The bullish tracks for the Cancun upgrade include: Rollup L2 networks, Raas service providers for building Layer2 networks, DA layer for solving data availability, LSD, and heavy staking tracks.
Author: Xiyu, ChainCatcher
Editor: Marco, ChainCatcher
On February 1st, Cointelegraph reported that Ethereum developers plan to determine the mainnet launch date for the Dencun upgrade on February 8th. In a Reddit community post, Ethereum core developer Tim Beiko stated that the recent progress of the Cancun upgrade testing has been smooth, and the Sepolia testnet upgrade on January 30th was also successful, with the final Holesky testnet upgrade scheduled for February 7th.
Christine Kim, Vice President of Research at Galaxy Digital, stated that there is an 80% chance of the Dencun mainnet being activated by the end of March.
As the Cancun upgrade approaches, which tracks and projects will benefit from the Dencun upgrade?
According to the previous article "Understanding which aspects of Ethereum will be improved by the Cancun upgrade," one of the core aspects of the Dencun upgrade is to reduce the cost of publishing L2 data, which will drive demand for decentralized storage, DA, and RaaS infra tracks.
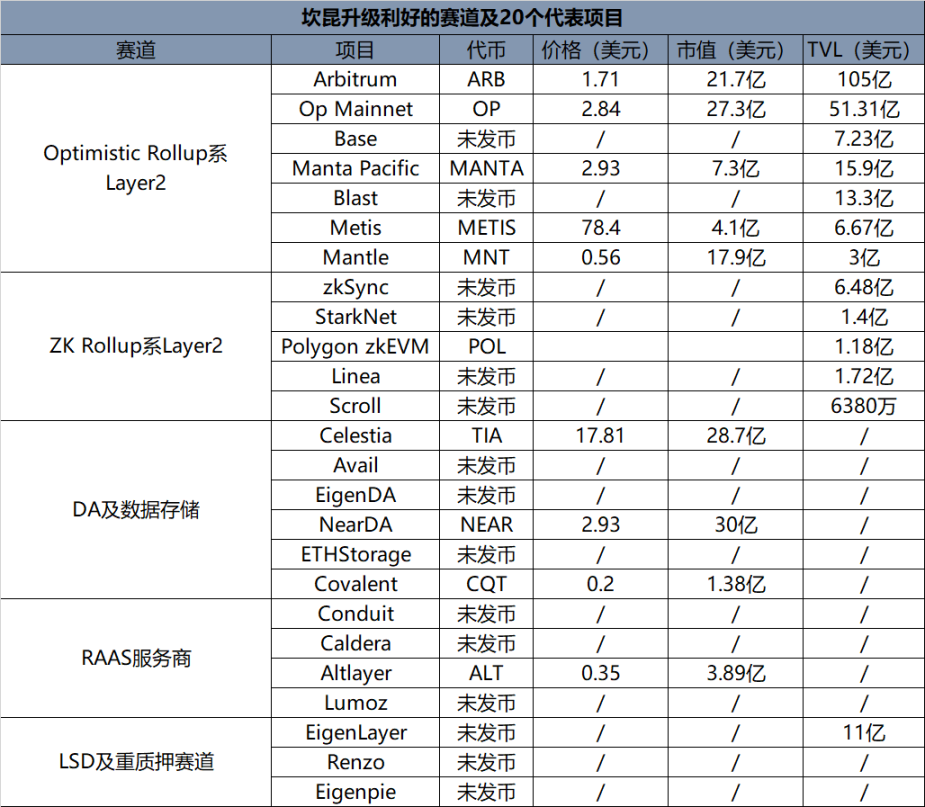
L2 Networks and Their Ecosystem
One of the most direct bullish tracks for the Dencun upgrade is the L2 track. The introduction of Blob data format allows the transaction fees for L2 to be reduced to one-thousandth of the original cost. Lower costs and better performance will not only attract more users but also promote the prosperity of its network ecosystem.
