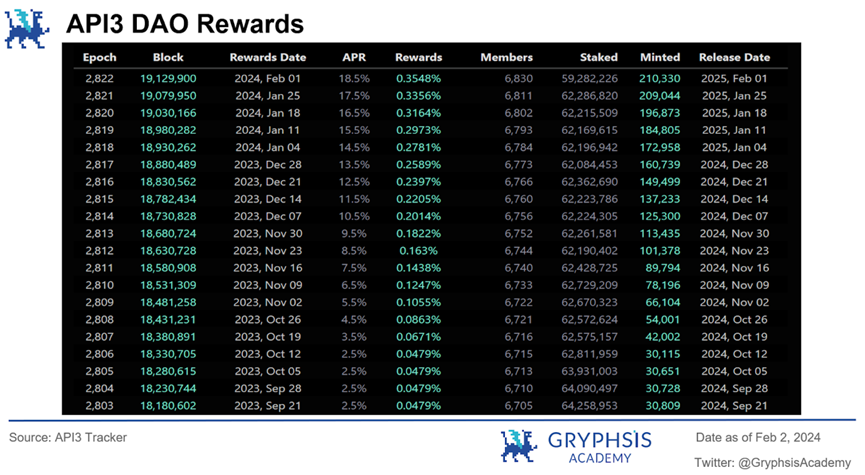
To ensure service continuity, product quality, and fully decentralized governance, API3 has set a "staking target," always striving for the staked token amount to reach a specific percentage of the total token supply.
Currently, API3's staking target is 64,097,566 tokens, and the actual staked amount has not yet reached the target. Therefore, as shown in the diagram, API3 DAO will increase the APR by 1% at each reward date to incentivize more holders to stake tokens until the staking target is reached or the APR is increased to 75%.
Since the token rewards received by stakers are minted, theoretically, this would lead to token inflation. To achieve balance, API3 has designed a deflationary mechanism to address the issue. Firstly, as shown in the diagram, the minted token rewards will be unlocked one year after the reward date, encouraging participants to hold and stake tokens for the long term rather than short-term speculation.

Secondly, API3 DAO will require dAPI users to burn or lock a specific amount of $API3 tokens for a certain period to access data services. As shown in the diagram, by reviewing API3's open-source code, it is found that any address can independently decide whether to enable or disable their burning permission and can burn a specific quantity of tokens by calling the Burn function.
This approach to some extent offsets the inflation caused by newly minted tokens, effectively reducing market supply pressure for $API3, benefiting all token holders, and enhancing the staking confidence of long-term investors and participants.
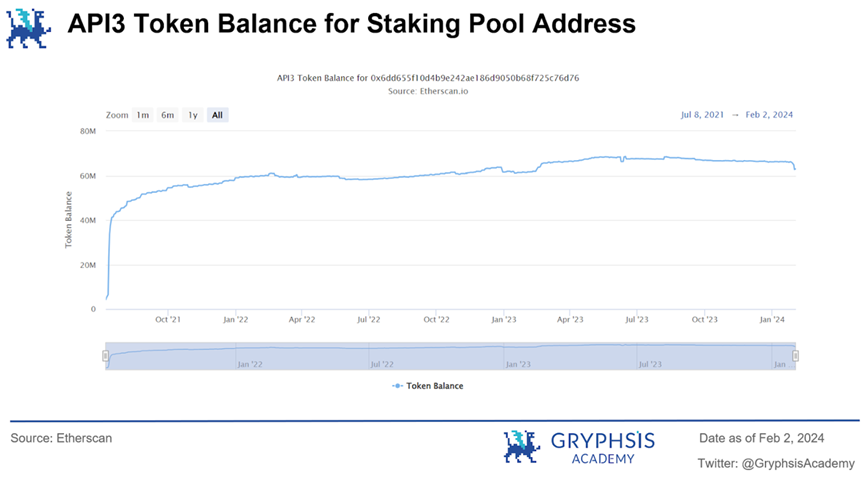
By examining the historical staking status of $API3, it is found that since 2021, the staked token amount has remained very stable and has not experienced significant fluctuations. Even in the recent scenario of a significant increase in the price of $API3 tokens, the staked amount has remained overall stable, without significant selling, indirectly proving the effectiveness of API3's staking mechanism.
