Blayer's BTC Layer2 solution solves the decentralized cross-chain problem and bilateral verification challenge of block information from the Bitcoin network to Layer2 through its core technology, while also achieving efficient use of Bitcoin in smart contract applications.
Author: Blayer
The huge potential of the Bitcoin ecosystem
When it comes to blockchain, the first thing that comes to mind for people around the world is often Bitcoin. In 2023, the recovery of the digital currency market was mainly driven by Bitcoin. Despite experiencing the impact of the pandemic, the digital currency market continued to create historic milestones, with Bitcoin leading the way. Especially since the Taproot upgrade in 2021, the technical foundation of Bitcoin has opened up new possibilities for embedding more data on the blockchain, sparking a new wave of enthusiasm for Bitcoin and the entire digital currency world. In 2023, Bitcoin's share of the total market value in the crypto market rose from 38% at the beginning of the year to 52% by the end of the year. The Taproot upgrade once again made the Bitcoin ecosystem the focus of attention.
The ecosystem of Bitcoin is not a new concept. Since the birth of Bitcoin, exploration of its ecosystem has never stopped. The recent popularity of inscriptions reflects the strong demand of the Bitcoin community for ecosystem expansion.
In April 2024, Bitcoin will undergo its fourth halving, which will pose a huge challenge to miners' income, and price fluctuations will seriously affect miners' enthusiasm. Bitcoin, with security and decentralization at its core, will face a severe test, and the expansion of the Bitcoin ecosystem has become extremely urgent.
Currently, the market value of Bitcoin has exceeded 850 billion US dollars. If blockchain development leads the value trajectory, then Bitcoin is likely to enter the next major growth cycle. Bitcoin is standing at the forefront of a new era, perfectly combining traditional finance with decentralized, trustless financial models.
Taking Ethereum as an example, with a market value only one-third of Bitcoin's, its ecosystem accounts for 20% of its total market value, with on-chain assets of approximately 50 billion US dollars. If this proportion is used to calculate, the Bitcoin ecosystem should have at least 200 billion US dollars of development space. However, the current staked assets in the Bitcoin ecosystem are only 300 million US dollars. This indicates that the Bitcoin ecosystem has a growth potential of up to 600 times, demonstrating its huge potential for development.
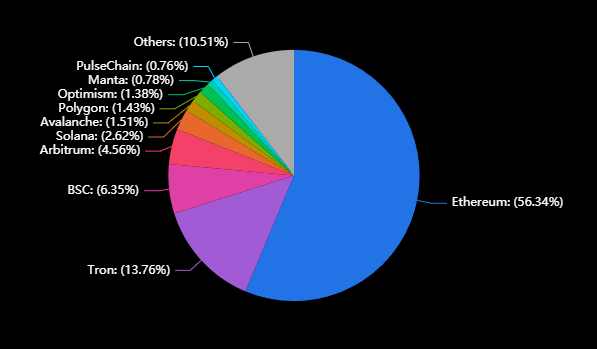
ETH and ETH Layer2 TVL is approximately $50B, accounting for about 18% of ETH market value
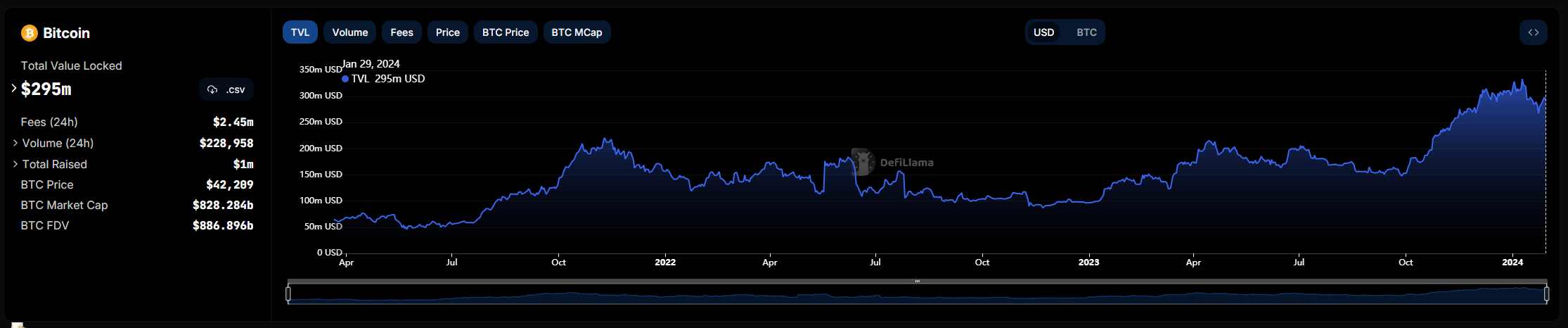
Bitcoin network TVL is $305M (total value locked)
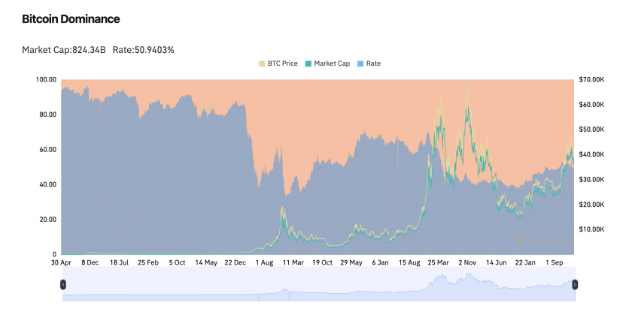
Current market value and total market share of Bitcoin
Bitcoin needs L2
