The token will undergo a parallel EVM upgrade in the first quarter after the recent unlocking, which may be beneficial to the ecological development and price.
Author: LD Capital
I. Fundamental Analysis
1. Basic Information
Sei is built on Cosmos SDK and Tendermint Core, and is a Layer 1 blockchain targeting the DeFi field, aiming to bring the order book model onto the chain, thereby narrowing the speed gap between DEX and CEX, and becoming the "crypto Nasdaq."
Sei is a general chain focused on trading, rather than an application chain specifically tailored for a particular application. In other words, Sei is a blockchain optimized for trading, achieving this positioning through features such as order matching system, native matching engine, twin-turbo consensus, and transaction parallelism:
(1) Core - Order Matching System and Native Matching Engine:
As a "born for trading" Layer 1, Sei does not solely adopt any one of AMM or traditional order book mechanisms when processing transactions. Instead, it has chosen a set of compromise solutions - Central Limit Order Book (CLOB). CLOB constructs an order matching engine at a lower level in the chain, attempting to solve the problem by "embedding" the order book in the chain (Sei does not manage the order book, but only provides an order matching framework). Various DeFi protocols built on top of Sei can utilize this order matching engine. One major problem in the existing DeFi ecosystem is the fragmented liquidity of each DeFi protocol. However, with Sei, all DeFi protocols share an order matching engine that can provide deep liquidity.
To illustrate, suppose there are "Red Dex" and "Blue Dex" on SEI. If user A submits an order to sell 1 ETH at a price of $2,000 on Red Dex, and user B submits an order to buy 1 ETH at the market price on Blue Dex, Sei's order matching engine will match these two orders. Typically, the DeFi network suffers from fragmented liquidity because each DeFi protocol tends to maintain its own liquidity. However, with Sei, it provides a very deep liquidity pool, consolidating all liquidity related to the order matching engine, thereby minimizing the financial losses caused by slippage and other associated impacts for users.
(2) Twin-Turbo Consensus:
Twin-Turbo consensus includes two functions: 1) Smart block propagation for efficient block propagation; 2) Optimistic block processing to improve scalability by reducing block time.
1) Smart block propagation: In a typical blockchain network, block proposers collect transactions in their local memory pool, form them into a block, and propagate it to the network. During this process, a single block containing all transaction data is propagated to the network, meaning that even if full nodes already have almost all transactions, conventional blockchain networks still propagate blocks with the same transaction data. This is a waste of bandwidth.
In Sei, block proposers do not include transaction data in the block proposal, but rather the hash value of the transactions, along with the block ID, which is a reference to the block. The hash value of the transactions is a summarized hash function of the existing transaction data, thus having the advantage of being small in size. Block proposers first propagate the block proposal to the network, as shown in the figure below, and then divide the complete block into smaller blocks for propagation. If a validator receives a block proposal from a block proposer and already has all the transactions corresponding to that hash value in its local memory pool, they will reconstruct the block from their local memory pool, rather than waiting for the complete block to arrive. If a specific validator loses a transaction in its local memory pool during the pre-vote and pre-commit process (very unlikely), it can simply wait for the entire block to arrive.
The benefit of this smart block propagation process is that it significantly reduces the time required for validators to receive blocks. According to co-founder Jay, this process has been proven to increase Sei's overall scalability by 40%.
2) Optimistic block processing:
Sei uses Tendermint Core but has made some modifications to significantly reduce block time and improve scalability. Tendermint Core is a consensus engine that combines Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and PBFT consensus algorithms. The Tendermint BFT consensus process is: Propose - Prevote (2/3 consensus) - Precommit (2/3 consensus) - Commit.
Sei's Optimistic Block Processing modifies the BFT process, introducing a block processing step between Precommit and Commit in the general BFT process. Assuming that malicious nodes are rare and validators have received the data required for computation in the Propose stage from the Prevote stage, Sei begins parallel processing with Prevote to further reduce block time. By reducing block time through optimistic block processing, it should not be a problem, as most of the time the block's validity is not in question. However, if the block is rejected by the network during the pre-vote and pre-commit process while executing the computation, it can simply be discarded.
(Images were not translated)
Taking a set of Sei data, according to the normal Tendermint BFT method, the total block time is 200+150+150+400+100, i.e., 1000ms. If optimistic block processing is carried out, it would save 300 milliseconds of pre-vote and pre-commit time, reducing the block time to 700 milliseconds. If the block size remains unchanged, the reduction in block time from 1000ms to 700ms means there are approximately 1000/700 blocks in the same time, an increase of about 1.43 times, improving scalability by 43%.
(3) Transaction Parallel Processing:
Another method Sei uses to enhance scalability is transaction parallelism. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the most popular virtual machine in the blockchain industry, processing transactions sequentially, which fundamentally limits scalability. By default, the Cosmos SDK, on which Sei is based, also processes transactions in a serial manner. In Cosmos application chains, when a block is received, validators execute BeginBlock logic, DeliverTx, and EndBlock logic in sequence, while Sei modifies DeliverTx and EndBlock to process transactions in parallel.
