Authors: Xiyu, ChainCatcher
Editors: Marco, ChainCatcher
The Cancun upgrade (Dencun) can be said to be the most noteworthy event for the Ethereum network in 2024, and it is another major update following last year's Shanghai upgrade (Shapella), expected to be completed by the end of February.
According to an Ethereum blog post on January 24th, the Cancun upgrade was activated on the Ethereum Goerli test network on January 17th, and it is planned to be activated on the Sepolia test network on January 30th and the Holesky test network on February 7th.
Once the Dencun upgrade is successfully completed on these three test networks, the next step will be its activation on the Ethereum mainnet, expected to take place at the end of February.
Due to the numerous opportunities hidden in each Ethereum upgrade, monitoring the progress of Ethereum upgrades has become a top priority for the crypto community. In September 2022, Ethereum completed the merge upgrade, transitioning from PoW to PoS, making ETH a deflationary asset. In May of last year, Ethereum opened up staking and withdrawal functions to users through the Shanghai upgrade. In the months leading up to the upgrade, Ethereum staking-related projects such as Lido and SSV Network saw a significant increase in asset value.
So, what exactly is the Cancun upgrade? What aspects of Ethereum's performance will this upgrade change? What is the EIP-4844 proposal? Which projects and sectors will benefit from this upgrade? What are the potential trading opportunities?
What is the Cancun upgrade?
The Cancun upgrade, also known as "Cancun-Deneb," is a combination of the Cancun and Deneb upgrades, abbreviated as "Dencun" in English. The Chinese term "坎昆升级" actually only represents the first part, "Cancun," and omits the Deneb part. The complete name is "坎昆 -Deneb" upgrade.
Each upgrade name of Ethereum corresponds to a specific layer of the Ethereum network. The Cancun upgrade aims to improve the performance of the Ethereum execution layer, while the Deneb upgrade focuses on the consensus layer.
To better understand these concepts, it is necessary to first understand the current architecture and state of Ethereum.
Before the Ethereum merge, the Ethereum network was mainly composed of two parts: the "execution layer and consensus layer," which operated independently of each other.
The execution layer is mainly responsible for processing the logic execution of smart contracts, where transaction calculations take place. It is the original Ethereum mainnet, also known as "Ethereum 1.0," and is responsible for maintaining the state of the Ethereum network and executing Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) code.
The upgrade of the execution layer is named after cities that previously hosted Devcon: Berlin -> London -> Shanghai -> Cancun -> Prague -> Osaka -> Bogota.
The consensus layer ensures the validation of all transactions and smart contracts through staking PoS, achieving consensus among all nodes and clients to maintain a consistent state. It is the beacon chain formed after the merge with the execution layer, also known as "Ethereum 2.0."
Each consensus layer upgrade is given the name of a star, chosen in alphabetical order: Altair->Bellatrix->Capella->Deneb->Electra->(F)unknown.
After the merge, the execution and consensus layers of Ethereum run in parallel, communicating or exchanging information through the Engine API interface. The Engine API allows execution clients to request block information from consensus clients, and allows consensus clients to send new blocks to execution clients or request execution validity proofs, etc.
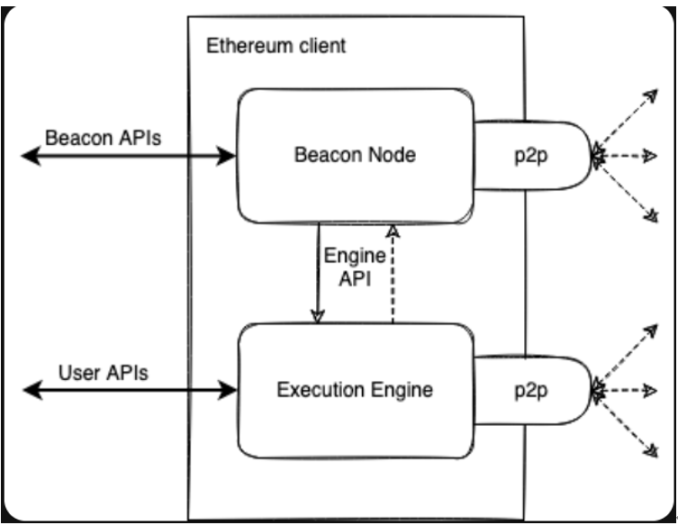
The upgrade of the execution layer is called Cancun, and the upgrade of the consensus layer will be called Deneb. The name of the entire upgrade is Cancun-Deneb. Although the upcoming Cancun upgrade and Deneb upgrade are technically different, they will be implemented simultaneously, so the compound term "Dencun" is also used to refer to this combined upgrade.