4.3 Collateralization Mechanism
API3's collateralization mechanism can be considered as an on-chain oracle service insurance product, which is achieved by providing quantifiable security in the form of Service Coverage.
The entire process can be summarized into the following key steps:
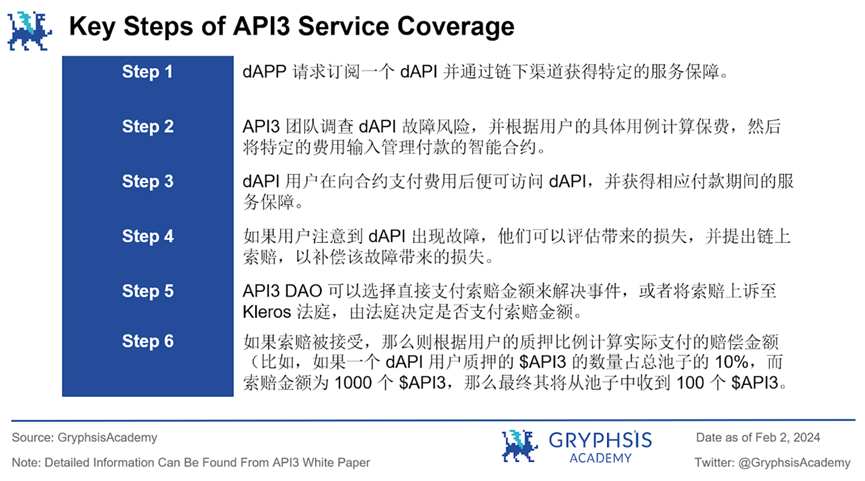
Essentially, this process is similar to purchasing insurance, but it does not require any traditional insurance policies. Once the protocol confirms a dAPI malfunction, users will receive compensation from the staking pool. Additionally, API3 supports multiple types of cryptocurrencies (such as ETH), indicating the diversification of its service and collateralization mechanisms.
More importantly, API3's collateral model design brings a self-regulating mechanism of negative feedback loop to avoid the system's over-expansion and potential self-destruction. Specifically, as API3 DAO expands and adds new dAPI users, the risk of overloading leading to dAPI malfunctions and triggering compensation payouts also increases.
Therefore, the potential compensation demand provides API3 DAO with the motivation to not excessively increase the load during governance, ensuring that API3 does not take unnecessary risks for short-term gains. This approach helps encourage and promote responsible and sustainable growth and development of API3 DAO.
In this way, the incentives for dAPI users and other token stakers become aligned, as they both share the common goal of avoiding system malfunctions. Stakers are motivated to monitor and maintain the healthy operation of dAPI due to the potential insurance payouts, while users benefit from the stability and reliability of the system.
Furthermore, since claimants for service coverage must stake tokens to make a claim, this increases the cost of making a claim, thereby reducing the likelihood of false or abusive claims. This mechanism prevents the system from being abused by those who may exploit the coverage mechanism for personal gain rather than the health of the system.
Ultimately, the self-regulating mechanism of the negative feedback loop will help suppress drastic fluctuations in token value. In token economics, stability is crucial for attracting long-term investors and users. By mitigating excessive risks and failure rates, this loop helps build confidence in $API3 tokens as a long-term store of value.
4.4 Governance Mechanism
In the API3 DAO, the only way to obtain governance voting rights is by staking $API3 tokens. Therefore, governance bears all the risks and rewards of API3. As mentioned earlier, if governance is not actively involved, leading to a large number of claims, they will incur losses, and the tokens they staked will re-enter the market to be purchased by new governance participants.
Conversely, if governance is effective, the supply of $API3 tokens in the market will decrease accordingly, potentially leading to a rise in token prices due to scarcity, allowing governance to earn more rewards. This approach enables API3 DAO to continuously improve itself and recover from failures, achieving true decentralization.
4.5 Summary of Token Economic Model
Overall, API3's token economic model is a carefully designed complex model. $API3 tokens serve multiple purposes and fulfill various demands, including staking, acting as collateral, contributing to the insurance pool, providing governance voting rights, and accessing dAPI services. It not only combats potential token inflation through mechanisms such as reward lock-up periods and token burning but also reduces selling pressure.