First, the DeliverTx process handles token transfers, governance proposals, and smart contract calls, ensuring that parallel transactions do not reference the same key. For example, two transactions of A sending X tokens to B and C sending Y tokens to D can be processed in parallel, but two transactions of A sending X tokens to B and B sending X tokens to C cannot be processed in parallel, and thus will be processed consecutively.
To parallelize multiple transactions, it is necessary to ensure that they do not reference the same keys. To achieve this, Sei constructs a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) to check the dependencies between transactions before executing them. In the figure below, assuming the DAG shows R3 in the middle depends on R2 in the first column, and R3 in the third column depends on W1 in the middle. As a result, transactions will be processed as shown in the right figure.
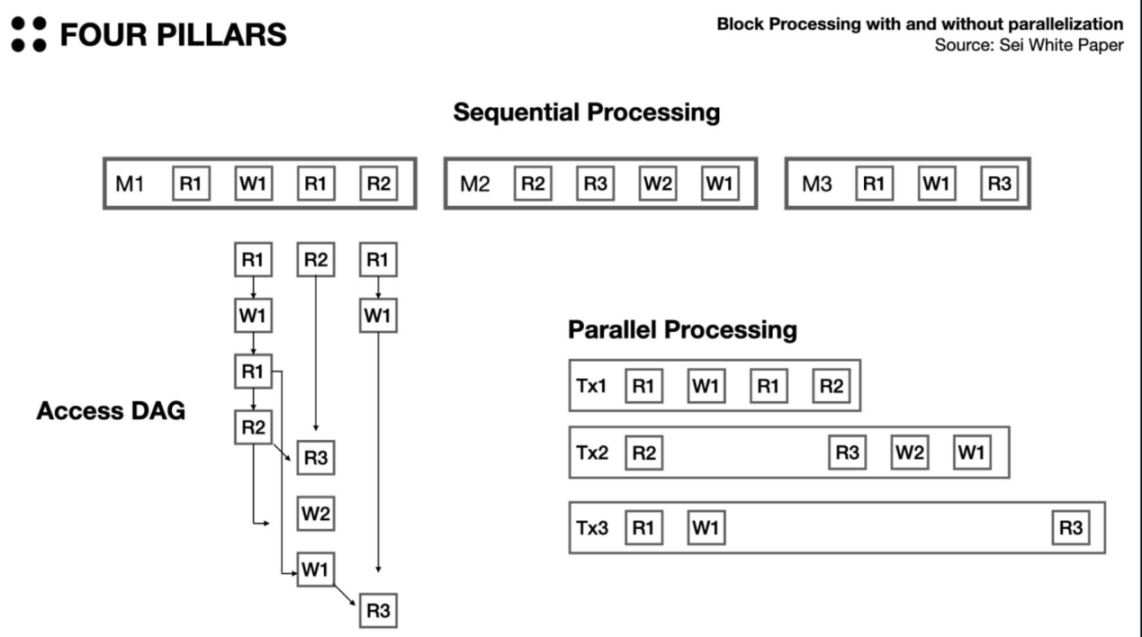
In the last part of the block, EndBlock, transactions related to the matching engine are executed by the native order matching engine. Similarly, transactions related to the matching engine are not processed in sequential order, but in parallel after confirming that they are unrelated to each other.
By default, the network is designed to assume that all transactions are unrelated and processes them immediately. If there are related transactions, only those transactions will fail. Therefore, application developers based on the Sei order matching engine must first filter out which transactions are related and which are unrelated. Experimental data on parallelization on Sei shows a 60-90% improvement in block time, TPS, and other performance aspects compared to non-parallelized scenarios.