As the cornerstone of cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin is renowned for its security, reliability, and decentralization, and is seen as the spiritual totem of the cryptocurrency field. Since its inception, Bitcoin has always insisted on protecting value in the safest way possible, ensuring the inviolability of personal property.
Although the Bitcoin network does not have Turing completeness and cannot execute smart contracts, and its TPS is much lower than other public chains, supporters of Bitcoin still believe that it does not need major changes or risky technological innovations to maintain its core decentralization and security.
The introduction of the BRC20 protocol doubled the price of Bitcoin, attracting a large number of inscription users to the Bitcoin mainnet. However, as the mainnet for storing value, it also faces problems such as high interaction costs, slow confirmation speeds, and difficulty in scaling applications.
The community urgently expects the expansion of applications, and miners need stable income. Directly improving the underlying protocol of Bitcoin would face high complexity, leading to hard forks and community splits, increasing system risks, and even threatening its most important decentralization and security. Drawing on the verified experience in Ethereum, the community is more inclined to adopt Layer2 solutions. By processing a large number of operations off the mainnet and only writing the final state back to the mainnet, this technology aims to increase transaction speed, reduce transaction costs, and solve the problems currently faced by the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Considering the actual situation, the Layer2 solution for Bitcoin should have the following characteristics:
- Decentralized cross-chain: Decentralized cross-chain based on the mainnet consensus is crucial and is a continuation of the security concept of Bitcoin. Current traditional cross-chain technologies such as hash time locks and multi-signatures are mostly centralized and cannot provide sufficient trust guarantees. Only by achieving true decentralized cross-chain can user trust be ensured, laying a solid trust foundation for Layer2.
- Secure and efficient Layer2: Layer2 should not only support smart contracts and allow various protocols to use BTC as assets, but also fully inherit the security features of Bitcoin and provide fast and efficient transaction processing. At the same time, the state results should be effectively synchronized to the mainnet for confirmation.
- Nourishing the Bitcoin ecosystem: For Bitcoin users, if Layer2 lacks participation in Bitcoin consensus, it loses its core meaning. Using BTC as transaction fees (gas) is an important part of the Layer2 narrative. From a strategic perspective, increasing miner income, stimulating community developer interest, and promoting the development and innovation of Layer2 will help drive the overall development of Bitcoin.