Significant reduction in on-chain data costs
The Cancun upgrade is another upgrade to the Ethereum main chain following the Shanghai upgrade, aiming to solve the previously criticized issues of low performance, high fees, and network congestion. It aims to improve the main chain's TPS and reduce user Gas fees by promoting the Ethereum scaling process, while enhancing scalability and security to improve network performance.
Based on the naming of the Dencun upgrade, it can be seen that this upgrade will mainly improve and optimize smart contracts, EVM, and data consensus in the execution layer, as well as the consensus layer in the Ethereum network. In this upgrade, the Ethereum community has proposed a series of improvement solutions called EIPs, with 6 technical specifications that have been discussed, tested, and voted on by community members for implementation.
Among them, EIP-4844 is the core of the Cancun update, also known as the proto-danksharding proposal, which is the initial version of the shard Danksharding scaling solution and a temporary scaling solution.
By implementing off-chain data storage and access, it reduces the Gas cost of publishing Layer2 data to the Ethereum mainnet, especially for Rollup solutions, reducing the cost to less than one-thousandth of the current level, thereby reducing the Gas fees for users using the network.
The EIP-4844 proposal introduces the Blob transaction type, a new data format that helps to expand Ethereum, representing data returned from Layer2, distinguishing it from the native data Calldata generated on Layer1 Ethereum mainnet. The data carried by Blob is downloaded and stored by the Ethereum consensus layer, but does not support EVM access, and this data has a limited validity period of about 18 days.
Blob is an external temporary storage that does not actually store Layer2 transaction data in Layer1, and it regularly expires, greatly reducing data storage costs.
In simple terms, Blob is a separate channel built by the Ethereum mainnet for the transmission, storage, and verification of Layer2 transaction data, with customized Gas fees and storage costs independent of the activity of the Ethereum network.
The main goal of EIP-4844 is to reduce L2 Gas fees by using the new Blob data format to carry transactions, making the transition to fully sharded systems easier, as all future upgrades will only be made at the consensus layer.
At the product architecture level, EIP-4844 introduces Blob-carrying transactions, marking the first time Ethereum has built a data layer specifically for L2, laying the foundation for the subsequent fully sharded Danksharding.
At the economic model level, EIP-4844 will introduce a new fee market for Blob, marking Ethereum's first step towards a multi-dimensional market.
At the user experience level, the most immediate perception for users will be the significant reduction in L2 fees, providing an important foundation for the explosion of L2 and its application layer.
As StarkWare co-founder Eli Ben-Sasson stated, this upgrade will reduce the data availability costs for all L2.
What other aspects of Ethereum's performance will the Cancun upgrade improve?
In addition to EIP-4844 reducing Rollup data on-chain costs, there are also proposals such as EIP-6780 and EIP-5656 to improve EVM efficiency, EIP-7044 to improve staking experience, and EIP-4788 to optimize communication between the consensus layer and the execution layer.
In terms of the EVM in the execution layer, EIP-6780 and EIP-5656 proposals enhance smart contract security and processing efficiency by modifying related code functionality.
EIP-6780 restricts the functionality of the SELFDESTRUCT opcode in smart contracts to certain conditions, enhancing the security of smart contract code.
SELFDESTRUCT, also known as self-destruct code, is mainly used to automatically destroy smart contracts, allowing smart contracts to remove themselves from blocks automatically.
When a contract executes a self-destruct operation, the remaining Ethereum in the contract account is sent to a specified target, and its storage and code state are also deleted. While this feature can help developers delete smart contracts and transfer the contract's balance to a specified address in emergency situations, it can also be exploited by malicious actors, making it a potential attack vector.
The EIP-6780 proposal aims to reduce the vulnerability risk in smart contracts by limiting the functionality of the SELFDESTRUCT opcode, which could potentially disrupt smart contracts. For example, the smart contract will only execute the self-destruct operation when the developer calls this opcode, sending the remaining ETH in the account to the caller.
EIP-5656 mainly involves fine-tuning the EVM code, introducing a new opcode called MCOPY to optimize the process and performance of data copying in memory during smart contract execution. MCOPY simplifies the operation instructions in the EVM data processing process, improving the efficiency of data movement in the EVM and reducing the Gas fees associated with data processing operations.
In the current EVM architecture, using existing opcodes to copy large amounts of data segments results in excessive operation instructions, inefficiency, and high costs. Under EIP-5656, copying 256 bytes of memory using MCOPY only costs 27Gas, compared to 96Gas using the previous method, resulting in a quarter reduction in Gas fees.
Faster memory operations also mean faster contract execution, giving developers an advantage when dealing with large data structures or complex operations involving memory.
While EIP-5656 and EIP-6780 do not change the overall direction of Ethereum, they improve the efficiency of Ethereum developers in smart contract development and reduce the occurrence of vulnerabilities by modifying or introducing EVM-related opcodes.