2. New Narrative of Parallel EVM
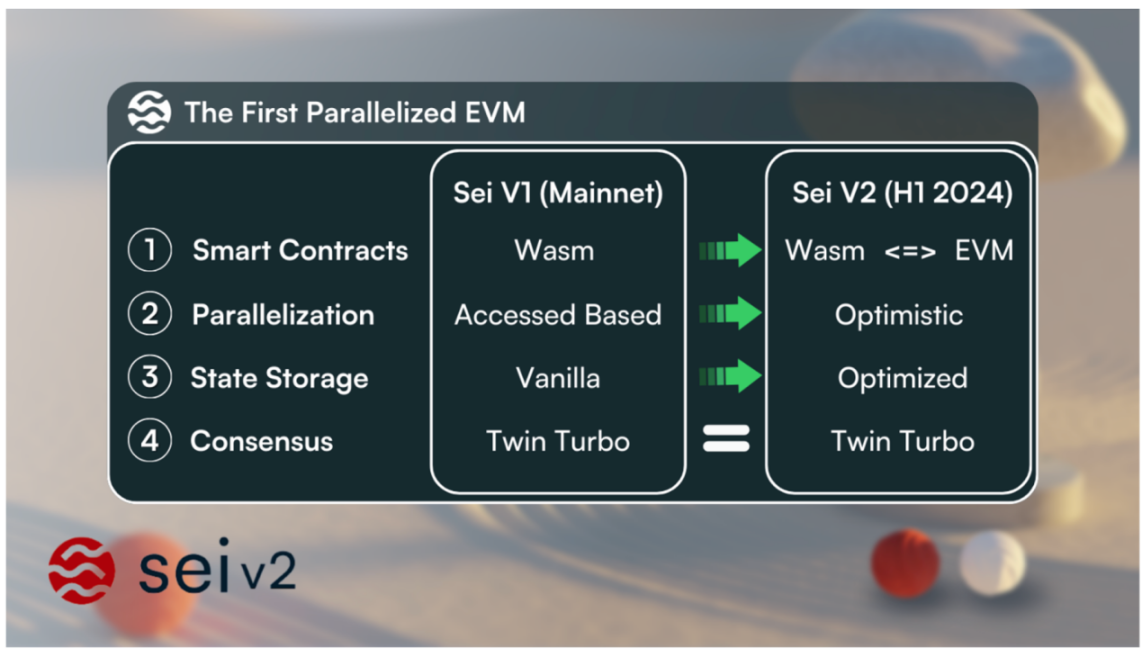
Since the official launch of Sei's public mainnet Pacific-1 on August 16, 2023, and the release of the Sei-V2 version plan on November 29, 2023, it will support the first parallel EVM.
Sei currently allows the use of Cosmwasm smart contracts written in Rust. As Sei continues to attract more developers' interest and expand its ecosystem, the developers' biggest demand is for the execution environment supported by Sei to have greater flexibility. With support for parallel EVM, Sei is available for global EVM developers to use.
(1) What is Parallel EVM?
Parallel EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) is a concept aimed at improving the performance and efficiency of the existing EVM, which is the core of Ethereum, responsible for running smart contracts and processing transactions. The current EVM has a very important feature: transactions are executed sequentially.
Sequential execution ensures that transactions and smart contracts can be executed in a deterministic order, making it easier to manage and predict the state of the blockchain. This design choice prioritizes security and reduces the potential complexity and vulnerabilities associated with parallel execution. However, in the face of high loads, it may lead to network congestion and delays.
Imagine the original design of EVM as vehicles on a single-lane road moving one after the other, with each vehicle having to travel at the speed of the preceding vehicle. Once there is a traffic jam (transaction congestion), subsequent vehicles will be stuck on the road. In contrast, parallel EVM is like expanding this single-lane road into a multi-lane highway, allowing multiple vehicles to travel simultaneously. From a technical perspective, parallel EVM allows different independent transactions or smart contracts to proceed simultaneously, greatly improving EVM processing speed and system throughput.
General methods for parallel EVM processing:
- Partitioning or sharding: Transactions are partitioned or grouped so that they can be executed in parallel. This means different transactions can be executed simultaneously on different processing units, rather than one after another. Additionally, Solana's SVM adopts a similar processing logic.
- Optimization algorithms: Developing new scheduling algorithms and optimization techniques to effectively manage and execute parallel tasks while maintaining transaction correctness and order.
- Security and consistency assurance: Implementing complex synchronization mechanisms and consistency models to ensure the security and data consistency of the entire system even during parallel processing.
In summary, by processing transactions in parallel, EVM can handle more transactions at the same time, significantly increasing TPS, alleviating network congestion, and improving scalability.
(2) Key Implementations of Sei V2
1) Backward compatibility of EVM smart contracts - Allows developers to deploy audited smart contracts from EVM-compatible blockchains without changing the code, supporting the reusability of familiar and widely used applications and tools (such as Metamask):
Backward compatibility means that new products are designed with consideration for previous products and can be used as they were originally, even if they were made for previous products. The backward compatibility in the design of Sei V2 means that most existing smart contracts on Ethereum can be deployed on the Sei blockchain without changing any code.