Current status of Bitcoin ecosystem development
Technical challenges of decentralized cross-chain for Bitcoin Layer2
Layer2 refers to off-chain solutions built on top of the Bitcoin mainnet, aiming to maintain the decentralization and security of Bitcoin without sacrificing them. Due to the Turing incompleteness of the Bitcoin mainnet and the limitation of block space at the base layer, as well as the adoption of a simple UTXO model, Bitcoin faces unique challenges. For example, Ethereum's L2 project such as Scroll verifies the ZK Proof generated by the second-layer network computation by deploying contracts on the first layer, but even after the Taproot upgrade, Bitcoin cannot achieve complex OP/ZKP verification logic. Bitcoin's UTXO model, which means one-time use, implies that the cost of generating a new contract is required for each contract call, which helps prevent double spending attacks and maintain security, but limits Bitcoin's ability to directly replicate Ethereum-style cross-chain designs. In addition, although Bitcoin's supported Script Code is stack-based, the supported OpCode types are very limited and difficult to extend to the level of computation required for contracts like Scroll's ZK verification contract.
Nevertheless, exploration of the Bitcoin ecosystem has been ongoing for many years, with multiple teams dedicated to solving these technical challenges:
- Lightning Network: Supports fast, low-cost micro-payments achieved by creating payment channels, with only critical steps being confirmed on-chain. Key technologies include revocable sequence contracts and time lock contracts, but it requires sufficient funds to be locked in payment channels, which may lead to liquidity issues. Effective operation depends on widespread participation and sufficient channels.
- Stacks: Provides decentralized mining and bridging technology for Bitcoin, bringing Bitcoin liquidity into Stacks applications through protocols such as sBTC. It adopts a proof-of-transfer consensus mechanism, where miners need to use BTC for STX mining. Cross-chain uses a centralized bridge project, and Stacks has its own chain, compiler, and programming language Clarity.
- RGB: Integrates the Lightning Network into the Bitcoin smart contract system. Transaction verification is completed by the client and is mainly used for asset issuance and trading, with limited application scenarios.
- Rootstock (RSK): Allows Bitcoin miners to process BTC and RSK transactions simultaneously. It supports EVM and achieves Bitcoin expansion, but its security model differs from Bitcoin, and the cross-chain security is questionable.
- Liquid: Allows users to move Bitcoin between two networks through two-way pegs, with cross-chain use involving 11 multi-signature nodes, relatively centralized. The sidechain design limits the use of complex smart contracts.
Currently, various Bitcoin Layer2 projects continue to emerge, each with different compatibility designs. The main challenge for current Layer2 teams is to achieve decentralized cross-chain and efficient second-layer solutions. There is currently no solution that perfectly balances these two aspects among existing projects.
Blayer Solution
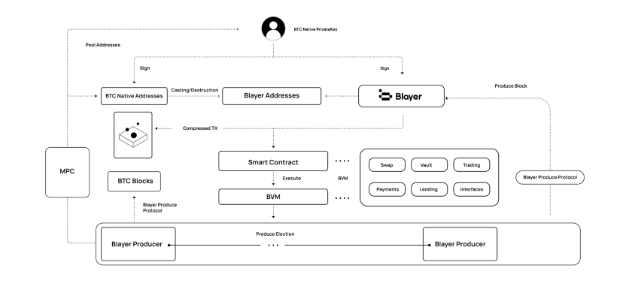
The Blayer protocol aims to bring revolutionary changes to the Bitcoin ecosystem. As an innovative BTC Layer 2 solution, the core of Blayer lies in achieving efficient and secure transfer from Bitcoin to Layer2 in a decentralized manner. It not only provides an efficient, secure, and scalable value application platform, but also supports the use of native BTC as gas fees through the developer-friendly BVM protocol. This not only enriches and improves the Bitcoin ecosystem but also helps unlock the value on the Bitcoin chain, transforming it into a foundational asset for blockchain and promoting the development of the Bitcoin Web3 ecosystem.