Optimistic Rollup and 7 Major Networks
1. Arbitrum's on-chain TVL surpasses $10 billion, expanding vertically through the Orbit L3 stack
As of 2024, the value of locked-in encrypted assets on the Arbitrum One mainnet has exceeded $10.5 billion. According to L2Beat data, on February 1st, Arbitrum One's on-chain TVL market share accounted for 49.8%, consistently ranking first among many Layer2 projects.
According to Dune data, as of February 1st, the total stored value (TVB) of ETH bridged by the Arbitrum official bridge was 3.354 million, while the value bridged by Optimism's official bridge was 320,000, zkSync was 2.975 million, and Starknet was 860,000.
The market value of the native token ARB is $2.17 billion, ranking 41st among encrypted assets.
On January 31st, the Arbitrum community initiated the implementation of the ArbOS20 version proposal to support most of the improvements in the Dencun upgrade, including the ability to publish L2 transaction batch data in Blob form on the L1 Ethereum at a cheaper price using EIP4844. The ArbOS20 upgrade will support any Arbitrum chain based on L1 Ethereum and its on-chain applications, allowing them to benefit from the Cancun upgrade without any modifications or actions.
The official ecosystem portal page Portal of Arbitrum has recorded 689 ecosystem projects, covering areas such as cross-chain, DeFi, infrastructure and tool products, games, and NFT, representing applications such as decentralized perpetual contract GMX and Hyperliquid, multi-chain lending Radiant, native DEX Camelot, and metaverse game ecosystem Treasure, among others.
Regarding ecosystem development, on January 20th, the Arbitrum Foundation announced the launch of the second phase of the funding program to provide financial support for builders. Grants distributed through this program will be used to improve the adoption of Arbitrum, create a more robust technical structure, and establish a sustainable community in the Arbitrum ecosystem.
Subsequently, blockchain game The Beacon, token management tool Collab.Land, and LayerZero-supported yield strategy platform Mozaic announced that they had received funding from the Arbitrum Foundation.
Additionally, Arbitrum is also attracting projects and developers through the Orbit technology stack program. According to Steven Goldfeder, co-founder of Offchain Labs, more than 50 Arbitrum Orbit chains are currently under development, with a forecast of 150 Orbit chains on the mainnet in 2024.
On January 16th, Arbitrum announced the launch of the Arbitrum Orbit expansion plan to support developers in building their own L2 or L3, settling directly to Ethereum or other Ethereum L2 networks such as Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups.
At the end of December last year, Xai Network, a network built based on Arbitrum Orbit technology for gaming, announced the airdrop of the XDAI token to community users, sparking interest in the Arbitrum L3 network.
Currently, nearly 20 Layer3 networks built based on Arbitrum Orbit technology have been publicly announced, including projects such as game development platform Cometh, arcade game SankoGameCorp, metaverse game Hytopiagg, multi-chain NFT collection platform Polychain Monsters, music copyright protection and creation platform Oursong, points service application Melior, derivative trading platform Syndr and DeriProtocol, liquidity platform Superposition, and NFT derivative trading platform HookProtocol.
On January 29th, the NFT trading platform Rari Foundation announced that the L3 network Rari Chain mainnet, built based on Arbitrum for protecting NFT royalties, had gone live.
On January 30th, co-founder Karel Vuong of the metaverse game platform TreasureDAO stated that TreasureDAO is building a game chain, possibly based on Arbitrum.
2. Optimism horizontally builds L2 superchains through the OP Stack
In terms of TVL, Op Mainnet is the second-largest network in the current Layer2 market, second only to Arbitrum.
According to L2beat data, as of February 1st, Op Mainnet's on-chain locked-in encrypted asset value was $5.13 billion, with a market share of 24.4%. Its native token OP is currently priced at $2.84, with a market value of $2.73 billion, ranking 34th among encrypted assets.
Currently, the Optimism ecosystem mainly consists of Op Mainnet and various Layer2 networks built based on the OP Stack.
Regarding Op Mainnet, the DeFiLlama data platform has recorded 208 ecosystem applications, including DEX platform Velodrome, lending application Sonne Finance, and various derivative platforms built based on Synthetix such as Kwenta and Lyra.