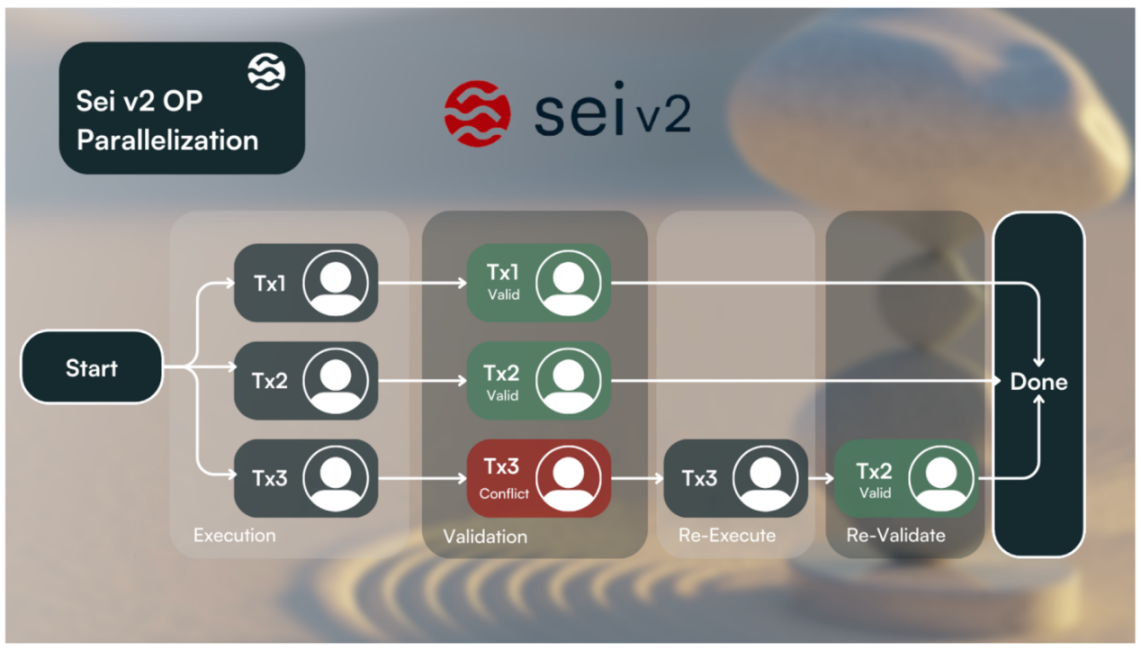
2) Optimistic parallelization - Allows the chain to support parallelization without developers defining any dependencies:
Sei V2 processes transactions in parallel, assuming all operations are valid, executing them first, and then rerunning them in case of issues during validation. The results of processing should be the same as those of sequential processing. In short, Sei V2 adopts an optimistic approach, processing transactions first and using information about any issues that arise to process transactions, rather than validating transaction relationships in advance. Optimistic parallelization will apply to all transactions running on Sei, including Sei native transactions, Cosmwasm transactions, and EVM transactions.
3) Interoperability with existing chains, allowing seamless integration between EVM and any other execution environment supported by Sei:
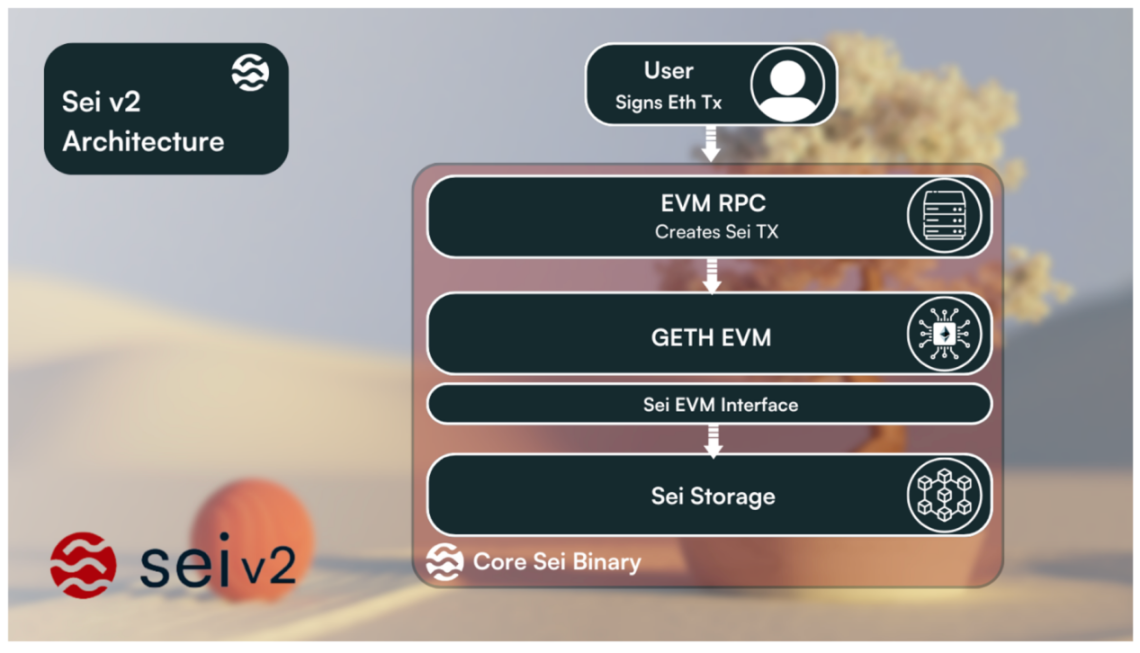
As Sei is an integrated chain, all transactions entering different components of Sei (Cosmwasm, EVM, banking, staking) are able to communicate with each other. Although these transactions serve different purposes, they ultimately share many similar features, such as gas, sender, and transaction subject. When the chain receives these transactions, they are processed as native Sei transactions and forwarded to the appropriate storage sections (i.e., CosmWasm transactions are sent to the wasm module and executed). This brings a more seamless developer experience - EVM developers can easily access native tokens and other chain functionalities (such as staking).