The launch of the Blayer protocol marks an important step towards a more efficient, secure, and diverse future for the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Pioneering decentralized cross-chain communication for Bitcoin Layer2
The Blayer protocol innovatively introduces the Decentralized Cross-chain Protocol (DC2P), which achieves decentralized cross-chain communication between Bitcoin and the Blayer network. Through this mechanism, users can securely lock Bitcoin and cross-chain to the Blayer network, utilizing the powerful capabilities of smart contracts within Blayer.
When a user initiates a cross-chain request, the Blayer protocol automatically performs Merkle hash verification of the user's operation. Once the protocol verifies that the user has transferred Bitcoin to a decentralized custody pool, the Privacy Fragment Integration Protocol takes over and locks the funds, ensuring that nodes do not generate the target private key while safeguarding the encrypted privacy fragments. These privacy fragments can only be aggregated through computation, ensuring the security of the keys even in the event of partial fragment loss or error. This mechanism achieves decentralized private key management.
The Blayer protocol maps user assets on the second layer network and ensures bidirectional synchronization verification through the Mirror Consensus Protocol, guaranteeing the security of the mainnet and the second layer network. The management of second layer network nodes adopts a Byzantine Proof of Stake mechanism, ensuring network efficiency and decentralization. Through Blayer's decentralized cross-chain technology, Bitcoin users' assets can circulate securely and efficiently between the mainnet and the Blayer network.
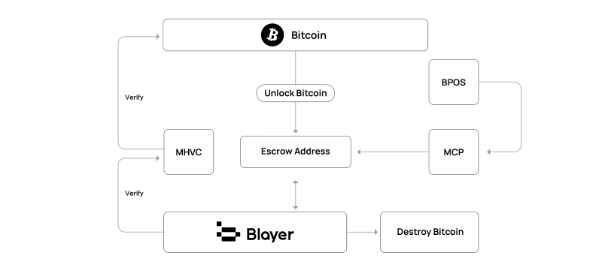
(Cross-chain process diagram)
Innovation in Blayer's Cross-chain Technology
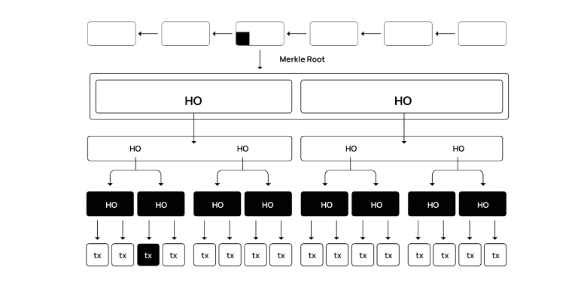
1. Merkle Hash Verification Computation (MHVC)
In the decentralized cross-chain process of Blayer, a key innovative technology is Merkle Hash Verification Computation (MHVC), which aims to address the verification challenges of cross-chain transactions.
The core of the MHVC protocol lies in verifying the operations of each party involved in cross-chain transactions. It quickly confirms the legitimacy of transactions by comparing the Merkle hash of transaction data with the Merkle root hash in the block header, without the need to download complete block information. The process involves the following steps:
- The protocol first retrieves the header information of all nodes on the longest blockchain from the network.
- It then calculates the transaction hash to be verified.
- By traversing the hashes of the block header nodes, the protocol locates and confirms whether the calculated transaction hash exists in the chain and retrieves the block height containing the transaction.
- Based on the transaction hash, it calculates the Merkle root hash. If the node's Merkle root hash matches the computed result, the transaction is considered verified.
This approach not only improves the efficiency of transaction verification but also reduces the burden of data processing, thereby enhancing the performance of the entire system without sacrificing security.