Currently, there are dozens of Layer networks built based on the OP Stack. Among them, the most well-known is the Base network, with a TVL of $723 million, ranking fourth in the Layer2 market. The Manta Pacific network, which ranks third in TVL, was initially built based on the OP Stack but later migrated to the Polygon CDK by Manta.
In addition, there are the opBNB launched by BNB Chain, the application chain of Worldcoin ID, the Zora Network of NFT trading market Zora, the Loot Chain built by the Loot ecosystem project Adventure Gold DAO, and the OPCraft, a dedicated chain for online virtual world games created by Lattice, an online game developer.
The Lyra V2 options protocol has built a custom chain on the OP Stack, the growth incentive network Mode has launched the developer mainnet, Web3 cross-chain infrastructure Swan has introduced Swan Chain, and Lattice, a game studio, has launched the L2 chain Redstone, among others.
On January 30th, Optimism co-founder Ben Jones proposed that Treasure join the Optimism Superchain and build the Treasure Chain based on the OP Stack.
3. Base, backed by Coinbase
Base is an L2 built by Coinbase based on the OP Stack. As of February 1st, the TVL is $723 million, and the amount of ETH stored through cross-chain bridging has reached 320,000.
Among the 209 ecosystem applications recorded by DeFiLlama, representative applications include the DEX platform Aerodrome, lending platform Seamless Protocol, and the once popular social application friend.tech.
4. Manta Pacific, a Layer2 network launched by Manta
Manta Pacific is an L2 launched in July last year by Manta, a ZK-based L1 network, initially built based on the OP Stack but later announced its migration to the zkEVM architecture of Polygon CDK.
In January alone, the Manta network received investments from two institutional investors, Newman Capital and ArkStream Capital, and during this period, it announced its governance token MANTA's economic model and airdrop plan, entering a period of rapid growth.
On January 30th, DWF Labs stated that it had contributed $3 million TVL to the DEX on the Manta network since November last year. At the time of writing, the price of MANTA is $2.93, with a market value of $730 million. According to L2beat, as of February 1st, Manta Pacific's TVL is $1.59 billion, with 39 applications recorded, including lending applications LayerBank and ZeroLend, and DEX platforms Aperture Finance and PacificSwap.
5. Blast, a rising star in L2
Blast is an L2 network built on Optimistic Rollups technology by the founder of Blur. Since its launch on November 21st last year, the network's TVL has attracted funds worth over $1.33 billion as of February 1st, and has received $20 million in funding support from Paradigm and Standard Crypto.
On January 17th, Blast announced the launch of the testnet and simultaneously started the "Big Bang" airdrop competition, attracting a large number of crypto enthusiasts.
However, on February 1st, former EVM engineer @0xKaden revealed that Blast's codebase had issues, plagiarized Optimism's code, and changed Optimism's MIT license to BSL, indicating Blast's intention to fork Optimism's codebase.
6. Decentralized sequencer Metis
Metis Network, originally built on Optimistic Rollup technology, announced in July last year that it would upgrade to a Hybrid Rollup solution and introduced decentralized sequencer pools and other innovative technologies, making it unique among many Layer2 networks.
The decentralized sequencer introduces a PoS staking pool, allowing users to become sequencer operators by staking the token METIS. Currently, to become a Metis sequencer node, one needs to stake 20,000 METIS tokens, worth about $1.6 million.
As of February 1st, the TVL of locked-in encrypted assets on the Metis network is $667 million, ranking in the top five in the Layer2 market. The token METIS is priced at $78.4, with a market value of $410 million, ranking 140th.
7. Modular L2 network Mantle Network
Mantle Network, incubated by BitDAO, is a modular Layer2 scaling solution based on Optimistic Rollup technology, which launched the Sepolia testnet on January 12th.
In Mantle, the mainnet provides the execution layer, with consensus and settlement on the L1 Ethereum, data availability is managed by the dedicated Mantle DA layer, and the modular data service provider Eigenlayer provides underlying technical support. This division of labor is more conducive to improving on-chain efficiency.