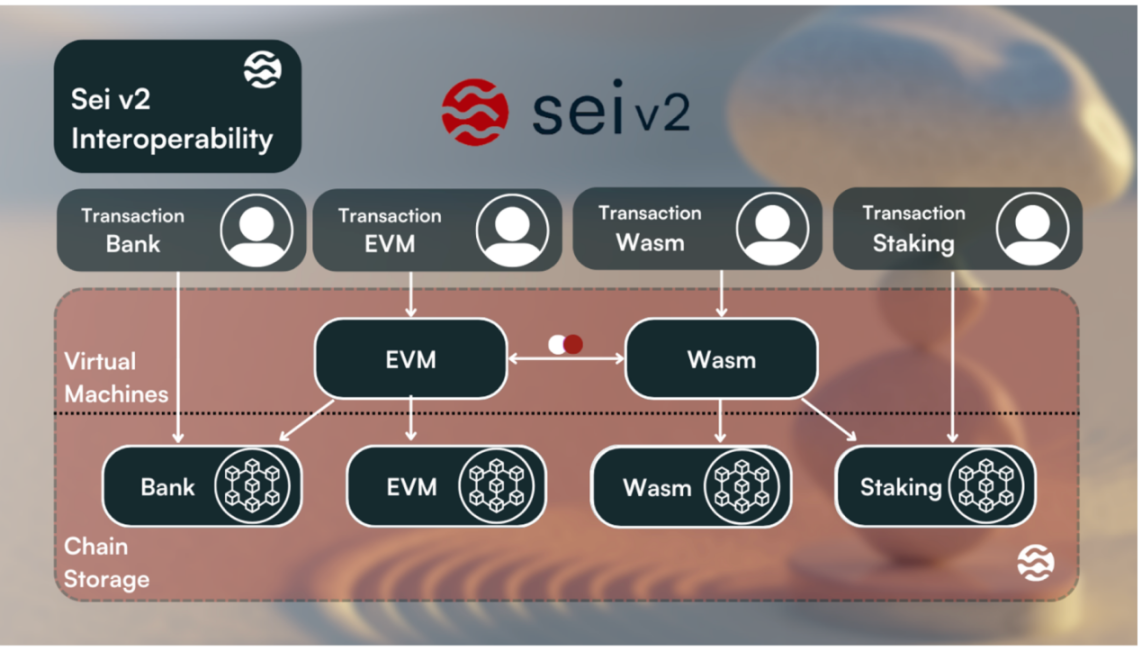
4) SeiDB - Improvements to the storage layer to prevent state bloat, improve state read/write performance, and make it easier for new nodes to synchronize state and catch up.
(3) The Significance of Parallel EVM
Former Polygon co-founder JD previously stated on social media that he had a premonition that every L2 in 2024 would rebrand itself and label itself as "parallel EVM," while Paradigm's CTO Georgios also believes that 2024 will be the "year of parallel EVM," and stated that Paradigm is also exploring and designing related technologies internally.
For developers, blockchain development has always been quite unfriendly. Every time a different virtual machine or language is used, builders must adapt to a new environment. If the clients of the blockchain are the builders, then these actions have not taken into account the convenience of the clients. Ultimately, the blockchain is destined to change what it offers to meet the needs and environment of the builders. Currently, the EVM ecosystem is the most active, and parallel EVM can address this issue.
Supporting EVM in Sei V2 does not mean abandoning WASM. It plans to support both virtual machines simultaneously, and even support interoperability between the two, providing a seamless development environment. If V2 is successful, Sei V2 may become the most successful integrated blockchain supporting multiple virtual machines.
Sei Labs co-founder Jay23 posted on social media at the end of the year, stating that Sei v2 will enable EVM and Cosmwasm contracts to call each other through the use of stateful precompiles and chain-level message scheduling. After the audit is completed, this upgrade will be released on the public testnet in the first quarter of 2024 and deployed on the mainnet in the first half of 2024.
3. On-chain Ecosystem Development
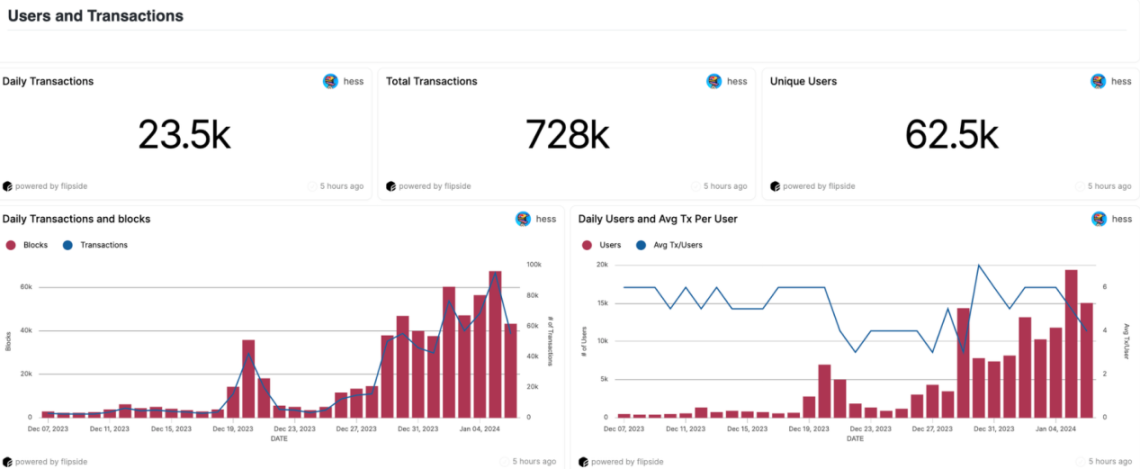
In the past 30 days, the total transaction volume on Sei Mainnet was 728,000, with 62,500 independent users, and an average of 23,500 transactions per day, showing an increasing trend in transaction volume and user numbers.