2. Privacy Fragment Integration Protocol (PFIP)
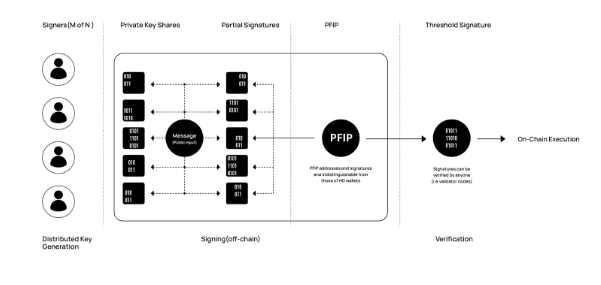
A core feature of the Blayer protocol is the secure decentralized cross-chain implementation of Bitcoin between the second layer network and the mainnet. Users can lock Bitcoin into Blayer, conduct transactions in the second layer wallet, and efficiently transfer assets back to the mainnet account. The key to this process lies in the Privacy Fragment Integration Protocol (PFIP) technology.
The standout feature of PFIP technology is the consistency of second layer wallet addresses with mainnet addresses, ensuring the secure circulation of Bitcoin. This technology employs several key innovative algorithms:
- Bridge Address Generation algorithm: Used to create a dedicated custody address pool generated by a decentralized protocol, ensuring the secure custody of assets.
- Privacy Fragment Processing mechanism: When handling sensitive data (such as private keys), the algorithm divides it into multiple encrypted fragments. These fragments are processed and dispersed among different nodes, rather than directly generating the target private key. Each node only processes a portion of the data, meaning that even if some data is leaked, it cannot reconstruct the complete sensitive information.
- Bitcoin Address Mapping algorithm: Ensures the accurate and secure correspondence of addresses between the second layer network and the mainnet.
The comprehensive application of these technologies not only enhances the security of transactions but also strengthens the overall system's privacy protection capabilities, providing robust technical support for the efficient and secure circulation of Bitcoin between the mainnet and the second layer network.
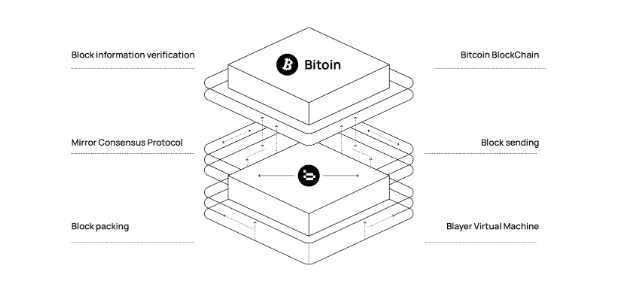
3. Mirror Consensus Protocol
Through its unique Mirror Consensus Protocol (MCP), Blayer achieves bidirectional synchronization between the Bitcoin network and the Blayer network, enhancing the security and integrity of data. This protocol allows data to be mutually synchronized and verified between the two networks, ensuring the authenticity and tamper resistance of transaction data.
By leveraging Bitcoin's consensus mechanism as a security foundation, MCP not only maintains the core integrity of Bitcoin but also provides a framework for bidirectional communication and verification. This framework enables the Bitcoin network to interact more flexibly with the applications in the Blayer ecosystem, greatly enhancing the scalability and diversity of the entire ecosystem.
Overall, the MCP protocol is a key component of the Blayer protocol, providing a secure and efficient bridge for interaction between Bitcoin and Blayer, while promoting the diversification and innovation of the ecosystem. This innovative protocol opens up new possibilities for Bitcoin's Layer2 solution and paves the way for the future development of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
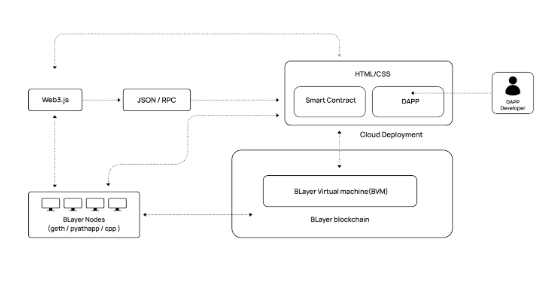
4. Efficient Second Layer: BVM Virtual Machine
The ecosystem of the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) has multiple mature and market-validated projects. For the development of Bitcoin Layer2, the ideal scenario is for these developers to directly build on Bitcoin Layer2. To achieve this, the Blayer (BVM) virtual machine supports the development and deployment of smart contracts using the Solidity language, allowing developers to build decentralized applications (DApps) on the Blayer platform using their familiar smart contract language.