On December 4th last year, Mantle announced the launch of the Mantle LSP liquidity staking protocol on the Ethereum mainnet, entering the LSD track. Users can stake ETH to obtain benefits from the Ethereum PoS network and receive liquidity staking certificates mETH, the second core product in the Mantle ecosystem.
As of February 1st, the amount of ETH staked in Mantle LSP is approximately 339,000, worth $810 million.
On January 18th, the Mantle community's ecosystem venture capital fund, Mantle EcoFund, announced the deployment of $10 million to invest in 6 DeFi projects within the ecosystem. These projects include the automatic market maker DEX Merchant Moe built by the Trader Joe team, the native DEX platform Butter.xyz, the stablecoin trading market INIT Capital, EigenLayer's liquidity re-collateralization platform Renzo, the multi-chain decentralized perpetual trading platform MUFEX, and the spot and derivative trading platform TsunamiX.
As of February 1st, the token MNT is priced at $0.56, with a market value of $17.9 billion, ranking 47th.
Top 5 Layer2 Networks in the ZK Rollup Series
1. ZkSync
As of February 1st, the TVL on the ZkSync Era chain is $648 million, making it the largest network in the ZK Rollup series and ranking 6th in the entire Layer2 market.
Since June last year, zkSync announced the launch of ZK Stack, a component for building custom zkRollup L2 and L3 (also known as HyperChain). The zkSync ecosystem includes the zkSync Era mainnet and L2 or L3 networks built based on ZK Stack.
On January 31st, the developer of zkSync, Omar from Matter Labs BD, proposed in the TreasureDAO community that the Treasure Chain use ZK Stack as L2 and be able to use L3 chains for vertical scaling. Matter Labs also stated that they are collaborating with the zero-knowledge proof research team Lambda Class to enable ZK Stack chains to have their native Gas token, allowing Treasure Chain to use MAGIC or any other ERC-20 as the Gas token.
Regarding the zkSync Era mainnet, DeFiLlama data platform has recorded 96 ecosystem applications, including DEX platforms Mute.io and Velocore, lending application ZeroLend, and derivative trading protocol Rollup.Finance. On January 30th, the lending protocol ZeroLend announced an airdrop to Pyth Network's oracle stakers.
However, during the public chain frenzy in December last year, the zkSync Era network's performance did not withstand the test and was reported to have experienced downtime on December 15th, with no blocks produced for nearly 2 hours.
2. Starknet
On January 31st, data posted by the core developer @antiyro on social media showed that transactions on the Starknet network had used STRK to pay Gas fees. By February 1st, the Starknet ecosystem's smart contract wallet Braavos had listed the STRK token by default. Community users speculated that this was in preparation for the issuance of the STRK token by Starknet.
Prior to this, on January 10th, the Starknet mainnet completed the v0.13 upgrade, which significantly reduces costs through more efficient transactions and prepares for using STRK to pay fees.
In terms of application chains, on January 20th, Starknet announced on social media that it would collaborate with the modular DA layer Celestia to achieve a high-throughput Layer3 network.
As of February 1st, the TVL on Starknet's chain is $140 million, with 18 applications recorded, including DEX platforms JediSwap and mySwap, lending application zkLend, and derivative trading protocol ZKX.
3. Polygon zkEVM
As of February 1st, the TVL on the Polygon zkEVM chain is $116 million, ranking 13th among many Layer2 networks.
Compared to the average on-chain ecosystem, the performance of the Polygon CDK development stack has been quite outstanding.
Since announcing the launch of the CDK chain development kit for developing and connecting Ethereum L2 in August last year, several well-known projects have developed Layer2 networks based on its technology architecture.
This includes the recently popular community-driven network ZKFair, a ZKRollup built based on Polygon CDK and Celestia DA technology, and the Manta Pacific, which migrated from the OP Stack.
On January 30th, the game public chain Immutable announced that the zkEVM mainnet launched in collaboration with Polygon will be open to the public in the coming weeks.
In December last year, Indian e-commerce company Flipkart announced that it would build an L2 network based on Polygon CDK to expand its Web3 loyalty program. In November last year, OKX announced a collaboration with Polygon to launch the zkEVM L2 network X1. In October last year, Polygon Labs co-founder also proposed that ApeCoin DAO use Polygon CDK to develop its L2 network ApeChain, among others.