Data from the past 30 days shows that the most active applications on Sei Mainnet are Astroport, Tatami, Dagora, and Webump.
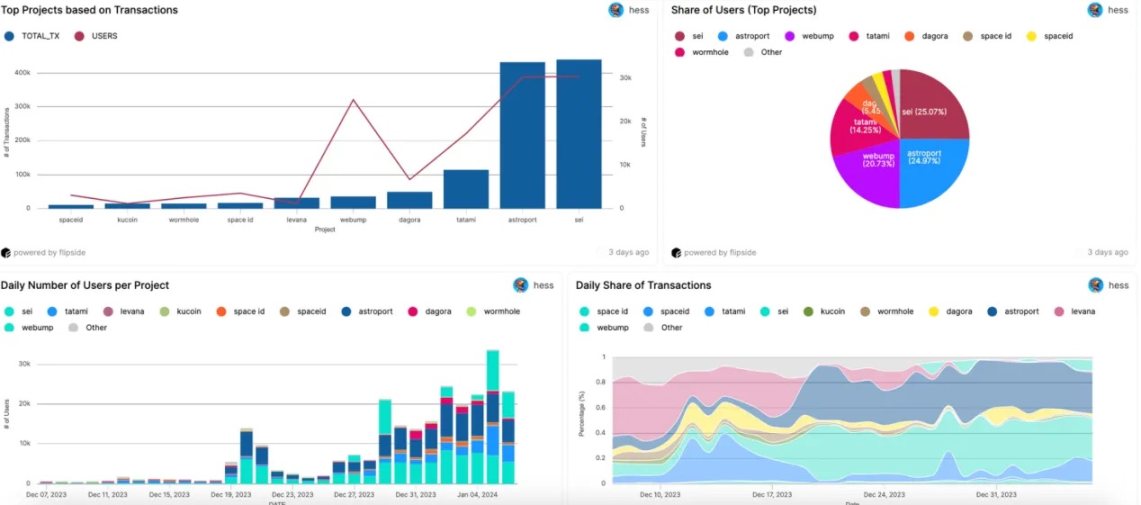
- Astroport (Dex): Astroport aims to become the next-generation mainstream AMM, providing deep liquidity pools and high trading volume for the Cosmos ecosystem. Better pricing will attract more liquidity to Astroport, forming a self-reinforcing cycle. Ultimately, Astroport aims to operate as the foundational liquidity layer for Cosmos. Currently, Astroport operates on four chains: Sei, Neutron, Terra2, and Injective.
- Tatami (Gaming): Tatami meets a prominent need in the Web3 space - a dedicated game publisher. As countless games are scattered across various chains, Tatami provides users with a unique position to play games, collect assets, and complete tasks on a single platform, bringing a unique fusion of game development, market integration, and launchpad services, aiming to change the experience, creation, and distribution of games in the Web3 space.
- Dagora (NFTs): Dagora is a multi-chain NFT marketplace in the Coin 98 ecosystem, supporting BNB Chain, Polygon, Sei, and others. Dagora's features include Marketplace (NFT trading market), Launchpad (NFT release platform), and Hot Drops (free minting section). Additionally, Dagora allows C98 token holders to participate in auctions, launchpads, and hot drops.
- Webump (NFTs): Webump is dedicated to supporting development teams and creator communities on the Sei blockchain and has partnered with Lighthouse to provide open-source smart contracts designed for seamless NFT creation on Sei. Lighthouse is its open protocol and toolset that enhances the NFT creation process, making it easier for NFT creators and developers to access and be more efficient.
As a blockchain focused on providing high-performance DeFi, Sei's on-chain DeFi TVL is still in the early stages in terms of overall data performance and product development.