More importantly, its economic model deeply integrates $API3 tokens with the project's operations, risks, and token value (supply), in which governance is no longer a trivial option but becomes the most important tool for implementing incentives, maximizing the participation of token stakers in governance to minimize their own risks.
In this way, API3 tightly links the long-term development of the project with stakeholders, ensuring the project's long-term stable development and greatly promoting the realization of true decentralization.
5. Market Analysis and Competitive Landscape
In recent years, the oracle sector has experienced significant growth and development due to its unique technical capabilities and wide range of applications. According to CoinGecko data, the total market value of the oracle sector has exceeded $13 billion. As an indispensable part of blockchain technology, oracles bridge the information gap between the crypto world and the real world, providing a way for smart contracts to access external data.
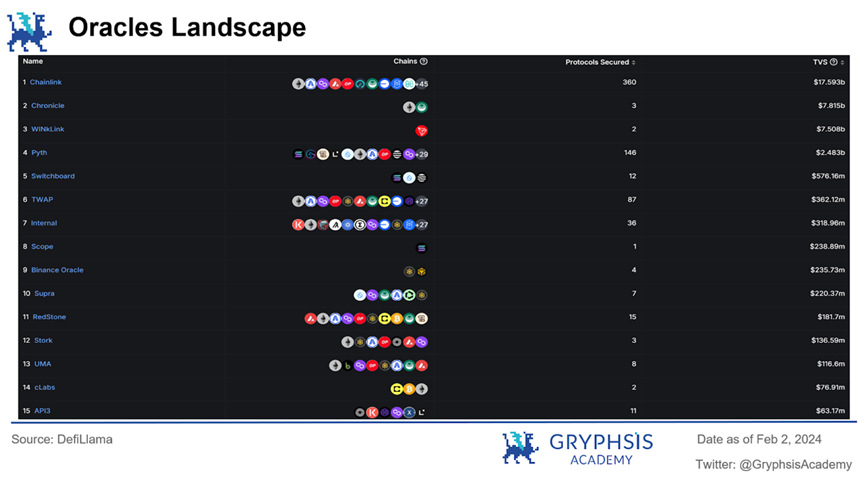
Chainlink has always been the absolute leader in the oracle sector. According to DefiLlama data, Chainlink currently provides services to over 50 different networks and 360 protocols, with a Total Value Secured (TVS) exceeding $17 billion, and its market value far surpasses that of its competitors.
However, this market landscape does not mean there are no challenges and competitors. For example, API3 positions itself as a first-party oracle solution, emphasizing direct data feeding from data providers to the blockchain, aiming to reduce dependency and potential failure points associated with third-party oracles like Chainlink, and providing greater advantages in data accuracy and latency.
5.1 Why First-Party Oracles Matter
In August 2020, nine Chainlink node operators were attacked. Since Chainlink's nodes operate by responding to smart contract requests, retrieving and verifying real-world data, and then passing the data to smart contracts, this process requires consuming Ethereum Gas fees to pay for these operations.
The attackers initiated the attack by sending a large number of seemingly valid price feed requests to Chainlink nodes, causing the node operators to suddenly face significant Ethereum Gas fees. They then hedged the gas price fluctuations by minting $Chi, a Gas token developed by 1inch at the time, and selling these tokens for $ETH, effectively extracting about 700 $ETH from the node wallets, resulting in approximately 700 $ETH in losses.
Although Chainlink took remedial measures promptly after this incident and continuously worked to improve its protocol to enhance network security and reliability, considering the significant importance of oracles to the on-chain ecosystem, the risks associated with oracles will be a long-term and important consideration that we cannot ignore, as seen in the significant losses suffered by Mango Markets and Bonq DAO due to oracle attacks.
In fact, the attackers exploited the mechanism of third-party oracles to carry out these attacks. In contrast, first-party oracles offer a different solution.