Currently, Polygon 2.0 is a multi-chain network ecosystem driven by ZK technology at the L2 layer, including zkEVM, PoS, and L2 networks built based on CDK.
On January 28th, Polygon zkEVM announced plans to undergo the Etrog upgrade, which will make Polygon zkEVM a Type2 zkEVM (fully equivalent to EVM), allowing developers to deploy code on Polygon zkEVM with an experience similar to Ethereum.
On February 1st, Polygon Labs CEO Marc Boiron announced that 60 employees, accounting for 19% of the team, have been laid off.
4. Linea, Ethereum L2 solution under ConsenSys
According to Dune data, as of February 2nd, the Linea mainnet has bridged nearly 380,000 ETH, with 418,000 interacting addresses.
On January 28th, Linea announced on social media that users who participated in their DeFi Voyage event and completed Proof of Humanity (PoH) personal identity verification on the identity platform Verax before January 22nd will receive an airdrop of the SBT token LXP (Linea Voyage XP) to their wallets.
In December last year, Linea announced the Linea Voyage XP (LXP) ecosystem incentive program, which will distribute non-transferable SBT tokens LXP to users who participated in the DeFi Voyage event to recognize the community's contributions to the development of the Linea ecosystem.
5. Scroll
Since its mainnet launch in October last year, the TVL of locked-in encrypted assets on the Scroll chain has increased to $63.8 million, and the official cross-chain bridge Scroll Bridge has bridged over $138 million worth of ETH.
On January 2nd, Scroll co-founder Sandy Peng released the 2024 roadmap, outlining plans to reduce cross-chain costs by 50%, lower transaction fees using EIP-4844 Blob, add multiple validators, incorporate decentralized proof, and implement parallel EVM, among other features.
In a public statement on December 27th last year, Sandy Peng stated that the tools needed by developers such as Chainlink, The Graph, and RPC are basically all online. In the future, some familiar Ethereum ecosystem projects will gradually be deployed on Scroll, and the focus of development in 2024 will also lean towards native projects on Scroll. Next year, there will also be encouragement for ecosystem projects to have more Fair Launches, supporting fair community participation.
Data Availability Layer (DA) and Storage Track
The core module EIP-4844 upgraded by Dencun introduces the Blob data storage format in the process of L2 data submission to L1, creating a dedicated channel for L2 transaction data to be uploaded to the L1 mainnet, allowing Ethereum to carry more data, increase Ethereum's TPS, and reduce costs. However, Blob data storage is not permanent; it is temporary and is regularly cleared or discarded at regular intervals (currently every 18 days).
Because Blob data can only be stored temporarily, there are issues with accessing historical data, which still has potential value for retrieval and analysis.
Therefore, the storage of this data will also drive the demand for decentralized storage services. The modular Data Availability Layer (DA) can provide programmable L2 data solutions at a lower storage cost, ensuring that on-chain data is available for all network participants to use and access. After the EIP-4844 upgrade, the cost of data availability can be further reduced to one-fifth to one-tenth of the original cost.
Representative Projects in the DA Layer
Leading DA Layer Project Celestia
Celestia is a PoS network based on CometBFT and Cosmos SDK, and it is also a modular blockchain project focused on data availability. It deconstructs the blockchain into consensus layer, execution layer, data availability layer, etc., through modular architecture, completing their respective tasks in a collaborative manner to improve network performance and efficiency.
Its DA layer mainly consists of Data Availability Sampling (DAS) and Namespaced Merkle Trees (NMT). DAS allows light nodes to verify data availability even when the entire block is not downloaded, while NMT allows the network to categorize data into different "namespaces," allowing applications to download only relevant data. This selective data retrieval makes Celestia more efficient and scalable, especially for applications that only need specific blockchain data.
Currently, Celestia has become the preferred data solution for developers building L2 networks. Its technology has been integrated into L2 network developer stacks such as Polygon CDK, OP Stack, and ZK Stack. On January 30th, Starknet announced a partnership with Celestia to build an L3 network. Additionally, Manta Pacific is also a representative L2 network based on Celestia.