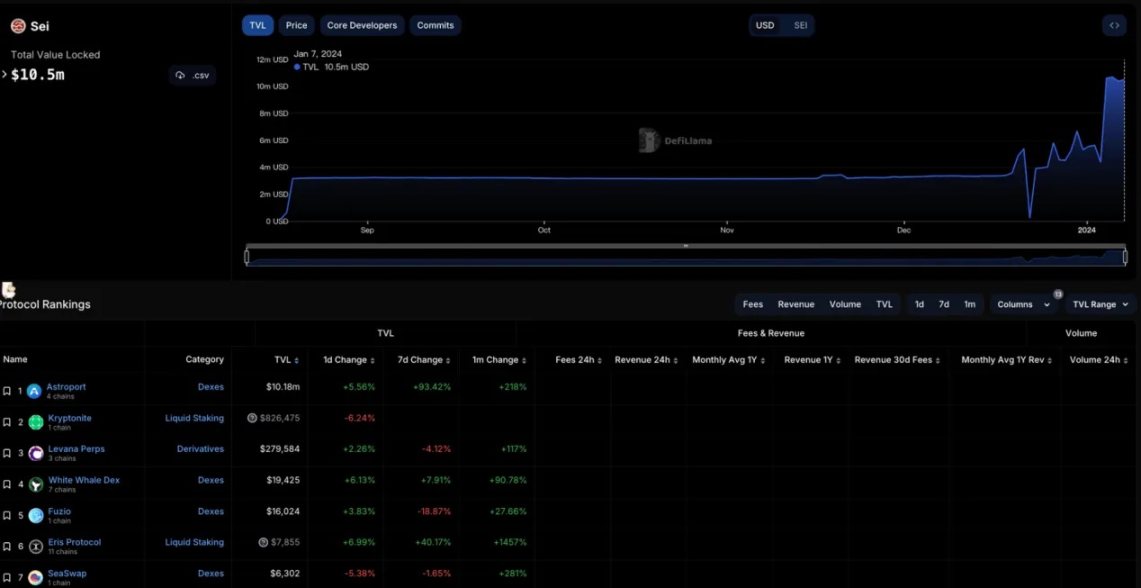
- Kryptonite: Kryptonite is a decentralized AMM and staking protocol based on Sei, compatible with any bAssets on the Cosmos blockchain and other blockchains, aiming to bring a robust native currency market to the Cosmos ecosystem, driving financial innovation and flexibility. Users can stake Sei Network token SEI and receive liquidity staking token bSEI, which can then be used as collateral to mint stablecoin kUSD at a 200% collateral ratio.
- Levana Perps: A perpetual contract trading platform on Sei, supporting up to 30x leverage. Currently, Levana supports leveraged contract trading for BTC, ETH, ATOM, and OSMO.
- Yaka Finance: A native Dex set to launch on Sei, currently available for interaction on the official website, with potential future airdrops.
- Sushiswap and Vortex Protocol: On February 23, 2023, Sushi announced the acquisition of derivative Dex-Vortex and collaboration with Sei, planning to launch a decentralized derivative exchange on Sei in the future. However, there have been no new developments disclosed for this project, with Vortex's latest official tweet dating back to February 2023.
- Team, Financing, and Partnerships
1. Team Background
Sei Network was founded by Jeff Feng and Jayendra Jog in 2022. Jeff Feng is the co-founder of Sei Labs, a graduate of the University of California, Berkeley, and worked in the TMT investment banking department at Goldman Sachs from 2017 to 2020. He co-founded Sei Labs with Jay in 2022.
Jayendra Jog is the co-founder of Sei Labs, a graduate of the University of California, Los Angeles, and worked as a software engineer at Robinhood from 2018 to 2021.
Phillip Kassab is the Growth and Marketing Director of Sei Network, a graduate of the Stephen M. Ross School of Business at the University of Michigan. He previously served as the marketing director for Trader Joe and Swim.
Other team members have worked at companies such as Google, Amazon, Airbnb, and Goldman Sachs.
2. Financing History
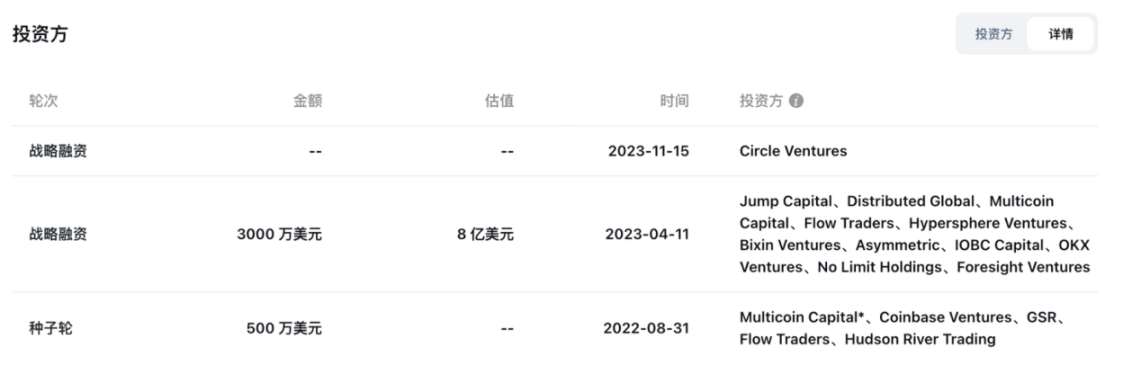
In August 2022, the team behind Sei Network, Sei Labs, completed a $5 million seed round of financing, led by Multicoin Capital, with participation from Coinbase Ventures, GSR, and others.
