UTXO not only can assist in the consensus mechanism, solve the double spending problem in blockchain, but also endows the blockchain with traceable characteristics.
Author: Echo, BiHelix; Satoshi Labs
Guidance: Hong Shuning
Introduction
"The UTXO blockchain has laid the foundation and indisputable foundation of today's blockchain industry. The UTXO technology reflects Satoshi Nakamoto's core vision of ultimate financial freedom." The UTXO model ensures the security of core financial activities, data privacy, and scalability, and is a more secure alternative to the Ethereum account model.
Blockchain Principle: The Foundation of the UTXO Model
Blockchain is a digital, decentralized, and distributed ledger. Blockchain utilizes a P2P (peer-to-peer) network, with participants on the network referred to as nodes. The ledger stores data about transactions. The most important feature of blockchain is that blocks are linked together through encryption.
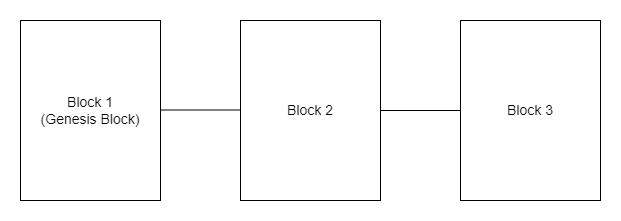
Blockchain: Linked Together in a Cryptographic Manner
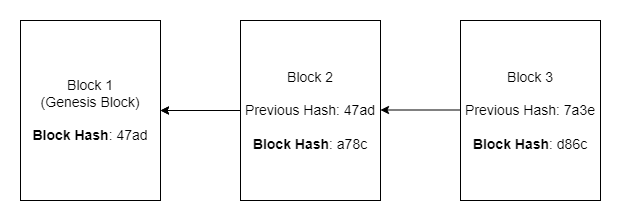
- In addition to the first block (called the genesis block), each block in the blockchain contains a field called "previous hash." It is the hash value of the previous block in the blockchain and is the basis of the security of the blockchain.
- Factors determining the block hash value. If any of these four factors change, even by 1 bit, the hash will completely change due to the avalanche effect. Transactions stored in the block are also one of the four factors that change the block hash. This means that if a miner chooses different transactions and keeps the other 4 factors the same, the hash value will be different.
- Timestamp
- Block Number: The sequence number of the current block in the chain.
- Data: Transactions stored on the block.
- Nonce
- If an attacker tries to change the block's data, the block's hash value will change. As mentioned earlier, the next block will store the hash value of the current block, and if the hash value changes, the chain will be broken. Alternatively, the attacker would have to mine all the blocks again from that point. This is one possibility in a 51% attack.
What is a "Block"?
Blocks in the blockchain store transactions. In the case of Bitcoin, a block is added to the blockchain every 10 minutes, and the time to mine a new block may vary depending on the complexity of the target hash.
When a miner successfully mines a block, it is added to the blockchain. When a block is added to the chain, the status of all transactions within the block changes from unconfirmed to confirmed.
In the case of Bitcoin, the number of transactions that can be stored in a block is not fixed, but the average size of a block is 1 MB.
Empty blocks are valid, meaning they can be mined and added to the chain.
Blockchain Transaction Structure
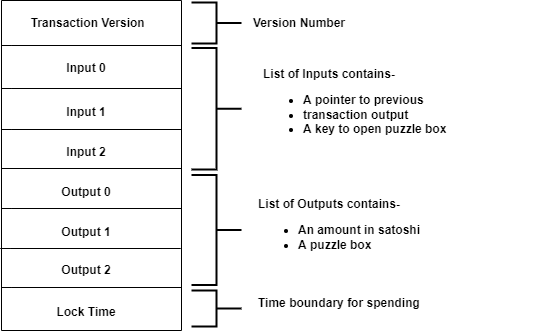
When individual transactions are stripped, several different structures with different semantics are found in the transactions. The following are the different structures present in transactions:
Transaction Version Number: It is the version number that specifies the type of transaction to the network. Through the transaction number, nodes can determine the rule set used to verify that specific transaction.
Outputs: Transaction outputs consist of a lock and time.
Inputs: Transaction inputs consist of a pointer and an unlocking key. The pointer points to a previous transaction output. The unlocking key is used to unlock the input pointing to the previous output. Each time an input unlocks an output, it is marked as spent in the blockchain database.
Lock Time: Specifies whether the transaction can be included in the blockchain immediately or at a specified time in the future.
UTXO is all the unspent transaction outputs.
Once the outputs are spent, they are removed from the circulating supply. New outputs replace them. Therefore, the sum of the unlocked outputs will always equal the sum of the newly created output values.
What is the UTXO Model?
UTXO is not a cryptocurrency denomination, such as satoshi for Bitcoin (BTC) or gwei for Ethereum (ETH); however, UTXO can be measured in these denominations. UTXO represents unspent transaction outputs. In the case of Bitcoin, a transaction remains until it is executed, until another transaction completes from that UTXO. When a transaction is completed, the unused outputs are stored back in the database and can be used for another transaction later.
When a user initiates a transaction through a wallet, the UTXOs containing transaction information are located, unlocked, and associated with the new owners. And the user can use them in a transaction through the same process. As the transactions continue, records of ownership changes are filled in the database. Outputs are a part of the cryptocurrency sent by the user but not spent. They are recorded as input in the database.
How are UTXOs Created?