Avail
Avail was originally a project founded by Polygon Labs in 2020 to address data availability issues. In March last year, it became an independent DA public chain, no longer limited to Polygon or Ethereum. Avail efficiently sorts and records transactions, providing storage and data feasibility verification.
In November last year, Avail announced the launch of the incentive testnet "Clash of Nodes," inviting existing validators from the Kate testnet to test, verify, and operate to earn points and potential rewards.
EigenDA
EigenDA is a decentralized data availability layer (DA) developed based on the Ethereum re-collateralization protocol EigenLayer, and its data availability layer for the modular L2 network Mantle is supported by it. Unlike general DA projects like Celestia and Avail, EigenDA is a middleware without its own consensus mechanism. Its security is obtained through EigenLayer's Ethereum validator re-collateralization mode.
EigenDA is also the first active verification service (AVS) on EigenLayer, where re-collateralizers re-collateralize ETH into EigenDA to perform data verification services and receive rewards. L2 publishes data to EigenDA, resulting in lower transaction costs and higher TPS.
In November last year, EigenLayer announced the second phase testnet of EigenDA, where operators can register on the network and start verifying EigenDA. Restakers can delegate their collateral to operators and start using shared security with EigenDA. As for Rollups developers, they can integrate EigenDA as a data availability layer.
On December 5th of the same year, EigenDA announced the launch of a partner program, with the first batch of 8 networks using EigenDA for data availability, including AltLayer, Caldera, Celo, Layer N, Mantle, Movement, Polymer Labs, and Versatus.
NearDA
In November last year, the Near Foundation announced the launch of the data availability solution Near DA. It is reported that publishing data with Near DA is about 8000 times cheaper than publishing data directly on Ethereum. Initial users include Starknet's Madara, Caldera, and Movement Labs.
On January 19th, Near DA announced integration with Polygon CDK for developers to build Ethereum ZK Rollups. Prior to this, on December 21st last year, Near DA announced integration with Arbitrum Orbit.
Data Storage Track
Ethereum L2 Data Storage Project ETHStorage
ETHStorage is focused on solving Ethereum's dynamic storage issues and is positioned as the first storage L2 in the Ethereum ecosystem. Based on Ethereum's data availability DA, ETHStorage can provide programmable storage L2 solutions at a lower cost, significantly reducing the storage costs of large amounts of data on Ethereum. Programmable storage can save 100 to 1000 times the cost when it expands to hundreds of TB or even PB levels.
In July last year, the Ethereum L2 data storage project EthStorage completed a $7 million seed round financing at a valuation of $100 million.
Decentralized Data Infrastructure Covalent
Covalent provides Blockchain Indexer services, offering developers a unified API for retrieving blockchain data, allowing developers to reuse queries across multiple blockchains. It extracts data from various blockchains, uploads this data to a storage instance, indexes and transforms the stored data objects, and loads the data into a local data warehouse queried by API users.
In November last year, Covalent launched the "Ethereum Wayback Machine (EWM)" to address long-term data availability issues, used for long-term storage of L2 state data discarded by Blob. Additionally, Covalent will integrate L2 data into its existing decentralized data analysis infrastructure services, not just simple storage.
In addition, in the storage track, there are also established decentralized storage projects such as Filecoin, Arweave, Storj, and BNB Greenfield.
LSD and Re-staking Track
In addition to reducing the cost of L2 data publishing to L1, the Dencun upgrade also introduces EIP-4788, which places the block root of the Ethereum beacon chain into the execution layer EVM mainnet. This allows the Ethereum mainnet EVM layer to directly read the data consensus state on the beacon chain without relying on third-party information and data transmission, eliminating the impact of external failures.
EIP-4788 enables smart contracts on the Ethereum execution layer EVM to directly read key data such as the ETH balance and status staked by validators on the beacon chain, improving security and capital utilization.