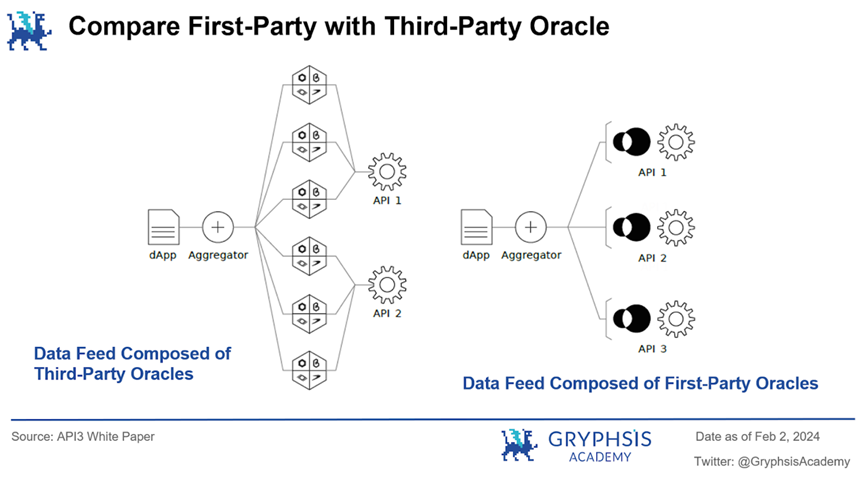

Traditional third-party oracles are hosted by third-party intermediaries to manage oracle nodes. These intermediaries need to aggregate external data and input it into smart contracts. This mechanism not only requires data consumers to trust data providers but also introduces an additional layer of trust and potential costs, and may raise concerns about central failure points, data manipulation risks, transparency, and trust.
For example, to incentivize third-party node operators to provide reliable services, third-party oracles typically require a middleman tax to incentivize honest behavior, which is not present in the first-party oracle model. Additionally, in a sense, the mechanism of third-party oracles may not be considered truly decentralized.
In contrast, as a first-party oracle, API3 allows API providers to operate oracle nodes, providing a more secure and cost-effective way to enhance data reliability and integrity while offering a greater degree of decentralization.
5.2 Competition for First-Party Oracles
When it comes to first-party oracles, we have to mention the recently popular Pyth Network protocol. Next, we will analyze API3 and Pyth Network through a comparative approach.
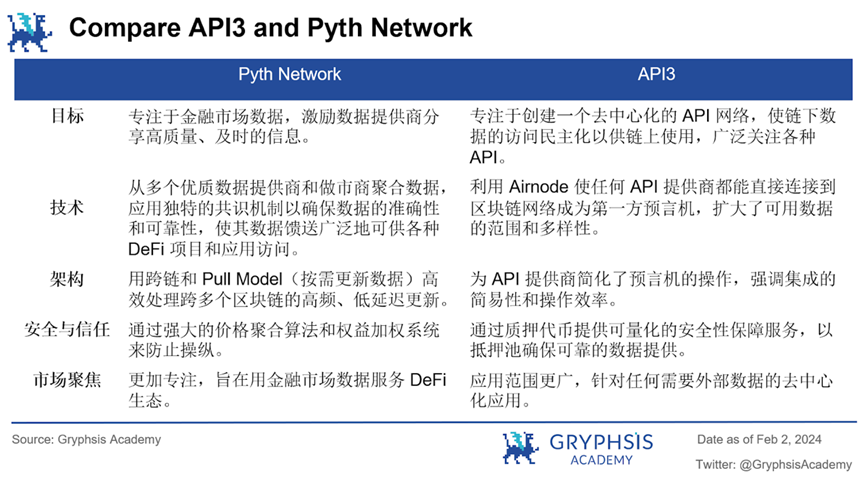
It is clear that both projects have made significant contributions to the Web3.0 ecosystem by addressing the critical need for reliable, decentralized data sources. The main advantages of API3 include: a wider range of data applications, a fully decentralized DAO governance model, low operational complexity, cost-effectiveness, high transparency, and a more robust token economic model.