In February 2023, Sei announced a $400 million Series A financing round and mentioned an airdrop plan. In April, Sei Network announced a $30 million financing at an $800 million valuation, with participation from Jump Capital, Distributed Global, Multicoin Capital, Bixin Ventures, and others. This round of funding was used for development and market expansion in the Asia-Pacific region. In the same month, Sei Labs' ecosystem fund completed a new round of financing of $50 million, including OKX Ventures, Foresight Ventures, and others.
In November 2023, Circle made a strategic investment in Sei Network, supporting the launch of native USDC on the network.
3. Operations and Partnerships
Testnet Activities and Airdrops: During the Atlantic 2 testnet phase, Sei explicitly stated that token incentives would be distributed to reward early members of the Sei community using the chain. When the Pacific-1 mainnet is publicly released, **, ** rewards will be open for claiming, encouraging user interaction on the network.
Sei Ambassador Program: Introducing the Sei Marines Ambassador Program and designing levels and gradient rewards for ambassadors with different contributions to stimulate promotional activities in relevant regions.
Sei Launchpad Accelerator Program: Launching the sei/acc program to invest in and support on-chain ecosystem projects by providing resources, guidance, and incentives. A product manager will be assigned to assist in developing a strategic roadmap and collaborate with key members of the Sei Foundation team.
Expansion in the Asia-Pacific Region: In December 2023, Sei sponsored Binance's event in the Maldives. On December 21, Sei announced a strategic partnership with KudasaiJP to expand its market share in Japan. In January 2024, South Korean research firm Four Pillars indicated that they are preparing various initiatives to further expand their influence and cooperation in the South Korean market.
Token Situation
1. Basic Information
SEI's current market value is $16.74 billion, with a fully diluted valuation of $79.47 billion. The total supply is 10 billion, with a circulation rate of 23% and a 24-hour trading volume of $7.93 billion. The main trading venues are Binance (26.91%), Upbit (25.85%), and Coinbase (8.37%).
Compared to other new public chains, Sei's market value is lower than Aptos and higher than Sui, accounting for 0.5% of Eth's market value and approximately 3.9% of Solana's market value. In terms of TVL in DeFi applications, Sei is much smaller than Sui and Aptos, with only 12.19 million, indicating an early stage.
2. Token Economics
The use cases of SEI tokens include network fees, DPoS validator staking, governance, native collateral, fee market, and transaction fees. The total supply limit of the token is 10 billion, with 51% allocated to the community, 48% to the ecosystem reserve, 9% to the foundation, 20% to the team, 3% to the launch pool, and 20% to private sales. The ecosystem reserve of 48% will be distributed in three parts: staking rewards, ecosystem initiatives, and airdrops and rewards.
3. Recent Trading Situation
Since its launch on August 15, 2023, SEI's price has been declining for about 3 months. However, starting from November 22, the price has significantly risen from around $0.14 to a recent high of $0.88. On January 3, it touched the upper Bollinger band and then retraced, with a slight decrease in daily trading volume.
In terms of contract performance, with the recent price increase, both long and short contract liquidation volumes have significantly increased, while contract open interest has decreased. The difference between active buying and selling and the trading volume is negative, indicating an increase in the long/short ratio.
Summary
Fundamentals: Sei's core difference from other chains lies in its order book-based underlying architecture, which is very suitable for building DeFi. However, its on-chain ecosystem applications and TVL are still in the early stages, lacking outstanding DeFi applications. The introduction of parallel EVM in Sei V2 has provided a new narrative, but many other chains and L2 solutions may gradually support parallel EVM in the future. The effective introduction of SeiV2 could give it a certain first-mover advantage by attracting funds, quality projects, and users to Sei. The V2 upgrade is scheduled to be released on the public testnet in the first quarter of 2024 and deployed on the mainnet in the first half of 2024.
Team Background and Recent Developments: The core team is young but has a strong background, and the funding is robust. There has been continuous effort in promotion and operations in the Asia-Pacific region.
Token Economics: The total supply limit of the token is 10 billion, with 51% allocated to the community and 40% to the team and investors. The market value of Sei is lower than Aptos and higher than Sui, accounting for 0.5% of Eth's market value and approximately 3.9% of Solana's market value. The first significant unlock for private investors and the team is scheduled for August 15, 2024, with regular unlocks occurring on the 15th of each month, mainly for ecosystem releases and foundation unlocks, with a monthly unlock amount of 1.25 billion tokens, approximately $91.61 million.
Recent Trading Situation: Since November 22, the price has been rising from around $0.14 to a recent high of $0.88. The price recently touched the upper Bollinger band and retraced, with a slight decrease in daily trading volume and contract trading volume.
After the recent token unlock, the first quarter will see the launch of V2's parallel EVM upgrade, which may be favorable for ecosystem development and price.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