In terms of the Ethereum consensus layer, the community has proposed the EIP-7044 and EIP-7045 to improve the validator and staking-related processes, making Ethereum staking more secure.
EIP-7044 aims to simplify and improve the mechanism for exiting Ethereum staking, ensuring that voluntary exits signed before the Capella (Shanghai) upgrade remain permanently valid.
Currently, the Ethereum staking market mainly involves delegated staking, where users delegate their 32ETH or multiples to validator operators who are responsible for managing and operating Ethereum validators. When users exit Ethereum validators, they need to use the validator's signing key to sign a "voluntary exit" or "voluntary exit operation" application, which is only valid for two upgrades and will become invalid once the Deneb upgrade occurs. This means that if the Ethereum Cancun upgrade does not change this rule, users will need to comply with the new rules set by the validator operators to exit their staked Ethereum.
EIP-7045 expands the inclusion range in the Ethereum block proof slot to reduce block confirmation time and decrease user delays.
Additionally, there are proposals such as EIP-4788, which focuses on improving communication between the Ethereum execution layer and consensus layer, and EIP-1153, which aims to reduce data storage costs during contract execution and optimize block space for more cost-effective and efficient transactions.
The Cancun upgrade will focus on reducing the cost of on-chain data for Layer2 networks, improving EVM performance, and optimizing the staking experience for Ethereum.
About the Timing of the Cancun Upgrade
According to the roadmap provided by the Ethereum ACDE meeting, the Cancun upgrade testing will proceed in the order of the Goerli, Holesky, and Sepolia test networks.
According to an Ethereum blog post on January 24th, the Cancun upgrade was activated on the Ethereum Goerli test network on January 17th. It is planned to be activated on the Sepolia test network on January 30th and the Holesky test network on February 7th.
Once the Dencun upgrade is completed on these three test networks, the next step will be its activation on the Ethereum mainnet, expected to take place at the end of February.
However, in the latest ACDE Ethereum core developer call on January 18th, when developers were asked about their confidence in the Dencun Layer2 upgrade, a developer named "Protolambda" from the Optimism L2 network expressed concerns about the readiness of infrastructure and tools for Blob transactions. Additionally, there are many infrastructure updates needed on the Layer1 Ethereum mainnet.
How Will the Cancun Upgrade Impact Developers and Users?
The Cancun upgrade, through the implementation of proposals such as EIP-4844 and EIP-1153, optimizes network transaction throughput, data storage, and block space to reduce Ethereum transaction fees and improve processing speed, providing a seamless experience for developers and users, and opening a new milestone for on-chain applications in the Ethereum ecosystem.
Furthermore, the introduction of the Blob concept has propelled the progress of the Ethereum Danksharding sharding plan. It is expected that through Proto-danksharding, Ethereum's throughput will increase by over 100 times, and the cost of Layer2 transactions will be less than $0.001. It will also reduce the Gas fees for Rollup-based Layer2 networks to one-thousandth.
So, how will the Cancun upgrade impact developers, users, and the broader Ethereum ecosystem?
For users, the Cancun upgrade reduces the cost of on-chain data for Layer2 networks through the introduction of Blob, allowing users to enjoy low Gas fee transactions and more on-chain use cases. The lower Gas fees and higher throughput will foster a more diverse range of use cases, especially those with high-frequency trading needs, such as games and derivative products.
Additionally, according to the current community plan, Ethereum will soon attempt the Danksharding sharding solution. If successful, combined with technologies like Layer2 and Rollup, Ethereum's TPS will see a significant increase, opening up new narratives.
For developers, EIP-4844 will enable them to develop Ethereum applications more flexibly, innovatively, and diversely.
Developers will be able to use proto-danksharding to store and retrieve on-chain data, supporting more Layer2 solutions and application scenarios. They will also be able to prepare for future complete danksharding, utilizing more shard resources and functionalities.
The improvements proposed in EIP-6780 and EIP-5656 will provide developers with a more efficient and cost-effective platform for deploying and developing smart contracts, allowing them to focus more on product development rather than infrastructure performance improvements.
The optimization of Rollup-based network performance will make it a reality for developers to handle high-frequency and complex transaction scenarios, enabling them to integrate more complex functionalities into smart contracts or DeFi applications.
For the Ethereum ecosystem, the Cancun upgrade optimizes the performance of Ethereum Layer2 networks, driving the prosperity of on-chain applications and the explosion of the ecosystem. Additionally, the optimization of data storage and data availability will drive the development of decentralized applications and decentralized storage, and the improvement of the staking experience will benefit the development of LSD and LSDfi applications.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