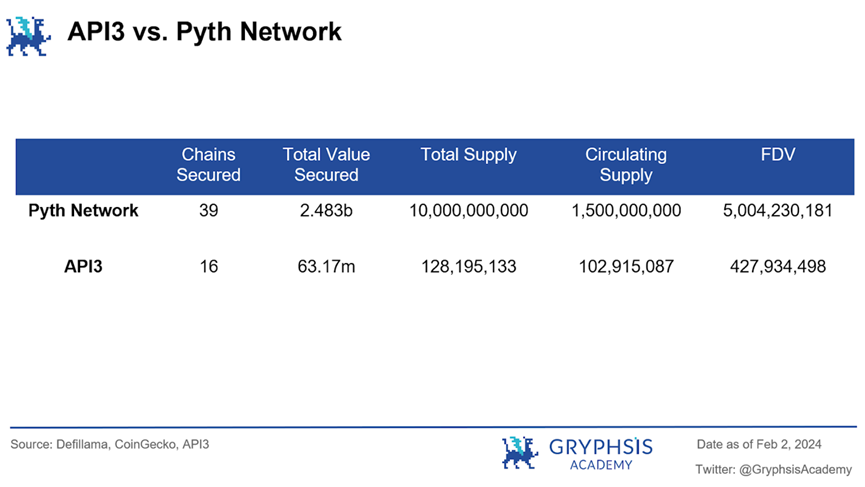
From this data, we can see that Pyth Network has a greater advantage in terms of current integration depth and coverage. However, this does not mean that API3 lacks competitiveness. The fewer integrated protocols currently allow API3 to focus on providing high-quality services and deepening its presence on the blockchains it serves. In the future, as blockchain technology continues to develop and more use cases emerge, API3 can expand its market share by increasing integration links, protocol support, and enhancing its value proposition.
Additionally, API3's relatively smaller market size may make it more flexible, enabling it to adapt quickly to market changes and user demands, providing greater room for growth and expansion. In the future, we expect API3 to enhance its position in the industry through innovation and optimization.
Therefore, we have reason to be optimistic about the future prospects of API3. Combined with the previously introduced OEV Network, when the architecture of dAPI is combined with OEV Network and ZK-Rollup, and governed through a fully decentralized DAO, we can see that the future of API3 may not only be about providing oracle services as an intermediary component, but also has the potential to become the infrastructure for on-chain ecosystems and dApp project development, and even has the potential to disrupt the market currently dominated by third-party oracles.
5.3 Risks
Although API3 brings strong expectations with its various advantages, any blockchain project faces a series of unique risks, and the main risks of API3 may include the following:
Adoption Rate: The future success of API3 largely depends on the adoption by API providers and their integration with blockchain projects. If API3 fails to gain sufficient attraction or the adoption rate does not meet expectations, this may have a negative impact on the project's success and the value of its tokens.
Provider Attrition: If, for any reason, a large number of API providers cease their services or choose not to adopt API3, this may limit the diversity and quality of available data, potentially affecting the utility of the API3 network.
Security Vulnerabilities: Like any blockchain project, API3 may be affected by potential security vulnerabilities in its protocol, smart contracts, or Airnode technology. Any security vulnerability or exploit could lead to loss of funds or data and weaken user trust in the platform.
Competitive Landscape: The oracle sector is highly competitive, and established players like Chainlink already have a significant market share. While API3's concept and design are highly creative, this does not guarantee the project's long-term success, so API3 still needs to stand out and prove its value proposition to overcome competitive pressure.
Therefore, in addition to its innovative approach and mechanisms, the success of API3 will also depend on factors such as technical execution, market adoption, competitive differentiation, regulatory environment, and more. Like all investments in the cryptocurrency space, before making investment decisions, we should thoroughly understand the strengths and risks involved in the project itself.
6. Conclusion
Overall, API3 brings a groundbreaking approach to the oracle sector, directly connecting data providers and blockchain networks through first-party oracles and dAPI, enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency, while reducing the risks associated with data tampering and the costs related to data feeding.
Furthermore, API3 has a carefully designed robust token economic model, allowing smart contract platforms to build meaningful dApps using dAPI in a truly decentralized and trust-minimized manner through DAO governance.
Combined with the launch of its OEV Network, we have reason to expect that API3 will be adopted by more blockchain networks and dApp protocols in the future, and has the potential to become an infrastructure for the development of on-chain ecosystems, promoting the development and innovation of decentralized applications.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