In simple terms, liquidity staking protocols deployed on the EVM layer such as Lido, Rocketpool, Swell, and re-staking protocols like Eigenlayer can directly access key data such as validator balances and status from the consensus layer, reducing previous trust assumptions in re-staking and improving operational efficiency.
EigenLayer
According to information on the EigenLayer official website, as of February 2nd, the amount of ETH staked in EigenLayer is approximately 460,000 coins, worth about 1.1 billion US dollars.
EigenLayer supports LST assets for re-staking to earn staking rewards outside of Ethereum PoS, such as staking on other sidechains, oracles, middleware, etc., as a node and receiving validation rewards. This allows third-party projects to enjoy the security of the ETH mainnet, and ETH stakers can earn more rewards.
Currently, EigenLayer supports various LST assets such as Lido's stETH, Rocket Pool's rETH, and Swell's swETH.
On February 6th, EigenLayer will add three new LST assets, including Frax Ether's sfrxETH, Mantle Staked Ether's mETH, and Liquid Collective Staked Ether's LsETH.
In addition, several re-staking protocols have been built based on EigenLayer, such as Renzo, which completed a $3.2 million seed round financing on January 16th without being subject to EigenLayer LST deposit limits.
On January 22nd, the multi-chain yield protocol Magpie announced integration with the Ethereum re-staking protocol EigenLayer and established the SubDAO organization Eigenpie to provide re-staking services.
RAAS Service Providers
With the launch of various Rollup network development components such as Polygon CDK, OP Stack, ZK Stack, developers can quickly deploy L2 networks through simple and easy-to-use tools, and even without code.
Faced with numerous L2 Stacks solutions, the important problem of how developers can choose the optimal solution has led to the emergence of Rollup as a Service (RaaS) providers. These providers not only help developers find the most suitable L2 Stack according to their needs but also provide related chain-building or supporting facilities, allowing projects to focus on building products rather than infrastructure.
Deployment of L2 or L3 is becoming increasingly simple through Rollup-as-a-service providers such as Caldera, AltLayer, and Conduit.
Conduit Focused on the Optimism Ecosystem
Conduit is an RAAS platform focused on Optimism Rollup, helping developers quickly build L2 based on OP Stack and successfully establishing OP series Rollup L2 networks such as Zora Network, Aevo, Lyra, and Orderly Network.
In September last year, Conduit added support for Arbitrum Orbit, allowing developers to quickly deploy L2 or L3 on Arbitrum and helping Parallel Network successfully build an L2 Rollup based on Arbitrum.
In March last year, Conduit received a $7 million seed round financing led by Paradigm.
Caldera
Caldera is also an RaaS service provider built on OP Stack, supporting developers to quickly build an OpL2 in a code-free manner.
Caldera is more like an all-in-one Rollup development service platform, providing all the tools and resources needed for project parties to build Caldera Chains based on OP Stack or Arbitrum Orbit frameworks.
In addition to L2 itself, Caldera has configured a series of blockchain infrastructure, such as blockchain browsers, testnet faucets, etc., further reducing the cost and barriers to entry, making it plug-and-play.
L2 networks such as Loot Chain, Manta Pacific, and Rari Chain are supported by Caldera.
In September last year, Caldera received a $9 million seed round financing led by Sequoia Capital and Dragonfly.
Restaked Rollups Service Solution Altlayer
Altlayer supports code-free deployment of L2, allowing developers to quickly create a Rollup chain through simple graphical interface operations.
The flagship product is Restaked Rollups, which combines with EigenLayer's re-staking service to enhance the security of the Rollup public chain through EigenLayer's Active Verification Service (AVS).
On January 17th, AltLayer (ALT) was launched on Binance's new coin mining platform.
ZK-based RaaS Solution Lumoz
Lumoz, formerly known as Opside, is a ZK-based RaaS solution that supports developers in deploying a ZK-Rollup or generating customized zkEVM application chains without the need for any knowledge of ZK-related information, only through simple frontend operations.
The recently popular Layer2 network ZKFair is one of the ZK-based L2 networks built on Lumoz.
In April last year, Lumoz received a $4 million seed round financing led by Web3.com Ventures and NGC Ventures.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