The Blayer protocol specifically adopts the "Swift Block Builder," an efficient data processing algorithm used for effective block sorting. This not only enhances the transaction processing speed and efficiency of the Blayer network but also provides significant support for the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Through this integration with the EVM ecosystem, Blayer aims to maximize the functionality and scope of Bitcoin, transforming it into a versatile and efficient blockchain platform, not limited to value storage.
Blayer Consensus Mechanism: Strengthening the Security and Decentralization of Bitcoin Layer 2
When designing its Layer 2 solution, Blayer closely adheres to the principles of the Bitcoin mainnet, prioritizing security and maintaining its commitment to decentralization. To achieve this, the Blayer consensus protocol cleverly integrates Byzantine Proof of Stake (BPOS) and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) mechanisms.
BPOS combines the efficiency of PoS with the robust security of BFT, enabling the Blayer network to effectively combat malicious nodes and system failures, ensuring reliable operation in various scenarios. BPOS not only reduces computational costs and improves transaction processing speed but also maintains high network security and fault tolerance, ensuring stable operation even in the face of internal dishonest behavior or external attacks.
In terms of node management, Blayer uses a hybrid token of BTC and native tokens as node staking and provides rewards to validators. By periodically rotating nodes holding fragment addresses, Blayer enhances network security. If nodes engage in improper or malicious operations, they face the risk of partial or complete loss of staked funds, or even permanent disqualification from validation. This mechanism ensures the fairness of network management and effectively prevents centralization risks, further strengthening the decentralization and security of the network.
Additionally, Blayer uses BTC as gas, not only promoting Bitcoin's entry into a deflationary era but also creating additional revenue for miners. This initiative undoubtedly further drives the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem, providing a solid foundation for the implementation of the Bitcoin Layer 2 solution.
(User usage process diagram)
Blayer's Grand Vision: Leading the Future of Bitcoin Layer 2
The technical team of Blayer consists mainly of members from the native Bitcoin technology community, with the core team deeply involved in the Bitcoin community for many years, possessing a deep understanding and practical experience with the Bitcoin mainnet, and having made significant contributions to the early Bitcoin code.
Blayer's vision is to become a leader in the Bitcoin Layer 2 field, driving the application and popularization of Bitcoin in broader domains. Blayer is committed to maintaining the purity and security of the Bitcoin network while responding to the community's demand for ecosystem development, promoting the prosperity of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The decentralized BTC Layer 2 solution based on mirror blockchain technology launched by the Blayer team solves the decentralized cross-chain problem from the Bitcoin network to Layer 2 and the bilateral verification challenge of block information through its core technologies—Merkle Hash Verification Protocol (MHVC), Privacy Fragment Integration Protocol (PFIP), Mirror Consensus Protocol (MCP), and Byzantine Proof of Stake (BPOS)—while also efficiently implementing Bitcoin in smart contract applications.
The launch of Blayer signifies explosive growth in the application of the Bitcoin ecosystem, with the potential to open up a trillion-dollar market for Bitcoin and provide long-term consensus security for the Bitcoin network. This is not only a milestone in the development of Bitcoin technology but also a significant contribution to the entire cryptocurrency field.
As the Bitcoin ecosystem continues to evolve and adapt, we can expect further development. The various Web3 platforms in the Bitcoin ecosystem may integrate with each other, potentially reshaping the global financial market and ultimately forging a true Web3 world. Blayer's goal is not only to achieve technological innovation but also to play a key role in advancing the overall progress of cryptocurrency culture and community.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