UTXOs are created by spending existing UTXOs. Every Bitcoin transaction consists of inputs and outputs. Inputs spend existing UTXOs, while outputs create new UTXOs. When deciding to spend Bitcoin, we can only see the amount deducted and the remaining amount in the wallet. For users, this is similar to buying a $0.50 item with a $1 bill—getting change and putting it in the pocket.
Advantages of the UTXO Model
The UTXO model does not include wallet at the protocol level. It is based on individual transactions grouped in blocks. The UTXO model is a common design in many cryptocurrencies (especially Bitcoin).
Cryptocurrencies using the UTXO model do not use accounts or balances. Instead, UTXOs are transferred between users, just like physical cash.
Each transaction in the UTXO model can transition the system to a new state, but it is not feasible for every transaction to transition to a new state.
Network participants must stay synchronized with the current state.
The total UTXO existing in the blockchain represents a set and is continuously maintained by each Bitcoin node in the network.
Each transaction consumes elements from this set and creates new elements added to this set. Every time a new block is accepted in the blockchain, the UTXO set is updated, and each Bitcoin node in the network will set an exact copy of the UTXO in its local storage.
The complete UTXO set can be summed to calculate the total supply of cryptocurrency at a given point in time. In the case of valid blockchain transactions, only unspent outputs can be used to provide funds for further transactions. It is necessary to prevent double spending and fraud that only unspent outputs can be used for further transactions.
Difference Between the UTXO Model and the Ethereum Account Model
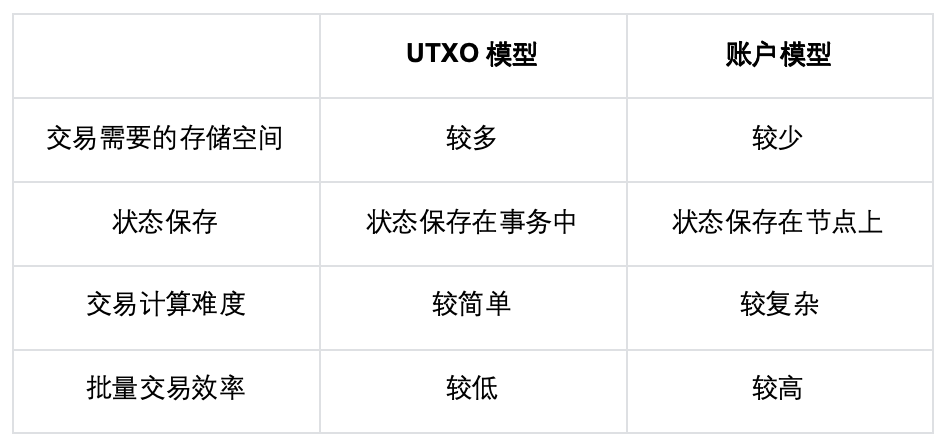
Unspent transaction outputs are part of the distributed database technology behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin uses UTXO, but it is not UTXO. In addition, Ethereum uses an account-based approach and account balances, so there are no UTXOs in the Ethereum virtual machine.
Technical Importance of UTXO
Language-Agnostic Smart Contracts: UTXO-based smart contracts are independent of language, allowing unique consensus mechanisms to be developed for UTXOs.
Support for Decentralized Exchanges and Atomic Swaps: The UTXO model can support atomic swaps, allowing for peer-to-peer encrypted transactions without the need for third-party involvement. The atomic swap feature of UTXO provides greater convenience for direct cryptocurrency transactions between user wallets.
Scalability Advantage: Facilities or parallel transaction processing reduce the computational load on the blockchain network.
Privacy and Security: Each UTXO transaction uses a new address, making it impossible to trace the transaction.
Prevention of Double Spending: UTXO can only be used once, which is the basis for the operation of blockchain technology and ensures that currency is not used multiple times.
More Flexibility: It provides greater flexibility than fiat currency.
Simple Parallelization: It allows for simpler parallelization of transactions in smart contracts.
The UTXO model is used in many cryptocurrencies because it allows users to track ownership of all parts of the cryptocurrency. Since anonymity is considered when creating cryptocurrencies, UTXO is associated with public addresses visible to the entire network.
Unless users disclose their addresses, they cannot be identified by their ownership, but this model allows for transparency through addresses.
UTXO Use Case Application - Off-Chain Transfer Scheme for RGB
The core idea of the RGB protocol is to call the Bitcoin blockchain only when necessary, using proof of work and decentralized network to achieve double spending protection and censorship resistance. The validation work for all token transfers is removed from the global consensus layer and placed off-chain, verified only by the receiving party's client.
How it Works:
In an RGB contract, the genesis tokens belong to a Bitcoin UTXO (whether existing or temporarily created), and to transfer the tokens, you need to spend this UTXO. When spending this UTXO, a Bitcoin transaction must include an additional output containing a commitment to a message, which is the RGB payment information. It defines the inputs, where the tokens will be sent, the asset's ID, quantity, the spending transaction, and the additional data it needs to attach.
Conclusion
The essence of UTXO is actually a form of ledger: it verifies the existence of transaction funds through the UTXO model, traces the origin of the transaction, confirms it through the consensus mechanism, and records it on the chain. Throughout this process, UTXO records all the information related to the account funds, transaction addresses, transferred funds, fund sources, etc., allowing for the tracing of the original source of each transaction. It is based on this characteristic that UTXO can solve the double spending problem together with the consensus mechanism. The security and integrity of transaction information in the RGB protocol are guaranteed by UTXO.
In summary, UTXO not only can assist in the consensus mechanism, solve the double spending problem in blockchain, but also endows the blockchain with traceable characteristics. This forms the basis for ensuring the authenticity and reliability of every transaction in the blockchain.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



